A Novel Electromagnetic Induction-Based Approach to Identify the State of Shallow Groundwater in the Oasis Group of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang During 2000–2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
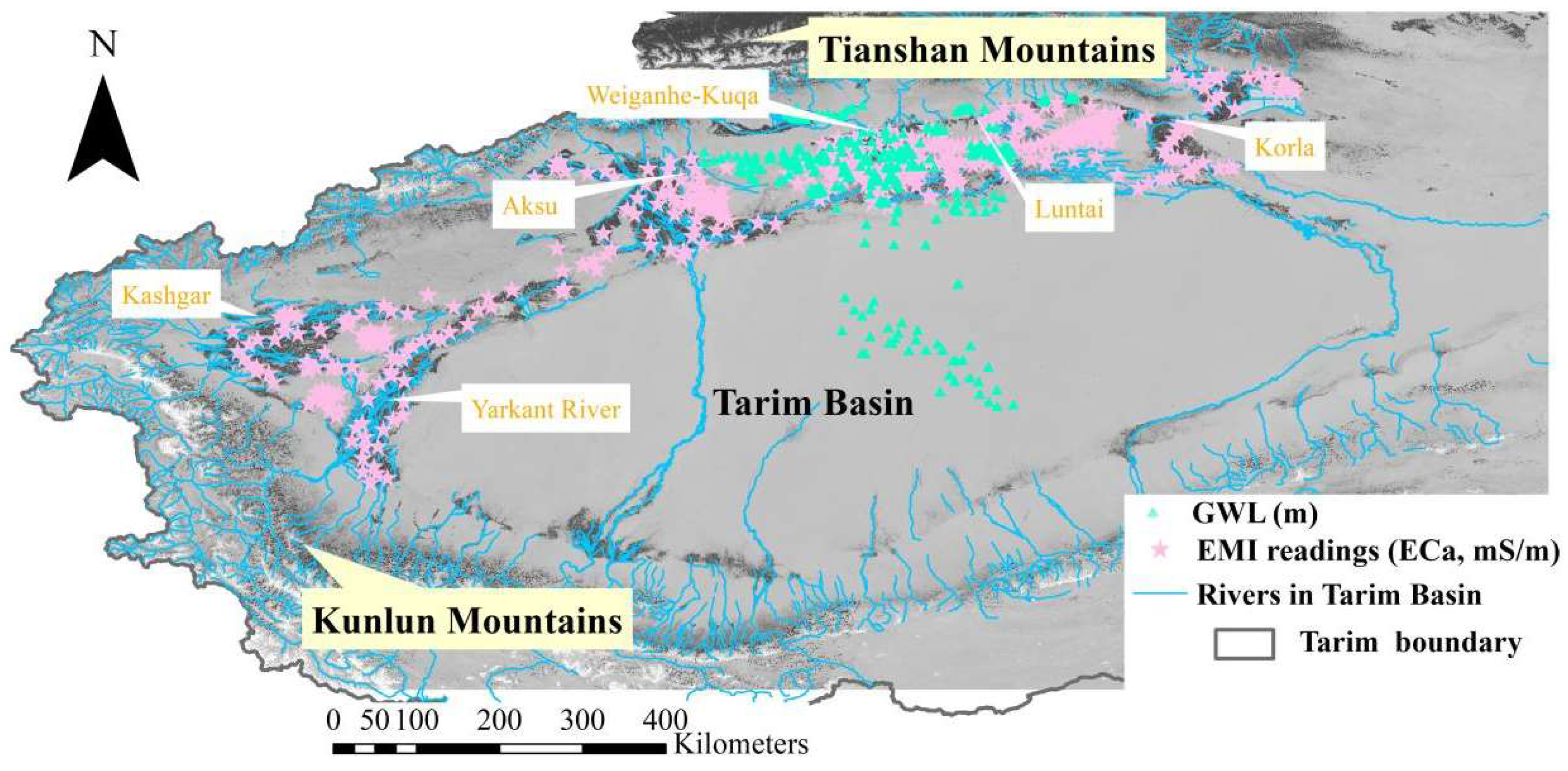
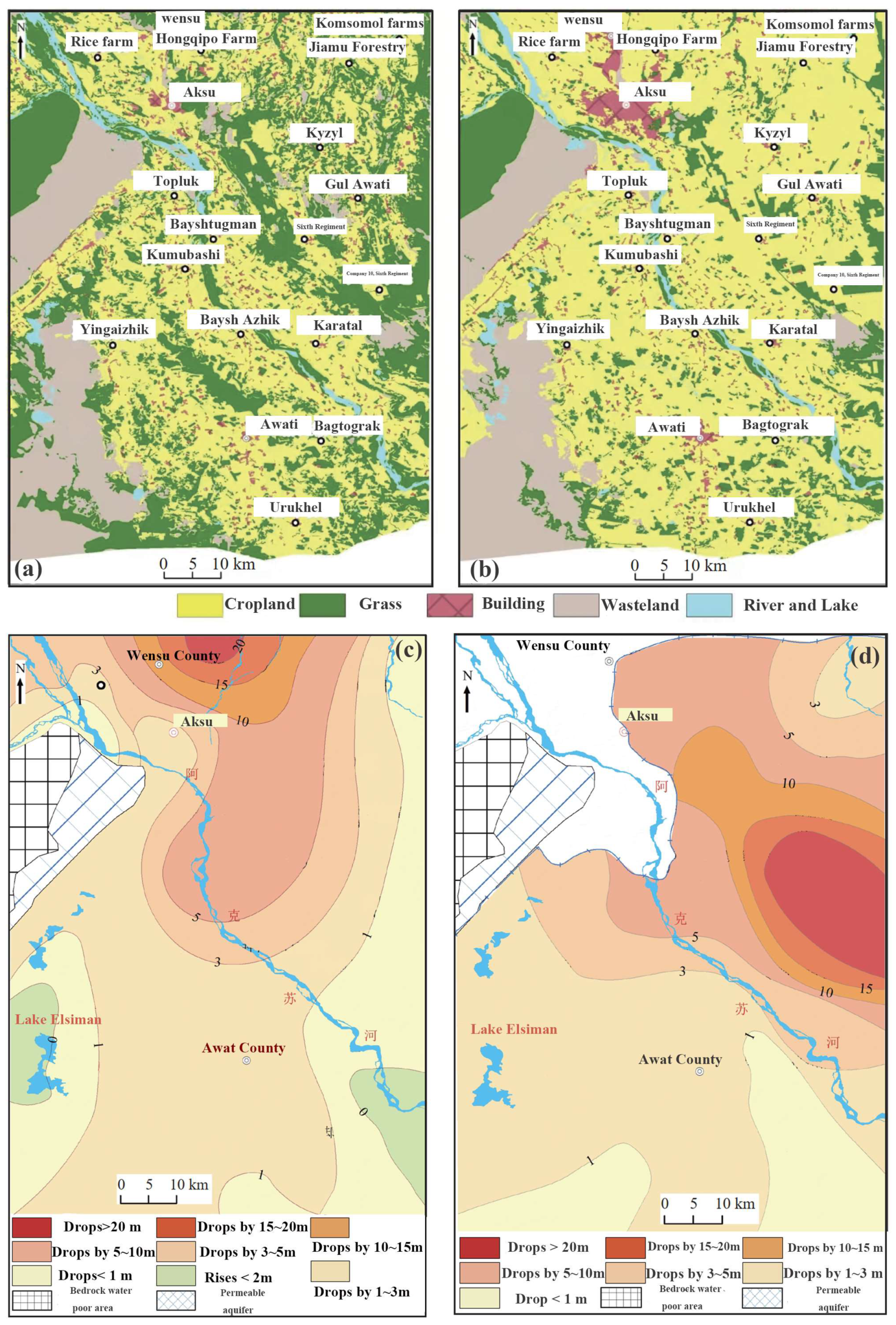
2.1. Study Area
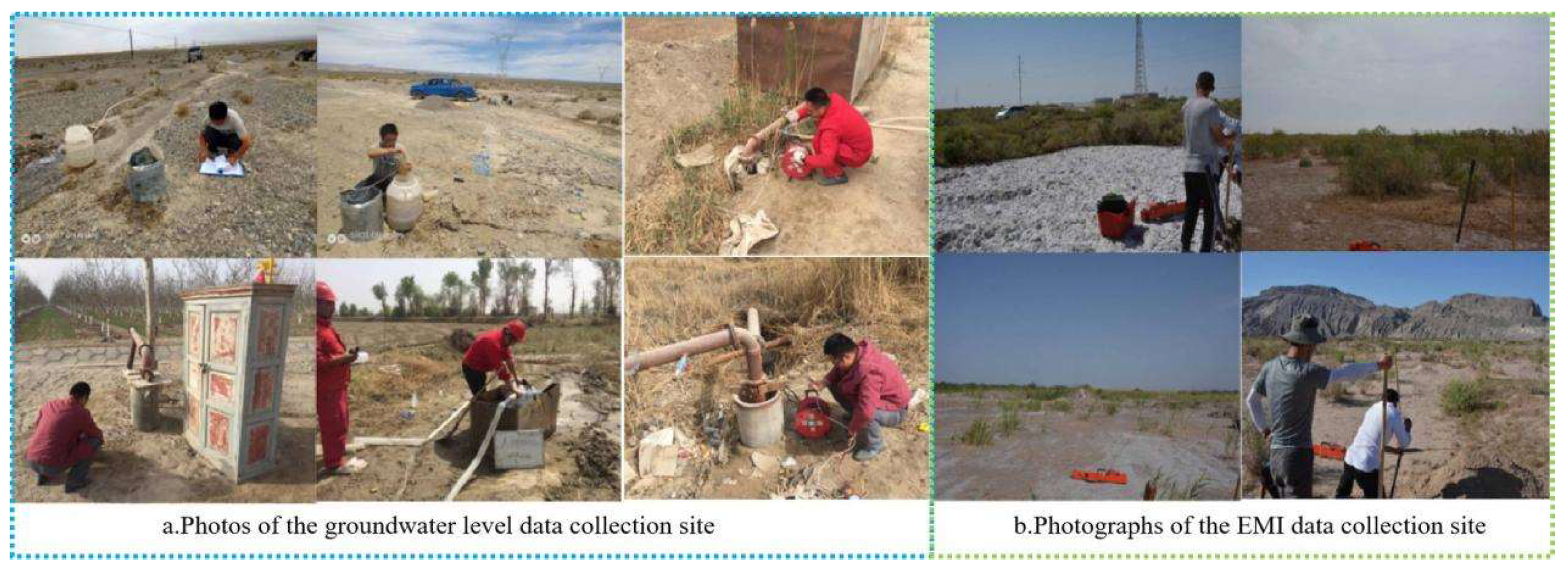
2.2. Field Measurements
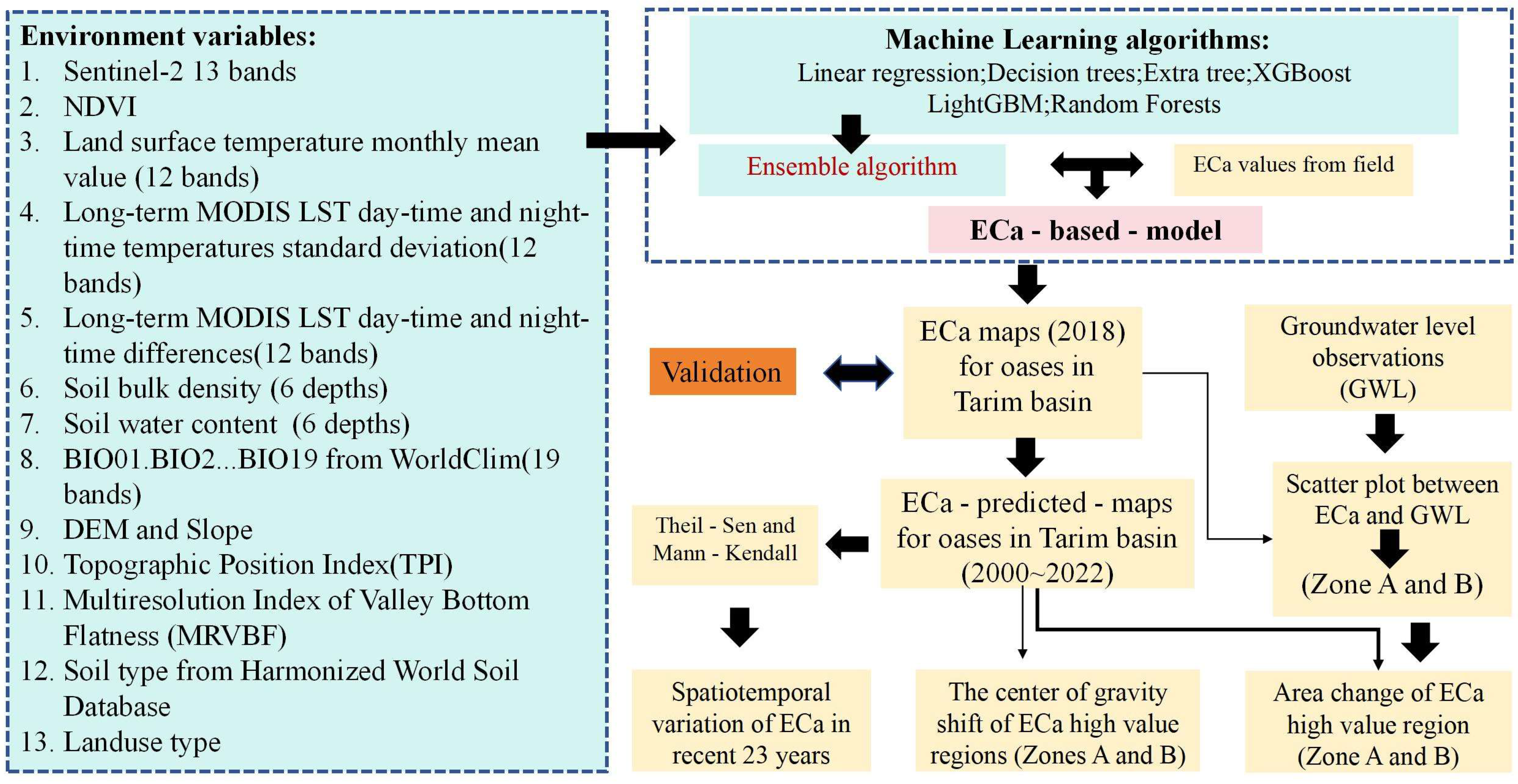
2.3. Environmental Variables
2.4. Machine Learning
2.5. Theil–Sen and Mann–Kendall
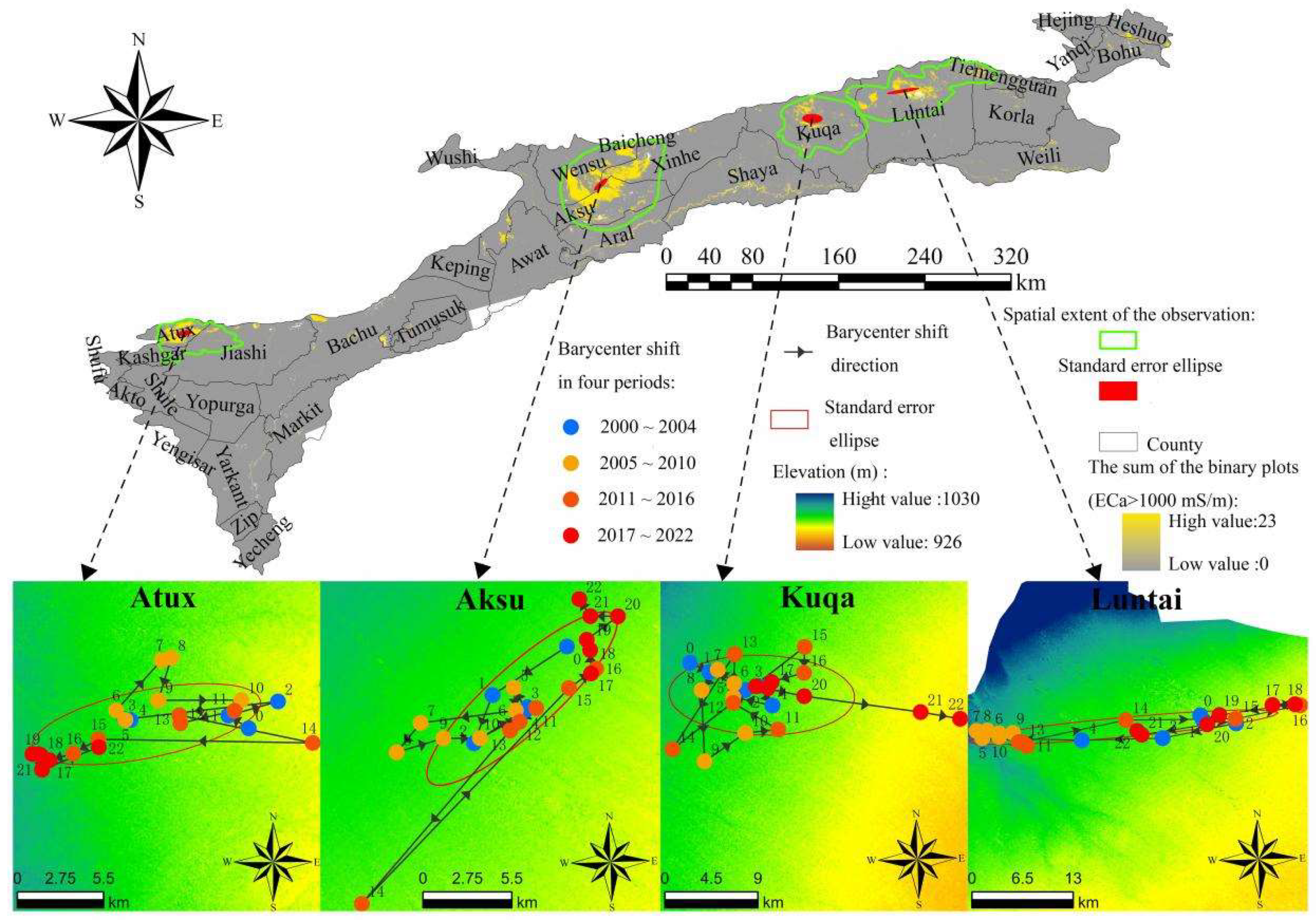
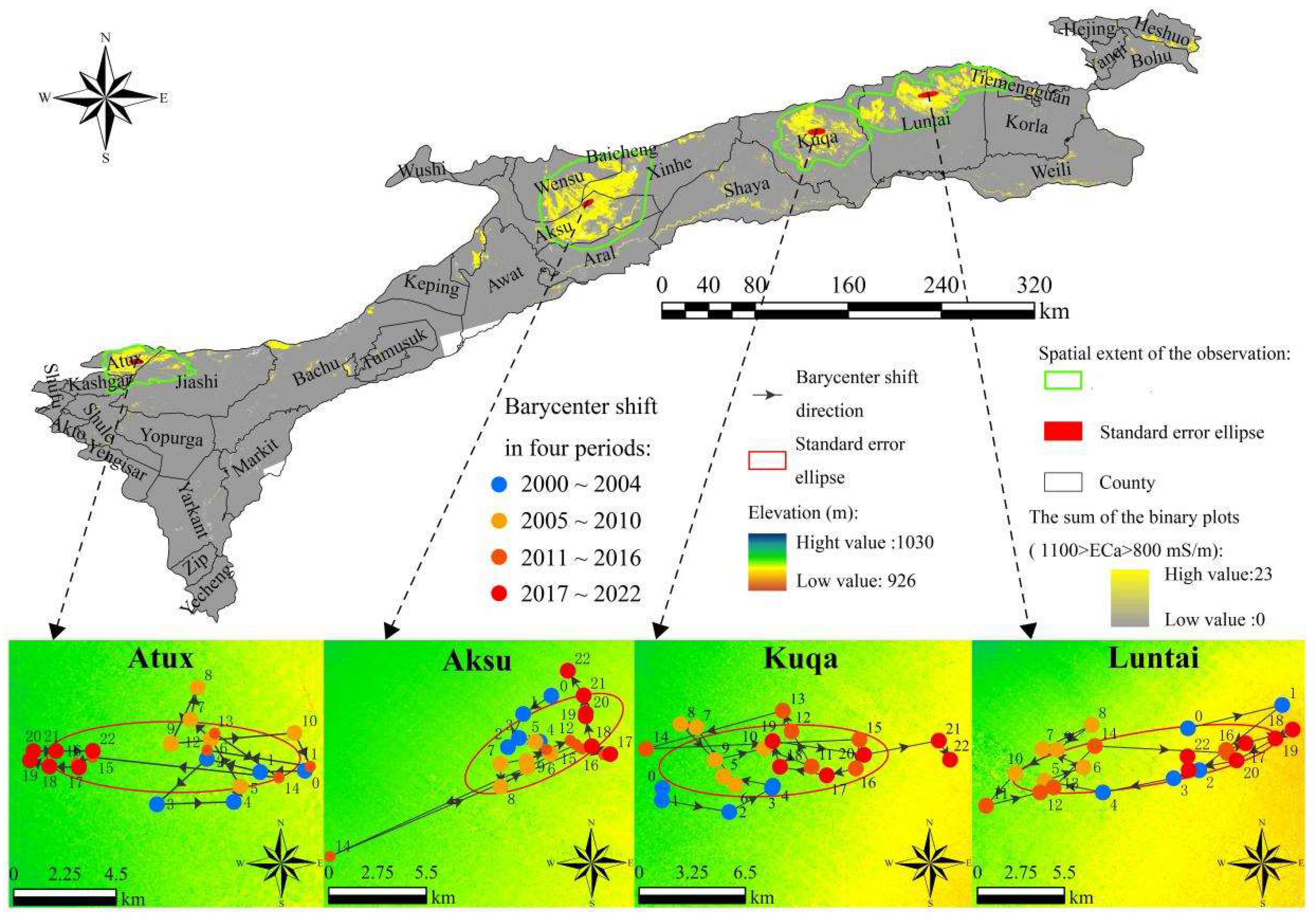
2.6. Barycenter Shift
2.7. Flowchart
2.8. Validation
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Characterization of GWL and ECa
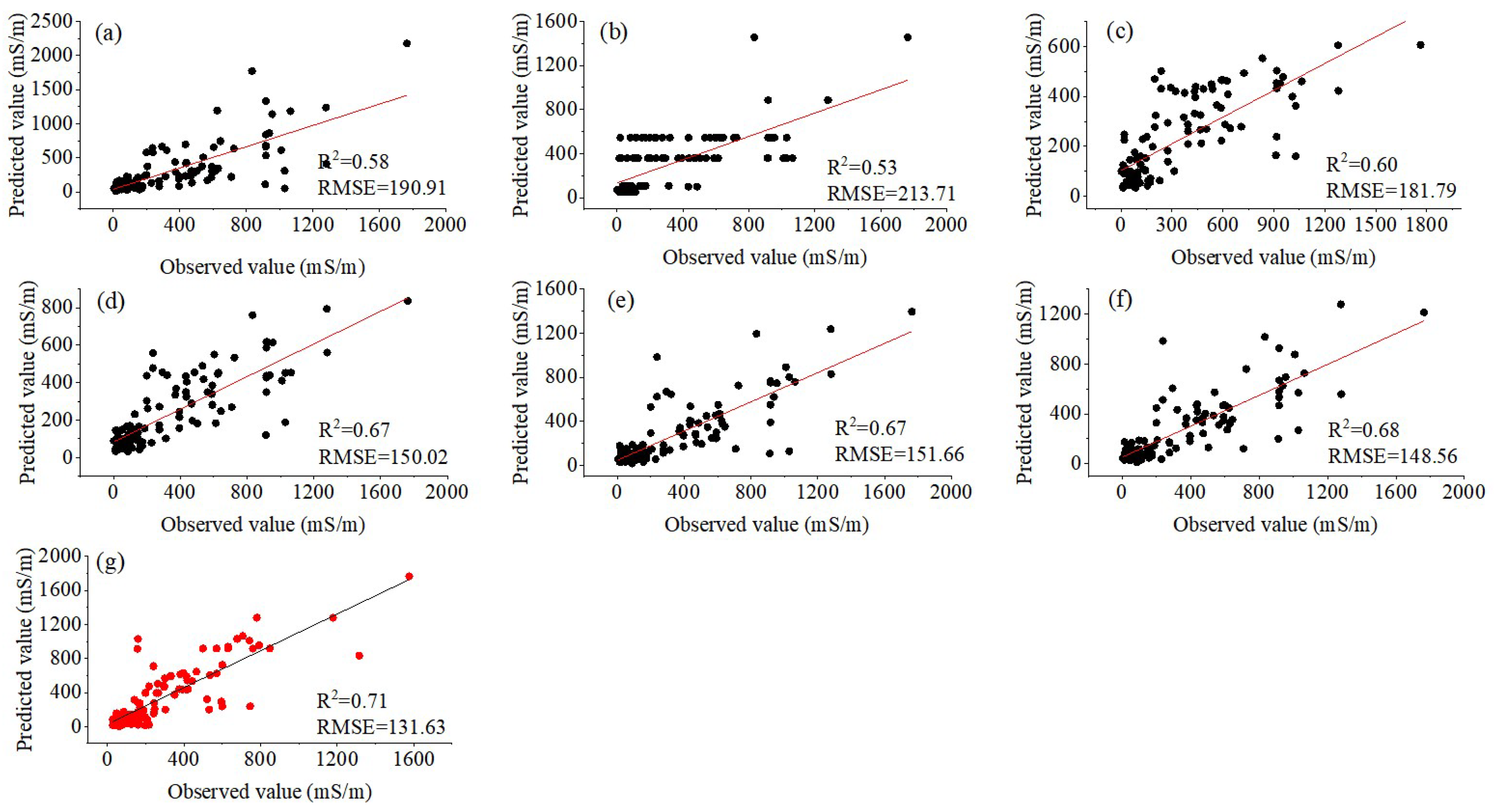
3.2. Validation of Apparent Conductivity Modeling
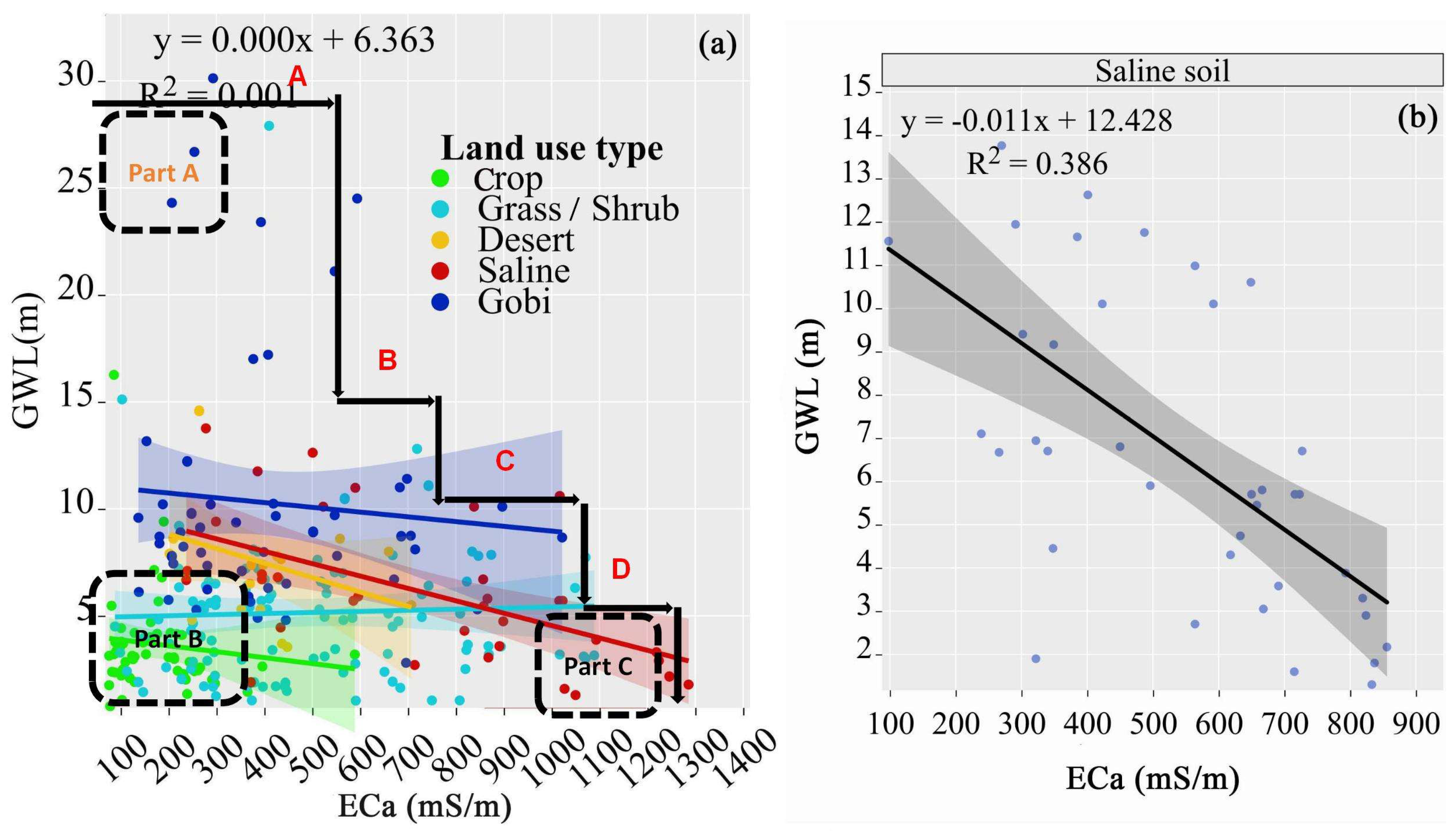
3.3. Relationship Between GWL and ECa
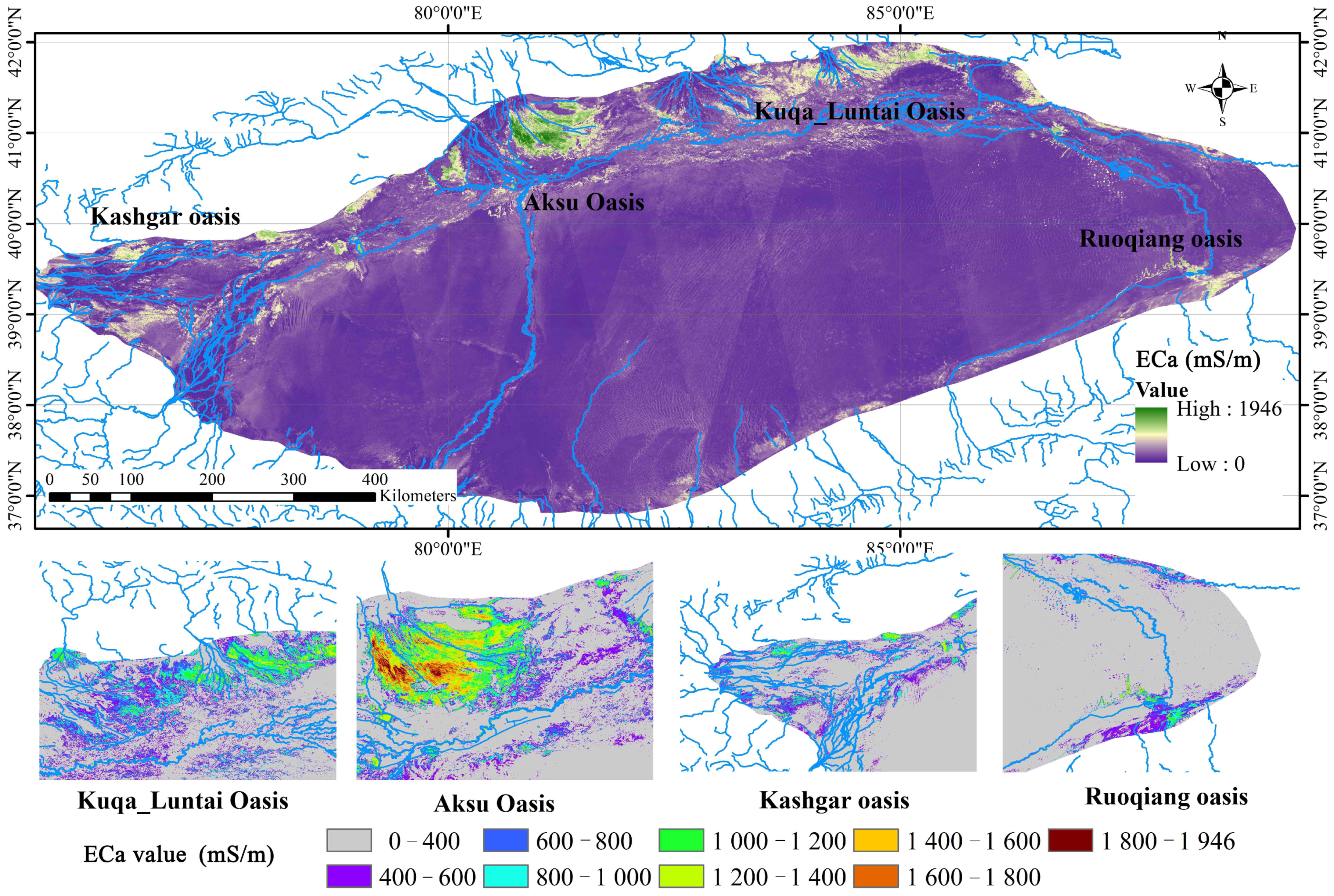
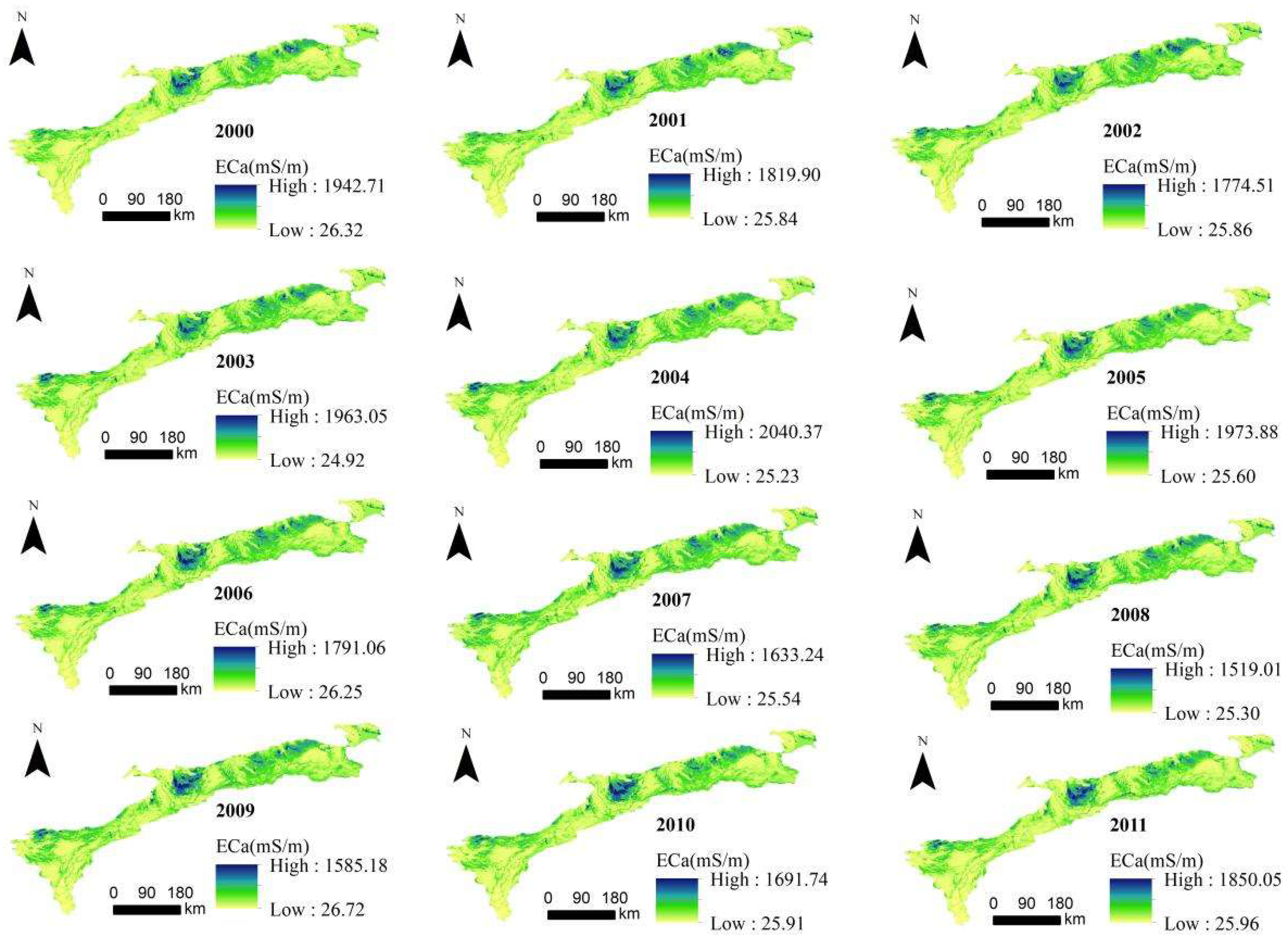
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of ECa
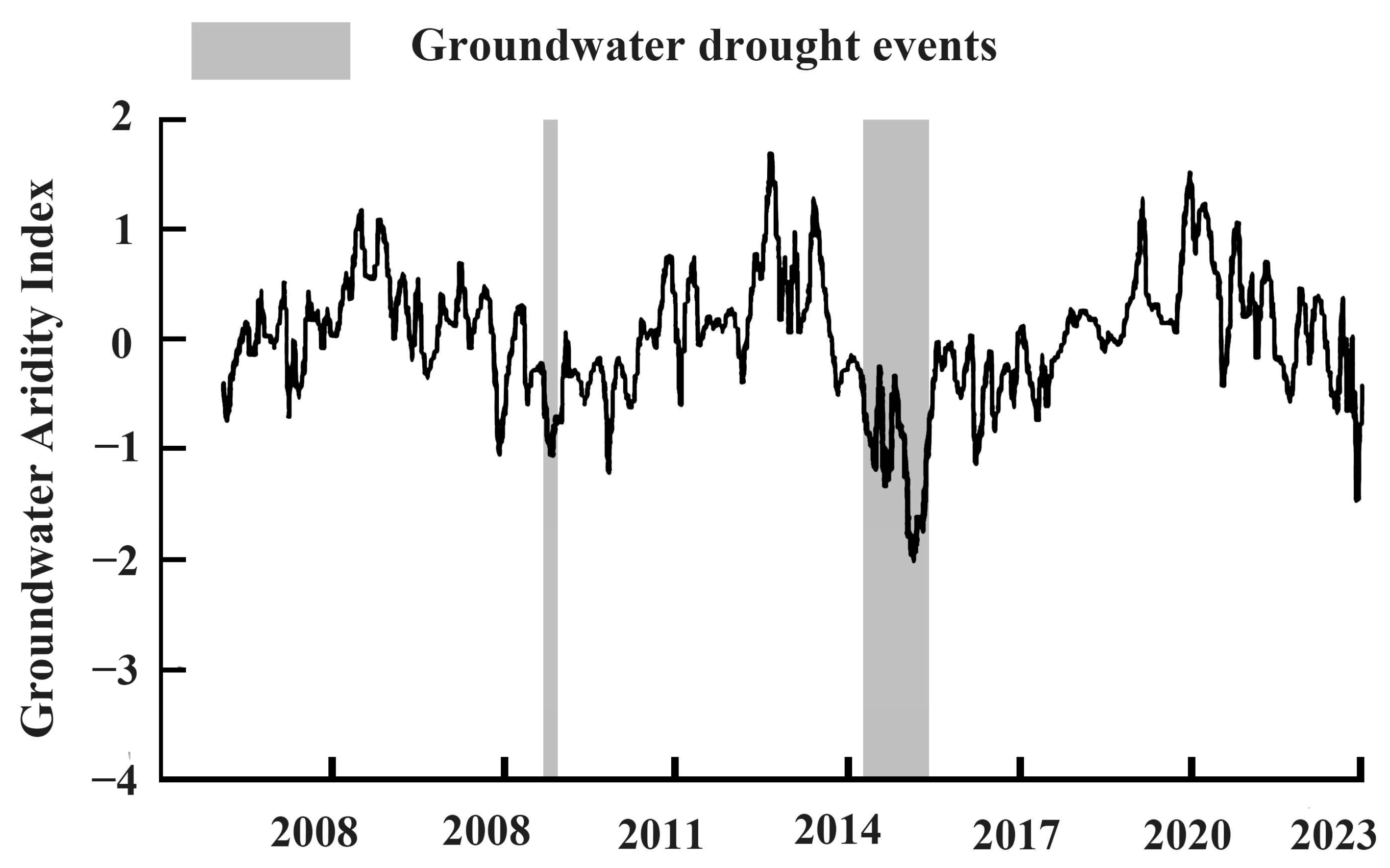
4. Discussion
4.1. ECa High Values Are Indicators of Shallow Groundwater (GWL < 5 m)
4.2. Land Use and Climate Change Are the Main Reasons for ECa Trends
4.3. The Relationship Between Groundwater Resource Reserves and the Area Change of the ECa High Value Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization management for sustainable development: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar]
- Khorrami, M.; Malekmohammadi, B. Effects of excessive water extraction on groundwater ecosystem services: Vulnerability assessments using biophysical approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wei, Y.; Yang, S. Enhanced Understanding of Key Soil Properties in Northern Xinjiang Using Water-Heat-Spectral Datasets Based on Bioclimatic Guidelines. Land 2023, 12, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J. Deterioration of groundwater quality along an increasing intensive land use pattern in a small catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106953. