Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
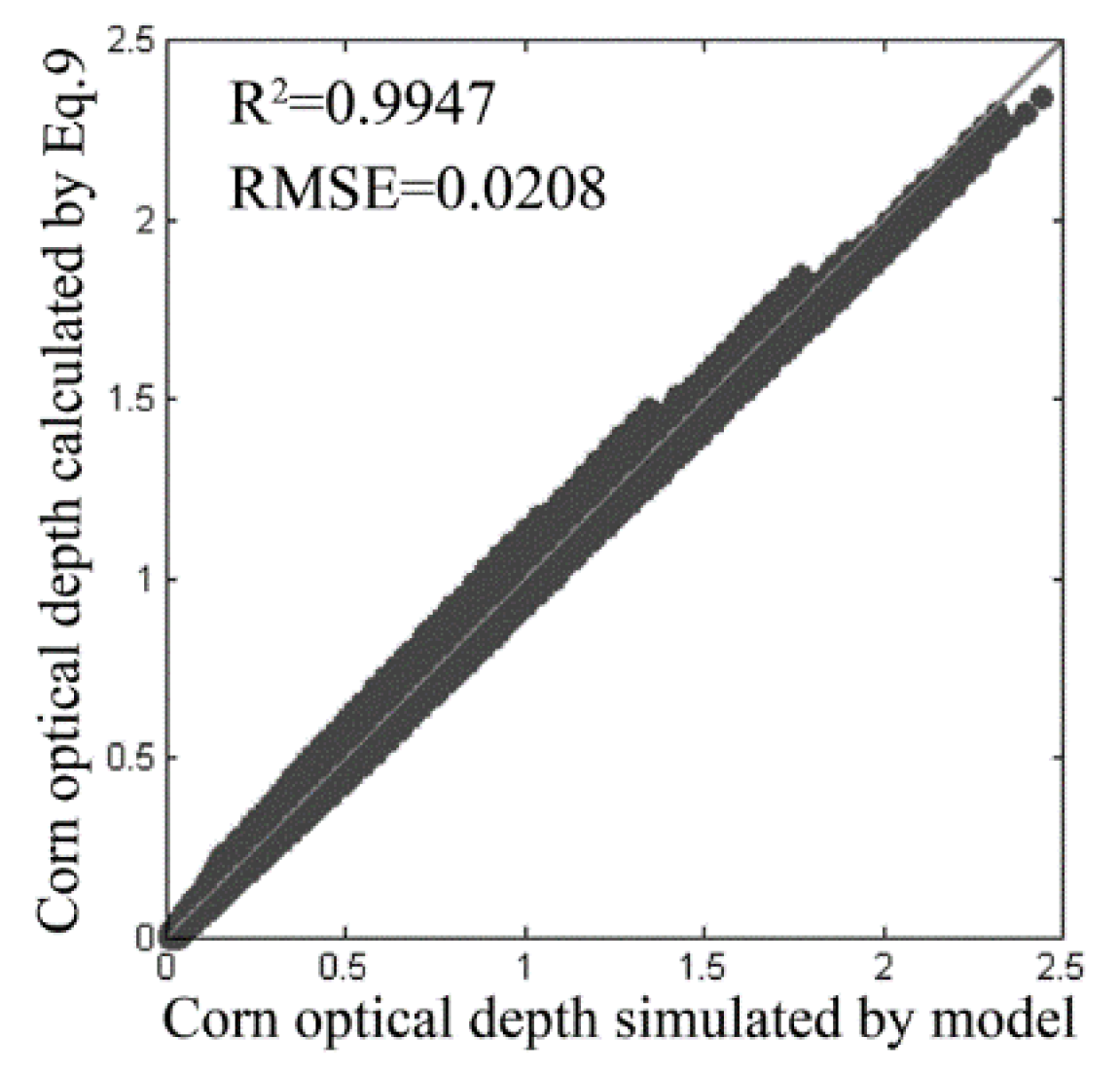
2.1. The Optical Depth Retrieval Method for Short Vegetation
| Parameters | Unit | Min | Max | Step |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incident angles | ° | 1 | 60 | 1 |
| Soil moisture content | % | 2 | 44 | 2 |
| RMs heights | cm | 0.25 | 3 | 0.25 |
| Correlation lengths | cm | 2.5 | 30 | 2.5 |

2.2. A Quantitative Relationship between the Corn GVWC, the Corn Optical Depth at L-band, the Corn LAI, and the Height and Areal Density of the Corn Stalks
| Parameters | Unit | Min | Max | Step | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn Leaves | Areal density (Md) | m−2 | 50 | 1250 | 150 |
| Radius (rd) | m | 0.005 | 0.065 | 0.01 | |
| Thickness (hd) | m | 0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.0001 | |
| GVWC (wd) | % | 60 | 90 | 5 | |
| Corn Stalks | Areal density (Mc) | m−2 | 5 | 9 | 1 |
| Radius (rc) | m | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.005 | |
| Length (hc) | m | 0.1 | 2 | 0.1 | |
| GVWC (wc) | % | 60 | 90 | 5 |
3. Study Region and Datasets
3.1. Description of the Study Region


3.2. Datasets
3.2.1. Remote Sensing Observations
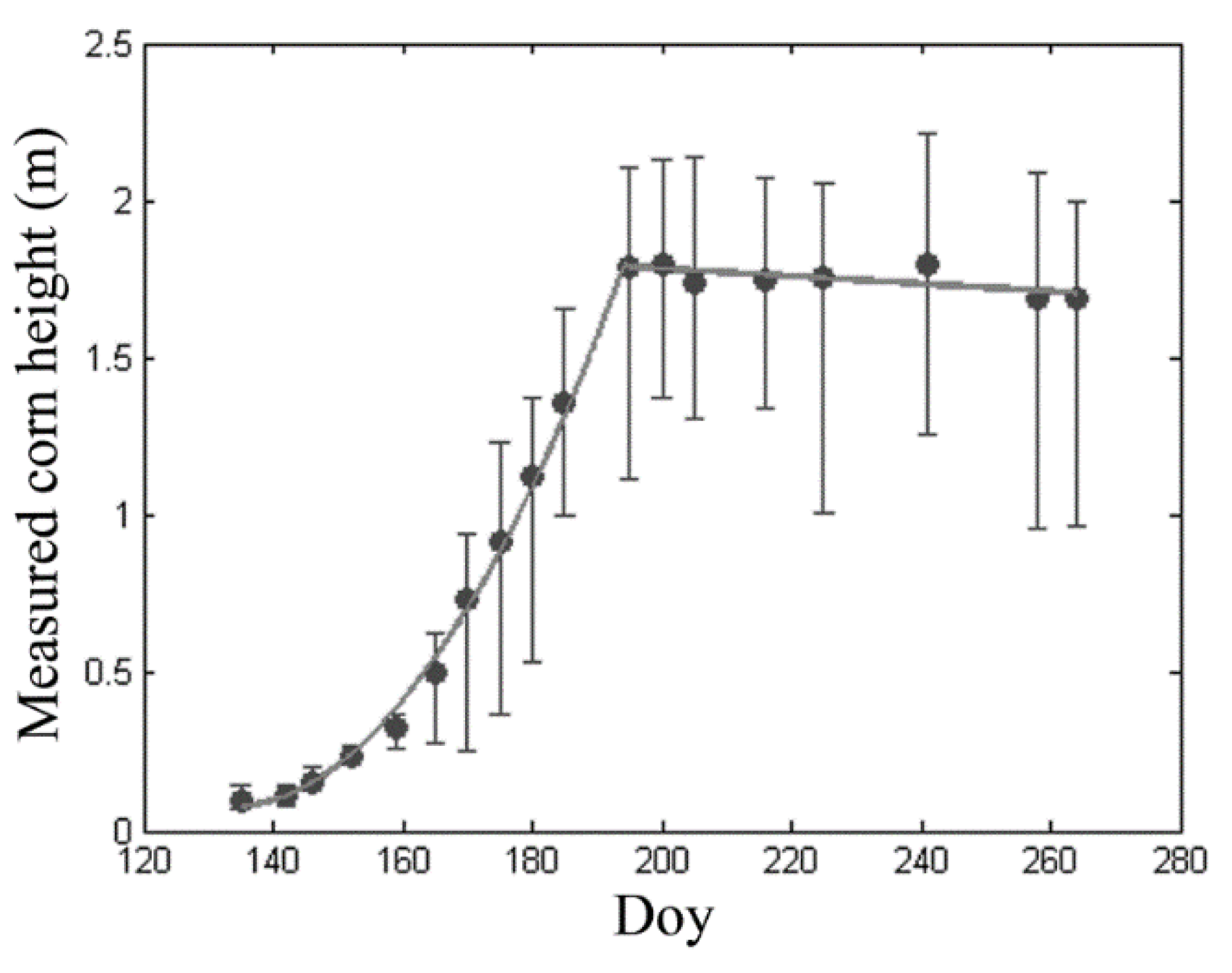
3.2.2. In-Situ Measurements
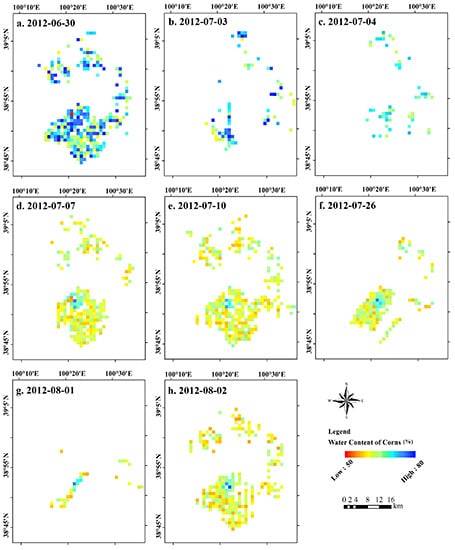
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. The Retrieval of Corn GLASS-GVWC



4.2. Discussion



5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Cosh, M.H. Sub-pixel reflectance unmixing in estimating vegetation water content and dry biomass of corn and soybeans cropland using normalized difference water index (NDWI) from satellites. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2075–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Bindlish, R.; Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, X. Estimating vegetation water content during a growing season of cotton. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 791–794.
