Modeling Relationships among 217 Fires Using Remote Sensing of Burn Severity in Southern Pine Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Site
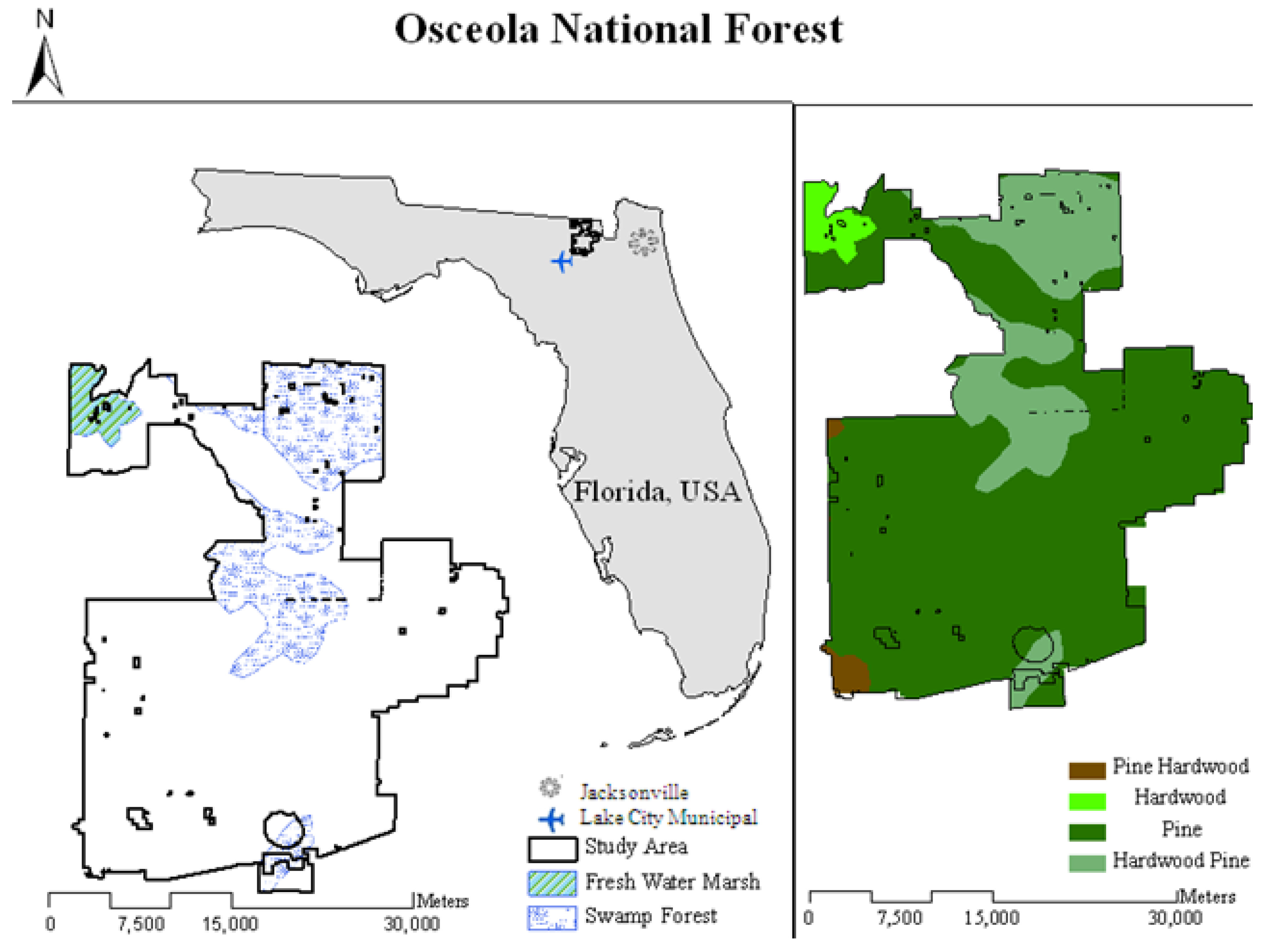
2.2. Image Analysis
2.3. Severity Classification
| USGS Severity Class | Reclassified Severity Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DNBR range | USGS Description | Description | |
| −100 to +99 | Unburned within a fire perimeter | Unburned | |
| −500 to −101 | Re-growth | Low Severity | |
| +100 to +269 | Low Severity | ||
| +270 to +439 | Low-Moderate Severity | Moderate Severity | |
| +440 to +659 | Moderate-High Severity | High Severity | |
| +660 to +1,300 | High Severity | ||
2.4. Model Development
| Models 1–4 |
| Severity Level of the Initial Fire (Low, Moderate, or High Burn Severity) |
| Palmer Drought Severity Index (−4 to +4) |
| Fire Type (Wildfire or Prescribed Burn) |
| Forest Type (Pine, Hardwood, Pine-Hardwood, or Hardwood-Pine) |
| Community Type (Hydric or Mesic) |
| Time since the initial Fire (1 to 10 years) |
| Model 5 |
| Severity Level of the Initial Fire (Low, Moderate, or High Burn Severity) |
| Palmer Drought Severity Index (−4 to +4) |
| Fire Type (Wildfire or Prescribed Burn) |
| Forest Type (Pine, Hardwood, Pine-Hardwood, or Hardwood-Pine) |
| Community Type (Hydric or Mesic) |
| Time since the initial Fire (1 to 10 years) |
| Fire Frequency (0.1 to 1) |
2.5. Logistic Regression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Predicting the Occurrence of Subsequent High Burn Severity
| Parameter | Model (a) | Model (b) | Model (c) | Model (d) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Std. Error | Estimate | Std. Error | Estimate | Std. Error | Estimate | Std. Error | P-value | |||
| Intercept | −5.34 | 0.12 | −1.31 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 0.03 | 1.22 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | ||
| Fire 1 Severity | Unburned | 2.97 | 0.02 | −0.73 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Low | −0.35 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 0.02 | −2.89 | 0.02 | −0.57 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | ||
| Moderate | −0.20 | 0.03 | Reference | −1.19 | 0.03 | −0.35 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | |||
| High | Reference | Reference | Reference | <0.0001 | |||||||
| Fire 1 Type | Wildfire | 1.19 | 0.02 | −0.51 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.01 | <0.0001 | |||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||||
| Fire 2 Type | Wildfire | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.01 | −1.02 | 0.03 | <0.0001 | |||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||||
| Time Interval Between Fires (Years) | 1–2 | 1.68 | 0.11 | −1.54 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 0.02 | −0.61 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | |
| 3–4 | 0.45 | 0.12 | −0.76 | 0.02 | 0.66 | 0.02 | −0.79 | 0.02 | <0.0002 | ||
| 5–6 | 4.66 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.03 | −0.57 | 0.03 | 1.19 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | ||
| 7–8 | 2.05 | 0.12 | −1.53 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | ||
| 9–10 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||
| Forest Type | Hydric | 0.21 | 0.12 | <0.0001 | |||||||
| Mesic | Reference | <0.0001 | |||||||||
| Palmer Drought Severity Index | Average for the year before the first fire | 0.65 | 0.01 | <0.0001 | |||||||