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Deo, R.C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R. An interplay of soil salinization and groundwater degradation threatening coexistence of oasis-desert ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Mann, M.E.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G. Climate change threatens terrestrial water storage over the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 801–807. [Google Scholar]
- Bogena, H.R.; Weuthen, A.; Huisman, J.A. Recent developments in wireless soil moisture sensing to support scientific research and agricultural management. Sensors 2022, 22, 9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, C.; Huisman, J.; Pätzold, S.; Von Hebel, C.; Weihermüller, L.; Kaufmann, M.; Van Der Kruk, J.; Vereecken, H. Large-scale soil mapping using multi-configuration EMI and supervised image classification. Geoderma 2019, 335, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Protocols and guidelines for field-scale measurement of soil salinity distribution with ECa-directed soil sampling. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2013, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Validation of the ANOCOVA model for regional-scale ECa to ECe calibration. Soil. Use. Manag. 2016, 33, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Brevik, E.C. The use of electromagnetic induction techniques in soils studies. Geoderma 2014, 223, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, P.; Schmutz, M.; Cavailhes, J.; Hubbard, S. Estimating grapevine-relevant physicochemical soil zones using apparent electrical conductivity and in-phase data from EMI methods. Geoderma 2022, 426, 116033. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, N.R.; Alesso, C.A.; Costa, J.L.; Martin, N.F. Mapping soil depth in southern pampas Argentina using ancillary data and statistical learning. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Brus, D.J.; Walvoort, D.J.J. Geostatistical monitoring of soil salinity in Uzbekistan by repeated EMI surveys. Geoderma 2014, 213, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Koganti, T.; Santos, F.A.M.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping soil salinity and a fresh-water intrusion in three-dimensions using a quasi-3d joint-inversion of DUALEM-421S and EM34 data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Remote sensing prediction and characteristic analysis of cultivated land salinization in different seasons and multiple soil layers in the coastal area. