An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Imaging Model of Remote Sensing Images Covered by Thin Clouds

- (a)
- The transmission attenuation of the imaging light by thin clouds. This type of light refers to the effective imaging, but the cloud reduces the contrast of the ground objects.
- (b)
- The reflection and scattering of the non-imaging light by thin clouds. This type of the light increases the brightness but decreases the saturation.
- (c)
- The scattering of the imaging light by thin clouds. This type of light causes blur of ground objects and decrease in contrast.
3. Image Uneven Illumination Correction Principle
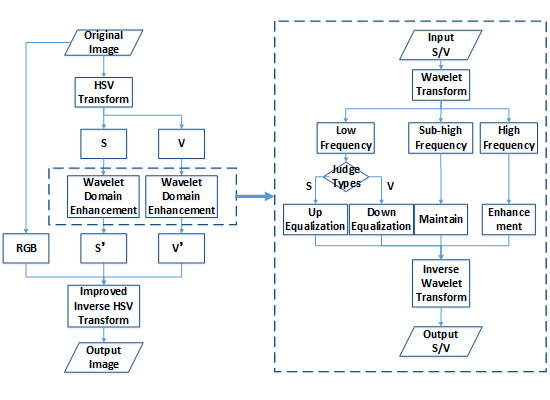
3.1. Improved HSV Color Space Transform
3.2. Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm Based on Wavelet Domain Enhancement



4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experiments and Effects Evaluation



