First Results of Estimating Surface Soil Moisture in the Vegetated Areas Using ASAR and Hyperion Data: The Chinese Heihe River Basin Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
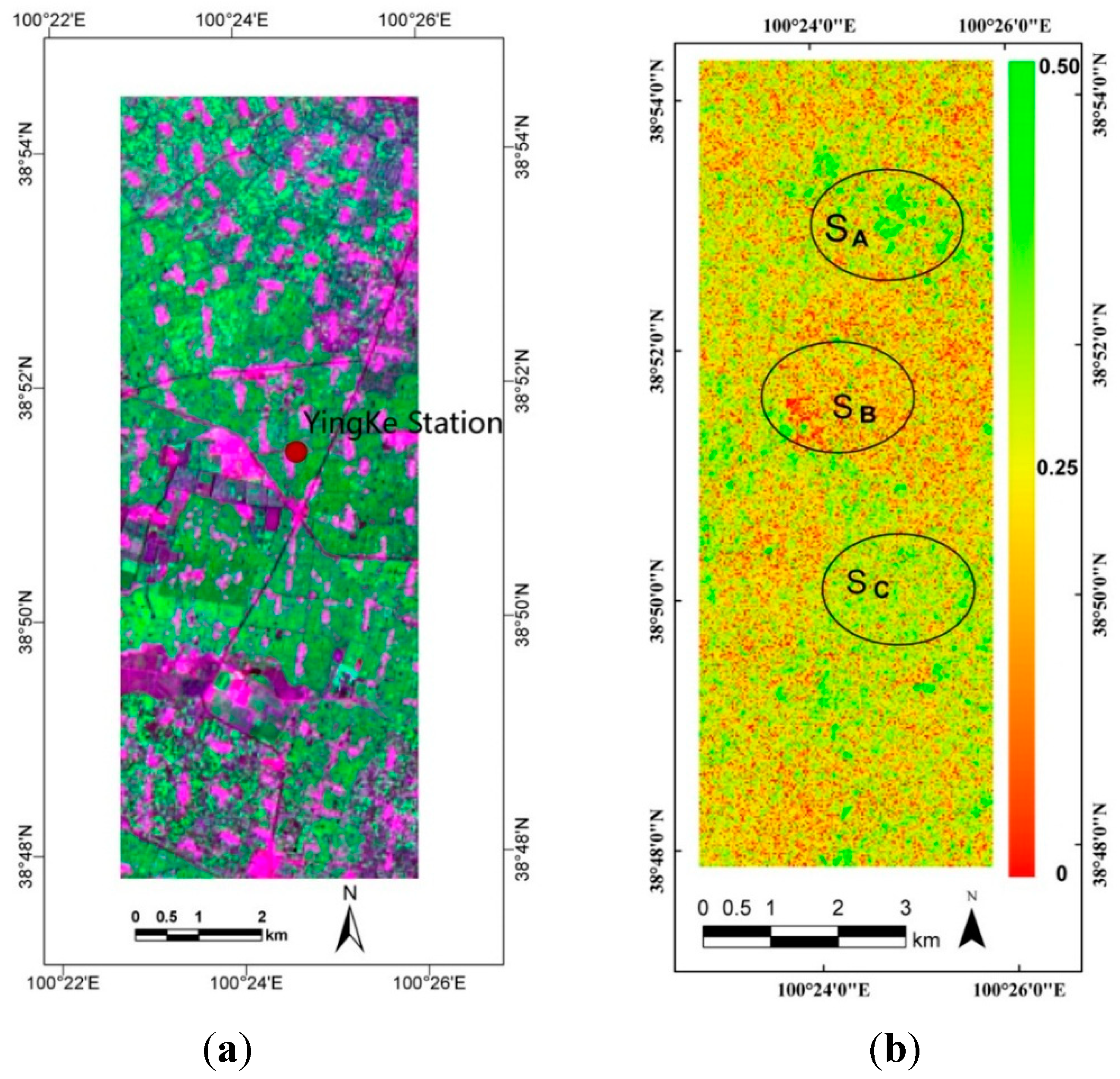
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Field Data
| Type | MIMICS Model Input Parameters | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Soil surface | Soil moisture | 0.2 cm3∙cm−3 |
| Surface correlation length | 12 cm | |
| RMS height | 1 cm | |
| Surface temperature | 24° | |
| Soil sand | 16.7% | |
| Soil clay | 8.5% | |
| Branch | Branch length | 1.17 m |
| Branch diameter | 2.9 cm | |
| Branch weight water | 0.6 | |
| Branch dry matter density | 0.1 g∙cm−2 | |
| Branch density | 15.0 N∙m−3 | |
| leaf | Leaf weight water | 0.78 |
| Leaf dry matter density | 0.005 g·cm−2 | |
| Leaf thickness | 0.024 cm | |
| Leaf width | 6 cm | |
| Leaf length | 60 cm | |
| Leaf diameter | 9 cm | |
| Leaf density | 20, 30, ..., 400 N∙m−3 | |
| Leaf angle distribution | Plagiophile | |
| Sensor | Angle of incidence | 31.5° |
| Frequency | 1.4, 3.0, 5.33 GHz |
3. Methodology
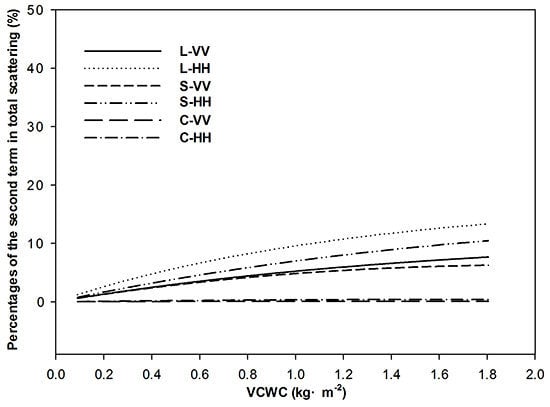
3.1. Scattering Characteristics in Agricultural Regions

3.2. Scattering Model in Agricultural Regions
3.3. Calculation of Vegetation Canopy Water Content
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Soil Moisture Retrieval Model

4.2. Sensitivity Analysis

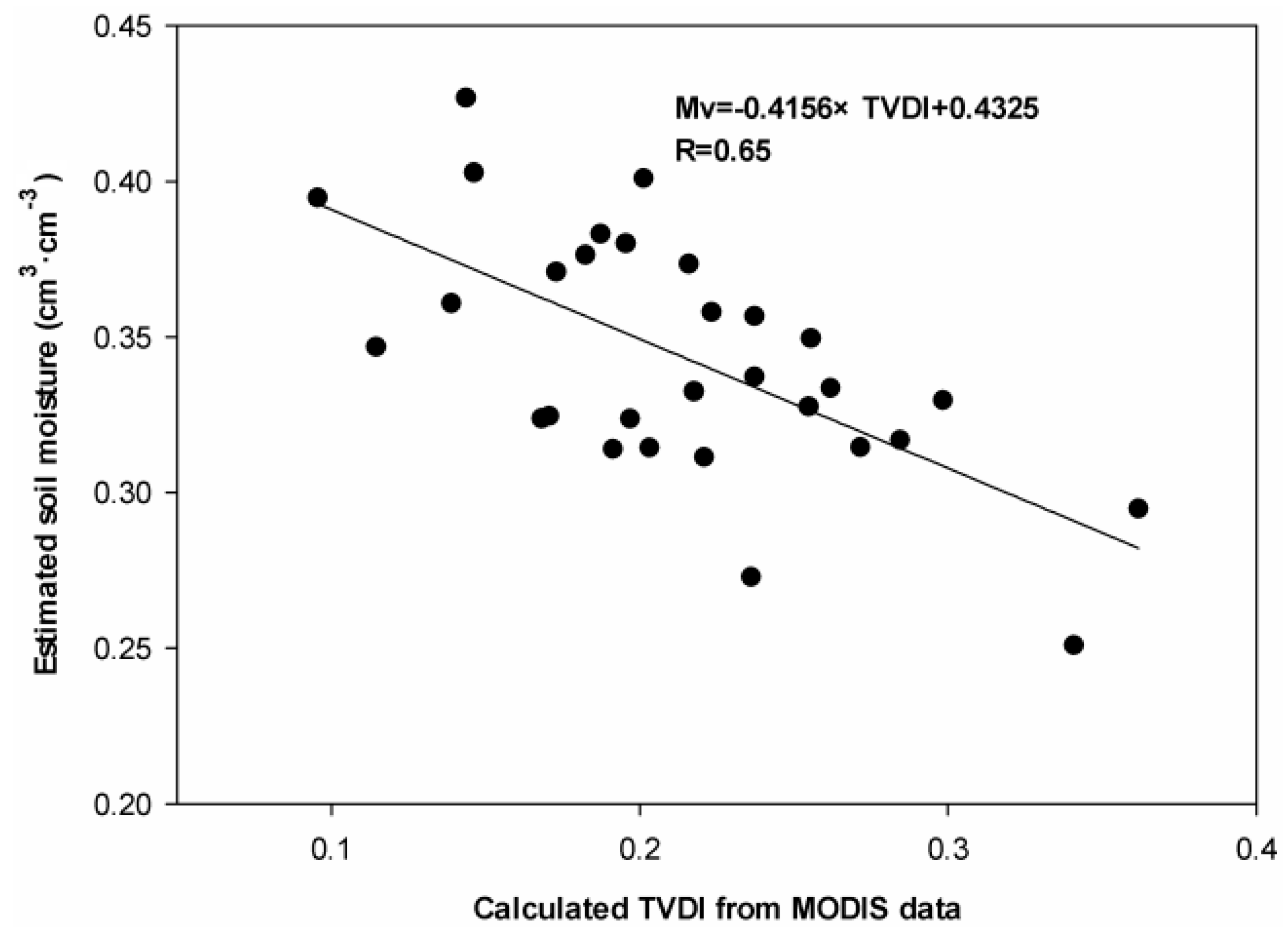
4.3. Soil Moisture Estimation

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baghdadi, N.; Holah, N.; Zribi, M. Soil moisture estimation using multi-incidence and multi-polarization ASAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 10, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M. Evaluation of radar backscatter models IEM, OH and Dubois using experimental observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3831–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Lemoine, G.; Rott, H. A method for estimating soil moisture from ERS scatterometer and soil data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudena, M.; Bevilacqua, I.; Canone, D.; Ferraris, S.; Previati, M.; Provenzale, A. Soil water dynamics at a midlatitude test site: Field measurements and box modeling approaches. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, K.C.; Coulibaly, P. Advances in soil moisture retrieval from synthetic aperture radar and hydrological applications. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowski, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Caudaro, M.; Ratto, S.; Ferraris, S.; Berni, N.; Ponziani, F.; Wagner, W.; et al. Soil moisture estimation in alpine catchments through modelling and satellite observations. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Guerin, C. Analysis of surface roughness heterogeneity and scattering behavior for radar measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Li, X.; Han, X.J.; Jin, R. Estimation of surface soil moisture and roughness from multi-angular ASAR imagery in the watershed allied telemetry experimental research (WATER). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; Elrayes, M.A. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil 2: Dielectric mixing models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Ulaby, F.T. An empirical model and an inversion technique for radar scattering from bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoray, T.; Shoshany, M. Multi-scale analysis of intrinsic soil factors from SAR-based mapping of drying rates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Saux-Picart, S.; Andre, C.; Descroix, L.; Ottle, C.; Kallel, A. Soil moisture mapping based on ASAR/ENVISAT radar data over a Sahelian region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3547–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouki, A.; McNairn, H.; Pacheco, A. Mapping soil moisture using RADARSAT-2 data and local autocorrelation statistics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Spatial and temporal soil moisture estimation from RADARSAT-2 imagery over Flevoland, The Netherlands. J. Hydrol. 