Sustainable Urban Land Management Based on Earth Observation Data—State of the Art and Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Philosophical Pilgrimage on Sustainable Development
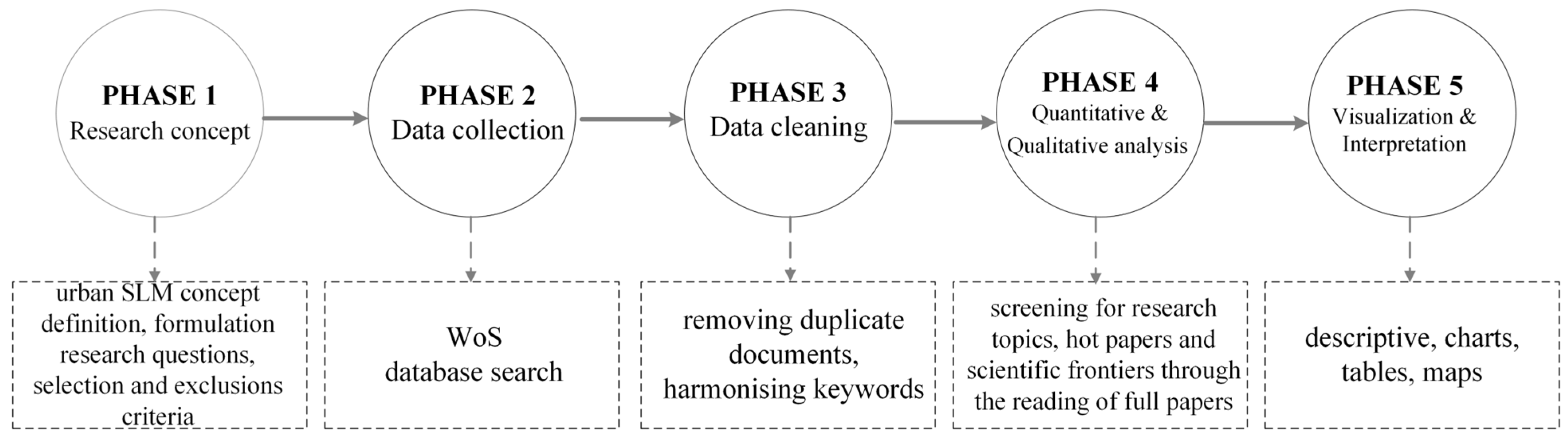
3. Methodological Approach
- Q1:
- Are the main intellectual foundations of EO-based SULM rooted in interdisciplinary approaches?
- Q2:
- Is research on SULM using earth observation data unevenly distributed across regions and environmental challenges?
- Q3:
- What emerging technologies have supported recent advancements in EO-based SULM research?
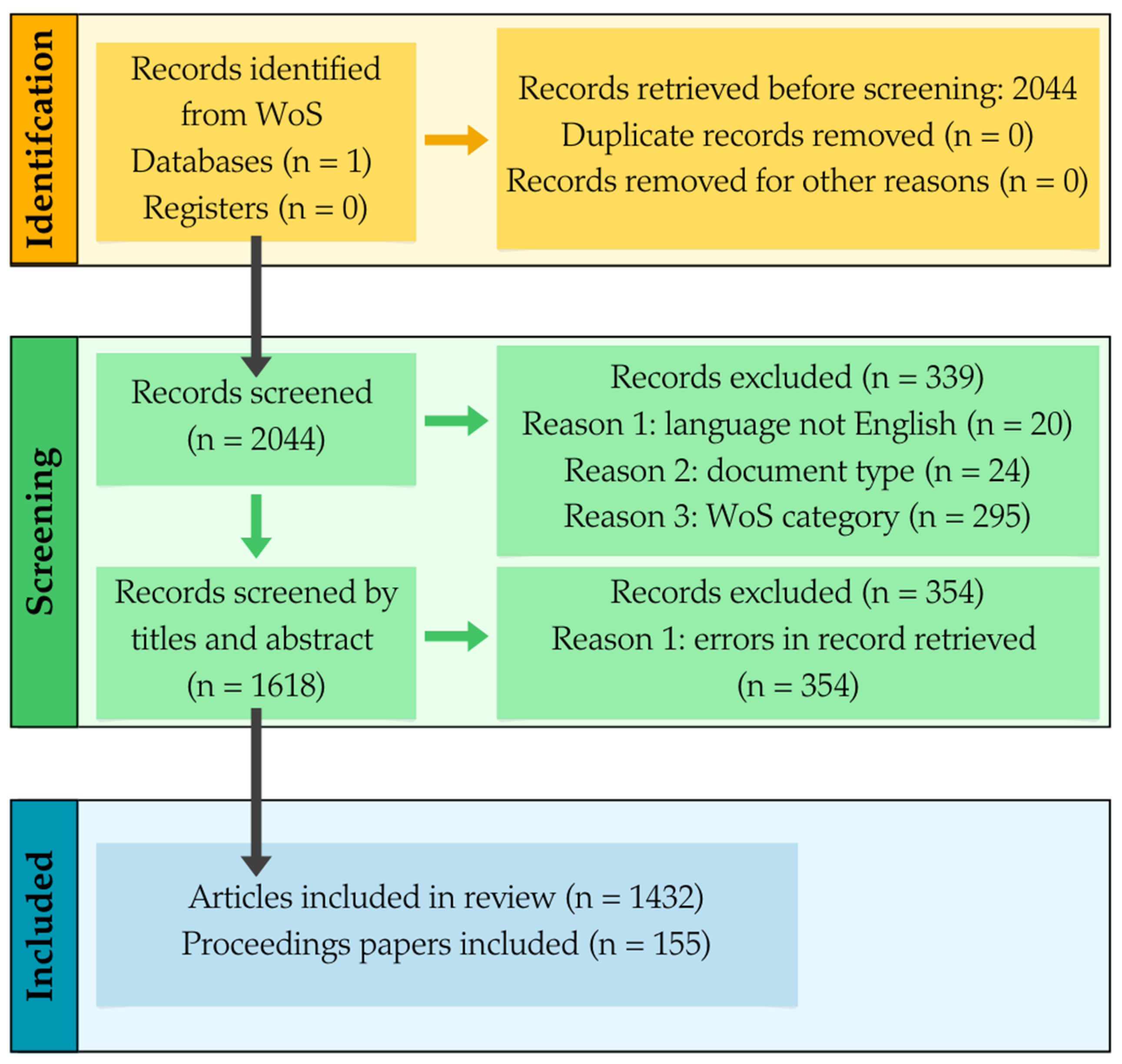
- WoS categories not related to environmental sciences (e.g., medicine, engineering, electronics, information technology).
