Testing the Applicability of Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeological Prospection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
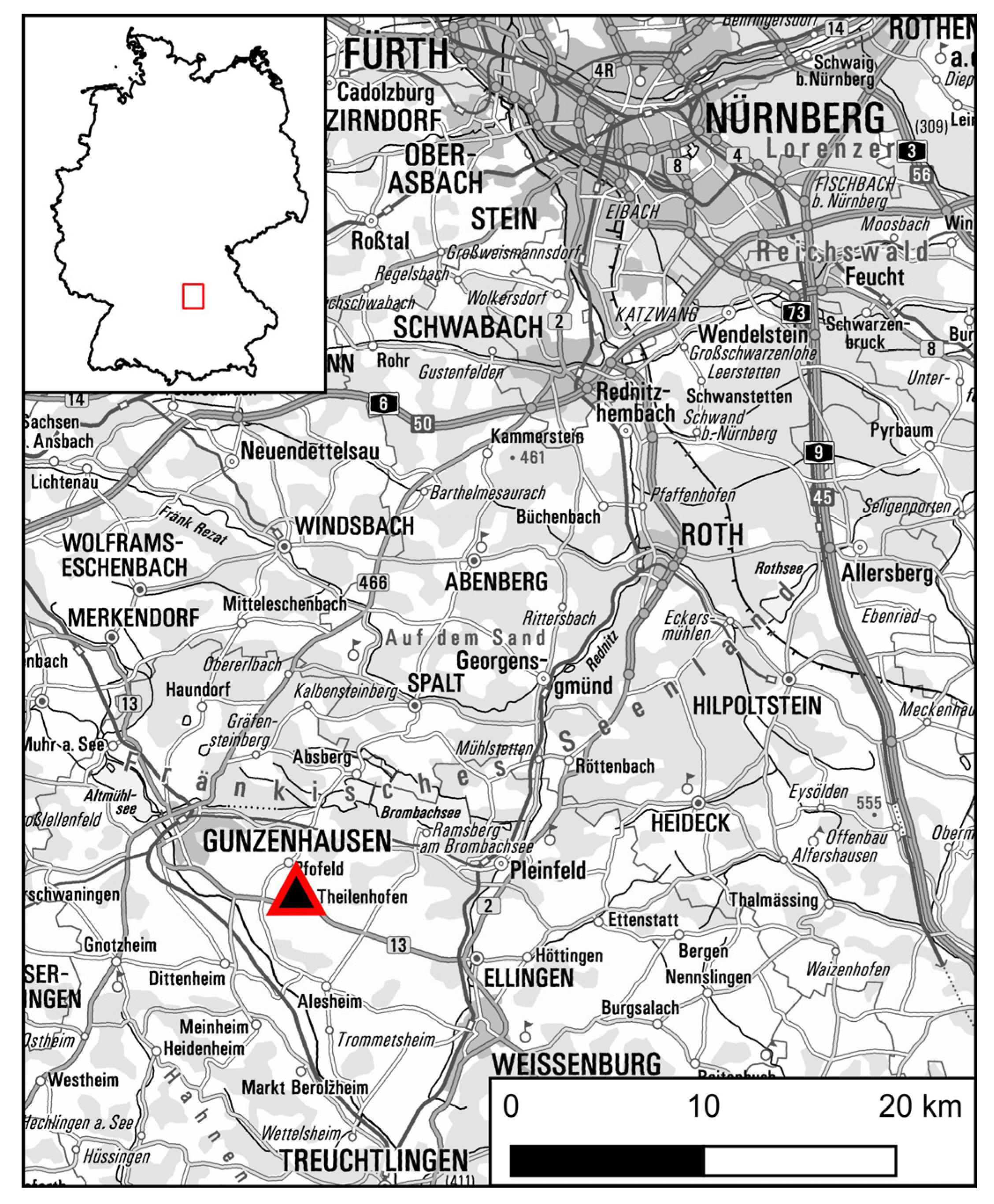
2. Site Location and Archaeological Background
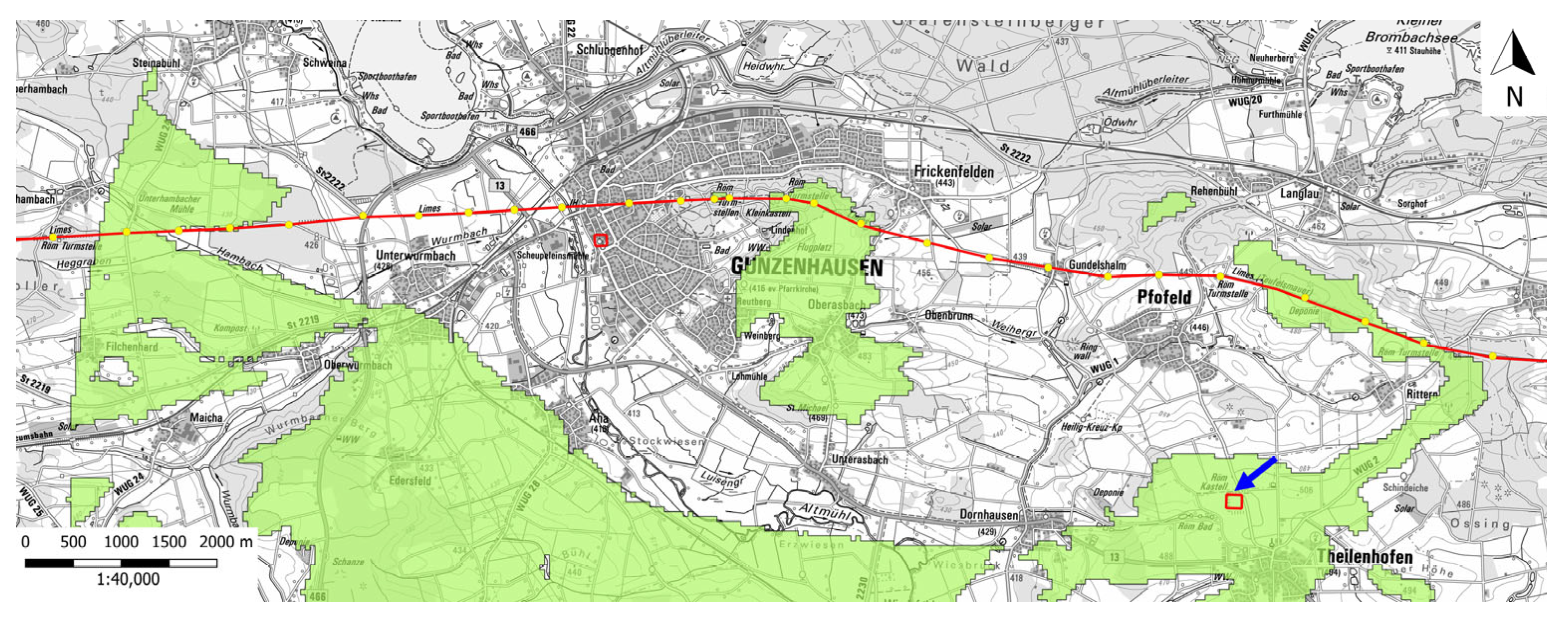
2.1. Description of the Test Site
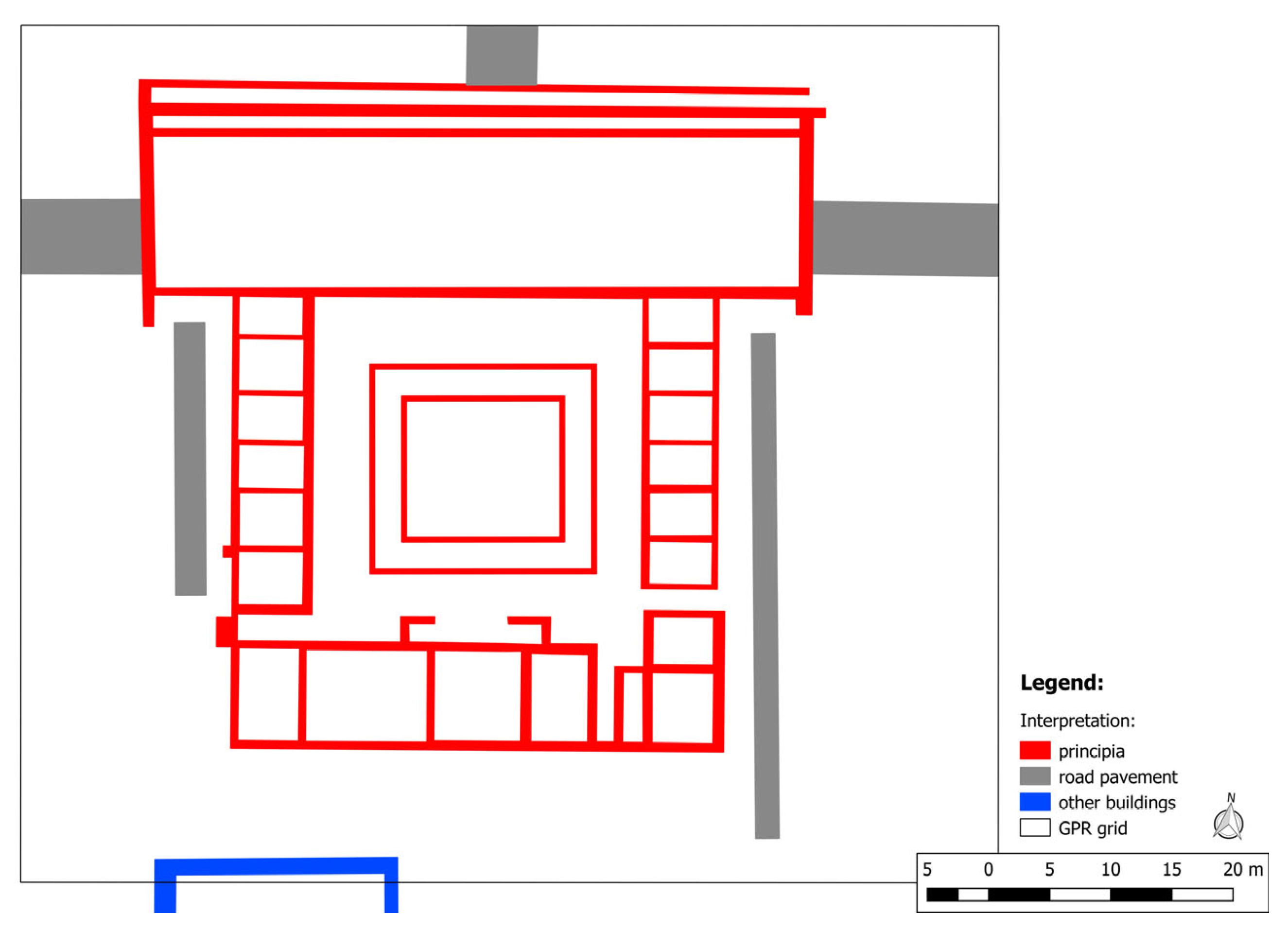
2.2. Introduction to Roman Principia
3. Methodology
3.1. Material Properties and Signal Reflection
3.2. Signal Polarisation
4. Survey Instrumentation and Layout
4.1. Ground-Based GPR Survey
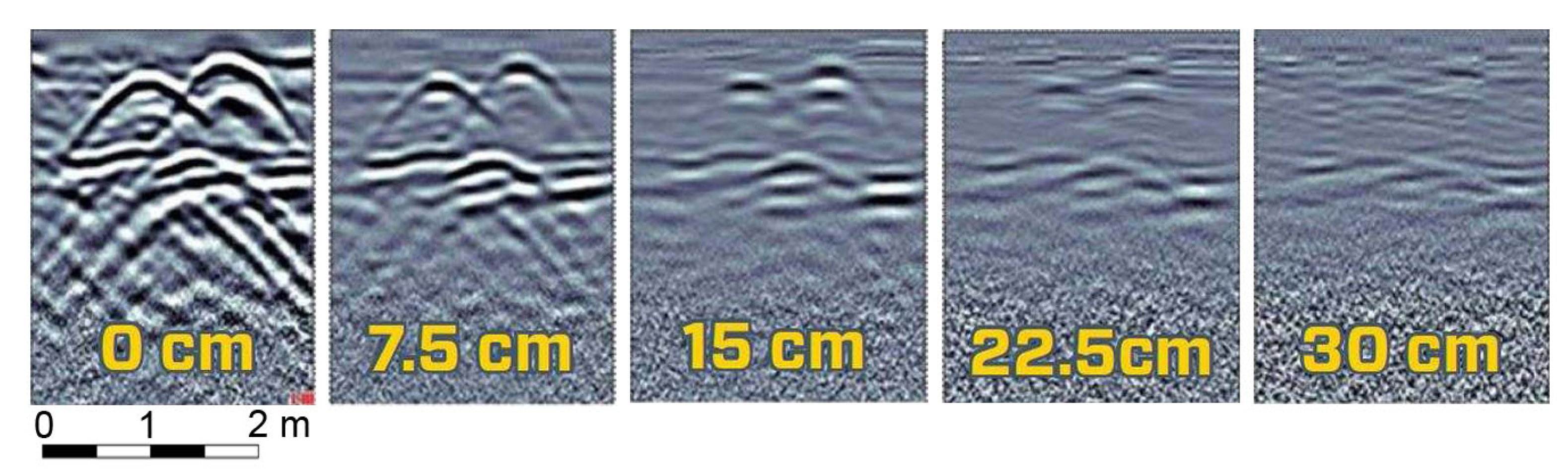
4.2. Drone-Based GPR Survey
5. Data Processing
5.1. Remove Range
5.2. Subtracting Average
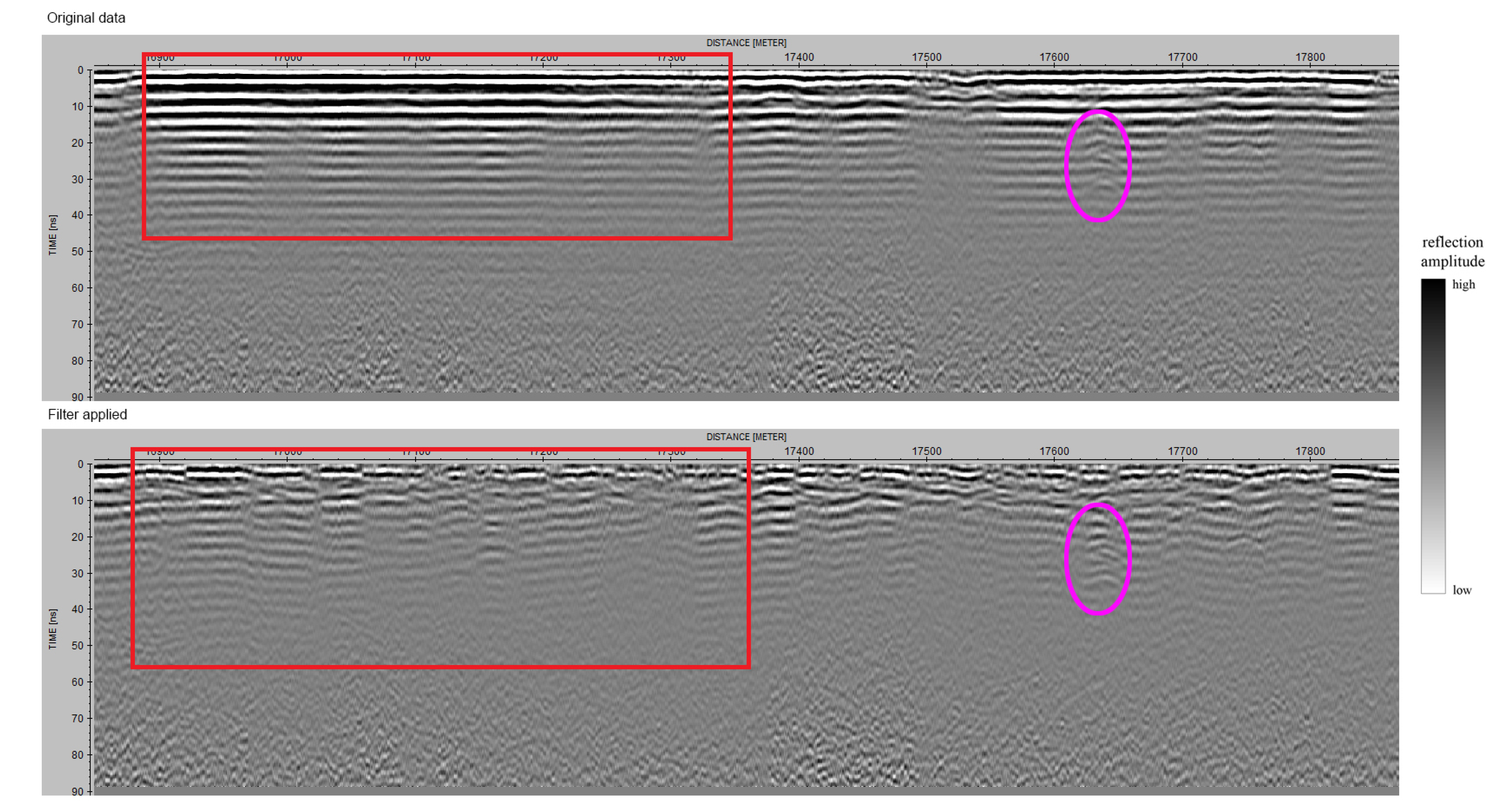
6. Results
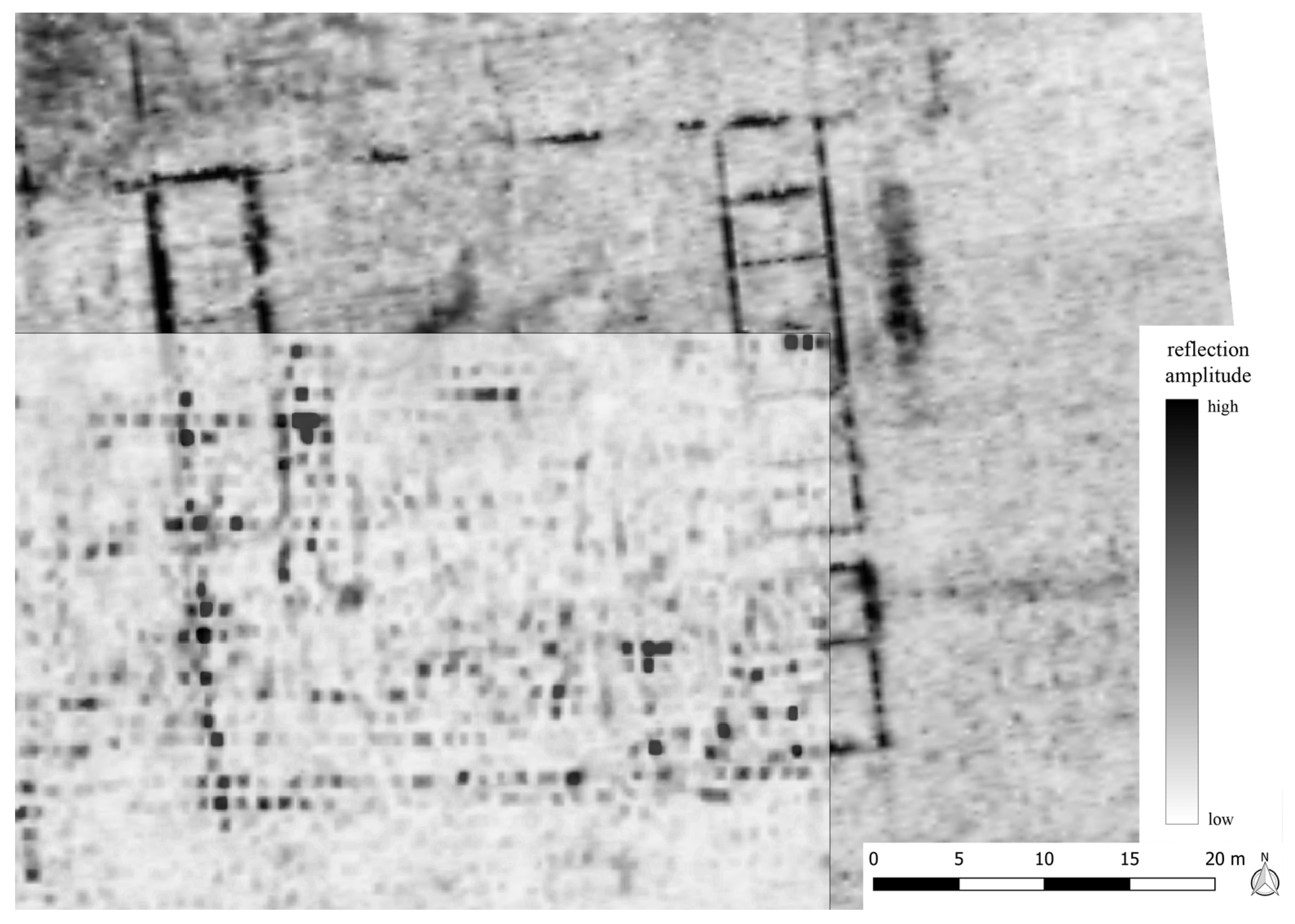
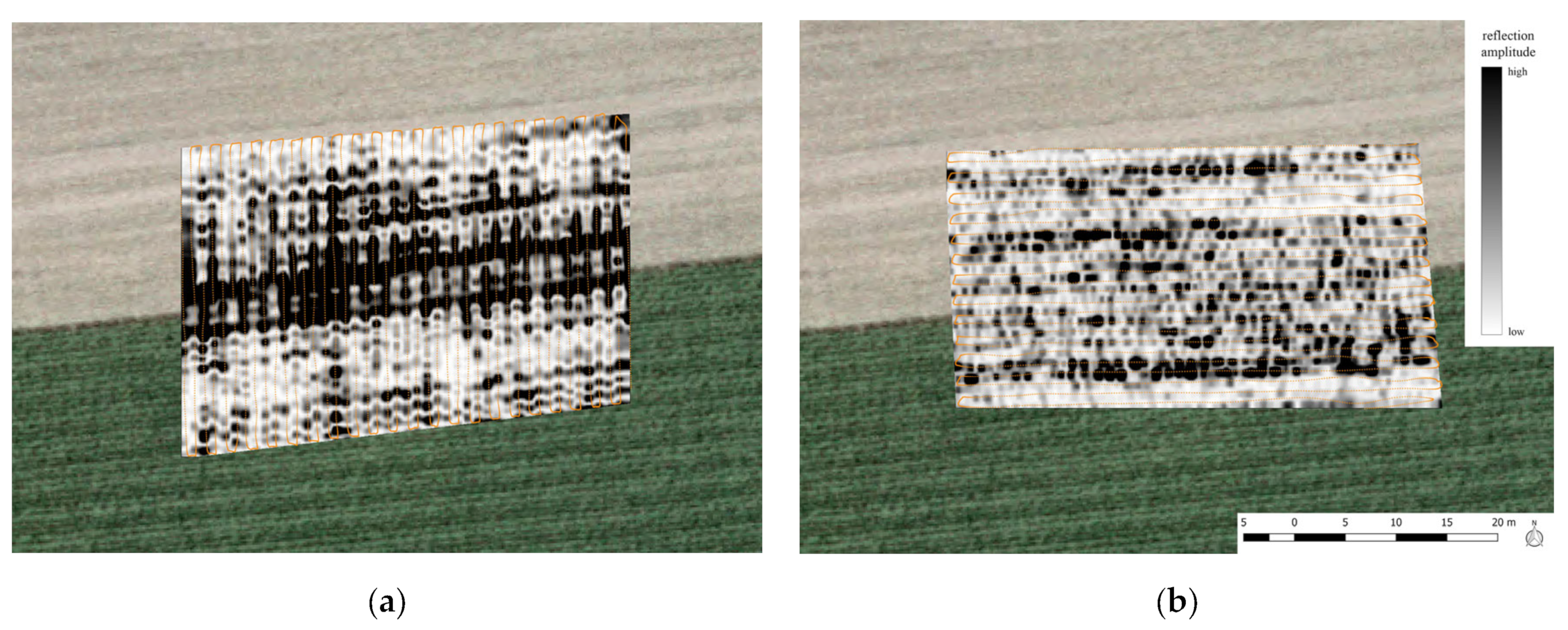
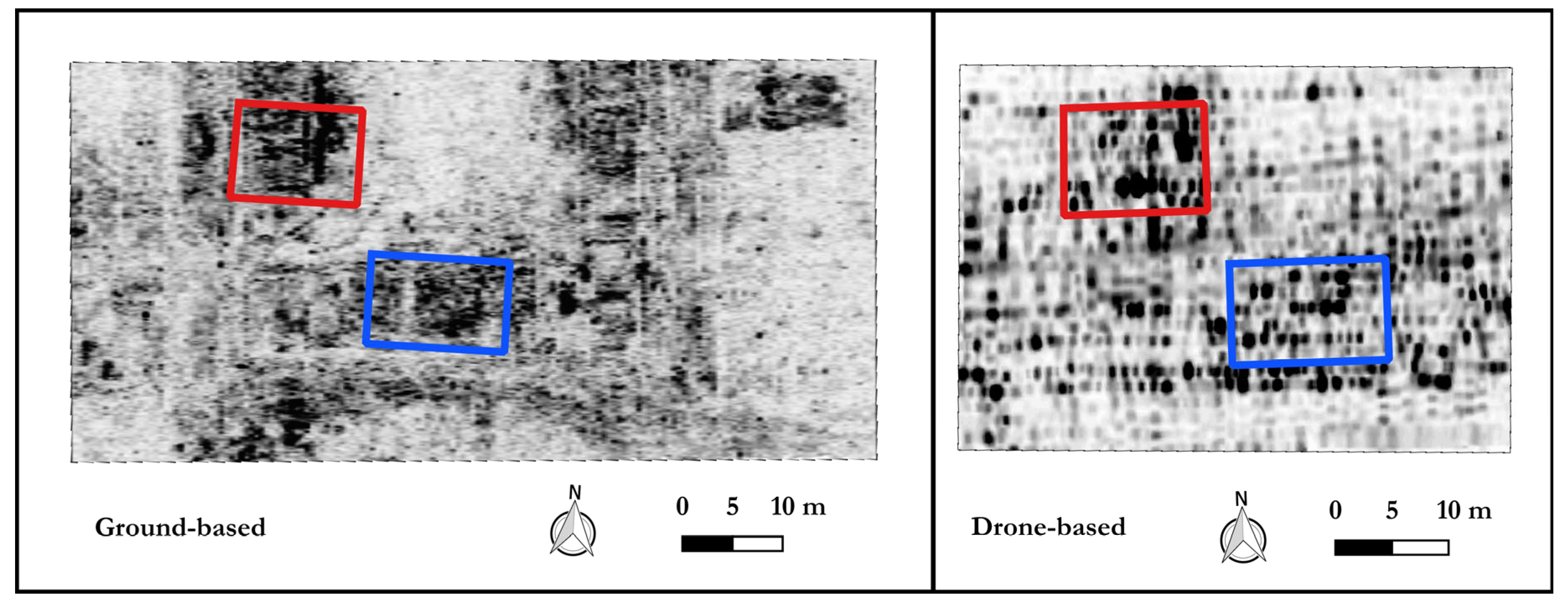
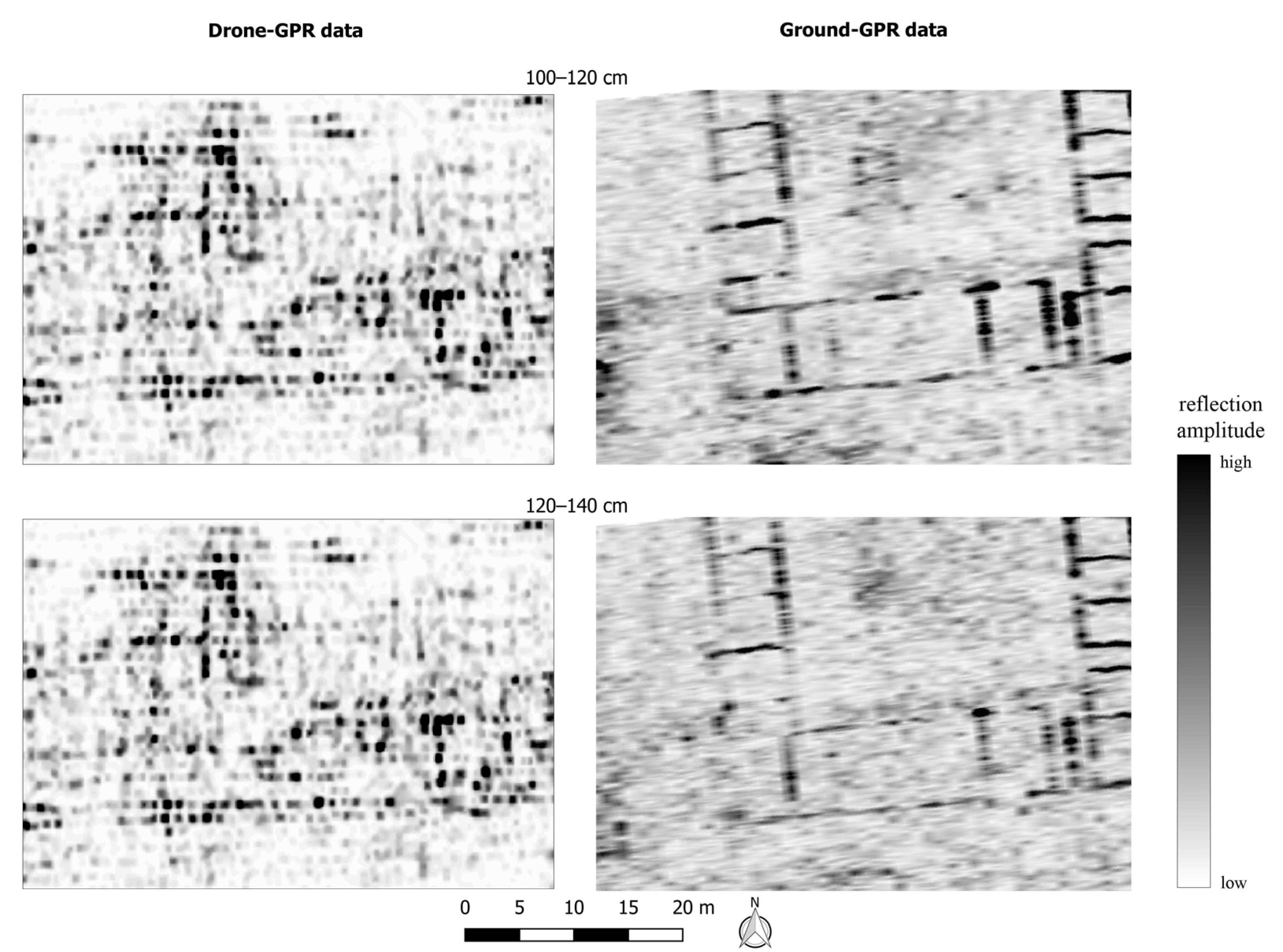
6.1. Ground-Based Data
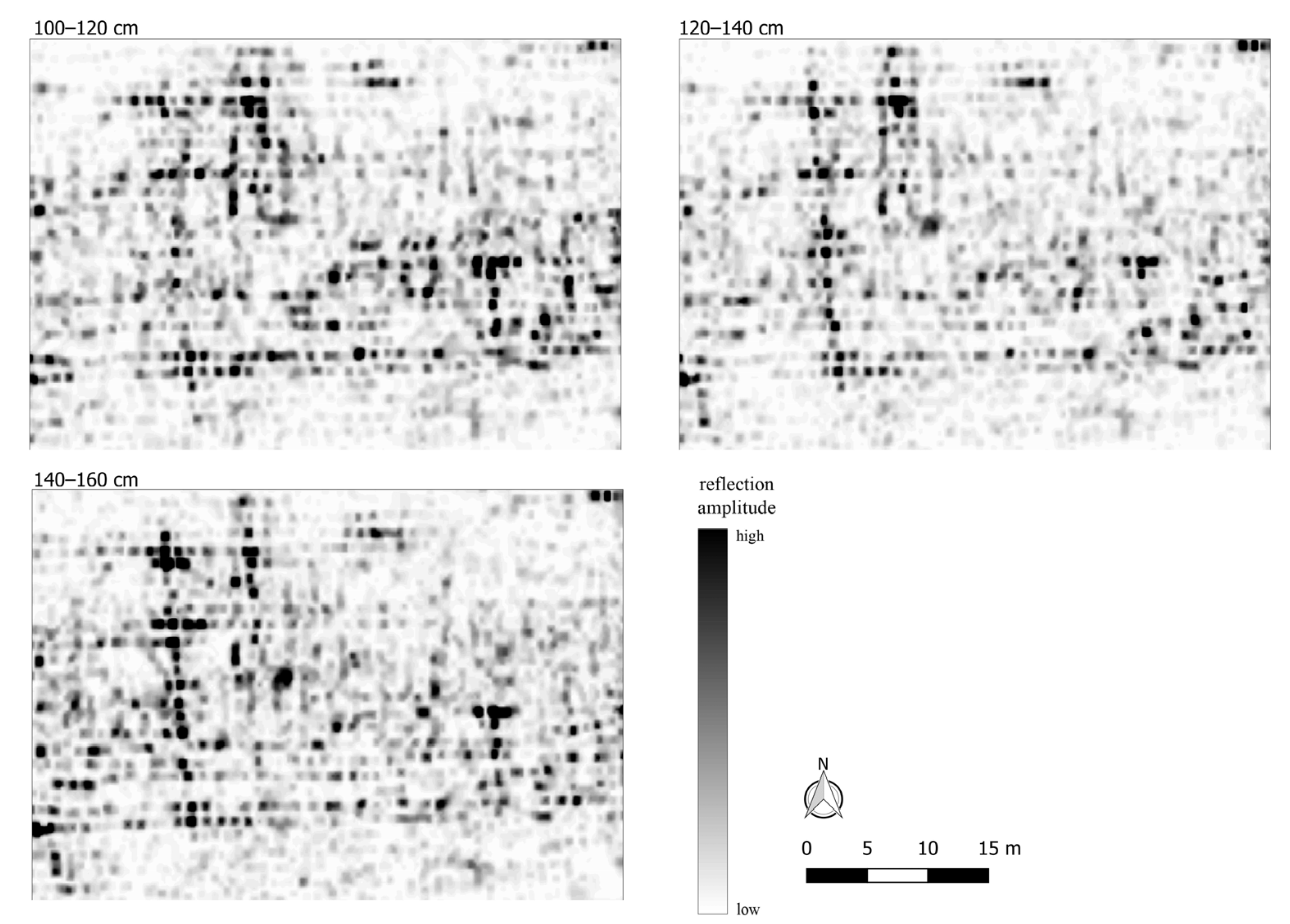
6.2. Drone-Based Data
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belshé, J.C. Recent magnetic investigations at Cambridge University. Adv. Phys. 1957, 6, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.J. Magnetic prospecting I. Archaeometry 1958, 1, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, R.S.; Dolphin, L.T. A Communication on an Archaeological Radar Experiment at Chaco Canyon, New Mexico. MASCA Newsl. 1975, 11, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon, J.L.; Bevan, B. Ground-penetrating radar and its application to a historical archaeological site. Hist. Archaeol. 1977, 11, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.; Dolphin, L.T.; el Dessouki, T.; el Hennawi, H.; Moussa, A.H.; Tolba, M.F.; Abdel-Wahab, S.; Bollen, R.L.; Johnson, D.A.; Oetzel, G.N.; et al. Electromagnetic Sounder Experiments at the Pyramids of Giza; Stanford Research International: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Batey, R.A. Subsurface Interface Radar at Sepphoris, Israel, 1985. J. Field Archaeol. 1987, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, P.D.; Loker, W.M.; Spetzler, H.A.W.; Ware, R.W. Geophysical Exploration for Ancient Maya Housing at Ceren, El Salvador. Natl. Geogr. Res. Rep. 1985, 20, 645–656. [Google Scholar]