2012, s456–s457, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Study on Soil Moisture Inversion and Application with Polarization Radar in Vegetated Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Attema, E.P.W.; Ulaby, F.T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Sarabandi, K.; McDonald, K.; Whitt, M.; Dobson, M.C. Michigan microwave canopy scattering model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1223–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ding, J.L.; Wang, F.; Guljamal, U.; Zhang, Z.G. Retrieval methods of soil water content in vegetation covering areas based on multi-source remote sensing data. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 966–972. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Qi, J.; Moran, S.; Marsett, R. Soil moisture estimation in a semiarid rangeland using ERS-2 and TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, Y.S. A new semi-empirical model for soil moisture content retrieval by ASAR and TM data in vegetation-covered areas. Sci. China: Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 532–540. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Saradjian, M.R.; Hosseini, M. Soil moisture estimation by using multipolarization SAR image. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 2, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.B.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Riaño, D.; Rueda, C.A.; Ustin, S.L. Estimating vegetation water content with hyperspectral data for different canopy scenarios: Relationships between AVIRIS and MODIS indexes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.S. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.D.; Chen, K.S. A reappraisal of the validity of the IEM model for backscattering from rough surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.W.; Li, Z.Y.; Ma, M.G.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q. Watershed allied telemetry experimental research. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, D22103, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.W.; Roth, K.; Menenti, M.; Wagner, W. Preface “observing and modeling the catchment scale water cycle”. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 2, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEST. Next ESA SAR toolbox Website. European Space Agency 2013. Available online: http://nest.array.ca/web/nest (accessed on 20 May 2014).
