Inundations in the Inner Niger Delta: Monitoring and Analysis Using MODIS and Global Precipitation Datasets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Floods over the IND
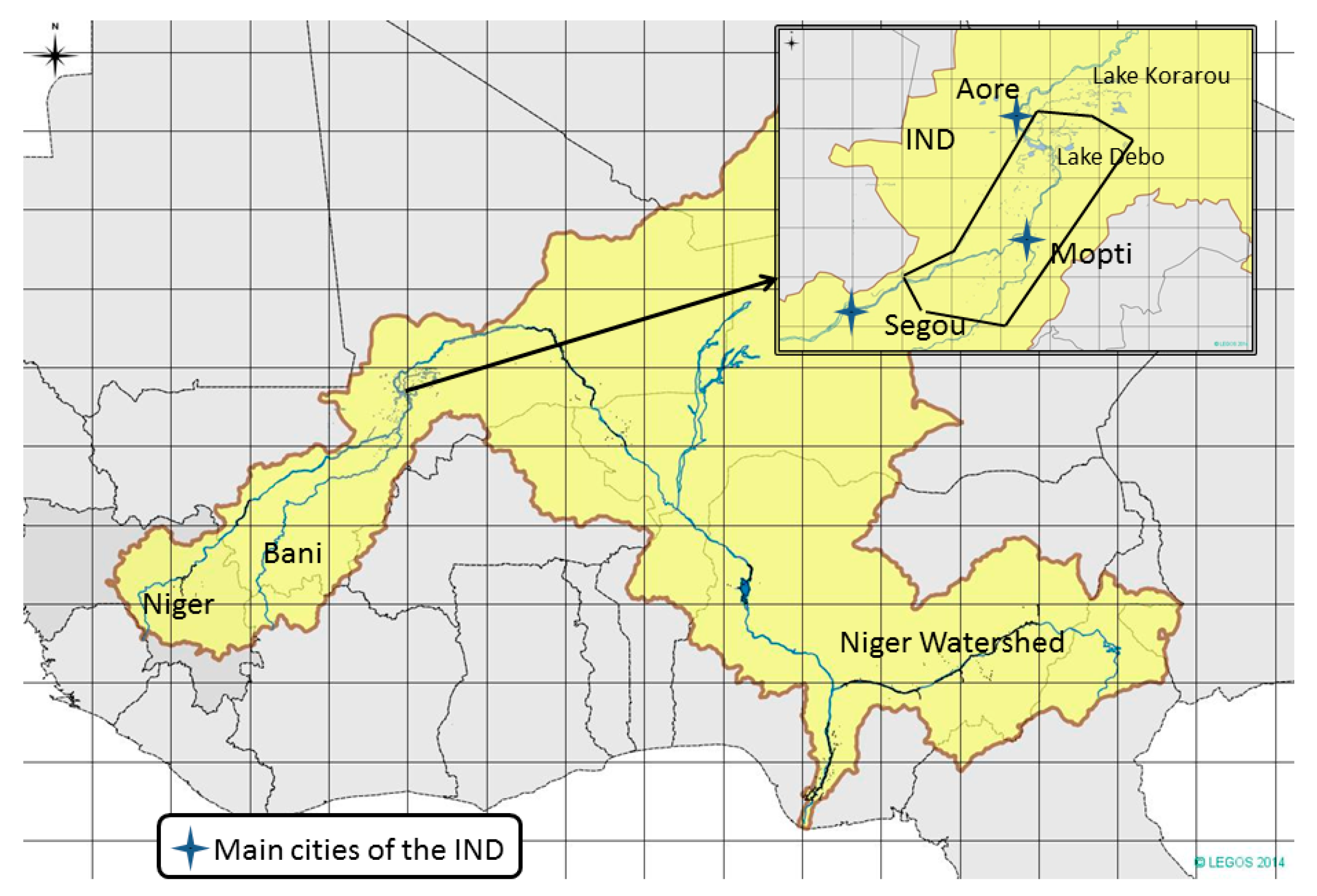
3. Data Sets and Methodologies
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Preamble
3.1.2. MODIS
- Band 1: 620–670 nm.
- Band 2: 841–876 nm.
- Band 3: 459–479 nm.
- Band 4: 545–565 nm.
- Band 5: 1230–1250 nm.
- Band 6: 1628–1652 nm.
- Band 7: 2107–2155 nm.