| Average for the year of the first fire | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.00 | -0.47 | 0.01 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Average for the year before the second fire | 0.48 | 0.00 | -0.25 | 0.01 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Average for the year of the second fire | −0.09 | 0.01 | -0.08 | 0.00 | -0.03 | 0.00 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Interaction Between Time Interval Between Fire 1 and Fire 2 (Years) and Fire Type 2 | 1–2 | Wildfire | 1.30 | 1.30 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | ||||||||||
| 3–4 | Wildfire | 0.13 | 0.13 | <0.0005 | |||||||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | ||||||||||
| 5–6 | Wildfire | 1.95 | 1.95 | <0.0001 | |||||||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | . | |||||||||
| 7–8 | Wildfire | −1.27 | −1.27 | <0.0001 | |||||||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | ||||||||||
| 9–10 | Wildfire | Reference | |||||||||
| Prescribed burn | Reference | ||||||||||
| Residual | 1.15 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |||||||
3.2. Probability of Burn Severity Increasing from the First to the Second fire
3.3. Probability of Burn Severity Decreasing from the First to the Second Fire

3.4. Probability of Repeated Fires during the Study Period
3.5. Temporal Thresholds and the Importance of Fire Type
3.6. Creating the Predictive Model to Use for Testing Known Fire Patterns
| Parameter | Estimate | Std. Error | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.9676 | 0.3210 | <0.0001 |
| Fire Frequency | −2.1424 | 0.1899 | <0.0001 |
| Time Since Last Fire | −0.2796 | 0.02556 | <0.0001 |
| Fire Frequency * Time Since Last Fire | −0.5907 | 0.1458 | <0.0001 |
| Fire Type: Wildfire | −3.3071 | 0.07704 | <0.0001 |
| Fire Type: Prescribed Burns | Reference | ||
| Residual | 0.9359 |

3.7. Testing the Predictive Model against Known Fire Patterns


4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations Associated with dNBRs in the Southeastern US
4.2. Time and Severity Thresholds for Preventing High Burn Severity Effects
4.3. The Influence of Fire Frequency and Time since Last Fire on Severity
4.4. Burn Severity in Relation to Fire Type, Community Type, and Forest Moisture
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Acknowledgements
References
- Davis, L.S.; Cooper, R.W. How prescribed burning affects wildfire occurrence. J. For. 1963, 61, 915–917. [Google Scholar]
- Outcalt, K.W.; Wade, D.D. Fuels management reduces tree mortality from wildfires in southeastern United States. South. J. Appl. For. 2004, 28, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Main, M.B.; Richardson, L.W. Response of wildlife to prescribed fire in southwest Florida pine flatwoods. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2002, 30, 213–133. [Google Scholar]
- Heuberger, K.A.; Putz, F.E. Fire in the suburbs: Ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine sandhill. Restor. Ecol. 2003, 11, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lear, D.H.; Carroll, W.D.; Kapeluck, P.R.; Johnson, R. History and restoration of the longleaf pine-grassland ecosystem: Implication for species at risk. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 211, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, C.L.; Andersen, A.N. Patch mosaic burning for biodiversity conservation: A critique of the pyro diversity paradigm. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolcott, L.; O’Brien, J.J.; Mordecai, K. A survey of land managers on wildland hazardous fuels issues in Florida: A technical note. South. J. Appl. For. 2007, 31, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Agee, J.K. Fire Ecology of Pacific Northwest Forest; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 417. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, C.C. Wildland fire hazard and risk: Problems, definitions, and context. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 211, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocke, A.E.; Fule, P.Z.; Crouse, J.E. Comparison of burn severity assessment using difference Normalized Burn Ratio and ground data. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2005, 14, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.; Morgan, P.; Evans, J. A predictive model of burn severity based on 20-year satellite-infrared burn severity data in a large southwestern US wilderness area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.M.; Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E.; Kelly, M.; Wagtendonk, J.W.; Stephens, S. Interactions among wildland fires in a long-established sierra nevada natural fire area. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E. Quantifying burn severity in a heterogeneous landscape with relative version of the delta Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wagtendonk, J.W.; Root, R.R.; Key, C.H. Comparison of AVIRS and Landsat ETM+ detection capabilities for burn severity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, D.R. Burn severity in a central Florida sand pine scrub wilderness area. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Florida Press, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, E.E.; French, N.H.; Turetsky, M.R.; Trigg, S.N.; Kasischke, E.S. Evaluating the potential of landsat TM/ETM+ imagery for assessing fire severity in Alaska black spruce forest. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2008, 17, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.D.; Ryan, K.C.; Key, C.C.; Runnig, S.W. Remote sensing of forest fire severity and vegetation recovery. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 1996, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, N.H.F.; Kasischke, E.S.; Hall, R.J.; Murphy, K.A.; Verbyla, D.L.; Hoy, E.E.; Allen, J.L. Using Landsat data to assess fire and burn severity in the North American boreal forest region: An overview and summary of results. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2008, 17, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotte, J.J.; Robertson, K.M. Validation of remote sensing of burn severity in southeastern US ecosystems. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2011, 20, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safford, H.D.; Schmidt, D.A.; Carson, C.H. Effects of fuel treatments on fire severity in an area of wildland-urban interface, Angora Fire, Lake Tahoe Basin, California. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzi, A.M.; Fule, P.Z.; Sieg, C.H. Effects of fire severity and pre-fire stand treatment on plant community recovery after a large wildfire. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras, I.; Gracia, M.; Moré, G.; Retana, J. Factors influencing the patterns of fire severity in large wildland fire under extreme meteorological conditions in the Mediterranean basin. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2009, 18, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenshink, J.; Schwind, B.; Brewer, K.; Zhu1, Z.; Quayle, B.; Howard, S. A project for monitoring trends in burn severity. Fire Ecol. 2007, 3, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchener, L.J.; Parker, A.J. Climate, lightning, and wildfire in the national forests of the southeastern United States: 1989–1998. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 26, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS). Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov/distribution/downloadnotices.shtml (accessed on 7 January 2010).
