Supervised Classification of Benthic Reflectance in Shallow Subtropical Waters Using a Generalized Pixel-Based Classifier across a Time Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Site
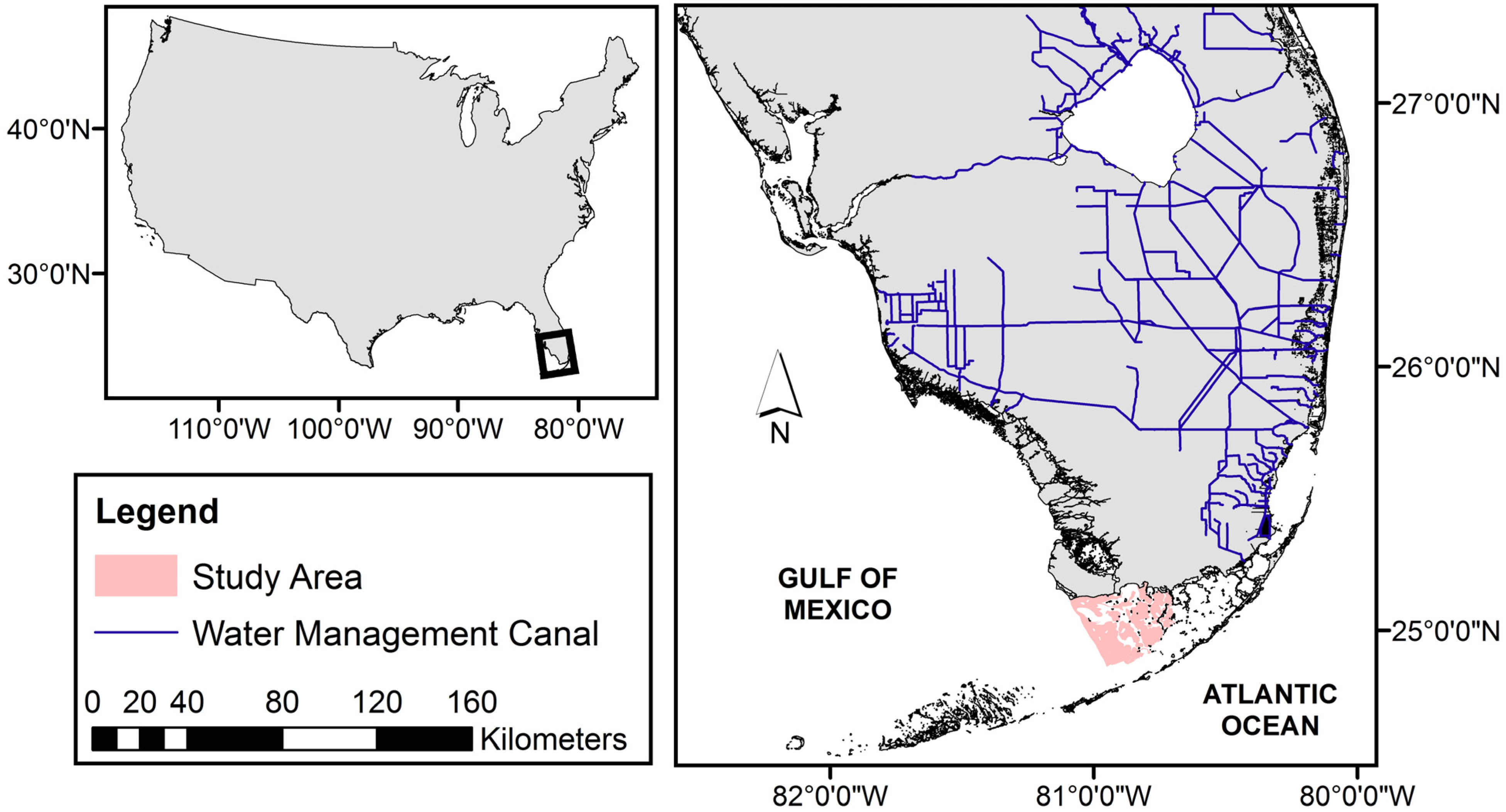

2.2. Data Sets
2.2.1. In-Situ Data
| Score | Percent Cover |
|---|---|
| 5 | 75 to 100 |
| 4 | 50 to 75 |
| 3 | 25 to 50 |
| 2 | 5 to 25 |
| 1 | <5 |
2.2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Satellite Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Seagrass Classification
| Class | Avg. Braun-Blanquet Score | Training Samples (Pixels) | Validation Samples (Pixels) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2007 | 2008 | ||
| Dense | >4.5 | 82 | 104 | 98 | 15 | 10 |
| Medium | 2.5 to 4.5 | 74 | 76 | |||
| Low | 1.5 to 2.5 | 25 | 13 | 26 | 19 | 40 |
| Sparse | <1.5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 8 |
2.5. Error Matrix and Accuracy Assessment
| Reference Class | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dense | Medium | Low | Sparse | Total | ** Users Accuracy | |||
| Map Class | 2007 | Med-Dense | 9% | 48% | 5% | 0% | 63% | 93% |
| Low | 2% | 8% | 6% | 4% | 20% | 31% | ||
| Sparse | 0% | 2% | 4% | 12% | 17% | 68% | ||
| Total | 12% | 58% | 4% | 16% | *** Overall Accuracy = 76% | |||
| * Producers Accuracy | 80% | 84% | 42% | 75% | ||||
| 2008 | Med-Dense | 7% | 51% | 8% | 0% | 66% | 88% | |
| Low | 0% | 4% | 4% | 1% | 8% | 45% | ||
| Sparse | 0% | 2% | 18% | 5% | 25% | 21% | ||
| Total | 7% | 57% | 30% | 6% | Overall Accuracy = 67% | |||
| Producers Accuracy | 100% | 89% | 13% | 88% | ||||
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In-Situ Data Description and Distribution

3.2. Image Classification


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, M.S.; Schopmeye, S.; Holmer, M.; Madden, C.; Kyn-Hansen, C. Thalassia testudinum response to the interactive stressors hypersalinity, sulfide and hypoxia. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 87, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, C.J.; Rudnick, D.T.; McDonald, A.A.; Cunniff, K.M.; Fourqurean, J.W. Ecological indicators for assessing and communicating seagrass status and trends in Florida Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, S68–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakub, S.M.; Chen, E.; Bouma, T.; Erftemeijer, P.; Todd, P. Chronic light reduction reduces overall resilience to additional shading stress in the seagrass Halophila ovalis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 83, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.; Kennedy, H.; Marba, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.; Apostolaki, E.; Kendrick, G.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.; et al. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Kendrick, G.A.; Collins, L.S.; Chambers, R.M.; Vanderklift, M.A. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous storage in subtropical seagrass meadows: Examples from Florida Bay and Shark Bay. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.J.; Waycott, M.; Ospina, A. Responses of four Indo-West Pacific seagrass species to shading. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, V.J.; Zimmerman, R.; Bissett, W.; Dierssen, H.; Kohler, D. Evaluating light availability, seagrass biomass, and productivity using hyperspectral airborne remote sensing in Saint Joseph’s Bay, Florida. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1467–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferweda, J.; de Leeuw, J.; Atzberger, C.; Vekerdy, Z. Satellite-based monitoring of tropical seagrass vegetation: Current techniques and future developments. Hydrobiologia 2007, 591, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorhaug, A.; Richardson, A.; Berlyn, G. Spectral reflectance of Thalassia testudinum (Hydrocharitaceae) seagrass: Low salinity effects. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakub, S.M.; McKenzie, L.; Erftemeijer, P.; Bouma, T.; Todd, P. Courage under fire: Seagrass persistence adjacent to a highly urbanized city-state. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J.; Fyfe, S.; Malthus, T.; Karpouzli, E. Remote sensing of seagrass ecosystems: Use of spaceborne and airborne sensors. In Seagrass: Biology, Ecology, and Conservation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Chapter 15; pp. 347–359. [Google Scholar]
- Mumby, P.J.; Green, E.P.; Edwards, A.J.; Clark, C.D. Measurement of seagrass standing crop using satellite and digital airborne remote sensing. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 159, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M. Long term land cover and seagrass mapping using Landsat and object-based image analysis from 1972 to 2010 in the coastal environment of South East Queensland, Australia. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 71, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.; Roelfsema, C.; Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J. Mapping seagrass species, cover and biomass in shallow waters: An assessment of satellite mutli-spectral and airborne hyperspectral imaging systems in Moreton Bay (Australia). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3413–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R.; Udy, N.; Maxwell, P. An integrated field and remote sensing approach for mapping seagrass cover, Moreton Bay, Australia. Spat. Sci. 2009, 54, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabnitz, C.C.; Andrefouet, S.; Torres-Pulliza, D.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Kramer, P.A. Regional scale seagrass habitat mapping in the Wider Caribbean region using Landsat sensors: Applications to conservation and ecology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3455–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S.; Meyer, C.; Baggett, L.; Zhao, Y. Mapping and assessing seagrass along the western coast of Florida using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Choi, J.; Ryu, J.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, K.; Park, M.G.; Kim, K.Y. Observation of typhoon-induced seagrass die-off using remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S.; Meyer, C. Mapping and assessing seagrass bed changes in Central Florida’s west coast using multitemporal Landsat TM imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 149, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.; Kovacs, E.; Saunders, M.I.; Phinn, S.; Lyons, M.; Maxwell, P. Challenges of remote sensing for quantifying changes in large complex seagrass environments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 133, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Miller, I.; Jupp, D. Mapping coral reef benthic substrates using hyperspectral space-borne images and spectral libraries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 70, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Brando, V.E.; Anstee, J.M. Retrospective change detection in a shallow coastal tidal Australian lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louchard, E.M.; Reid, P.; Stephens, F.; Davis, C.; Leathers, R.; Downes, V. Optical remote sensing of benthic habitats and bathymetry in coastal environments at Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas: A comparative spectral classification approach. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.; Robler, S.; Schneider, T.; Melzer, A. Collecting in situ remote sensing reflectances of submersed macrophytes to build up a spectral for lake monitoring. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 46, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.M.; Zimmerman, R.C.; Drake, L.A.; Burdige, D. Benthic ecology from space: Optics and net primary production in seagrass and benthic algae across the Great Bahama Bank. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 411, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Vahtmae, E.; Metsamaa, L. Spectral library of macroalgae and benthic substrates in Estonian coastal waters. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dierssen, H.; Zimmerman, R.C.; Leathers, R.A.; Downes, T.V.; Davis, C.O. Ocean color remote sensing of seagrass and bathymetry in the Bahamas Banks by high-resolution airborne imagery. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtmae, E.; Kutser, T. Classifying the Baltic Sea shallow water habitats using image-based and spectral library methods. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2451–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Ustin, S. Building spectral libraries for wetlands land cover classification and hyperspectral remote sensing. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R. Towards understanding temporal and spatial dynamics of seagrass landscapes using time-series remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 120, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Bujang, J.S.; Zakaria, M.H.; Hashim, M. The application of remote sensing to seagrass ecosystems: An overview and future prospects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 61–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C.; Holekamp, K.; Blonski, S.; Spiering, B.; Palandro, D.; Lapointe, B. Use of Landsat data to track historical water quality changes in Keys marine environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.L.; Hill, V.J.; Zimmerman, R.C.; Dierssen, H.M. The optical properties of Greater Florida Bay: Implications for seagrass abundance. Estuar. Coasts 2011, 34, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, J.L.; Kemp, W.M.; Cornwell, J.C.; Owens, M.S.; Hinkle, D.; Madden, C.J. Seasonal and regional variations in net ecosystem production in Thalassia testudinum communities throughout Florida Bay. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; Williams, E.; Johns, E.; Wilson, D.; Smith, N.P. Transport processes linking south Florida coastal systems. In The Evergades, Florida Bay and Coral Reefs of the Florida Keys: An Ecosystem Sourcebook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 309–341. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; Smith, N. Volume transport variability through the Florida Keys tidal channels. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.H.; Purkis, S.J. Evidence for the southward migration of mud banks in Florida Bay. Mar. Geol. 2012, 311, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.N.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Jones, R.D. Spatial characterization of water quality in Florida Bay and Whitewater Bay by multivariate analyses: Zones of similar influence. Estuaries 1997, 4, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieman, J.C.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Iverson, R.L. Distribution, abundance and productivity of seagrasses and macroalgae in Florida Bay. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 441, 292–311. [Google Scholar]