- Gavazzi, B.; Reiller, H.; Munschy, M. An Integrated Approach for Ground and Drone-Borne Magnetic Surveys and their Interpretation in Archaeological Prospection. ArcheoSciences 2021, 45, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, A.; Vitale, G.; Scudero, S.; Martorana, R.; Capizzi, P.; D’Alessandro, A. A Lightweight Prototype of a Magnetometric System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Sensors 2021, 21, 4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakova, O.A.; Balkov, E.V.; Dyadkov, P.G.; Marchenko, Z.V.; Grishin, A.E.; Evmenov, N.D. Integrative Geophysical Studies at the Novaya Kurya-1 Cemetery in the Kulunda Steppe. Archaeol. Ethnol. Anthropol. Eurasia 2022, 49, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stele, A.; Linck, R.; Schikorra, M.; Fassbinder, J.W.E. UAV magnetometer survey in low-level flight for archaeology: Case study of a Second World War airfield at Ganacker (Lower Bavaria, Germany). Archaeol. Prospect. 2022, 29, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stele, A.; Kaub, L.; Linck, R.; Schikorra, M.; Fassbinder, J.W.E. Drone-based magnetometer prospection for archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2023, 158, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Coolen, J.; Fritsch, T.; Klingen, S. Towards drone-based magnetometer measurements for archaeological prospection in challenging terrain. Drone Syst. Appl. 2024, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlequé, M.A.; Alvarez, S.; Martínez, H.J.; Canelo, A.C. FMCW GPR radar for archaeological applications: First analytical and measurement results. In Proceedings of the 2017 XXXIInd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (Ursi Gass), Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–26 August 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Salvini, R.; Beltramone, L.; De Lucia, V.; Ermini, A.; Vanneschi, C.; Zei, C.; Silvestri, D.; Rindinella, A. UAV-mounted Ground Penetrating Radar: An example for the stability analysis of a mountain rock debris slope. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 2804–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, M.; Frid, V. Vital Views into Drone-Based GPR Application: Precise Mapping of Soil-to-Rock Boundaries and Ground Water Level for Foundation Engineering and Site-Specific Response. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zajc, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Clément, M.; De Coster, A.; Lambot, S. A new drone-borne GPR for soil moisture mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, R.O.R.; Eckerstorfer, M.; Jacobsen, S. Drone-Mounted Ultrawideband Radar for Retrieval of Snowpack Properties. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valence, E.; Baraer, M.; Rosa, E.; Barbecot, F.; Monty, C. Drone-based ground-penetrating radar (GPR) application to snow hydrology. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 3843–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruols, B.; Baron, L.; Irving, J. Development of a drone-based ground-penetrating radar system for efficient and safe 3D and 4D surveying of alpine glaciers. J. Glaciol. 2023, 69, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Y.; Li, G. Morphology Dynamics of Ice Cover in a River Bend Revealed by the UAV-GPR and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjoelker, A.R.; Baraër, M.; Valence, E.; Charonnat, B.; Masse-Dufresne, J.; Mark, B.G.; McKenzie, J.M. Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar with Manual Transects for Improved Field Surveys of Buried Ice. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, A.; Dipierro, G.; Cannella, E.; Panarese, A.; Galiano, A.M.; Massaro, A. A UAV-GPR Fusion Approach for the Characterization of a Quarry Excavation Area in Falconara Albanese, Southern Italy. Drones 2021, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, F.; Liang, Z.; Ye, H. UAV-Mounted GPR for Object Detection Based on Cross-Correlation Background Subtraction Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.; Gennarelli, G.; Esposito, G.; Ludeno, G.; Fasano, G.; Capozzoli, L.; Soldovieri, F.; Catapano, I. An