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Wang, J.R. Passive microwave sensing of soil moisture under vegetation canopies. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Chen, D.; Cosh, M.; Li, F.; Anderson, M.; Walthall, C.; Doriaswamy, P.; Hunt, R.E. Vegetation water content mapping using Landsat data derived normalized difference water index for corn and soybeans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, P.; Flasse, S.; Tarantola, S.; Jacquemoud, S.; Grégoire, J. Detecting vegetation leaf water content using reflectance in the optical domain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Drusch, M.; Williams, M.; Law, B.E.; Novello, N.; Kerr, Y. Investigating temporal variations in vegetation water content derived from SMOS optical depth. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3331–3334.
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T.J. Vegetation effects on the microwave emission of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vine, D.M.; Karam, M.A. Dependence of attenuation in a vegetation canopy on frequency and plant water content. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; le Vine, D.M.; Hsu, A.Y.; Oldak, A.; Starks, P.J.; Swift, C.T.; Isham, J.D.; Haken, M. Soil moisture mapping at regional scales using microwave radiometry: The Southern Great Plains hydrology experiment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensi. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Griend, A.A.; Wigneron, J.P. The B-factor as a function of frequency and canopy type at H-polarization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Rivard, B.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, A.G.; Féret, J.B.; Jacquemoud, S.; Ustin, S.L. Predicting leaf gravimetric water content from foliar reflectance across a range of plant species using continuous wavelet analysis. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, D.X.; Viegas, M.T.S.P.; Ferreira, A.D. Moisture content of fine forest fuels and fire occurrence in central Portugal. Int. J. Wildl. Fire. 1992, 2, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive; Artech House Publishers: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, T.; Choudhury, B.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Wang, J.R.; Jackson, T.J. A model for microwave emission from vegetation-covered fields. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1982, 87, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, S.; Chai, L.; Jin, R. A new soil freeze/thaw discriminant algorithm using AMSR-E passive microwave imagery. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jackson, T.J.; Tao, J.; Du, J.; Bindlish, R.; Lu, L.; Chen, K.S. Microwave vegetation indices for short vegetation covers from satellite passive microwave sensor AMSR-E. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; Jeu, R.D.; Walker, J. A methodology for surface soil moisture and vegetation optical depth retrieval using the microwave polarization difference index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S.; Macelloni, G.; Santi, E. Soil moisture estimates from AMSR-E brightness temperatures by using a dual-frequency algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Griend, A.A.; Owe, M. Microwave vegetation optical depth and inverse modelling of soil emissivity using Nimbus/SMMR satellite observations. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1994, 54, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chai, L. Estimating vegetation optical depth using L-band passive microwave airborne data in HiWATER. In Proceedings of the SPIE Asia Pacific Remote Sensing International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 8 November 2014.