4.2. Quantitative Analysis
- (a)
- Mean value represents the average brightness of all pixels in the whole image:
- (b)
- Standard deviation represents the deviation extent of all pixels in the whole image, and reflects the whole contrast of the entire image. The higher standard deviation an image has, the more contrast information is highlighted:
- (c)
- Information entropy stands for the richness of the information of an image. The higher information entropy an image contains, the richer information it conveys. If the pixel value of the image ranges from 0 to 255, the information entropy is calculated as follows:where Pi denotes the probability of digital number i.
- (d)
- Average gradient represents the differences between neighbor pixels, and reflects the contrast of image details. The higher average gradient an image has, the more contrast of image details you will see and the more ground objects are highlighted:
- (e)
- Hue deviation index (HDI) denotes the variations of hue between an original image and the processed image. A lower hue deviation index represents the smaller hue variations. HDI less than 1% means that the uneven illumination correction process can keep the hue very well, and the processed images do not have color distortions:where HOri(x,y) and HRe(x,y) denote the hues of the pixel located in the xth row and yth column in the original image and the processed image, respectively.
| Indicator | Channel | Original Image | MSR Algorithm | HF-based Algorithm | WT-MASK Algorithm | The Proposed Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | R | 140.92 | 103.23 | 114.63 | 109.90 | 113.63 |
| G | 152.00 | 103.85 | 123.30 | 123.09 | 123.19 | |
| B | 161.97 | 104.73 | 130.64 | 134.17 | 131.31 | |
| Standard deviation | R | 39.12 | 59.26 | 25.77 | 35.16 | 56.60 |
| G | 38.10 | 55.24 | 20.46 | 30.08 | 51.08 | |
| B | 43.19 | 50.53 | 20.46 | 28.94 | 50.75 | |
| Information entropy | R | 7.31 | 7.54 | 6.68 | 7.15 | 7.72 |
| G | 7.25 | 7.55 | 6.34 | 6.91 | 7.61 | |
| B | 7.38 | 7.50 | 6.37 | 6.86 | 7.59 | |
| Average gradient | R | 7.17 | 16.10 | 5.89 | 8.34 | 14.34 |
| G | 6.72 | 16.63 | 5.51 | 7.82 | 13.95 | |
| B | 6.68 | 15.47 | 5.48 | 7.77 | 14.04 | |
| HDI | -- | -- | 17.89 | 0.29 | 7.47 | 0.34 |
| Indicator | Channel | Original Image | MSR Algorithm | HF-based Algorithm | WT-MASK Algorithm | The Proposed Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | R | 85.63 | 104.31 | 49.05 | 77.63 | 73.78 |
| G | 95.83 | 106.27 | 54.67 | 83.39 | 82.39 | |
| B | 101.96 | 106.38 | 57.18 | 84.32 | 86.90 | |
| Standard deviation | R | 28.72 | 46.74 | 13.17 | 20.34 | 33.95 |
| G | 29.14 | 38.17 | 11.23 | 17.41 | 31.97 | |
| B | 35.27 | 36.95 | 11.60 | 17.33 | 34.01 | |
| Information entropy | R | 6.82 | 7.45 | 5.54 | 6.27 | 6.97 |
| G | 6.89 | 7.18 | 5.39 | 6.06 | 6.95 | |
| B | 7.17 | 7.11 | 5.42 | 6.03 | 7.05 | |
| Average gradient | R | 5.77 | 16.67 | 3.68 | 5.89 | 10.97 |
| G | 5.59 | 15.20 | 3.59 | 5.71 | 10.88 | |
| B | 5.61 | 14.96 | 3.60 | 5.74 | 11.04 | |
| HDI | -- | -- | 16.82 | 0.55 | 11.94 | 0.43 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agapiou, A.; Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Papoutsa, C.; Alexakis, D.D.; Papadavid, G. The importance of accounting for atmospheric effects in the application of NDVI and interpretation of satellite imagery supporting archaeological research: The case studies of Palaepaphos and Nea Paphos Sites in Cyprus. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2605–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Papadavid, G.; Agapiou, A.; Themistocleous, K.; Retalis, A.; Michaelides, S.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Toulios, L.; Clayton, C.R.I. Atmospheric correction for satellite remotely sensed data intended for hydrological cycle applications: Impact on vegetation indices. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cihlar, J.; Beaubien, J.; Latifovic, R. Radiometric normalization, compositing, and quality control for satellite high resolution image mosaics over large areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.F.; Li, H.F.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Yuan, Q.Q. An effective thin cloud removal procedure for visible remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Atmospheric correction of Landsat ETM+ land surface imagery-part I: Methods. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H.; McCann, J.J. Lightness and Retinex theory. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. 1971, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci.Am. 1977, 237, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. A multiscale Retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Bae, Y.; Ra, J.B. Contrast-enhanced fusion of multisensor images using subband-decomposed multiscale retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.D.; Ra, J.B. Enhancement of optical remote sensing images by subband-decomposed multiscale retinex with hybrid intensity transfer function. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.S.; Lee, T.H.; Kyung, W.J. Local contrast enhancement based on adaptive multiscale retinex using intensity distribution of input image. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2011, 55, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G.A. Investigating the relationship between image enhancement and image compression in the context of the multi-scale retinex. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2011, 22, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. An efficient content-based image enhancement in the compressed domain using retinex theory. IEEE. Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2007, 17, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Zhang, L.P.; Shen, H.F. A perceptually inspired variational method for the uneven intensity correction of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guindon, B.; Cihlar, J. Haze detection and removal in high resolution satellite image with wavelet analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Nnolim, U.; Lee, P. Homomorphic Filtering of colour images using a Spatial Filter Kernel in the HSI colour space. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Victoria, Canada, 12–15 May 2008; pp. 1738–1743.
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, S.G.; Shao, Z.F.; Zhou, X.R.; Liu, P. Illumination and contrast balancing for remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, J.; Chen, S.Q.; Li, H. A method of removing the uneven illumination phenomenon for optical remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2005), Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 3243–3246.
- Yuan, X.X.; Han, Y.T.; Fang, Y. Improved mask dodging algorithm for aerial imagery. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 18, 630–641. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.S.; Zhu, S.L.; Cao, W. Improved Mask dodging method based on wavelet. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, W.K. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.R. Color gamut transform pairs. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1978, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsos, D.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Venetsanopoulos, A.N. A novel vector-based approach to color image retrieval using a vector angular-based distance measure. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1999, 75, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesley: MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.; Zhu, W.L. Fusion of Ikonos satellite imagery using IHS transform and local variation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Mallat, S.G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. The statistics of visual representation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Visual Information Processing XI, Orlando, FL, USA, 4 April 2002; pp. 25–35.
- Liu, J.; Shao, Z.F.; Cheng, Q.M. Color constancy enhancement under poor illumination. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4821–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Shen, L. An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11848-11862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911848
Shen X, Li Q, Tian Y, Shen L. An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(9):11848-11862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911848
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiaole, Qingquan Li, Yingjie Tian, and Linlin Shen. 2015. "An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds" Remote Sensing 7, no. 9: 11848-11862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911848
APA StyleShen, X., Li, Q., Tian, Y., & Shen, L. (2015). An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds. Remote Sensing, 7(9), 11848-11862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911848