Overview on Down-Looking UAV-Based GPR Systems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Tong, K.; Chetty, K. Feasibility Study of Multi-Frequency Ground Penetrating Radar for Rotary UAV Platforms. In Proceedings of the IET International Conference on Radar Systems (Radar 2012), Glasgow, UK, 22–25 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Colorado, J.; Perez, M.; Mondragon, I.; Mendez, D.; Parra, C.; Devia, C.; Martinez-Moritz, J.; Neira, L. An integrated aerial system for landmine detection: SDR-based Ground Penetrating Radar onboard an autonomous drone. Adv. Robot. 2017, 31, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šipoš, D.; Gleich, D. A Lightweight and Low-Power UAV-Borne Ground Penetrating Radar Design for Landmine Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijeholt, L.L.À.; Kronshorst, T.Y.; Van Teeffelen, K.; Van Manen, B.; Emaus, R.; Knotter, J.; Mersha, A. Utilizing Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Crime Investigations in Localizing and Identifying Clandestine Graves. Sensors 2023, 23, 7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javan, F.D.; Samadzadegan, F.; Toosi, A.; Van der Meijde, M. Unmanned Aerial Geophysical Remote Sensing: A Systematic review. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.; Esposito, G.; Fasano, G.; Renga, A.; Soldovieri, F.; Catapano, I. Small-UAV Radar Imaging System Performance with GPS and CDGPS Based Motion Compensation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, R.; Kaltak, A. Drone radar: A new survey approach for Archaeological Prospection? In New Global Perspectives on Archaeological Prospection; Bonsall, J., Ed.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Frid, M.; Frid, V. A Case Study of the Integration of Ground-Based and Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) for an Archaeological Survey in Hulata (Israel): Advancements, Challenges, and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidam, H. Das Kastell Theilenhofen. In Der Obergermanisch-Raetische Limes des Roemerreiches B VII Nr. 71a; Fabricius, E., Hettner, F., von Sarwey, O., Eds.; Verlag Otto Petters: Heidelberg, Germany, 1905. [Google Scholar]
