Analysis of the Land Surface Temperature Scaling Problem: A Case Study of Airborne and Satellite Data over the Heihe Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Regions and Data
2.1. HiWATER Experiment
2.2. Study Regions
| Sites | Vegetation (%) | Water (%) | Village (%) | Gobi/Bare Soil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | 0 | 0.9673 | 0 | 99.0327 |
| Site 2 | 0.1488 | 0 | 0 | 99.8512 |
| Site 3 | 95.5357 | 0 | 4.1171 | 0.3472 |
| Site 4 | 96.2798 | 0 | 3.6210 | 0.0992 |
| Site 5 | 9.176 | 26.4385 | 0.1488 | 64.2361 |

| Sites | Land Surface Type | mLST (K) (ASTER) | mLST (K) (TASI) | σLST (K) (ASTER) | σLST (K) (TASI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | Gobi | 321.04 | 321.07 | 1.24 | 2.29 |
| Site 2 | Gobi | 320.12 | 319.97 | 1.64 | 2.44 |
| Site 3 | Vegetation | 303.73 | 304.49 | 2.36 | 5.19 |
| Site 4 | Vegetation | 303.11 | 303.83 | 2.35 | 5.01 |
| Site 5 | Mixed | 313.81 | 313.81 | 5.33 | 8.62 |
2.3. Experimental Data Preprocessing
2.3.1. Description and Preprocessing of ASTER Data
2.3.2. Description and Preprocessing of TASI Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Quantification of the Spatial Heterogeneity of LST
3.2. Methods of Studying the LST Scaling Problem
3.2.1. Comparison between Distributed LST and Lumped LST
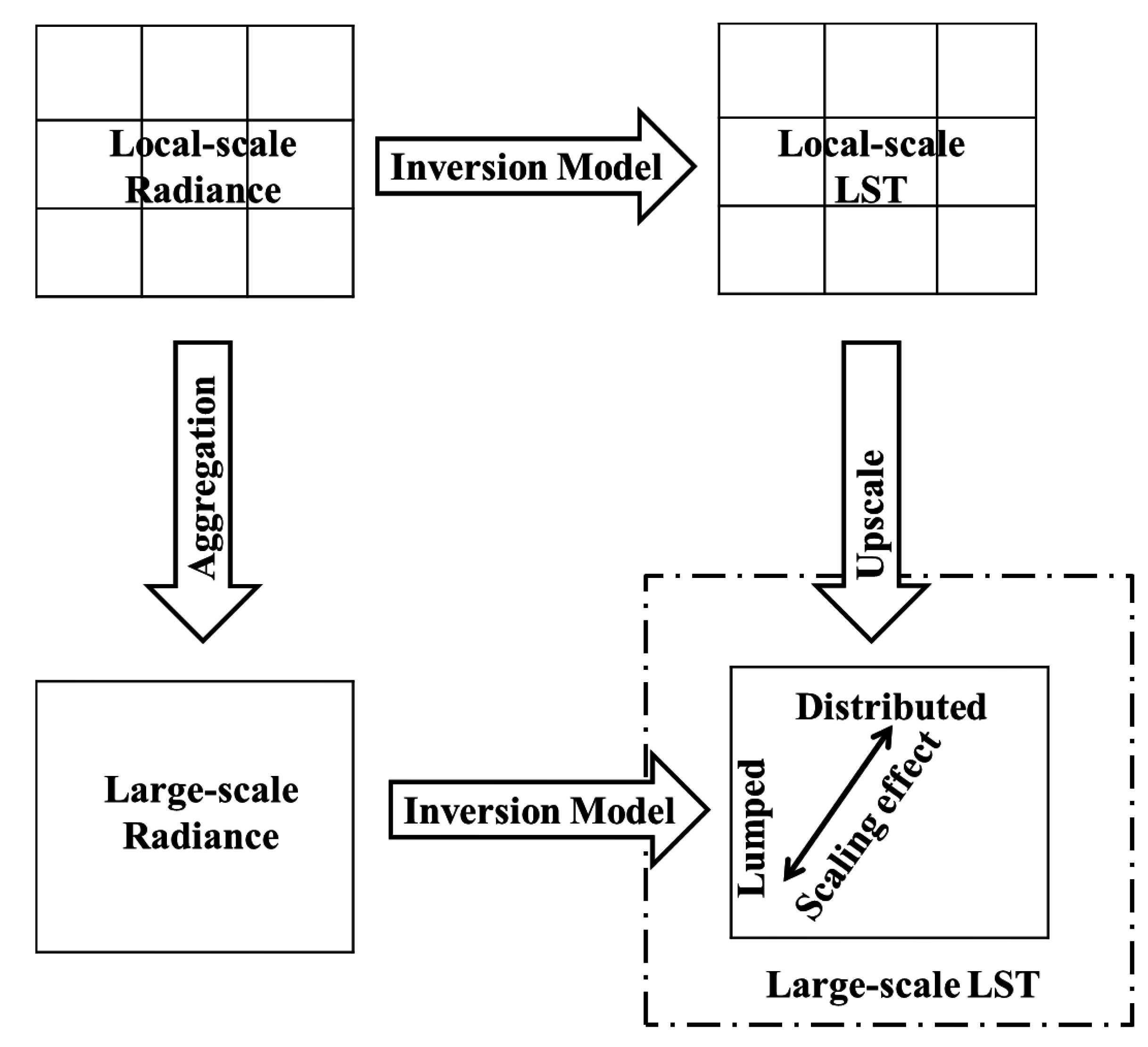
3.2.2. Comparison between the TASI and ASTER LSTs
3.3. Correction Methodology for the LST Scaling Effect
4. Results and Discussion
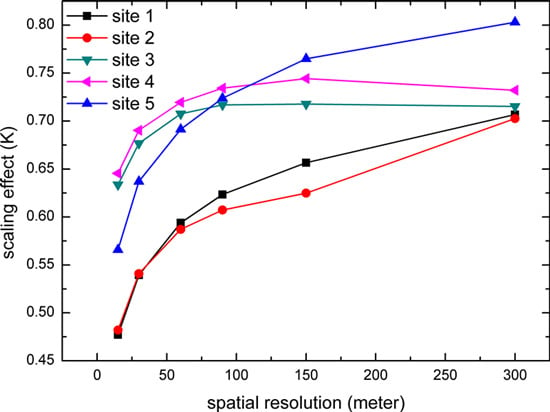
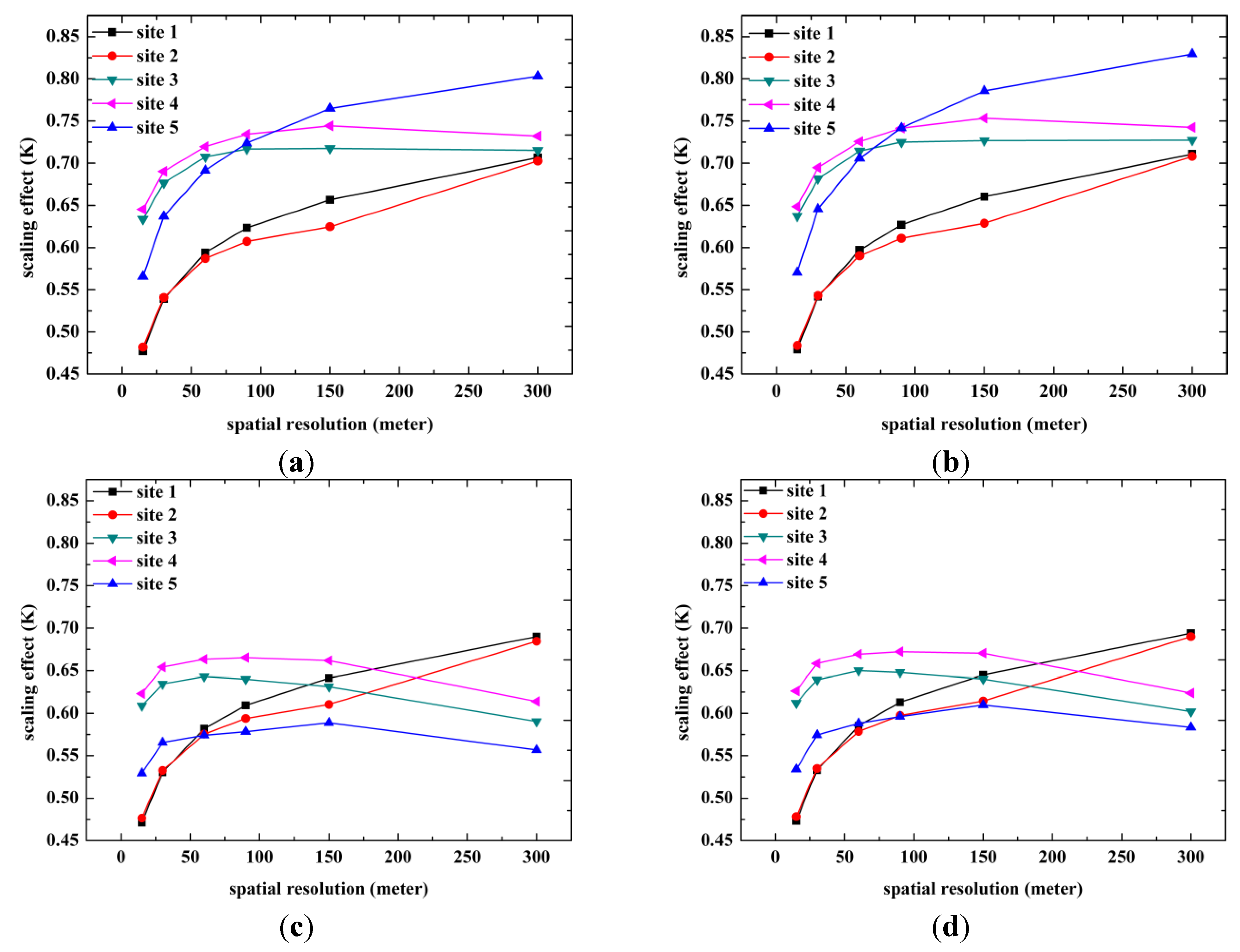
4.1. Analysis of the Comparison between the Distributed LST and the Lumped LST
4.1.1. Analysis of the TASI LST Data
| LST at Site 1 (K) | LST at Site 2 (K) | LST at Site 3 (K) | |||||||
| Min. | Max. | Mean | Min. | Max. | Mean | Min. | Max. | Mean | |
| M1 | 318.59 | 322.86 | 321.26 | 314.20 | 322.07 | 319.77 | 301.84 | 310.99 | 304.69 |
| M2 | 318.59 | 322.86 | 321.26 | 314.23 | 322.08 | 319.78 | 301.85 | 311.02 | 304.71 |