- Publication year: 2025.
- Document types: editorial material, retracted publication, or book chapter.
4. Results
4.1. Bibliometric Overview of Scientific Productivity
4.1.1. Publication and Citation Diachronic View
4.1.2. Journals and Conferences
4.2. Cooperation Between Parties Involved in Urban SLM
4.3. Keywords Exploration
4.4. Main Research Topics and Trends
| Topic | Methods | Satellites and Imageries | Publications 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem and ecosystem services | Coupling and coordination, RSEI correlation | Landsat, China’s HJ-1A/B, Tiangong-2 WIS | Ariken et al. [30], Szumacher and Pabjanek [31], Shao et al. [32], Xu et al. [33] |
| Heat island and land surface temperature (LST) | Spatial regression, spatial autocorrelation, cellular automata (CA), artificial neural network (ANN), landscape metrics | Landsat, MODIS, Sentinel-2/3 | Zhou et al. [34], Yin et al. [35], Kafy et al. [36], Dugord et al. [37], Ravanelli et al. [38] |
| Informal settlements/slums | OBIA, random forest classifier, deep learning (Deeplab V3 Plus model, Xception network), semantic segmentation | VHR, SPOT-6, Sentinel-2, Street View Images | Patino and Duque [39], Chulafak et al. [40], Zhang et al. [41], Stark et al. [42] |
| Land use/land cover changes and urbanization and urban sprawl | Coupling and coordination, supervised classification, machine learning (ML) algorithms, indexes (Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) Standardized Water Level Index (SWI), urban land use change models, Markov chains–cellular automata (MC-CA) | Multitemporal Landsat images, Sentinel-2A, ICONOS, MODIS, China’s HJ-1A/B | Shao et al. [32], Xu et al. [33], Yu et al. [43], Kumar et al. [44], Zhu et al. [45] |
4.4.1. Socio-Environmental Problems
4.4.2. Geoinformation Technologies and Methodology
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Geographical context. Understanding the physical, economic, and social characteristics of urban areas is essential for meaningful interpretation and for informing context-specific policy decisions.
- Remote sensing data. EO data, particularly when supplemented with vector datasets and crowdsourced or social media inputs, play a dominant role in urban SULM analysis and monitoring.
- Artificial intelligence. ML techniques and neural networks are now at the forefront of analytical methods, driving advances in data interpretation and urban diagnostics.
- Journals. The most impactful publications in the field appear in Remote Sensing, Sustainability, and Land published by MDPI (Switzerland).
- Countries. China and the United States lead in publication output and citation impact, highlighting their central role in shaping global research directions.
- Research trends in urban SLM can be categorized into two main principal streams: socio-environmental and technological–methodological. Key challenges in urban land management include land use transformation, urban heating, vegetation and landscape modification, pollution, and climate change.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| EO | Earth observation |
| ES, ESV | Ecosystem service, ecosystem services valuation |
| GIS | Geographic information system |
| OBIA | Object base image analysis |
| PRISMA | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses |
| RF | Random forest |
| RS | Remote sensing |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SLM | Sustainable land management |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| SULM | Sustainable urban land management |
| UN | United Nations |
| UNEP | United Nations Environment Program |
| USML | Urban sustainable land management |
| WoS | Web of Science |
References
- Malthus, T.R. An Essay on the Principle of Population; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1992; pp. 1–430. [Google Scholar]
- Sustainability for All. Do You Know When Sustainability First Appeared? Available online: https://www.activesustainability.com/sustainable-development/do-you-know-when-sustainability-first-appeared/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Luther, L. The National Environmental Policy Act: Background and Implementation; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–35. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=50c2a5bac14ebe05774a9f2200d61f4e9fb308f3 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- United Nations. Our Common Future. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Resolution 70/1. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, Adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015. Available online: https://docs.un.org/en/A/RES/70/1 (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Cornforth, I.C. Selecting indicators for assessing sustainable land management. J. Environ. Manag. 1999, 56, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Lin, P.; Gong, K.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A.; et al. High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, P.; He, X. Rapid urbanization and climate change significantly contribute to worsening urban human thermal comfort: A national 183-city, 26-year study in China. Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, R.; Krüger, E. Urban heat island and its impact on climate change resilience in a shrinking city: The case of Glasgow, UK. Build. Environ. 2012, 53, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, Z. Filozoficzne i społeczne uwarunkowania zrównoważonego rozwoju. Probl. Ekorozwoju 2008, 3, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Flannery, B.J.; Loi, N.M.; Schutte, N.S. The effect of humanising nature. Int. J. Psychol. 2024, 59, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątek, Z. Człowiek jako podmiot zrównoważonego rozwoju: Konsekwencje filozoficzno-społeczne. In Zrównoważony Rozwój. Od Utopii do Praw Człowieka; Papuziński, A., Ed.; Wydawnictwo Branta: Bydgoszcz, Poland, 2005; pp. 14–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rawls, J. Justice as Fairness: A Restatement; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenda 21. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/publications/agenda21 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Rąb, Ł. Filozoficzne podłoże koncepcji zrównoważonego rozwoju. Etyka Biznesu I Zrównoważony Rozw. Interdyscyplinarne Stud. Teoretyczno-Empiryczne 2016, 4, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gawor, L. Idea zrównoważonego rozwoju jako projekt nowej ogólnoludzkiej cywilizacji. Diametros 2006, 9, 84–104. [Google Scholar]