3.1.3. Rainfall Data
- Maps of monthly average climatology, and monthly and yearly anomalies.
- Time series for total precipitation over both rivers on the upstream part of the IND including the IND.
- EOF spatio-temporal modes for 14 years of data over the ROI.
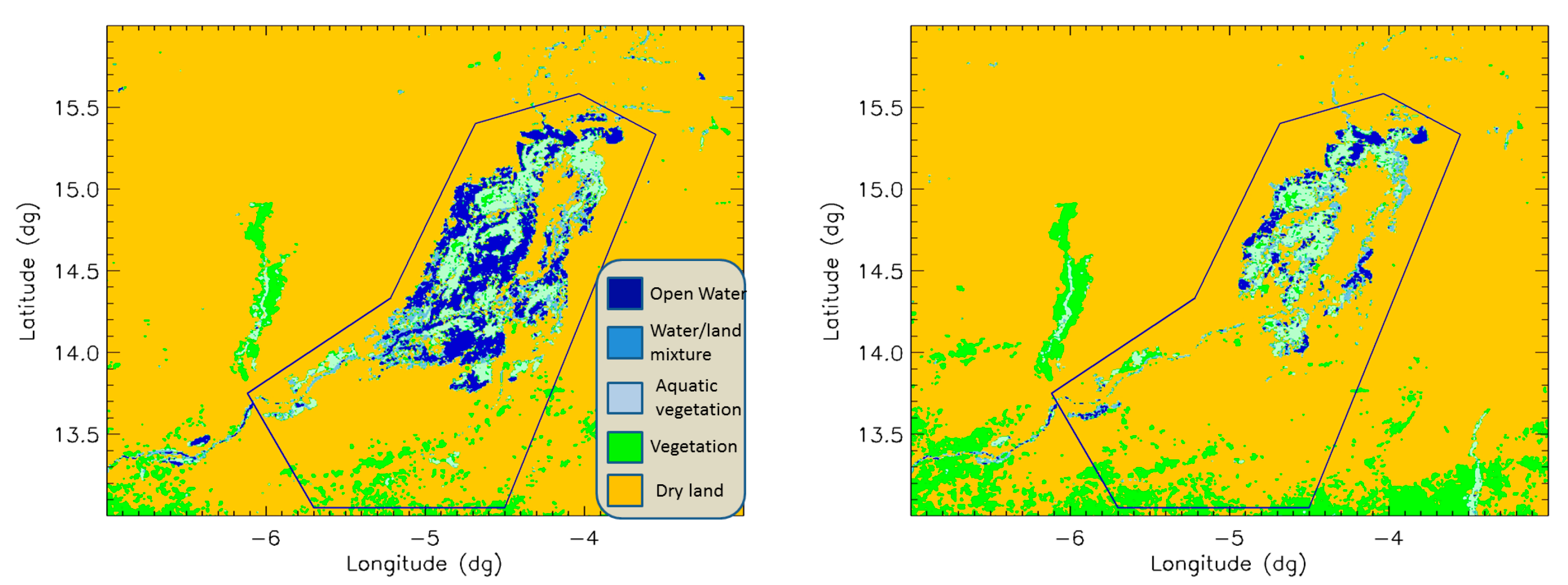
3.2. Methodology to Detect Water over the IND with MODIS and Validation
| Index | Open Water | Mix Water/Dry Land | Aquatic Vegetation | Vegetation | Dry Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band 5 | <1200 | >1200 & <2700 | >1200 & <2700 | >2700 | >2700 |
| NDVI | No Test | <0.4 | >0.4 | >0.4 | <0.4 |
- A synthetic map of ROI with classification obtained from MODIS images every 8 days.
- A map representing the average flood duration (in days) over the whole ROI, annual maps of flood duration anomalies with respect to average duration, and the Empirical Orthogonal Functions (EOFs, see Section 4.3) providing the spatio-temporal modes for each of the classes over the whole ROI.
- Evolution in time of the surface area of each class over the whole ROI.

4. Results and Interpretation
4.1. Land Surface Classification over the IND
4.1.1. Mean Annual Flooding over the IND


- The inundated surface is shallow.
- The vertical topography slope of the IND is small.
- Downstream water flow is probably slower due to the presence of vegetation.