| M3 | 318.56 | 322.85 | 321.24 | 314.09 | 322.06 | 319.75 | 301.81 | 310.72 | 304.57 |
| M4 | 318.57 | 322.86 | 321.24 | 314.13 | 322.07 | 319.76 | 301.82 | 310.75 | 304.58 |
| LST at Site 4 (K) | LST at Site 5 (K) | ||||||||
| Min. | Max. | Mean | Min. | Max. | Mean | ||||
| M1 | 301.34 | 308.79 | 304.08 | 301.71 | 320.37 | 313.55 | |||
| M2 | 301.35 | 308.79 | 304.09 | 301.76 | 320.38 | 313.57 | |||
| M3 | 301.34 | 308.49 | 303.96 | 301.31 | 320.35 | 313.30 | |||
| M4 | 301.34 | 308.49 | 303.97 | 301.36 | 320.35 | 313.33 | |||


4.1.2. Analysis of the ASTER LST Data

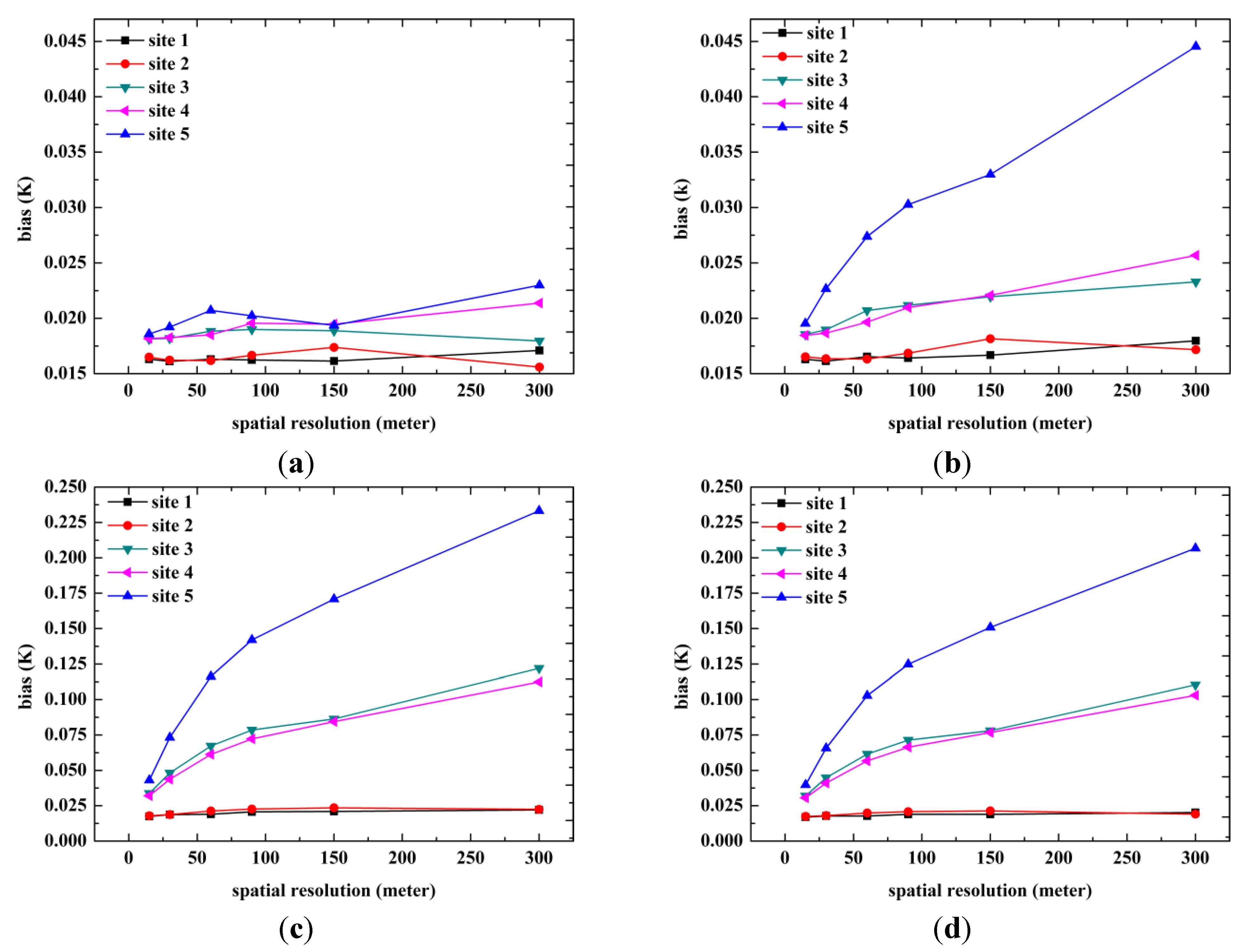
4.2. Analysis of the Comparison between the ASTER and TASI LSTs
| RMSE1 (K) | RMSE2 (K) | RMSE3 (K) | RMSE4 (K) | RMSE5 (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 1.93 | 1.91 | 2.68 |
| Method 2 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 1.94 | 1.92 | 2.68 |

4.3. Correcting the Scaling Effect


5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raffy, M. Change of scale in models of remote sensing: A general method for spatialization of models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 40, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenglin, H.; Islam, S. A framework for analyzing and designing scale invariant remote sensing algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Allard, D.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Influence of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the non-linear estimation of leaf area index from moderate spatial resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Chen, X.; Ju, W. Effects of vegetation heterogeneity and surface topography on spatial scaling of net primary productivity. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4879–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Humes, K.S.; Pinter, P.J., Jr. The scaling characteristics of remotely-sensed variables for sparsely-vegetated heterogeneous landscapes. J. Hydrol. 