- Czysz, W.; Dietz, K.; Fischer, T.; Kellner, H.-J. Die Römer in Bayern; Konrad Theiss Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1995; pp. 522–523. [Google Scholar]
- Linck, R.; Fassbinder, J.W.E. Proving a Roman technical masterstroke: GIS-based viewshed and intervisibility analysis of the Bavarian part of the Rhaetian Limes. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2022, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüssen, C.M. Theilenhofen. In Landkreis Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen: Denkmäler und Fundstätten.—Führer zu Archäologischen Denkmälern in Deutschland Bd. 15; Spindler, K., Ed.; Konrad Theiss Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1987; pp. 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kießling, G. Landkreis Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen: Ensembles, Baudenkmäler, Archäologische Denkmäler; Denkmäler in Bayern Bd. V.70/1; Karl M. Lipp Verlag: München, Germany, 2000; pp. 586–587. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, M. Das Ende des raetischen Limes im Jahr 254 n. Chr. Bayer. Vorgeschichtsblätter 2007, 27, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, V. Die mittelkaiserzeitliche Donaugrenze in Raetien—Die Ripa Danuvii provinciae Raetiae. Der Limes 2000, 2, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Flügel, C.; Obmann, J. Römische Wehrbauten: Befund und Rekonstruktion; Volk Verlag: München, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E. Geophysical prospection of the frontiers of the Roman Empire in southern Germany, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Archaeol. Prospect. 2010, 17, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E. Neue Ergebnisse der geophysikalischen Prospektion am Obergermanisch-Raetischen Limes. In Neue Forschungen am Limes. Beiträge zum Welterbe Limes Bd. 3; Thiel, A., Ed.; Konrad Theiss Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2008; pp. 154–171. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A. Römische Kastelle des 1. und 2. Jahrhunderts n. Chr. In Britannien und in den Germanischen Provinzen des Römerreiches; Kulturgeschichte der Antiken Welt Bd. 37; Philipp von Zabern: Mainz, Germany, 1990; pp. 123–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hoops, J. Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde, Bd. 23: Pfalzel—Quaden; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- von Petrikovits, H. Beiträge zur Römischen Geschichte und Archäologie; Rudolf Habelt Verlag: Bonn, Germany, 1976; pp. 519–545. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1997; pp. 681–749. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, L.B. Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology; AltaMira Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Milsom, J. Field Geophysics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.P. Ground Penetrating Radar Principles, Procedures & Applications; Sensors & Software: Mississsauga, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jol, H.M. Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Von der Osten, H. Geophysikalische Prospektion Archäologischer Denkmale unter Besonderer Berücksichtigung der Kombinierten Anwendung Geoelektrischer und Geomagnetischer Kartierung, Sowie der Verfahren der Elektromagnetischen Induktion und des Bodenradars; Shaker Verlag: Aachen, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández, M.; López, Y.Á.; De Mitri, A.; Martínez, D.C.; Álvarez-Narciandi, G.; Andrés, F.L.-H. Portable and Easily-Deployable Air-Launched GPR Scanner. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, R.; Fassbinder, J.W.E. Determination of the influence of soil parameters and sample density on ground-penetrating radar: A case study of a Roman picket in Lower Bavaria. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2013, 6, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiata, B.N.; Steinberg, J.M.; Bolender, D.J.; Zoëga, G.; Schoenfelder, J.W. Subsurface imaging a Viking-Age churchyard using GPR with TDR: Direct comparison to the archaeological record from an excavated site in northern Iceland. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 12, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurement in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkmann, B. DGG-Kolloquium Georadar: Geschichte, Grundlagen und Zukunft des GPR. In 66. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Geophysikalischen Gesellschaft; Deutsche Geophysikalische Gesellschaft e.V.: Leipzig, Germany, 2006; Volume II/2006, pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, M.E. Near-Surface Applied Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 239–278. [Google Scholar]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 3rd ed; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Antennas Manual MN30-903 Rev G. Available online: https://www.geophysical.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/GSSI-Antenna-Manual.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Radar Systems Zond Aero 500 GPR System: Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.sphengineering.com/integrated-systems (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Booth, A.D.; Koylass, T.M. Drone-mounted ground-penetrating radar surveying: Flight-height considerations for diffraction-based velocity analysis. Geophysics 2022, 87, WB69–WB79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reflexw—GPR and Seismic Processing Software. Available online: https://www.sandmeier-geo.de/reflexw.html (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-J.; Yi, M.-J. Removal of ringing noise in GPR data by signal processing. Geosci. J. 2007, 11, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.J. Surface-Penetrating Radar; Radar, Sonar, Navigation and Avionics Series 6; The Institution of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- TIPS: How High Can My GPR Be Off the Ground? Available online: https://www.sensoft.ca/blog/tips-how-high-can-my-gpr-be-off-the-ground/ (accessed on 12 February 2025).




| Material | Dielectric Value εr | Material | Dielectric Value εr |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air | 1 | Granite | 5–8 |