- Allen, J.L.; Sorbel, B. Assessing the differenced Normalized Burn Ratio’s ability to map burn severity in boreal forest and tundra ecosystems of Alaska’s national parks. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2008, 17, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Key, C.H.; Ohlen, D.; Benson, N.C. Evaluate Sensitivities of Burn Severity Mapping Algorithms for Different Ecosystems and Fire Histories in the United States; Technical Report; Joint Fire Science Program: Boise, ID, USA, October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Key, C.H. Ecological and sampling constraints on defining landscape fire severity. Fire Ecol. 2006, 2, 34–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geologic Service (USGS). Difference Normalized Burn Ratio. Available online: http://burnseverity.cr.usgs.gov/pdfs/LAv4_BR_ CheatSheet.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2010).
- Alley, W.M. The palmer drought severity index: Limitations and assumptions. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida Natural Areas Inventory and Department of Natural Resources. Guide to the Natural Communities of Florida; Florida Natural Areas Inventory and Department of Natural Resources: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.H. General Map of Natural Vegetation in Florida. Agricultural Experimentations; Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Littell, R.C.; Milliken, G.A.; Stroup, W.W.; Wolfinger, R.D.; Schabenberger, O. SAS for Mixed Models, 2nd ed.; SAS Publishing: Caryn, NC, USA, 2006; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT® 9.2 User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Key, C.H. Remote Sensing Sensitivity to Fire Severity and Fire Recovery. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Remote Sensing and GIS Applications to Forest Fire Management: Fire Effects Assessment, Zaragoza, Spain, 16–18 June 2005.
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape Assessment: Ground Measure of Severity, the Composite Burn Index; and Remote Sensing of Severity, the Normalized Burn Ratio; Technical Report of the USDA Forest Service; Rocky Mountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, M.; Starr, G.; Mack, M.C.; Martin, T.A.; Gholz, H.L. Effects of a prescribed fire on understory vegetation, carbon pools, and soil nutrients in longleaf pine-slash pine forest in Florida. Natl. Areas J. 2010, 30, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, P.C. Successional responses of herbs in the longleaf- slash pine forest after fire. Ecology 1949, 30, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.A.; Morgan, P.; Hudak, A.T. Burn severity of areas reburned by wildfires in the Gila National Forest, New Mexico, USA. Fire Ecol. 2010, 6, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K.; Hiers, J.K.; O’Brien, J.J.; Jack, S.B.; Engstrom, R.T. Silviculture that sustains: The nexus between silviculture, frequent prescribed fire, and conservation of biodiversity in longleaf pine forests of the southeastern United States. Can. J. For. Resour. 2006, 36, 2724–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamson, W.G. Species response to fire on the Florida Lake Wales Ridge. Am. J. Bot. 1984, 71, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamson, W.G.; Abrahamson, C.R. Effects of fire on long unburned Florida uplands. J. Veg. Sci. 1996, 7, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliakal, S.K.; Menges, E.S. Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in relation to time since last fire. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2000, 127, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.H.; Swindel, B.F.; Terry, S.W. Vegetative response to prescribed fire in a north Florida flatwoods forest. J. Range Manag. 1982, 35, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- DeBano, L.F.; Neary, D.G.; Ffolliott, P.F. Fire’s Effects on Ecosystems; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Kinghorn, S.; USFS Osceola National Forest. Olustee, Florida. Personal Communication, 2010.
- Van Wagtendonk, J.W.; Lutz, J.A. Fire regime attributes wildland fires in Yosemite National Park, USA. Fire Ecol. 2007, 3, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Malone, S.L.; Kobziar, L.N.; Staudhammer, C.L.; Abd-Elrahman, A. Modeling Relationships among 217 Fires Using Remote Sensing of Burn Severity in Southern Pine Forests. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2005-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs3092005
Malone SL, Kobziar LN, Staudhammer CL, Abd-Elrahman A. Modeling Relationships among 217 Fires Using Remote Sensing of Burn Severity in Southern Pine Forests. Remote Sensing. 2011; 3(9):2005-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs3092005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalone, Sparkle L., Leda N. Kobziar, Christina L. Staudhammer, and Amr Abd-Elrahman. 2011. "Modeling Relationships among 217 Fires Using Remote Sensing of Burn Severity in Southern Pine Forests" Remote Sensing 3, no. 9: 2005-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs3092005
APA StyleMalone, S. L., Kobziar, L. N., Staudhammer, C. L., & Abd-Elrahman, A. (2011). Modeling Relationships among 217 Fires Using Remote Sensing of Burn Severity in Southern Pine Forests. Remote Sensing, 3(9), 2005-2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs3092005