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 2022, 111, 102838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Long, R.; Yu, K.; Jiang, J.; Yang, B.; Lu, Y. Evolution and Genetic Pattern of Groundwater Flow Field in the Aksu River Basin of Xinjiang Over the Past 40 Years. Northw. Geol. 2024, 57, 252–261. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, D.; Tian, Z. Spatio-temporal changes and its driving forces of irrigation water requirements for cotton in Xinjiang, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Xia, Z.; Li, X.; Kayumba, P.M. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the dried-up river oasis of the Tarim Basin, Central Asia. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, A.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Source and enrichment mechanism of fluoride in groundwater of the Hotan Oasis within the Tarim Basin, Northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargrove, W.; Heyman, J.; Mayer, A.; Mirchi, A.; Granados-Olivas, A.; Ganjegunte, G.; Gutzler, D.; Pennington, D.; Ward, F.; Chavira, L.G. The future of water in a desert river basin facing climate change and competing demands: A holistic approach to water sustainability in arid and semi-arid regions. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2023, 46, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyan, K. Issues and challenges of groundwater and surface water management in semi-arid regions. In Groundwater Resources Development and Planning in the Semi-Arid Region; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Tiyip, T.; Feng, Z.; Kung, H.T.; Johnson, V.; Ding, J.; Tashpolat, N.; Sawut, M.; Gui, D. Spatio-temporal patterns of land use/cover changes over the past 20 years in the middle reaches of the Tarim River, Xinjiang, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Gu, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, J. Spatial and temporal mapping of cropland expansion in northwestern China with multisource remotely sensed data. Catena 2019, 183, 