- Small, D.; Schubert, A. Guide to ASAR Geocoding; RSL-ASAR-GC-AD (1.01). University of Zürich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: http://www.geo.unizh.ch/microsite/rsl-documents/research/publications/other-sci-communications/2008_RSL-ASAR-GC-AD-v101-0335607552/2008_RSL-ASAR-GC-AD-v101.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2014).
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4, Available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90 m Database 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 22 May 2014).
- Kellndorfer, J.M.; Pierce, L.E.; Dobson, M.C.; Member, S.; Ulaby, F.T. Toward consistent regional-to-global-scale vegetation characterization using orbital SAR systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1396–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, J.S.; Barry, P.S.; Segal, C.C.; Shepanski, J.; Beiso, D.; Carman, S.L. Hyperion, a space-based imaging spectrometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, S.G.; Pearlman, J.S.; Mendenhall, J.A.; Reuter, D. Overview of the Earth Observing One (EO-1) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Lewisb, M.M. Arid land characterisation with EO-1 Hyperion hyperspectral data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 19, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.G.; Niu, Z.; Wang, X.P. Atmospheric correction of Hyperion hyperspectral image based on FLAASH. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2009, 29, 1181–1185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Gao, S.; Dong, J.J. WATER: Dataset of Crop Biochemical Parameter Measurements in the Yingke Oasis Foci Experimental Area. Available online: http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn/data/e347aef0-5c3b-40cd-9a08-7c0e89470898 (accessed on 12 October 2012).
- Zhu, X.H.; Feng, X.M.; Zhao, Y.S.; Song, X.N. Scale effect and error analysis of crop LAI inversion. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 586–592. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- De Roo, R.D.; Du, Y.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. A semi-empirical backscattering model at L-band and C-band for a soybean canopy with soil moisture inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.S.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.H. Soil moisture estimation based on optical and microwave remote sensing data. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 43, 228–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.C.; Li, Z.; Li, X.W. Evaluate usage of decomposition technique in estimation of soil moisture with vegetated surface by multi-temporal measurements data. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 6, 412–415. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Shi, J.C. Applying the radar technology to estimate relative change of soil moisture in vegetated area. Adv. Water Sci. 2005, 16, 596–601. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.W.; Song, X.N.; Li, X.T.; Leng, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, F.C. Estimation of surface soil moisture from ASAR dual-polarized data in the middle stream of the Heihe River Basin. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2013, 02, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, W. Light scattering by leaf layers with application to canopy reflectance modeling: The SAIL model. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 16, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. Prospect-a model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F.; Andrieu, B.; Danson, F.M.; Jaggard, K. Extraction of vegetation biophysical parameters by inversion of the PROSPECT+SAIL models on sugar beet canopy reflectance data-Application to TM and AVIRIS sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 52, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; Francois, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT+SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L.; Schaepman, M.E. Estimating canopy water content using hyperspectral remote sensing data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2010, 12, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Biel, C.; Serrano, L.; Save, R. The reflectance at the 950–970 mm region as an indicator of plant water status. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 1993, 14, 1887–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Remote sensing of leaf water content in the near infrared. Remote Sens. Environ. 1980, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.N.; Ma, J.W.; Li, X.T.; Leng, P.; Zhou, F.C.; Li, S. Estimation of vegetation canopy water content using Hyperion hyperspectral data. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2013, 10, 2833–2837. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Leng, P.; Zhou, F.; Li, S. First Results of Estimating Surface Soil Moisture in the Vegetated Areas Using ASAR and Hyperion Data: The Chinese Heihe River Basin Case Study. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12055-12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61212055
Song X, Ma J, Li X, Leng P, Zhou F, Li S. First Results of Estimating Surface Soil Moisture in the Vegetated Areas Using ASAR and Hyperion Data: The Chinese Heihe River Basin Case Study. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(12):12055-12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61212055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xiaoning, Jianwei Ma, Xiaotao Li, Pei Leng, Fangcheng Zhou, and Shuang Li. 2014. "First Results of Estimating Surface Soil Moisture in the Vegetated Areas Using ASAR and Hyperion Data: The Chinese Heihe River Basin Case Study" Remote Sensing 6, no. 12: 12055-12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61212055
APA StyleSong, X., Ma, J., Li, X., Leng, P., Zhou, F., & Li, S. (2014). First Results of Estimating Surface Soil Moisture in the Vegetated Areas Using ASAR and Hyperion Data: The Chinese Heihe River Basin Case Study. Remote Sensing, 6(12), 12055-12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61212055