- Phlips, E.J.; Lynch, T.C.; Badylak, S. Chlorophyll a, tripton, color, and light availability in a shallow tropical inner-shelf lagoon, Florida Bay, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 127, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.O.; Durako, M.J.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Zieman, J.C. Decadal changes in seagrass distribution and abundance in Florida Bay. Estuaries 1999, 22, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Madley, K.; Durako, M.; Zieman, J.; Robblee, M. Florida Bay. In Seagrass Status and Trends in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: 1940–2002; Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5287; U.S. Geologic Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; pp. 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Durako, M.; Hall, M.; Hefty, L. Seagrass distribution in South Florida: A multi-agency coordinated monitoring program. In The Evergades, Florida Bay and Coral Reefs of the Florida Keys: An Ecosystem Sourcebook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 497–522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoffoli, M.L.; Frouin, R.; Kampel, M. Water column correction for coral reef studies by remote sensing. Sensors 2014, 14, 16881–16931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amran, M.A. Estimation of seagrass coverage by depth invariant indices on quickbird imagery. Biotropia 2010, 17, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Mumby, P.J.; Clark, C.D.; Green, E.P.; Edwards, A.J. Benefits of water column correction and contextual editing for mapping coral reefs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Remote sensing of bottom reflectance and water attenuation parameters in shallow water using aircraft and Landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1981, 2, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Barnes, B.; Melo, N.; English, D.; Lapointe, B.; Muller-Karger, F.; Schaeffer, B.; Hu, C. Assessment of satellite-derived diffuse attenuation coefficients and euphotic depths in south Florida coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Quegan, S. Analysis of Maximum Likelihood classification on multispectral data. Appl. Math. Sci. 2012, 6, 6425–6436. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Frazier, P.; Kumar, L. Comparative assessment of the measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practice for estimating area and assessing the accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restoration Coordination and Verification (RECOVER). 2009 System Status Report. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan; Restoration Coordination and Verification Program, c/o United States Army Corps of Engineers: Jacksonville, FL, USA; South Florida Water Management District: West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2010.
- Landry, J.B. Changes in the distribution and density of Florida Bay Macrophytes: 1995–2004. Master’s Thesis, University of North Carolina Wilmington, Wilmington, NC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blakey, T.; Melesse, A.; Hall, M.O. Supervised Classification of Benthic Reflectance in Shallow Subtropical Waters Using a Generalized Pixel-Based Classifier across a Time Series. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5098-5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505098
Blakey T, Melesse A, Hall MO. Supervised Classification of Benthic Reflectance in Shallow Subtropical Waters Using a Generalized Pixel-Based Classifier across a Time Series. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(5):5098-5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505098
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlakey, Tara, Assefa Melesse, and Margaret O. Hall. 2015. "Supervised Classification of Benthic Reflectance in Shallow Subtropical Waters Using a Generalized Pixel-Based Classifier across a Time Series" Remote Sensing 7, no. 5: 5098-5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505098
APA StyleBlakey, T., Melesse, A., & Hall, M. O. (2015). Supervised Classification of Benthic Reflectance in Shallow Subtropical Waters Using a Generalized Pixel-Based Classifier across a Time Series. Remote Sensing, 7(5), 5098-5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505098