104192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z. Assessment of the irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; He, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Salam, A.; Lu, B.; Yasheng, Y. Spatio-temporal changes of land surface temperature and the influencing factors in the Tarim basin, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, C.; Hao, X. Effects of climate change on water resources in Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, F.; Hong, B.; Yang, S. Revealing spatial variability of groundwater level in typical ecosystems of the Tarim Basin through ensemble algorithms and limited observations. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Somee, B.S.; Zadeh, M.R. Testing for long-term trends in climatic variables in Iran. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematchoua, M.K.; Orosa, J.A.; Afaifia, M. Prediction of daily global solar radiation and air temperature using six machine learning algorithms; a case of 27 European countries. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101643. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, L.; Agathokleous, E.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Y.; Sun, S. Modeling daily global solar radiation using only temperature data: Past, development, and future. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2022, 163, 112511. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhai, P.-M.; Qin, D.-H. New perspectives on ‘warming–wetting’trend in Xinjiang, China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Cai, M.; Xu, Y. Evolution characteristics of groundwater and its response to climate and land-cover changes in the oasis of dried-up river in Tarim Basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; He, H.; Zong, R.; Wang, D.; Jia, Z.; Wen, Y. Experiences and challenges of agricultural development in an artificial oasis: A review. Agric. Syst. 2021, 193, 103220. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Ding, J.; Huang, W.; Ma, X. Spatiotemporal Variation and Future Predictions of Soil Salinization in the Werigan–Kuqa River Delta Oasis of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Shi, G.; Feng, L.; Yang, J. Study on the evolution and optimization of the spatial structure of the oasis in the arid area: A case study of the Aksu River Basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R. Multi-scale assessments of droughts: A case study in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Shen, M.X.