4.1.2. Inter-Annual Variability of Floods over the IND

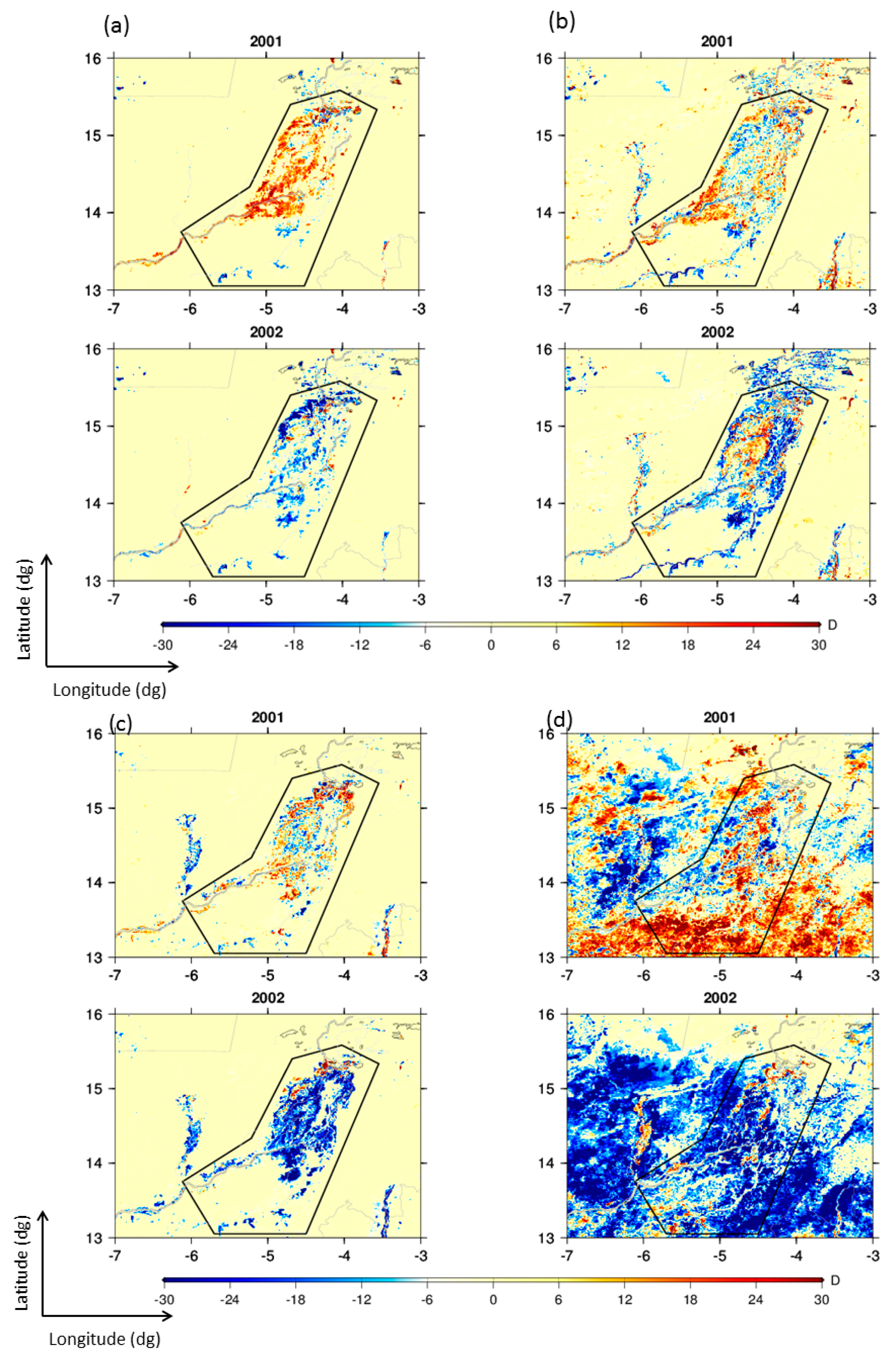

4.2. Rainfall
4.2.1. Seasonal Rainfall over West Africa



4.2.2. Rainfall Inter-Annual Variability
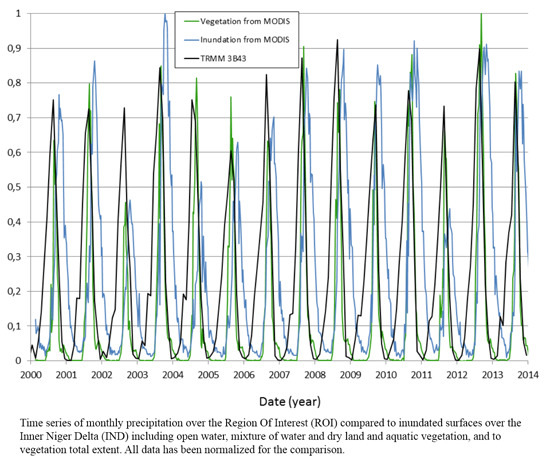
4.3. Links between Rainfall and Floods over the IND




5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Rodriguez, E.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Measuring surface water from Space. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwarts, L.; Cisse, N.; Diallo, N. Hydrology of the upper Niger. In The Niger, a Lifeline. Effective Water Management in the Upper Niger Basin; Zwarts, L., Van Beukering, P., Kone, B., Wymenga, E., Eds.; Inst. for Inland Water Management and Waste Water Treatment: Lelystad, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 15–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mahe, G.; Bamba, F.; Soumaguel, A.; Orange, D.; Olivry, J.-C. Water losses in the inner delta of the River Niger: Water balance and flooded area. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3157–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Y.; Coe, M.T.; Ramankutty, N. Investigation of hydrological variability in West Africa using land surface models. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liersch, S.; Cools, J.; Kone, B.; Koch, H.; Diallo, M.; Reinhardt, J.; Fournet, S.; Aich, V.; Hattermann, F.F. Vulnerability of rice production in the Inner Niger Delta to water resources management under climate variability and change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 34, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelland, D.; Collet, L.; Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Roucou, P. How could hydro-climatic conditions evolve in the long term in West Africa? The case study of the Bani River Catchment. Hydro-climatology: Variability and change. In Proceedings of the Symposium J-H02 Held during IUGG2011, Melbourne, Australia, 28 June–7 July 2011; pp. 195–201.
- Taylor, C.M. Feedbacks on precipitation from an African wetland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J.; Ashpole, I.; Harris, P.; Davies, H.N.; Clark, D.B.; Blyth, E.; Taylor, C.M. Wetland inundation dynamics in a model of land surface climate: Evaluation in the Niger inland delta region. J. Geophys. Res. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.T. Simulating continental surface waters: An application to Holocene northern Africa. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.E.; Saleous, N.; Roy, D.P.; Morisette, J.T. An overview of MODIS Land data processing and product status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.-F.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Leblanc, M.; Abarca-Del-Rio, R.; Delclaux, F.; Mognard, N.; Lion, C.; Pandey, R.K.; Tweed, S.; Calmant, S.; et al. Flood mapping inferred from remote sensing data. Int. Water Technol. J. 2011, 1, 48–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cretaux, J.-F.; Letolle, R.; Calmant, S. Investigations on Aral Sea regressions from Mirabilite deposits and remote sensing. Aquat. Geochem. 2009, 15, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-del-Rio, R.; Cretaux, J.-F.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Maisongrande, P. Does the Titicaca Lake still control the Poopo lake water levels? An investigation using satellite altimetry, and MODIS data (2000–2009). Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsen, A.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Abarca-Del-Rio, R. Remote sensing derived bathymetry of Lake Poopó. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedinotti, V.; Boone, A.; Decharme, B.; Cretaux, J.