| Water (fresh) | 81 | Limestone | 7–9 |
| Clay (dry) | 3 | Clay (wet) | 8–15 |
| Sand (dry) | 3–6 | Sand (wet) | 25–30 |
| Ground-Based | Drone-Based | |
|---|---|---|
| Model | GSSI Model 5103 | Zond Aero 500 |
| Centre Frequency [MHz] | 400 | 500 |
| Operating Bandwidth [MHz] | 100–800 | 200–900 |
| Set Time Range [ns] | 53 | 100 |
| Scan Rate [Scans/second] | 120 | 50 |
| Dimensions [cm] | 30 × 30 × 17 | 41 × 31 × 16 |
| Step Number | Ground-Based | Drone-Based |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Import data | Import data |
| 1 | Dewow/bandpass filter | Remove range |
| 2 | Correct max. phase | Bandpass filtering |
| 3 | Move start time | Correct max. phase |
| 4 | Gain function | Background removal |
| 5 | Background removal | Move start time |
| 6 | Stacking | Gain function |
| 7 | Velocity analysis | Subtracting average |
| 8 | 1D-Kirchhoff migration | Stacking |
| 9 | Time-depth conversion | Velocity analysis |
| 10 | 3D data interpretation | 1D-Kirchhoff migration |
| 11 | Time-depth conversion | |
| 12 | 3D data interpretation |
| Centre Frequency | Wavelength in Air | Wavelength/10 Height | Recommended Maximum Antenna Height |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 MHz | 300 cm | 30 cm | 10 cm |
| 250 MHz | 120 cm | 12 cm | 3 cm |
| 500 MHz | 60 cm | 6 cm | 1.5 cm |
| 1000 MHz | 30 cm | 3 cm | <1 cm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linck, R.; Kale, M.; Stele, A.; Schlechtriem, J. Testing the Applicability of Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091498
Linck R, Kale M, Stele A, Schlechtriem J. Testing the Applicability of Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091498
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinck, Roland, Mukta Kale, Andreas Stele, and Joachim Schlechtriem. 2025. "Testing the Applicability of Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeological Prospection" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091498
APA StyleLinck, R., Kale, M., Stele, A., & Schlechtriem, J. (2025). Testing the Applicability of Drone-Based Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091498