- Scheler, M. Resentyment a Moralność (Das Ressentiment im Aufbau der Moralen), 1st ed.; Spółdzielnia Wydawnicza Czytelnik: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, H. Kondycja Ludzka; Aletheia: Warsaw, Poland, 2010; pp. 1–363. [Google Scholar]
- Leopold, A. A Sand County Almanac: And Sketches Here and There; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, E.F. Small Is Beautiful: A Study of Economics as if People Mattered; Blond & Briggs: London, UK, 1973; pp. 1–223. [Google Scholar]
- Shiva, V. The Violence of the Green Revolution: Third World Agriculture, Ecology and Politics; Zed Books Ltd.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, C.; Grignon, J.; Steven, R.; Guitart, D.; Byrne, J. Publishing not perishing: How research students transition from novice to knowledgeable using systematic quantitative literature reviews. Stud. High. Educ. 2015, 40, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISMA Statement. Available online: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Garfield, E. Citation Indexing: Its Theory and Application in Science, Technology, and Humanities, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 1–274. [Google Scholar]
- Bielecka, E. GIS Spatial Analysis Modeling for Land Use Change. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Intellectual Base and Trends. Geosciences 2020, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ilan, J. Citations to the “Introduction to informetrics” indexed by WOS, Scopus and Google Scholar. Scientometrics 2010, 82, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. How to normalize cooccurrence data? An analysis of some well-known similarity measures. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1635–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwilch, G.; Bestelmeyer, B.; Bunning, S.; Critchley, W.; Herrick, J.; Kellner, K.; Liniger, H.P.; Nachtergaele, F.; Ritsema, C.J.; Schuster, B.; et al. Experiences in monitoring and assessment of sustainable land management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, H. Assessing sustainable land management (SLM). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 81, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Kung, H.T. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and eco-environment in Yanqi Basin based on multi-source remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumacher, I.; Pabjanek, P. Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Services in European Cities in the Continental Biogeographical Region in the Period from 1990–2012. Sustainability 2017, 9, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Sumari, N.S.; Portnov, A.; Ujoh, F.; Musakwa, W.; Mandela, P.J. Urban sprawl and its impact on sustainable urban development: A combination of remote sensing and social media data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 24, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Yuan, M.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of urban form on the urban heat island effect based on spatial regression model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.; Al Rakib, A.; Islam, M.A.; Khan, M.H.H.; Sattar, G.S. Prediction of seasonal urban thermal field variance index using machine learning algorithms in Cumilla, Bangladesh. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugord, P.A.; Lauf, S.; Schuster, C.; Kleinschmit, B. Land use patterns, temperature distribution, and potential heat stress risk–The case study Berlin, Germany. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 48, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, R.; Nascetti, A.; Cirigliano, R.V.; Di Rico, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Monti, P.; Crespi, M. Monitoring the Impact of Land Cover Change on Surface Urban Heat Island through Google Earth Engine: Proposal of a Global Methodology, First Applications and Problems. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, J.E.; Duque, J.C. A review of regional science applications of satellite remote sensing in urban settings. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2013, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulafak, G.A.; Khomarudin, M.R.; Roswintiarti, O.; Mehmood, H.; Nugroho, G.; Nugroho, U.C.; Ardha, M.; Sukowati, K.A.D.; Putra, I.K.Y.D.; Permana, S.A.B.S. Machine Learning-Based Local Knowledge Approach to Mapping Urban Slums in Bandung City, Indonesia. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Du, F. A large-scale extraction framework for mapping urban in-formal settlements using remote sensing and semantic segmentation. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2345135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, T.; Wurm, M.; Zhu, X.X.; Taubenböck, H. Satellite-based mapping of urban poverty with transfer-learned slum morphologies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5251–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zang, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Na, X. Analyzing and modeling land use land cover change (LUCC) in the Daqing City, China. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Mathew, S. Land use change modelling using a Markov model and remote sensing. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2013, 5, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.C.; Stokes, E.C.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.T.; Taubenböck, H. Understanding an urbanizing planet: Strategic directions for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.G.-O.; Li, X. A Constrained CA Model for the Simulation and Planning of Sustainable Urban Forms by Using GIS. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2001, 28, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Helbich, M. Spatiotemporal urbanization processes in the megacity of Mumbai, India: A Markov chains-cellular automata urban growth model. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 40, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Z. The balance between economic development and ecosystem service value in the process of land urbanization: A case study of China’s land urbanization from 2000 to 2015. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes: Implications for environmental sustainability planning for the rapidly urbanizing summer capital of the Philippines. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 116, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat). The Challenge of Slums—Global Report on Human Settlements 2003. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/the-challenge-of-slums-global-report-on-human-settlements-2003 (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R. Slums from Space—15 Years of Slum Mapping Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P.; Taubenböck, H.; Werthmann, C. Monitoring and modelling of informal settlements—A review on recent developments and challenges. In Proceedings of the IEEE Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 March–1 April 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Kraff, N. The physical face of slums: A structural comparison of slums in Mumbai, India, based on remotely sensed data. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2014, 29, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, T.; Pesaresi, M. Searching for Robust and Objective EO-Based Indicators for Slum Characterization; UN-Habitat, CIESIN, ITC: Enshede, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wurm, M.; Stark, T.; Xiang Zhu, X.; Weigand, M.; Taubenböck, H. Semantic segmentation of slums in satellite images using transfer learning on fully convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Baldinelli, G.; Verducci, P. Sustainable strategies for smart cities: Analysis of the town development effect on surface urban heat island through remote sensing methodologies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yao, L.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. How many metrics are required to identify the effects of the landscape pattern on land surface temperature? Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilek, M.U.; Cilek, A. Analyses of land surface temperature (LST) variability among local climate zones (LCZs) comparing Landsat-8 and ENVI-met model data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, H. Localizing urban SDGs indicators for an integrated assessment of urban sustainability: A case study of Hainan province. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2336059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, L.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Kemper, T.; Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Schiavina, M. Applying the degree of urbanisation to the globe: A new harmonised definition reveals a different picture of global urbanisation. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Calka, B. Towards sustainable development exemplified by monitoring land use efficiency in Europe using SDG 11.3.1. Misc. Geogr. 2022, 26, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Li, C.; Peng, S. Identification of urban land use efficiency by indicator-SDG 11.3.1. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, E. Coupling Sustainable Development Goal 11.3.1 with current planning tools: City of Hamilton, Canada. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Arfvidsson, H.; Anand, G.; Bazaz, A.; Fenna, G.; Foster, K.; Jain, G.; Hansson, S.; Evans, L.M.; Moodley, N.; et al. Developing and Testing the Urban Sustainable Development Goal’s Targets and Indicators—A Five-City Study. Environ. Urban. 