Estimating NOx Emissions in China via Multisource Satellite Data and Deep Learning Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Satellite Observation of NO2 Data
2.2. MEIC Emissions Inventory
2.3. Other Covariates
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. LightGBM Model
2.4.2. CNN-BiLSTM-ATT Model
3. Results
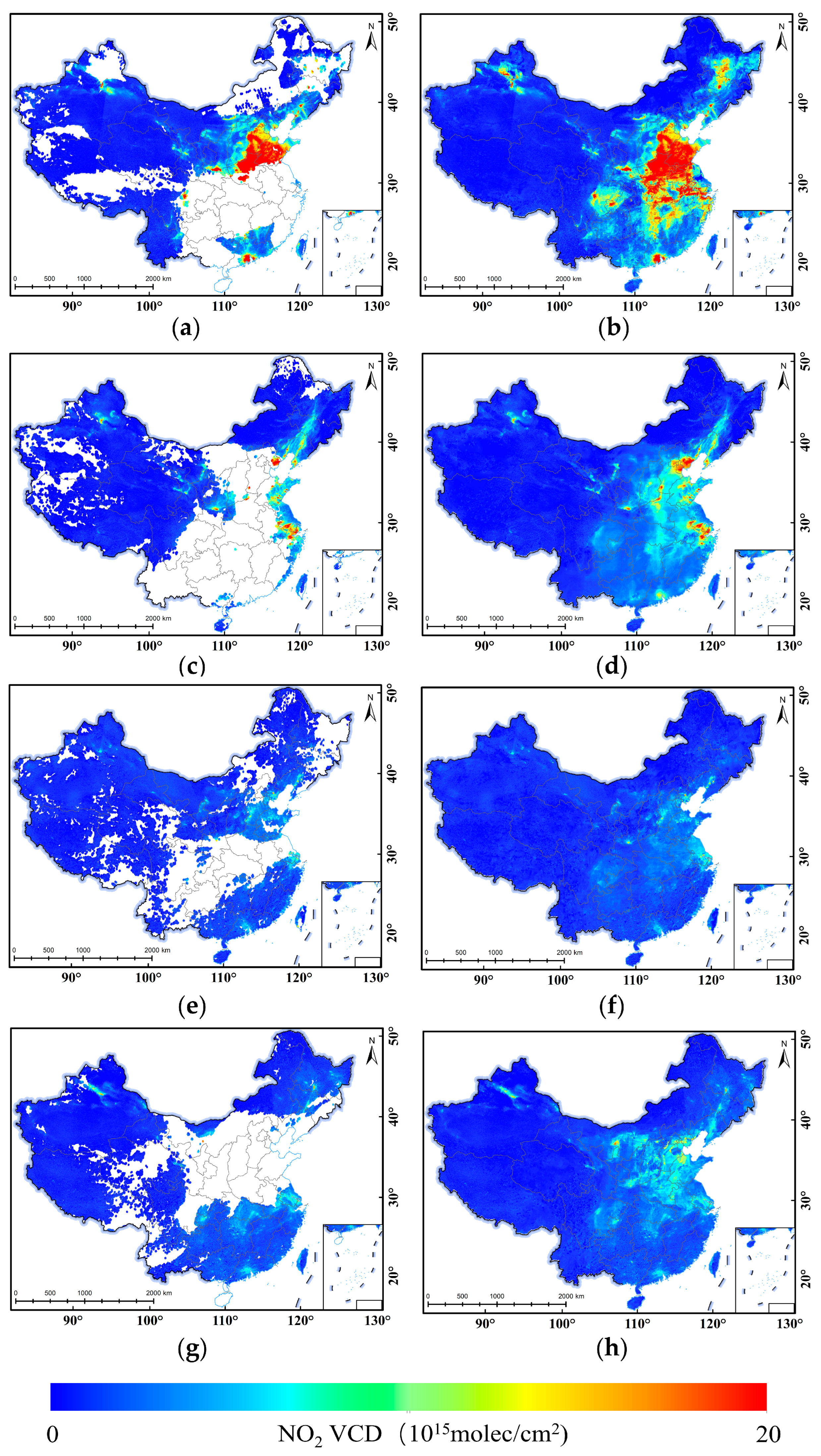
3.1. Gap Filling of Tropospheric NO2 VCD
3.1.1. Daily NO2 VCD and Verification
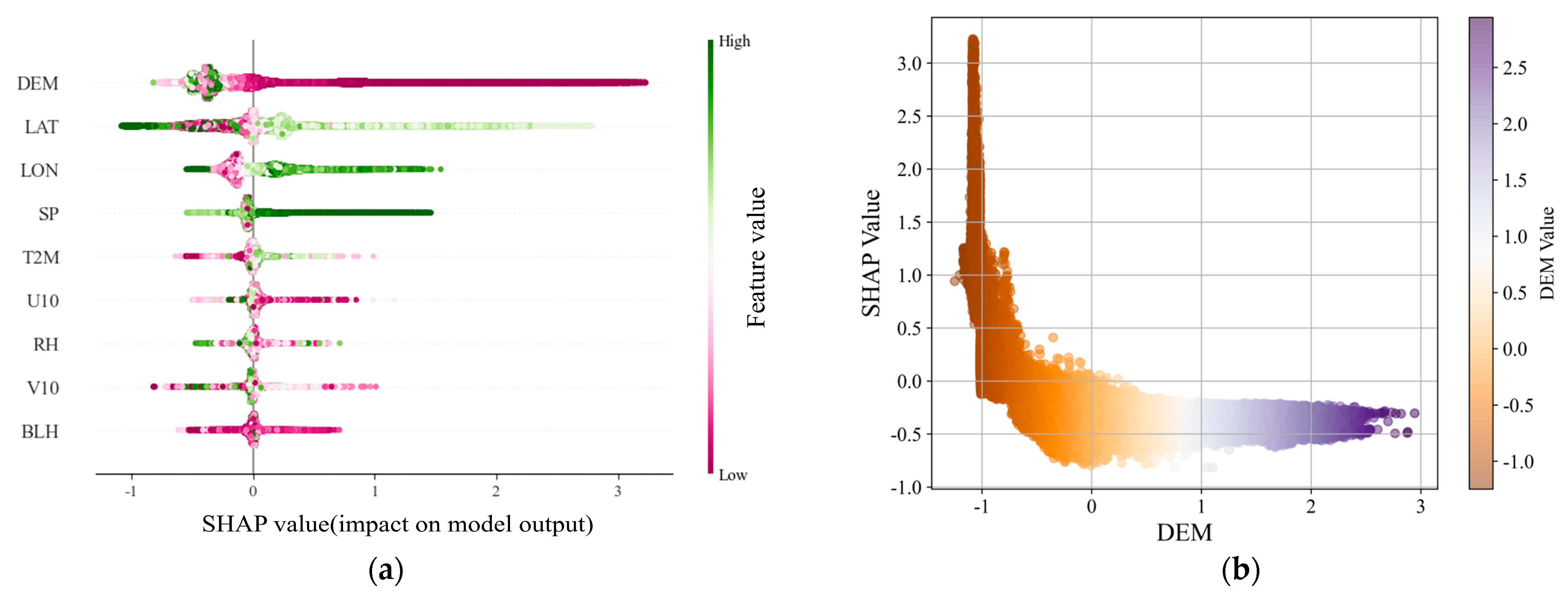
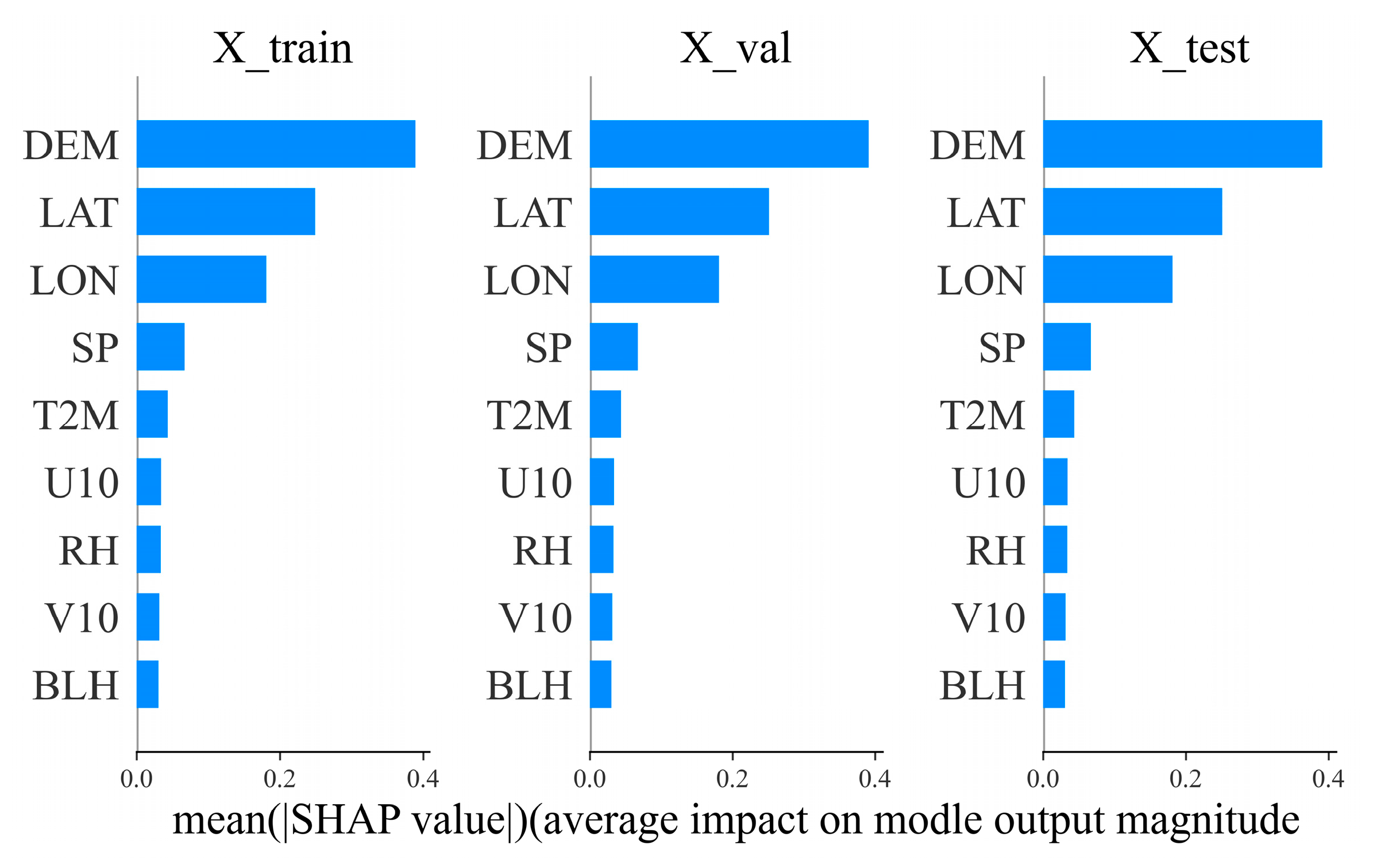
3.1.2. Analysis of Feature Contributions Using SHAP Values
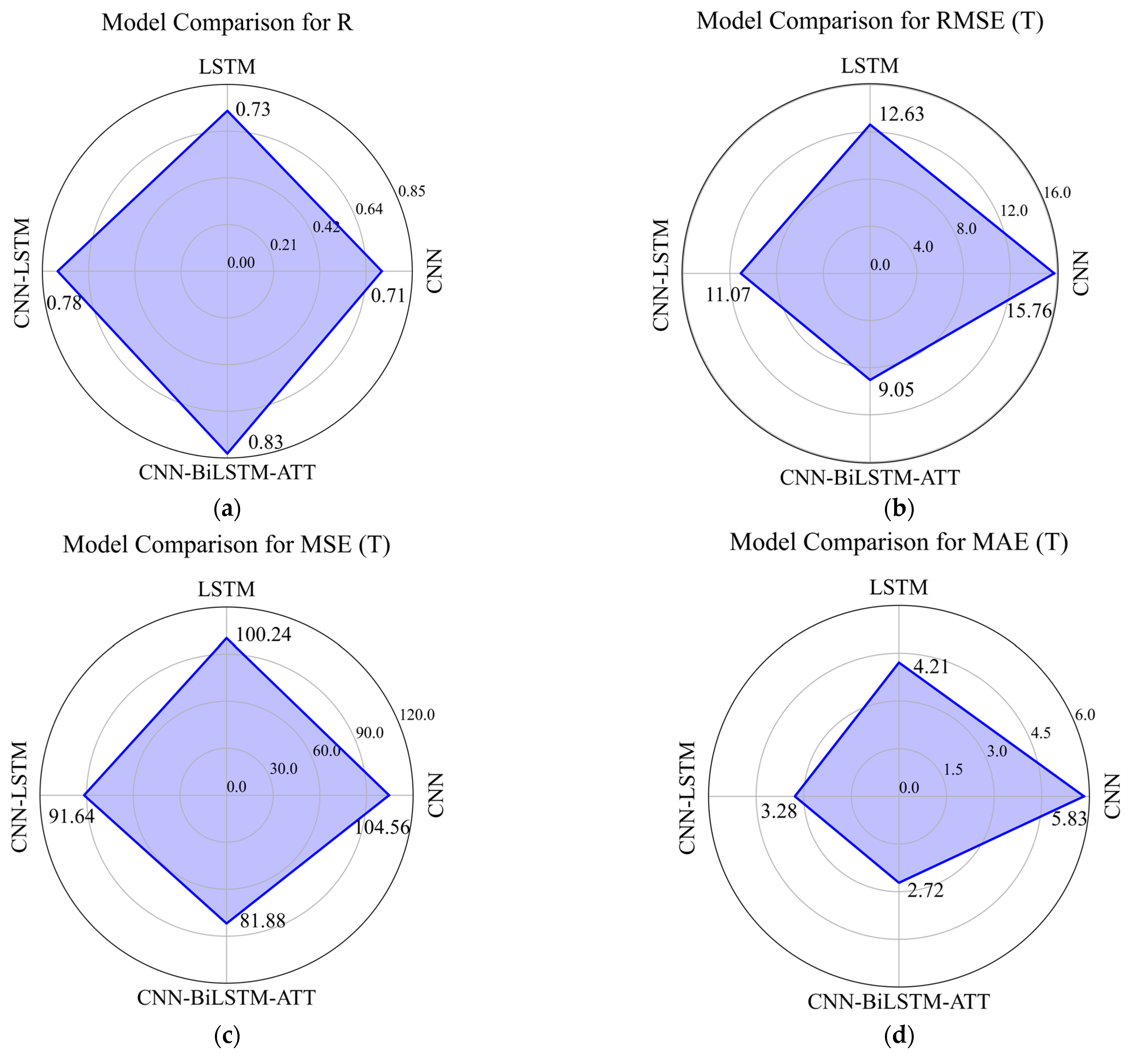
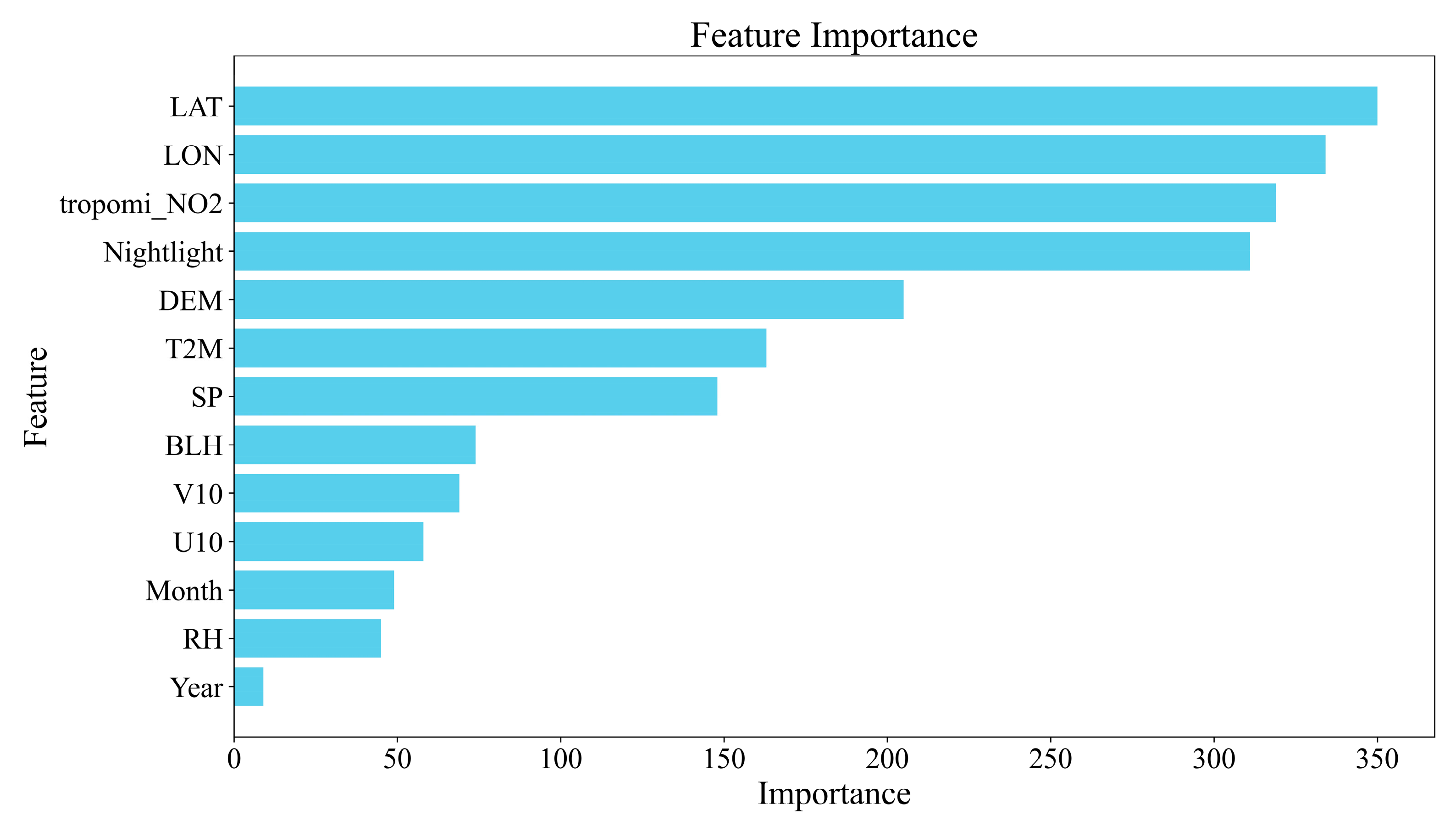
3.2. Model Comparison and Feature Importance
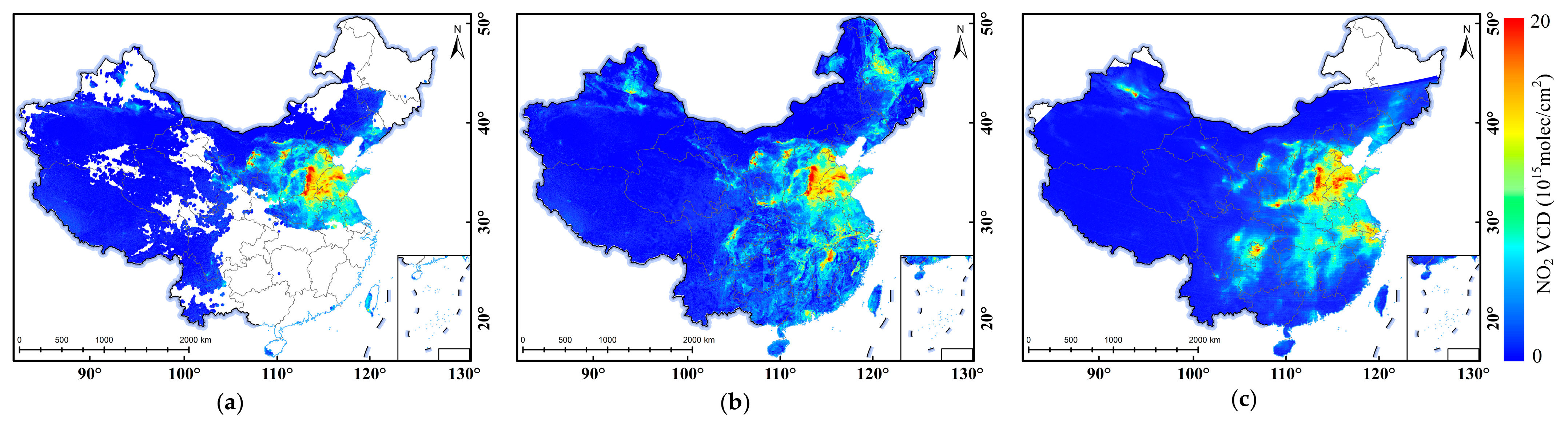
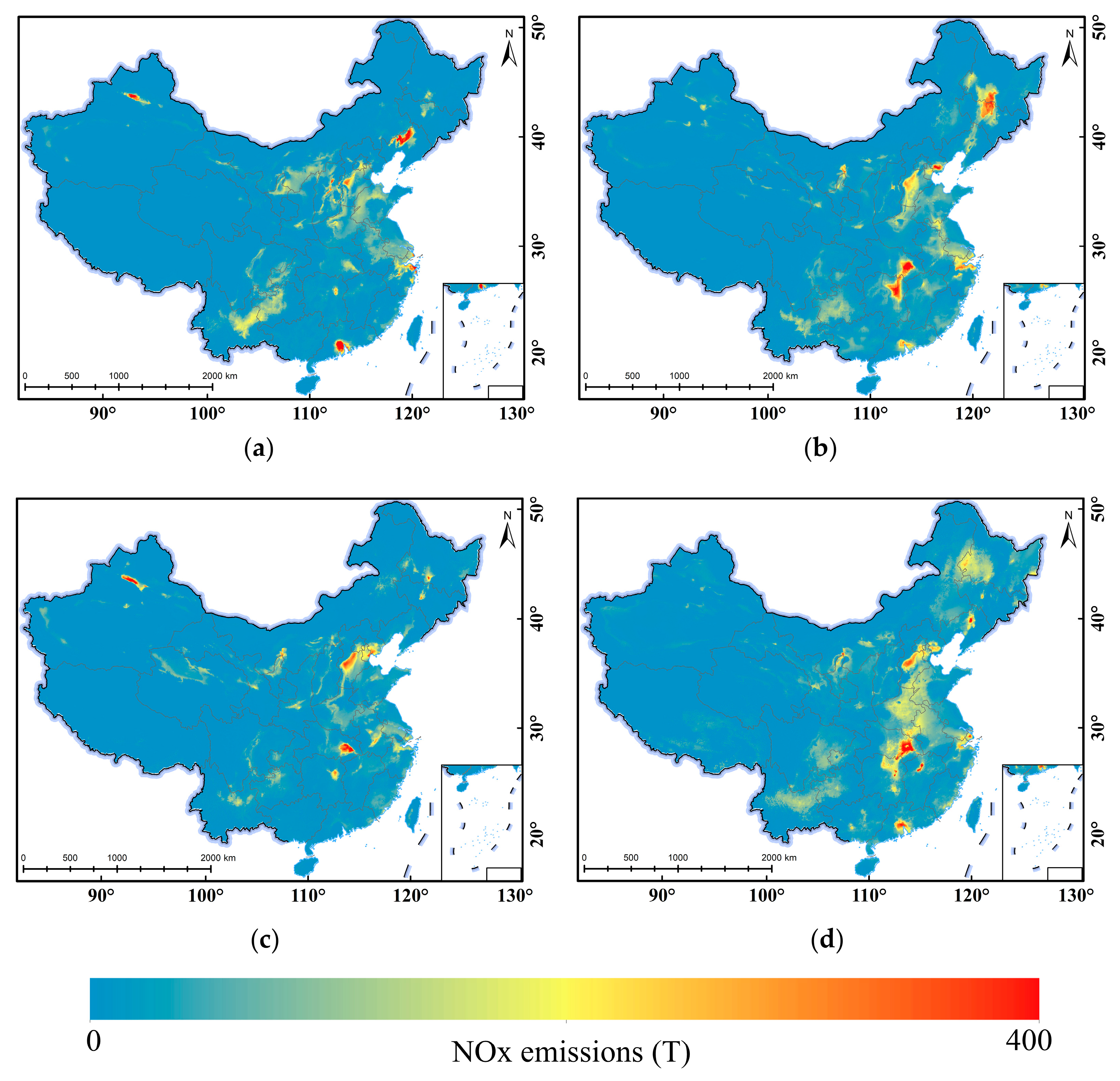
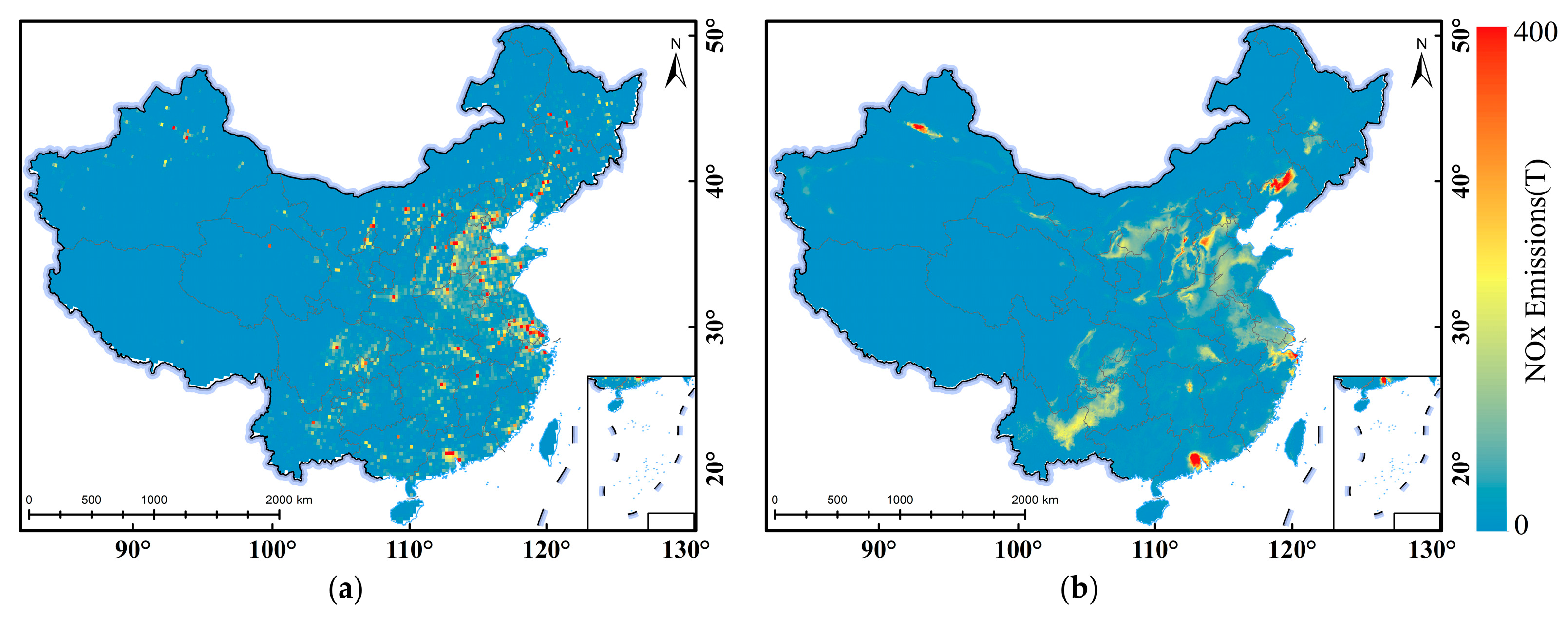
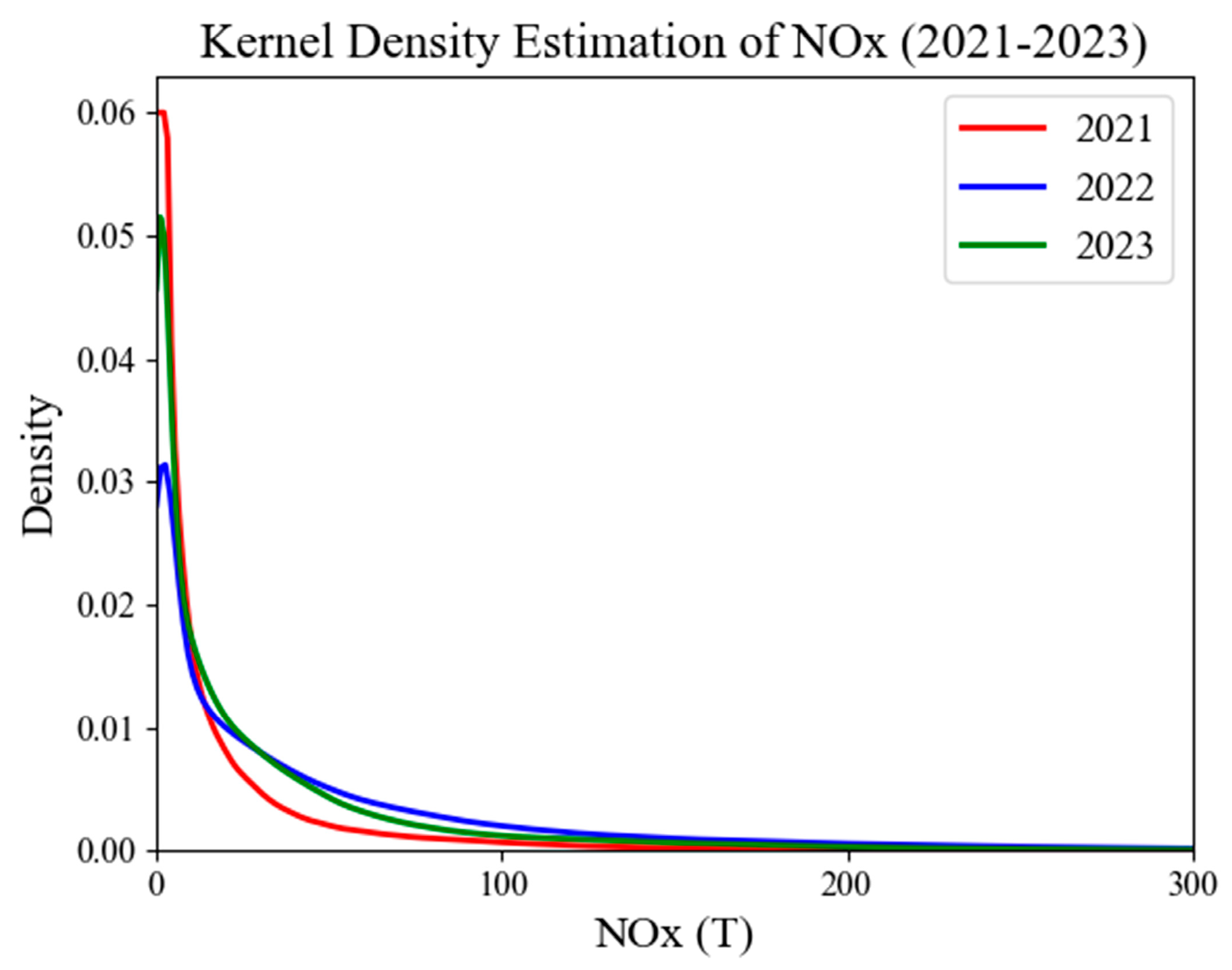
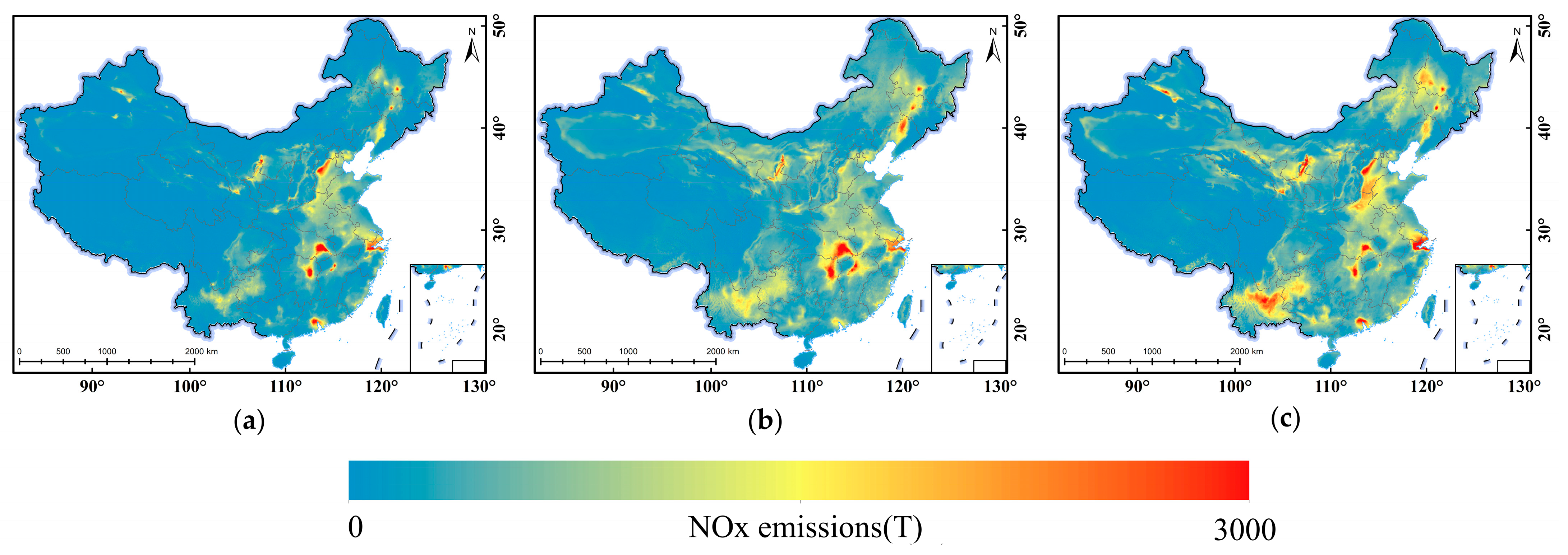
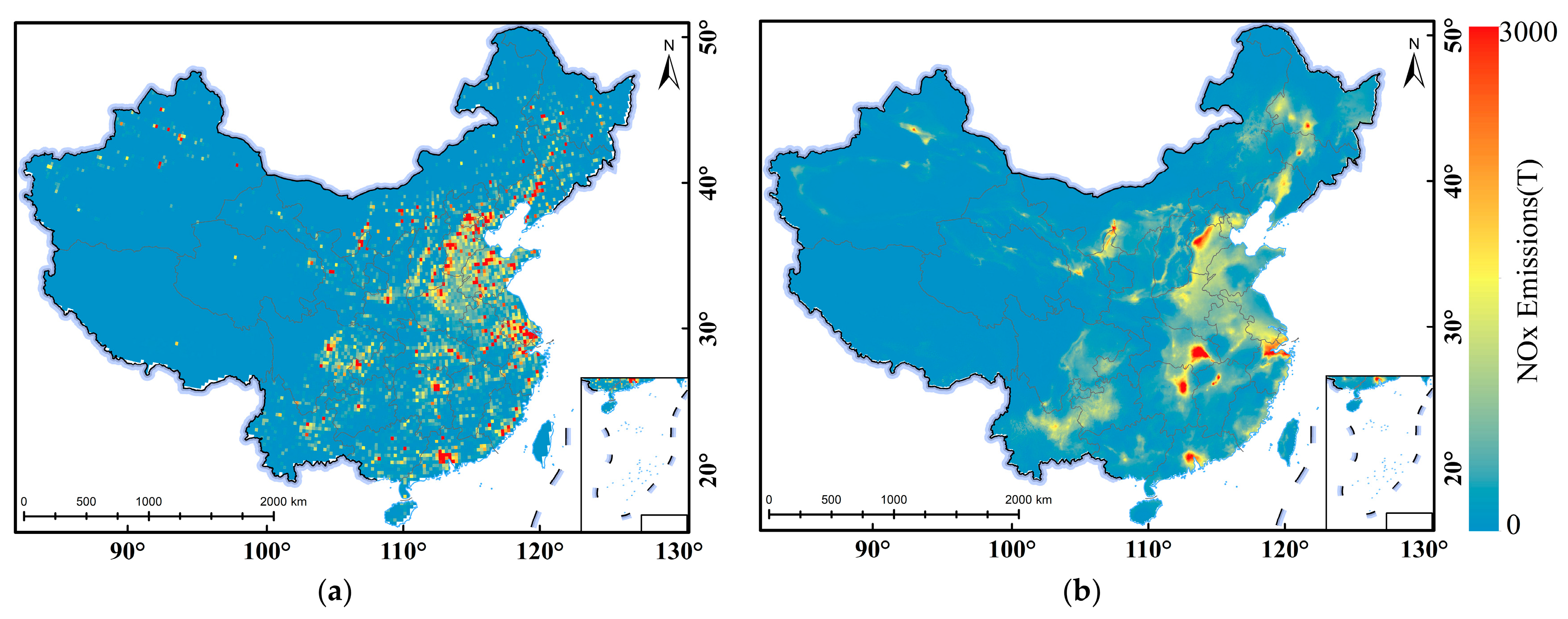
3.3. Monthly NOx Emissions Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noone, K. Physics Today. In Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 51, pp. 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, B.; Conibear, L.; Reddington, C.L.; Knote, C.; Arnold, S.R.; Spracklen, D.V. Pollutant emission reductions deliver decreased PM2.5-caused mortality across China during 2015–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11683–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H. Urban Air Pollution: State of the Science. Science 1989, 243, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, J.A. Nitrogen oxides in the troposphere: Global and regional budgets. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1983, 88, 10785–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, L.P.; Xu, R.Y.; Xie, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Y.Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Qin, H.X.; Wang, H.K.; Wu, X.C.; et al. Advantages of a city-scale emission inventory for urban air quality research and policy: The case of Nanjing, a typical industrial city in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12623–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Lei, Y.; McElroy, M.B.; Hao, J. Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Khorsandi, E.; Liu, S.; Baier, F.; Valks, P. Estimation of Surface NO2 Concentrations over Germany from TROPOMI Satellite Observations Using a Machine Learning Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes Jeffrey, A.; Martin Randall, V.; Boys Brian, L.; van Donkelaar, A. Long-Term Trends Worldwide in Ambient NO2 Concentrations Inferred from Satellite Observations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Di, B. Satellite-Based Estimates of Daily NO2 Exposure in China Using Hybrid Random Forest and Spatiotemporal Kriging Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. A machine learning model to estimate ground-level ozone concentrations in California using TROPOMI data and high-resolution meteorology. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Rao, L.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Zou, J.; Hao, N.; Li, S.; Yu, C. Estimating Ground Level NO2 Concentrations over Central-Eastern China Using a Satellite-Based Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bi, J. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, X.; Gu, D.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Long-Term Spatiotemporal Trends in Ambient NO(2) Concentrations and Attributable Health Burdens in China From 2005 to 2020. Geohealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Kong, F.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Feng, T. High-spatial resolution ground-level ozone in Yunnan, China: A spatiotemporal estimation based on comparative analyses of machine learning models. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Fang, W.; Hu, L.; Adams, M.; Bi, J.; Ma, Z. Estimation of daily NO2 with explainable machine learning model in China, 2007–2020. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 314, 120111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der, A.R.J.; Mijling, B.; Ding, J.; Koukouli, M.E.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Mao, H.; Theys, N. Cleaning up the air: Effectiveness of air quality policy for SO2 and NOx emissions in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirle, S.; Boersma, K.F.; Platt, U.; Lawrence, M.G.; Wagner, T. Megacity Emissions and Lifetimes of Nitrogen Oxides Probed from Space. Science 2011, 333, 1737–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Beirle, S.; Zhang, Q.; Dörner, S.; He, K.; Wagner, T. NOx