1997, 190, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J. Generating consistent land surface temperature and emissivity products between aster and modis data for earth science research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaofei, Y.; Jing, L.; Qinhuo, L.; Longhui, L.; Yelu, Z.; Baodong, X.; Le, Y.; Jing, Z. Improving leaf area index retrieval over heterogeneous surface by integrating textural and contextual information: A case study in the heihe river basin. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.-H.; Li, Z.-L. Impact of nonlinearity and discontinuity on the spatial scaling effects of the leaf area index retrieved from remotely sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.L. Scale issues in remote sensing: A review on analysis, processing and modeling. Sensors 2009, 9, 1768–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Bogaert, J.; Myneni, R.B. Radiative transfer based scaling of LAI retrievals from reflectance data of different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hiyama, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. Scaling of land surface temperature using satellite data: A case examination on ASTER and MODIS products over a heterogeneous terrain area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C. Minimum configuration of thermal infrared bands for land surface temperature and emissivity estimation in the context of potential future missions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huazhong, R.; Rongyuan, L.; Guangjian, Y.; Xihan, M.; Zhao-Liang, L.; Nerry, F.; Qiang, L. Angular normalization of land surface temperature and emissivity using multiangular middle and thermal infrared data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4913–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.; Li, Z.L. Surface temperature and emissivity at various scales: Definition, measurement and related problems. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 12, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Zehrfuhs, D. Normalization and comparison of surface temperatures across a range of scales. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Petitcolin, F.o.; Schmugge, T.; Vermote, É.; French, A.; Ogawa, K. Comparison of land surface emissivity and radiometric temperature derived from MODIS and ASTER sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Allard, D.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Quantifying spatial heterogeneity at the landscape scale using variogram models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, B. Evaluation of the VIIRS and MODIS LST products in an arid area of northwest China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Ma, P.; Nie, A.; Yang, A.; Yao, Y.; Lü, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Land cover mapping using time series HJ-1/CCD data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Nie, A.; Yang, A.; Zhang, H.; Ma, P.; Liu, Q. HiWATER: Land cover map of Heihe river basin. In Heihe Plan Science Data Center; Heihe Plan Science Data Center: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, A.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A temperature and emissivity separation algorithm for advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonooka, H. Accurate atmospheric correction of aster thermal infrared imagery using the WVS method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2778–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Thermal Infrared Emissivity Extraction from Remote Sensing Data and Soil Emissivity Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.J.; Johnson, B.R.; Hackwell, J.A. An in-scene method for atmospheric compensation of thermal hyperspectral data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X. Estimating the optimal broadband emissivity spectral range for calculating surface longwave net radiation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, X.Z.; Sun, X.M.; Su, H.B.