2016, 28, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Han, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Trustworthy remote sensing interpretation: Concepts, technologies, and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 209, 150–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Guneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, T.; Weeks, J.R.; Stow, D.; Fugate, D. Measuring temporal compositions of urban morphology through spectral mixture analysis: Toward a soft approach to change analysis in crowded cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, S.; Corpetti, T.; Kuffer, M.; Taubenbock, H.; Mallet, C. Foreword to the Special Issue on Paving the Way for the Future of Urban Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6533–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraff, N.J.; Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. Uncertainties of Human Perception in Visual Image Interpretation in Complex Urban Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4229–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Jenerowicz, A. Intellectual Structure of CORINE Land Cover Research Applications in Web of Science: A Europe-Wide Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieba, W. Philosophical and Axilogical Basis of Ecodevelopment. Probl. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 2, 19–25. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Karantzalos, K. Recent advances on 2D and 3D change detection in urban environments from remote sensing data. In Computational Approaches for Urban Environments; Helbich, M., Jokar Arsanjani, J., Leitner, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 13, pp. 237–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Komolafe, A.A.; Kouser, A.; Singh, D.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, R.D.; Johnson, B.A.; Minh, H.V.T.; et al. Assessing sustainable development prospects through remote sensing: A review. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K.; Vanmaercke, M.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Berihun, M.L.; Langendoen, E.J.; et al. Progress and challenges in sustainable land management initiatives: A Global Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

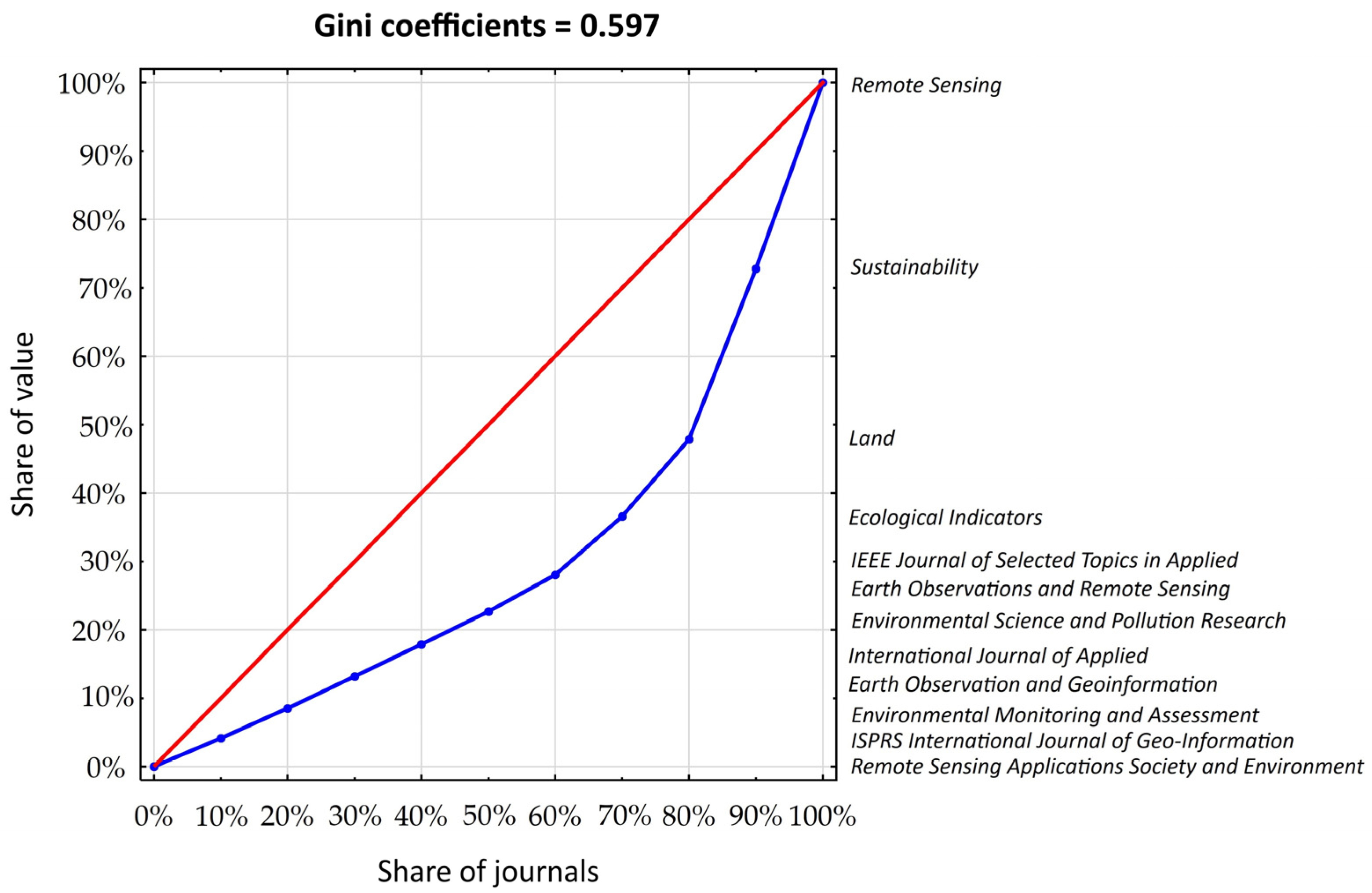
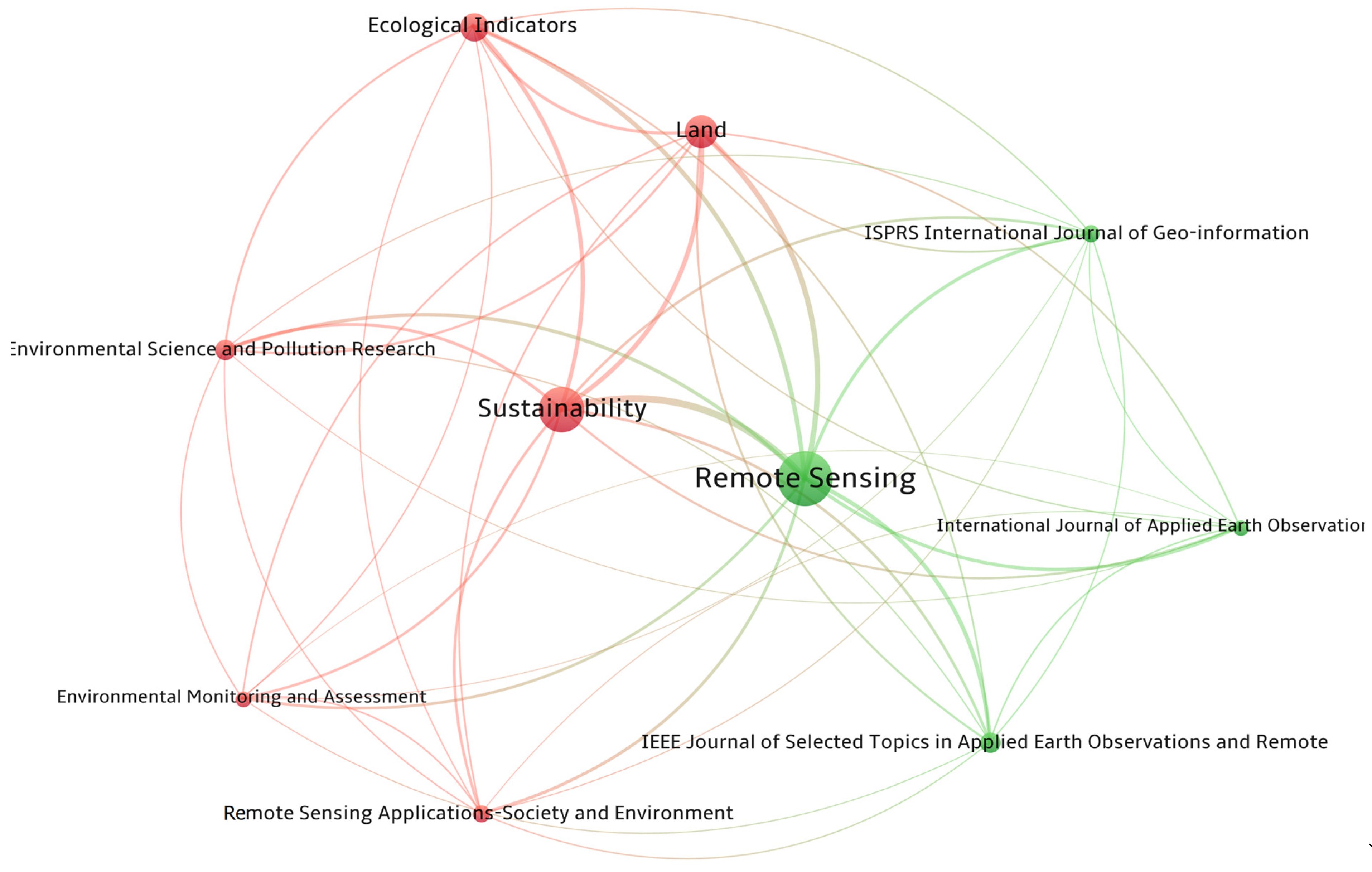
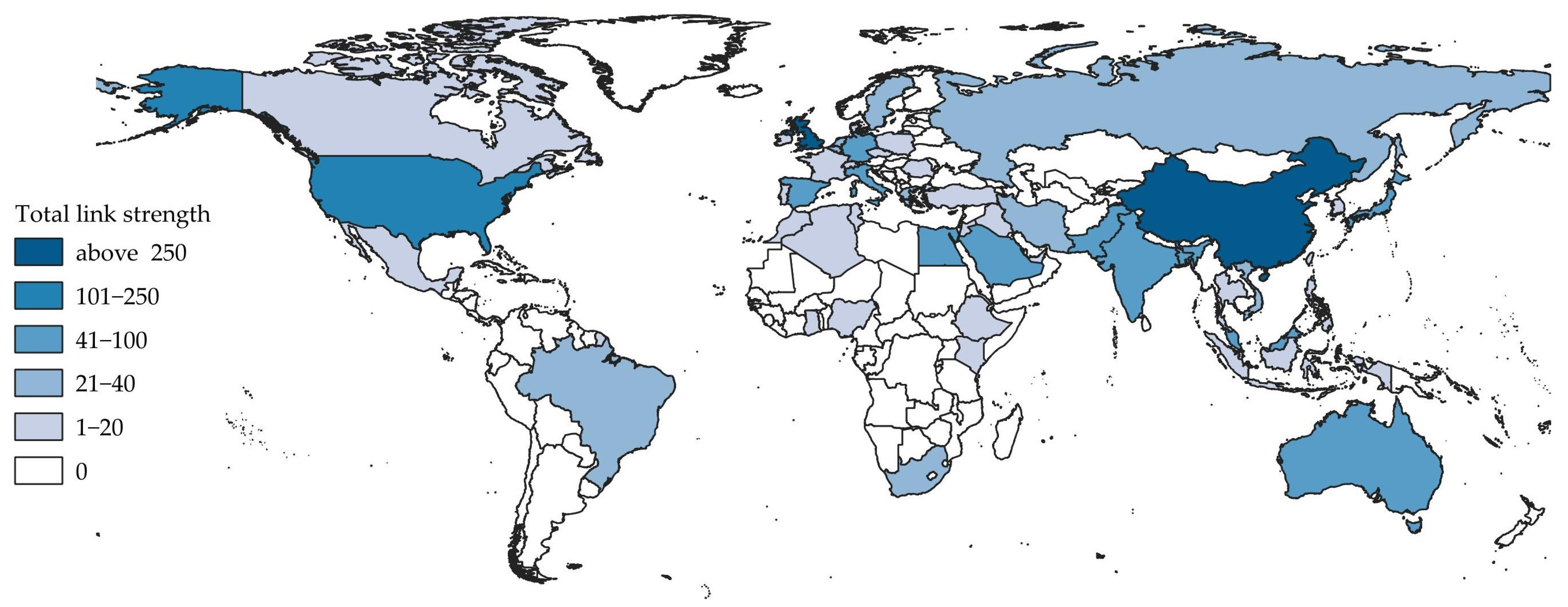
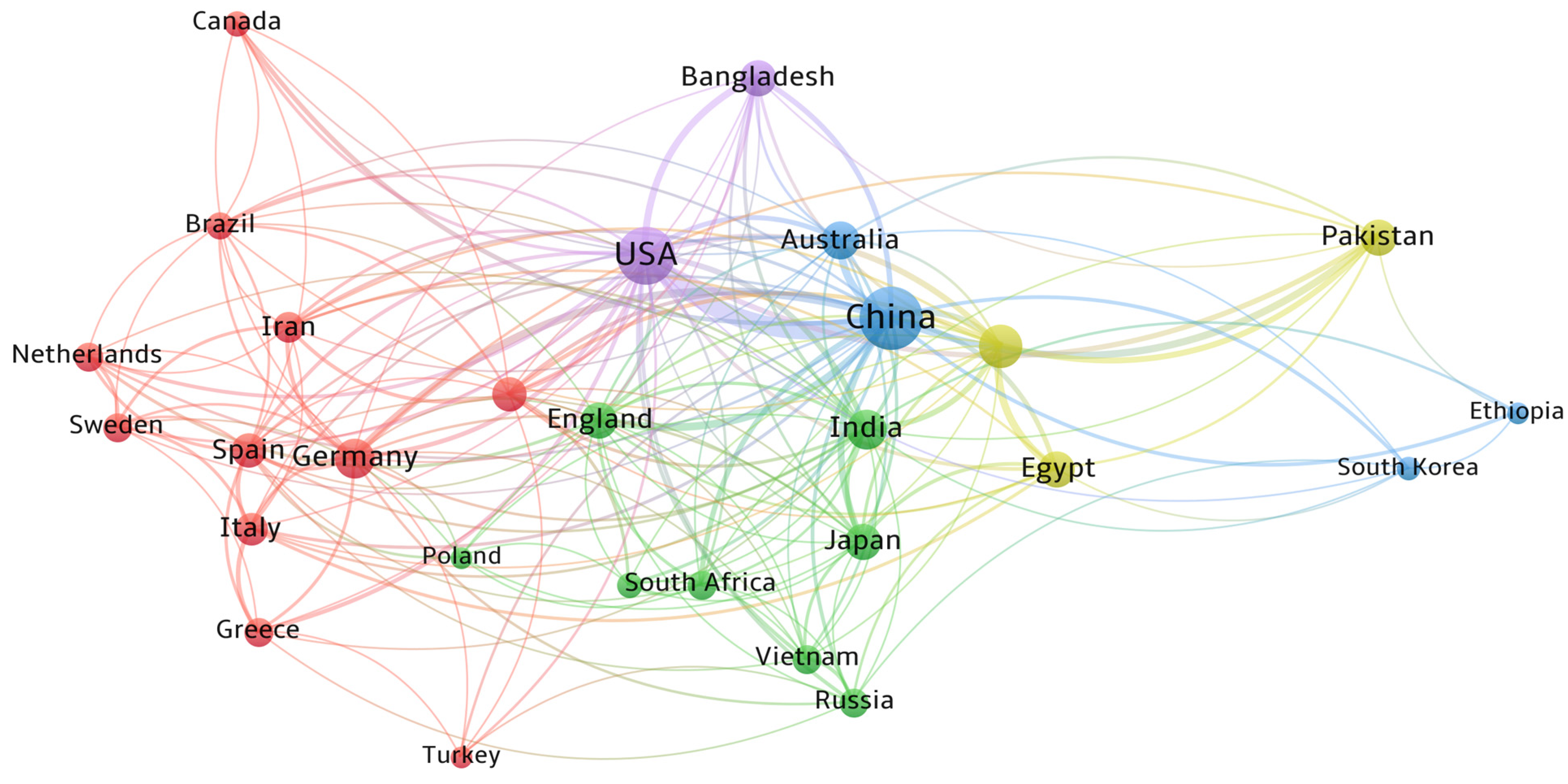
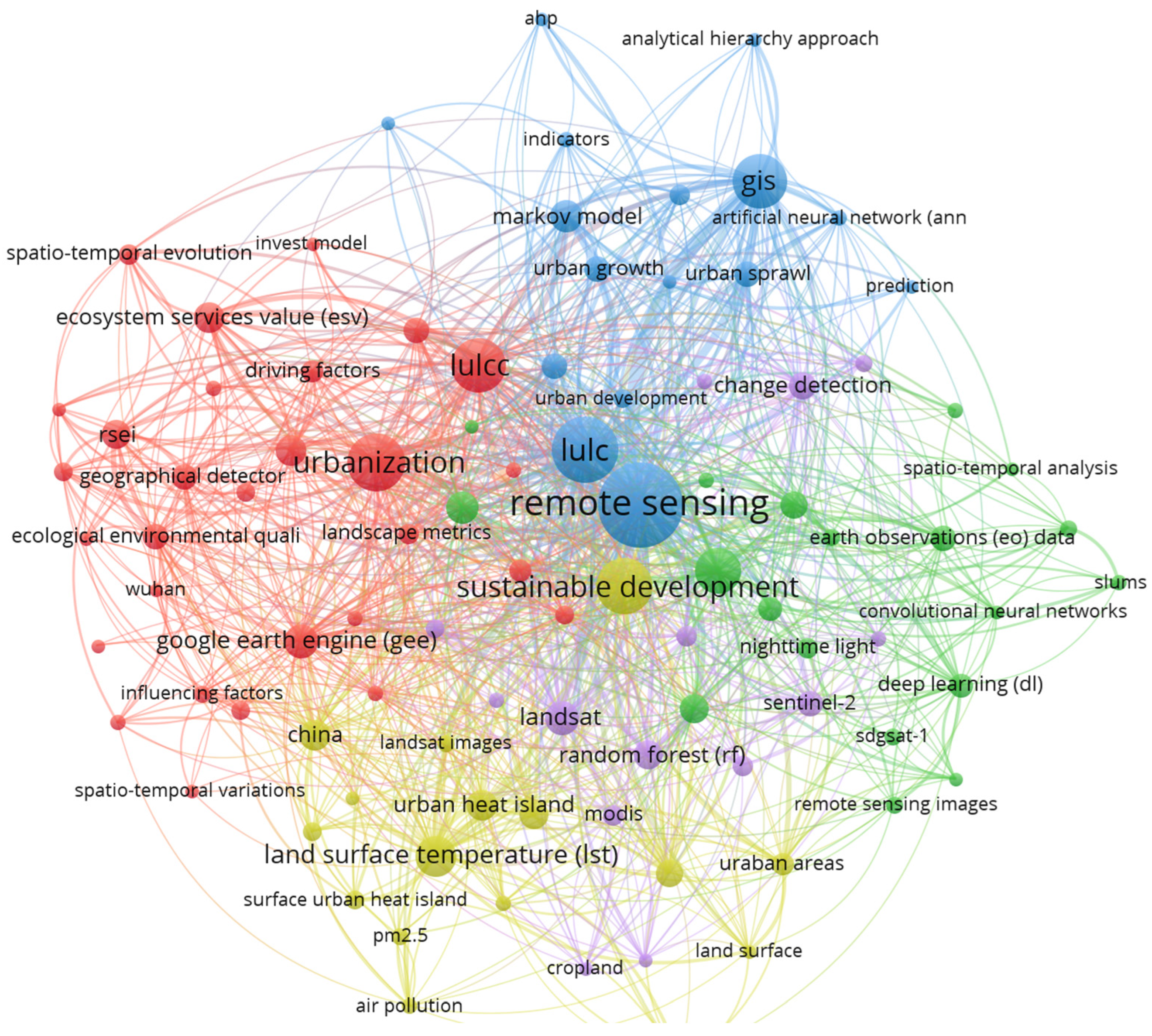

| Journal | TP 1 | IF 2 | IF 5 (R) 3 | TC 4 | CPP 5 | AU 6 | CU Countries 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing | 169 | 4.2 | 4.9 (4) | 3501 | 70.2 | 933 | China (67.5), USA (16.8), Italy (5.9) |
| Sustainability | 155 | 3.3 | 3.6 (5) | 1957 | 62.6 | 798 | China (68.4), USA (5.8), Egypt (5.2) |
| Land | 70 | 3.2 | 3.4 (6) | 744 | 67.0 | 342 | China (72.9), Germany (7.1), USA (7.1) |
| Ecological Indicators | 53 | 7.0 | 6.6 (2) | 1411 | 65.0 | 295 | China (67.5), USA (16.8), Bangladesh (3.7), England (3.7), Germany (3.7) |
| IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing | 33 | 4.7 | 5.0 (3) | 411 | 63.1 | 180 | China (93.9), USA (6.1), Australia (6.1), Germany (6.1), Pakistan (6.1) |
| Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 30 | 0 | 0.99 (10) | 368 | 68.0 | 133 | China (70.0), Iran (13.3), Saudi Arabia (13.3), Egypt (10.0) |
| Environmental Monitoring and Assessment | 29 | 2.9 | 3.1 (7) | 599 | 60.0 | 105 | India (34.5), China (13.8), Turkey (13.9), Egypt (6.9) |