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Hong, S. Trends of natural runoffs in the Tarim River Basin during the last 60 years. J. Arid Land 2018, 41, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.-A.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Lu, J.; Huang, H.Q.; Yi, Y. Effects of riparian plant roots on the unconsolidated bank stability of meandering channels in the Tarim River, China. Geomorphology 2020, 351, 106958. [Google Scholar]
- Tromp, H.; van Meerveld, I.; McDonnell, J. Assessment of multi-frequency electromagnetic induction for determining soil moisture patterns at the hillslope scale. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imin, B.; Dai, Y.; Shi, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Nijat, M. Responses of two dominant desert plant species to the changes in groundwater depth in hinterland natural oasis, Tarim Basin. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 9460–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahour, H.; Sultan, M.; Abdellatif, B.; Emil, M.; Abotalib, A.Z.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Vazifedan, M.; Mohammad, A.T.; Hassan, S.M.; Metwalli, M.R.; et al. Identification of shallow groundwater in arid lands using multi-sensor remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.; Lintner, B.R.; Findell, K.L.; Malyshev, S.; Loikith, P.C.; Gentine, P. Impact of soil moisture–atmosphere interactions on surface temperature distribution. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 7976–7993. [Google Scholar]
- Pablos, M.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; Vall-llossera, M.; Camps, A. Multi-temporal evaluation of soil moisture and land surface temperature dynamics using in situ and satellite observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.S. Evaluation of soil water retention models based on basic soil physical properties. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Ran, Q.; He, G.; Tiyip, T. A soil quality assessment under different land use types in Keriya river basin, Southern Xinjiang, China. Soil. Till Res. 2015, 146, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokach, L.; Maimon, O. Decision trees. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 165–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, United States, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R.; Niculescu-Mizil, A.; Crew, G.; Ksikes, A. Ensemble selection from libraries of models. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Garba, H.; Udokpoh, U.U. Analysis of trend in meteorological and hydrological time-series using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical test in Akwa Ibom state, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyikadzino, B.; Chitakira, M.; Muchuru, S. Rainfall and runoff trend analysis in the Limpopo river basin using the Mann Kendall statistic. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 117, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Ling, H.; Yan, J.; Deng, M.; Deng, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, W. Shift in the migration trajectory of the green biomass loss barycenter in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forests: A case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Qin, G. Characterizing spatiotemporal variations of soil salinization and its relationship with eco-hydrological parameters at the Regional Scale in the Kashi Area of Xinjiang, China from 2000 to 2017. Water 2021, 13, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, E.; Aydin, M.; Kapur, S.; Kume, T.; Nagano, T.; Watanabe, T.; Çilek, A.; Zorlu, K. Long-term monitoring of soil salinity in a semi-arid environment of Turkey. Catena 2020, 193, 104614. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, J.; Gui, Z.; Yu, Z. Evolution of soil salinity and the critical ratio of drainage to irrigation (CRDI) in the Weigan Oasis in the Tarim Basin. Catena 2021, 201, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Du, M.; Mu, Z.; Gao, F. Analysis on the variation of groundwater resources and influencing factorsin Xinjiang plain area from 1956 to 2016. Adv. Water Sci. 2021, 32, 660–669. [Google Scholar]