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Z.L. Study of emissivity scaling and relativity of homogeneity of surface temperature. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Becker, F. Terminology in thermal infrared remote sensing of natural surfaces. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 12, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, H. Analysis of land surface temperature spatial heterogeneity using variogram model. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015.
- Heshun, W.; Qing, X.; Hua, L.; Yongming, D.; Qinhuo, L. Investigating the impact of soil moisture on thermal infrared emissivity using ASTER data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, B. Analysis of the Land Surface Temperature Scaling Problem: A Case Study of Airborne and Satellite Data over the Heihe Basin. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6489-6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70506489
Hu T, Liu Q, Du Y, Li H, Wang H, Cao B. Analysis of the Land Surface Temperature Scaling Problem: A Case Study of Airborne and Satellite Data over the Heihe Basin. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(5):6489-6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70506489
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Tian, Qinhuo Liu, Yongming Du, Hua Li, Heshun Wang, and Biao Cao. 2015. "Analysis of the Land Surface Temperature Scaling Problem: A Case Study of Airborne and Satellite Data over the Heihe Basin" Remote Sensing 7, no. 5: 6489-6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70506489
APA StyleHu, T., Liu, Q., Du, Y., Li, H., Wang, H., & Cao, B. (2015). Analysis of the Land Surface Temperature Scaling Problem: A Case Study of Airborne and Satellite Data over the Heihe Basin. Remote Sensing, 7(5), 6489-6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70506489