lifetimes and emissions of cities and power plants in polluted background estimated by satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5283–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Van Der, A.R.J.; Ding, J. Detection and emission estimates of NOx sources over China North Plain using OMI observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2847–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Estimating daily full-coverage near surface O3, CO, and NO2 concentrations at a high spatial resolution over China based on S5P-TROPOMI and GEOS-FP. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Di, B.; Luo, Y.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Shi, G.; Yang, F.; et al. A robust approach to deriving long-term daily surface NO2 levels across China: Correction to substantial estimation bias in back-extrapolation. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Qin, K.; Liu, X.; Pinker, R.T.; Dickerson, R.R.; Lin, J.; Boersma, K.F.; et al. Ground-Level NO2 Surveillance from Space Across China for High Resolution Using Interpretable Spatiotemporally Weighted Artificial Intelligence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9988–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowski, P.T.; Markowicz, K.M.; Musiał, J.P. Estimations of the Ground-Level NO2 Concentrations Based on the Sentinel-5P NO2 Tropospheric Column Number Density Product. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno Jimenez, J.R.; Pugliese Viloria, A.d.J.; Brovelli, M.A. Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; de Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; de Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Rakitin, V. Comparison and Validation of TROPOMI and OMI NO2 Observations over China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Henze, D.K.; Ge, C.; Wang, W. Inverse modeling of SO2 and NOx emissions over China using multisensor satellite data—Part 2: Downscaling techniques for air quality analysis and forecasts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6651–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioletov, V.; McLinden, C.A.; Griffin, D.; Theys, N.; Loyola, D.G.; Hedelt, P.; Krotkov, N.A.; Li, C. Anthropogenic and volcanic point source SO2 emissions derived from TROPOMI on board Sentinel-5 Precursor: First results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5591–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Dan, T.; Meng, L.; Fei, L.; Chaopeng, H.; Guannan, G.; Haiyan, L.; Xin, L.; Liqun, P.; Ji, Q. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yan, L.; Wu, N.; Hu, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; et al. Efficacy of China’s clean air actions to tackle PM2.5 pollution between 2013 and 2020. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Fei, S. Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar]
- Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Jasemizad, T.; Govarthanan, M.; Karmegam, N.; Wijesekara, H.; Amarasiri, D.; Hou, D.; Zhou, P.; Biswal, B.K. Impacts of climate change on the fate of contaminants through extreme weather events. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 909, 168388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.; Crippen, R.; Fujisada, H. ASTER global digital elevation model (GDEM) and ASTER global water body dataset (ASTWBD). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisada, H.; Urai, M.; Iwasaki, A. Technical methodology for ASTER global DEM. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tian, G. Estimating nitrogen oxides emissions at city scale in China with a nightlight remote sensing model. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huo, T.; Streets, D.G.; Wang, C. Investigating the spatio-temporal influences of urbanization and other socioeconomic factors on city-level industrial NOx emissions: A case study in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 106998. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Li, R.; Cribb, M. Himawari-8-derived diurnal variations in ground-level PM2.5 pollution across China using the fast space-time Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7863–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.E.; Lu, S.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, X.H.; Ye, H.X.; Duan, Y.S.; Fu, Q.Y.; Li, J. Revealing the drivers of surface ozone pollution by explainable machine learning and satellite observations in Hangzhou Bay, China. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 440, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Gui, K.; Wang, Y.; Che, H.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W. Robust prediction of hourly PM2.5 from meteorological data using LightGBM. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raccagni, S.; Sangiorgi, L.; Carnevale, C.; Nardi, S.D. Convolutional Neural Network to forecast complex systems: The nitrogen oxides concentration case. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Valletta, Malta, 1–4 July 2024; pp. 860–865. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, H.; Thakkar, A. NOA-LSTM: An efficient LSTM cell architecture for time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Wang, B.; Gao, Q. A hybrid photovoltaic/wind power prediction model based on Time2Vec, WDCNN and BiLSTM. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 291, 117342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, W. Tutorial on time series prediction using 1D-CNN and BiLSTM: A case example of peak electricity demand and system marginal price prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Shao, S.; Liang, L. An evolutionary deep learning model based on EWKM, random forest algorithm, SSA and BiLSTM for building energy consumption prediction. Energy 2024, 288, 129795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Ali, S.; Eid, F.; El-Sappagh, S.; Abuhmed, T. Explainable machine learning models based on multimodal time-series data for the early detection of Parkinson’s disease. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 234, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
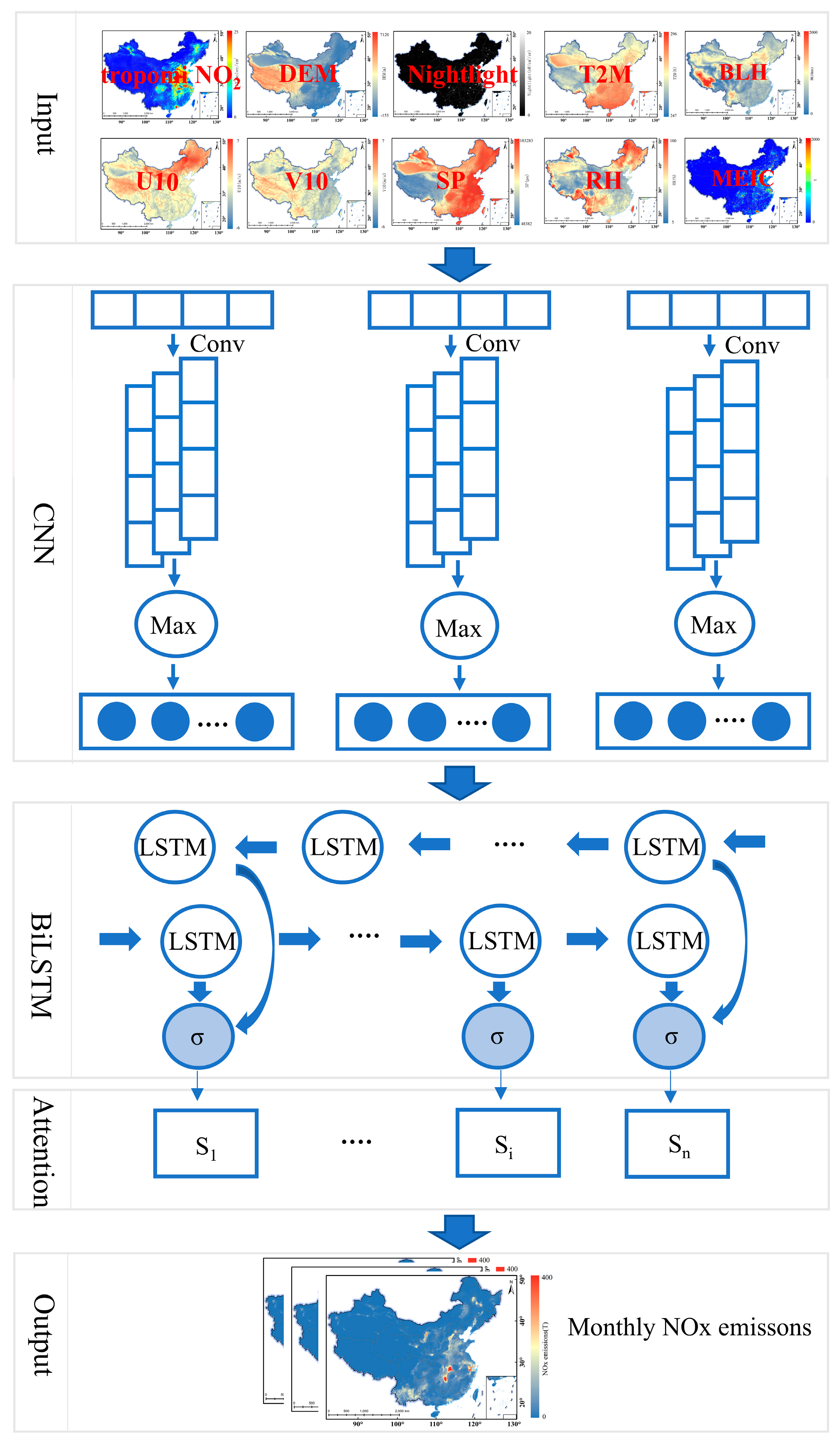