- Shean, D.E.; Bhushan, S.; Montesano, P.; Rounce, D.R.; Arendt, A.; Osmanoglu, B. A systematic, regional assessment of high mountain Asia glacier mass balance. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Bolch, T.; Farinotti, D.; Kriegel, D.; Vorogushyn, S.; Merz, B.; Pieczonka, T.; Jiang, T.; Su, B.; Güntner, A. Attribution of streamflow trends in snow and glacier melt-dominated catchments of the Tarim R iver, Central A sia. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Yu, F.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variation of land surface temperature and its driving factors in Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 373–395. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; He, H.; Gao, J.; Nie, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wei, C.; Xie, X. Analysis of temporal-spatial variation characteristics of drought: A case study from Xinjiang, China. Water 2020, 12, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Duethmann, D.; Wortmann, M.; Liu, S.; Disse, M. Declining glaciers endanger sustainable development of the oases along the Aksu-Tarim River (Central Asia). Int. J. Sust. Dev. World 2022, 29, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wortmann, M.; Duethmann, D.; Menz, C.; Shi, F.; Zhao, C.; Su, B.; Krysanova, V. Adaptation strategies of agriculture and water management to climate change in the Upper Tarim River basin, NW China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Analysis of groundwater depth status and countermeasures in Aksu River Basin. Water Resour. Plan. Des. 2018, 171, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Geruo, A.; Velicogna, I.; Kimball, J.S. A global gridded dataset of GRACE drought severity index for 2002–14: Comparison with PDSI and SPEI and a case study of the Australia millennium drought. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Feng, Y.; Xue, Y.; Pan, N. Analysis and application of drought characteristics based on run theory and Copula function. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Gao, F.; Wu, B.; Liu, K. Spatial and temporal change of groundwater drought in the Xinjiang plain based on GRACE and its response to meteorological drought. Arid Land Geogr. 2024, 44, 20–28. [Google Scholar]