-F.; Mognard, N.; Panthou, G.; Papa, F.; Tanimoun, B.A. Evaluation of the ISBA-TRIP continental hydrologic system over the Niger Basin using in situ and satellite derived datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1745–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aires, F.; Papa, F.; Prigent, C.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Bergé-Nguyen, M. Characterization and space/time downscaling 1 of the inundation extent over the Inner Niger Delta using GIEMS and MODIS data in preparation to the SWOT mission. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Cretaux, J.-F.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Tiwari, V.M.; Drolon, V.; Calmant, S. Water level estimation by remote sensing for 2008 flood of Kosi. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yésou, H.; Huber, C.; Lai, X.; Averty, S.; Li, J.; Daillet, S.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; James, B.; et al. Nine years of water resources monitoring over the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, with ENVISAT, MODIS, Beijing-1 time series, altimetric data and field measurements. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2011, 16, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, D.; Goldberg, M.; Stefanidis, A. Derivation of 30-m resolution water maps from TERRA/MODIS and SRTM. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenridge, G.R.; Anderson, E. MODIS-based flood detection, mapping and measurement: The potential for operational hydrological applications. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.L.; Yu, Y.Y.; Goldberg, M.D. Deriving water fraction and flood maps from MODIS images using a decision tree approach. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.L.; Yu, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Goldberg, M.D. Towards operational automatic flood detection using EOS/MODIS data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Nguyen, N.V.; Kotera, A.; Ohno, H.; Ishitsuka, N.; Yokozawa, M. Detecting temporal changes in the extent of annual flooding within the Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta from MODIS time series imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C. Satellite remote sensing of river inundation area, stage, and discharge, a review. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.-B.; Chastanet, P.; Fellah, K.; Desnos, Y.-L. Envisat multi-polarised ASAR data for flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Do Minh, K.; L’Hermitte, J.; Ramilllien, G.; Cazenave, A.; le Toan, T.; Mognard-Campbell, N. Water volume change in the lower Mekong Basin from satellite altimetry and imagery data. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 167, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töyrä, J.; Pietroniro, A.; Martz, L.W. Multisensor hydrologic assessment of a freshwater wetland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töyrä, J.; Pietroniro, A. Towards operational monitoring of a northern wetland using geomatics-based techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J-B.; Hoffman, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-derived river inundation areas, high-precision topographic data and a river flow model toward near real-time flood management. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.-M.; le Toan, T. Mapping of flood dynamics and spatial distribution of vegetation in the amazon floodplain using multitemporal SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, A.; Pathe, C.; Scipal, K.; Wagner, W. Detection of permanent open water surfaces in central Siberia with Envisat ASAR wide swath data with special emphasis on the estimation of methane fluxes from tundra wetlands. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, E.T.; Gurney, R.J. Remote Sensing in Hydrology; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1991; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Bukata, R.P. Satellite Monitoring of Inland and Coastal Water Quality: Retrospection, Introspection, Future Directions; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.-R.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Gao, B.-C.; Davis, C.O. Remote sensing of suspended sediments and shallow coastal waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, J.G.; Yuan, D.; Lunetta, R.S.; Elvidge, C.D. A change detection experiment using vegetation indices. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J.; Lyon, J.G.; Worthy, L.D. Land-cover change detection using multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.A.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Savenije, H.H.G. Spatial variability of evaporation and moisture storage in the swamps of the upper Nile studied by remote sensing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladin, N.V.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Plotnikov, I.S.; Kouraev, A.V.; Smurov, A.O.; Cazenave, A.; Egorov, A.N.; Papa, F. Modern hydro-biological state of the Small Aral Sea. Environmetric 2005, 16, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.-F.; Kouraev, A.V.; Papa, F.; Bergé Nguyen, M.; Cazenave, A.; Aladin, N.V.; Plotnikov, I.S. Water balance of the Big Aral sea from satellite remote sensing and in situ observations. J. Great Lakes Res. 2005, 31, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, R.; Csaplovis, E.; Vollmer, E. Monitoring land cover changes of the Niger inland delta ecosystem (Mali) by means of envisat-Meris data. In African Biodivers; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Preisendorfer, R.W. Principal Component Analysis in Meteorology and Oceanography; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 425. [Google Scholar]
- Von Storch, A.; Zwiers, W. Empirical orthogonal function. In Statistical Analysis in Climate Research, 3nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 293–312. [Google Scholar]
- Toumazou, V.; Crétaux, J.-F. Using a Lanczos eigen solver in the computation of Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.S.; Smith, C.N.; Mason, D. Integrating remote sensing observations of flood hydrology and hydraulic modelling. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1777–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Crétaux, J.-F. Inundations in the Inner Niger Delta: Monitoring and Analysis Using MODIS and Global Precipitation Datasets. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2127-2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202127
Bergé-Nguyen M, Crétaux J-F. Inundations in the Inner Niger Delta: Monitoring and Analysis Using MODIS and Global Precipitation Datasets. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(2):2127-2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202127
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergé-Nguyen, Muriel, and Jean-François Crétaux. 2015. "Inundations in the Inner Niger Delta: Monitoring and Analysis Using MODIS and Global Precipitation Datasets" Remote Sensing 7, no. 2: 2127-2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202127
APA StyleBergé-Nguyen, M., & Crétaux, J. -F. (2015). Inundations in the Inner Niger Delta: Monitoring and Analysis Using MODIS and Global Precipitation Datasets. Remote Sensing, 7(2), 2127-2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202127