| Dataset | Variable | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TROPOMI | Tropospheric NO2 column | 5.5 km × 3.5 km | Daily | Sentinel-5P |
| Meteorology | U10, V10, T2M RH, SP, BLH | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly | ERA5 |
| Emission | NOx | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | MEIC |
| Topography | DEM | 30 m × 30 m | - | ASTER GDEM |
| VIIRS DNB | Nightlight | 500 m × 500 m | Monthly | SNPP |
| Model | R | RMSE | MSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-BiLSTM | 0.80 | 10.71 | 87.36 | 3.02 |
| CNN-BiLSTM-ATT | 0.83 | 9.05 | 81.88 | 2.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, K.; Shao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, M. Estimating NOx Emissions in China via Multisource Satellite Data and Deep Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071231
Cai K, Shao Y, Lin Y, Li S, Fan M. Estimating NOx Emissions in China via Multisource Satellite Data and Deep Learning Model. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071231
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Kun, Yanfang Shao, Yinghao Lin, Shenshen Li, and Minghu Fan. 2025. "Estimating NOx Emissions in China via Multisource Satellite Data and Deep Learning Model" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071231
APA StyleCai, K., Shao, Y., Lin, Y., Li, S., & Fan, M. (2025). Estimating NOx Emissions in China via Multisource Satellite Data and Deep Learning Model. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071231