| β | Z | Interpretation of the Temperature Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Β > 0 | Z > 2.58 | Increasing Trend significant at 99% confidence level |
| 1.96 < Z ≤ 2.58 | Increasing Trend significant at 95% confidence level | |
| 1.65 < Z ≤ 1.96 | Increasing Trend significant at 90% confidence level | |
| 0 < Z ≤ 1.65 | Increasing Trend not significant | |
| Β = 0 | 0 | No Trend |
| Β < 0 | 0 > Z ≥ −1.65 | Decreasing Trend not significant |
| −1.65 > Z ≥ −1.96 | Decreasing Trend significant at 90% confidence level | |
| −1.96 > Z ≥ −2.58 | Decreasing Trend significant at 95% confidence level | |
| Z < −2.58 | Decreasing Trend significant at 99% confidence level |
| Observed Object | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECa (mS/m) | 1.39 | 1764.00 | 356.00 | 198.80 | 378.80 | 106.40% |
| GWL (m) | 0.79 | 150.30 | 11.28 | 5.98 | 21.07 | 186.71% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Wei, Y.; Li, R.; Hu, H.; Li, X. A Novel Electromagnetic Induction-Based Approach to Identify the State of Shallow Groundwater in the Oasis Group of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang During 2000–2022. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071312
Wang F, Wei Y, Li R, Hu H, Li X. A Novel Electromagnetic Induction-Based Approach to Identify the State of Shallow Groundwater in the Oasis Group of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang During 2000–2022. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071312
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fei, Yang Wei, Rongrong Li, Hongjiang Hu, and Xiaojing Li. 2025. "A Novel Electromagnetic Induction-Based Approach to Identify the State of Shallow Groundwater in the Oasis Group of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang During 2000–2022" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071312
APA StyleWang, F., Wei, Y., Li, R., Hu, H., & Li, X. (2025). A Novel Electromagnetic Induction-Based Approach to Identify the State of Shallow Groundwater in the Oasis Group of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang During 2000–2022. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071312