| International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation | 29 | 7.6 | 7.5 (1) | 580 | 55.1 | 160 | China (62.1), USA (17.2), Canada (13.8), England (13.8), Australia (10.3) |
| ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information | 27 | 2.8 | 3.0 (8) | 656 | 56.2 | 139 | China (44.4), Italy (11.1), Netherlands (11.1), Germany (7.4) |
| Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment | 26 | 3.8 | 0.0 (9) | 564 | 77.9 | 108 | India (30.8), USA (23.1), Bangladesh (19.2), Nigeria (11.5), China (11.5) |
| Author, Affiliation | No. of Documents | No. of Citations | Research Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guo Huadong, China International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals | 12 | 221 | Drought, settlement, urban SDG indicators |
| Lu Linlin, Chinese Academy of Sciences | 12 | 217 | Air pollution, heat-related health risk, land use changes |
| Li Xuecao, USA Iowa State University | 11 | 861 | Image classification, built-up height, urban heat |
| Kuffer Monika, Netherlands University of Twente | 10 | 374 | Informal urbanization (slums), urban sprawl |
| Li Qingting, Chinese Academy of Sciences | 10 | 198 | Sensors, image classification, environmental monitoring |
| Zhou Yuyu, University of Hong Kong | 9 | 689 | Nighttime light (NTL) satellite, heat island, imperviousness |
| Murayama Yuji, Japan University of Tsukuba | 8 | 412 | Land use change, land use efficiency, surface temperature, heat island |
| Sun ZhongChang, Chinese Academy of Sciences | 8 | 166 | Ecosystems, SDG indicators |
| Tariq Aqil, USA Mississippi State University | 8 | 136 | Land use change, land temperature, cropland, image classification |
| Weng Qihao, Hong Kong Polytechnic University | 8 | 280 | Image classification, cooling effect, landscape |
| Keywords | Occurrence | Total Link Strength | Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote sensing | 367 | 712 | blue |
| LULC (land use and land cover) | 218 | 493 | blue |
| Urbanization | 166 | 319 | red |
| Sustainable development | 146 | 302 | green |
| GIS (geographic information system) | 163 | 302 | blue |
| LUCCS (land use and land cover change) | 153 | 294 | red |
| Land surface temperature (LST) | 104 | 189 | yellow |
| SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) | 85 | 185 | green |
| Google Earth Engine (GEE) | 62 | 137 | red |
| Landsat | 60 | 134 | purple |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bielecka, E.; Markowska, A.; Wiatkowska, B.; Calka, B. Sustainable Urban Land Management Based on Earth Observation Data—State of the Art and Trends. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091537
Bielecka E, Markowska A, Wiatkowska B, Calka B. Sustainable Urban Land Management Based on Earth Observation Data—State of the Art and Trends. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091537
Chicago/Turabian StyleBielecka, Elzbieta, Anna Markowska, Barbara Wiatkowska, and Beata Calka. 2025. "Sustainable Urban Land Management Based on Earth Observation Data—State of the Art and Trends" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091537
APA StyleBielecka, E., Markowska, A., Wiatkowska, B., & Calka, B. (2025). Sustainable Urban Land Management Based on Earth Observation Data—State of the Art and Trends. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091537