- Chen, K.; Wu, T.; Tsang, L.; Qin, L.; Shi, J.; Fung, A.K. Emission of rough surfaces calculated by the integral equation method with comparison to three-dimensional moment method simulations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vine, D.M.; Meneghini, R.; Lang, R.H. Scattering from arbitrarily orientated dielectric disks in the physical optics regime. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, G. Scattering and attenuation characteristics of corn at multiple frequencies and view angles by model simulation and truck-mounted microwave radiometer. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 14, 396–408. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, M.A.; Fung, A.K. Electromagnetic scattering from a layer of finite length, randomly oriented, dielectric, circular cylinders over a rough interface with application to vegetation. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1109–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mätzler, C. Microwave (1–100 GHz) dielectric model of leaves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, M.A.; Fung, A.K. Scattering from randomly oriented circular discs with application to vegetation. Radio Sci. 1983, 18, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, M.A.; Fung, A.K.; Antar, Y.M.M. Electromagnetic wave scattering from some vegetation samples. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.G.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, H. Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 13, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Ma, P.; Nie, A.; Yang, A.; Yao, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Land cover mapping using time series HJ-1/CCD data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 44, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Montzka, C.; Rüdiger, C.; Ali, M.; Bogena, H.; Vereecken, H. Soil moisture retrieval from airborne L-band passive microwave using high resolution multispectral data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 91, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X. Regression kriging-based upscaling of soil moisture measurements from a wireless sensor network and multiresource remote sensing information over heterogeneous cropland. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tan, L.; Gao, S.; Jiao, Q. Observation on soil moisture of irrigation cropland by cosmic-ray probe. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sensi. Lett. 2015, 12, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Jeff, W. HiWATER: Dataset of Airborne Microwave Radiometers (L Bands) Mission in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin on June 30, July 3, July 4, July 7, July 10, July 26, August 1, and August 2, 2012; Heihe Plan Science Data Center: Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Global Land Surface Satellite (GLASS) remote sensing data processing system and products. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2436–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Use of general regression neural networks for generating the GLASS leaf area index product from time-series MODIS surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Li, X.; Yan, B.P.; Li, X.H.; Luo, W.M.; Ma, M.G.; Guo, J.W.; Kang, J.; Zhu, Z.L.; Zhao, S.J. A nested eco-hydrological wireless sensor network for capturing the surface heterogeneity in the midstream area of the Heihe River Basin, China. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, C.; Wang, J. HiWATER: Dataset of Biomass Observed in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin; Heihe Plan Science Data Center: Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Jiang, F. Design and experiment of crop structural parameters automatic measurement system. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agri. Eng. 2012, 28, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, W. HiWATER: Dataset of LAINet Observations in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin; Heihe Plan Science Data Center: Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hanway, J.J. Growth stages of corn (Zea mays, L.). Agron. J. 1963, 55, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholczyk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.; Calvet, J.-C.; Lafont, S.; Albergel, C.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Pardé, M.; Kerr, Y.; Zribi, M. Spatial and temporal variability of biophysical variables in southwestern France from airborne L-band radiometry. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1725–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I.E.; Jackson, T.J.; Njoku, E.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Cosh, M.H.; Holmes, T.R.H.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Jones, L.; Kimball, J.; et al. Remote monitoring of soil moisture using passive microwave-based techniques—Theoretical basis and overview of selected algorithms for AMSR-E. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.P.; Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Saleh, K.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Richaume, P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Rosnay, P.D.; Gurney, R.; Calvet, J.C.; et al. L-band Microwave Emission of the Biosphere (L-MEB) model: Description and calibration against experimental data sets over crop fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS mission: New tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Weihermüller, L.; Jiang, L.; Vereecken, H. Measurement and simulation of topographic effects on passive microwave remote sensing over mountain areas: A case study from the Tibetan Plateau. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Chai, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z. Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10543-10561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810543
Wang Q, Chai L, Zhao S, Zhang Z. Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(8):10543-10561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810543
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qi, Linna Chai, Shaojie Zhao, and Zhongjun Zhang. 2015. "Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index" Remote Sensing 7, no. 8: 10543-10561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810543
APA StyleWang, Q., Chai, L., Zhao, S., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Gravimetric Vegetation Water Content Estimation for Corn Using L-Band Bi-Angular, Dual-Polarized Brightness Temperatures and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sensing, 7(8), 10543-10561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810543