Application of Synthetic NDVI Time Series Blended from Landsat and MODIS Data for Grassland Biomass Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Field Data
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
| Year | Landsat TM Path = 124, Row = 29/30 | MODIS (DOY) Tile = h26v04 |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 09/02/2005 | 241/2005 |
| 2006 | 09/21/2006 | 265/2006 |
| 2007 | 09/08/2007 | 249/2007 |
| 2008 | 09/08/2007 | 249/2007 |
| 2009 | 08/12/2009 | 225/2009 |
| 2010 | 08/31/2010 | 241/2010 |
| 2011 | 08/02/2011 | 209/2011 |
| 2012 | 08/02/2011 | 209/2011 |
| 2013 | 08/02/2011 | 209/2011 |
3. Methods
3.1. Procedure for Grassland AGB Estimation

3.2. The STARFM Algorithm for NDVI Image Fusion
| Input MODIS | Input Landsat | Input MODIS | Validation Landsat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 09/06/2007–09/13/2007 DOY 249 | 09/08/2007 | 05/17/2007–05/24/2007 DOY 137 | 05/19/2007 |
| Scheme 2 | 09/22/2006–09/29/2006 DOY 265 | 09/21/2006 | 05/17/2007–05/24/2007 DOY 137 | 05/19/2007 |
| Scheme 3 | 08/29/2005–09/05/2005 DOY 241 | 09/02/2005 | 05/17/2007–05/24/2007 DOY 137 | 05/19/2007 |
| Statistics | Formula a |
|---|---|
| Mean value | |
| Standard deviation | |
| Entropy | |
| Average gradient | |
| Mean absolute difference |
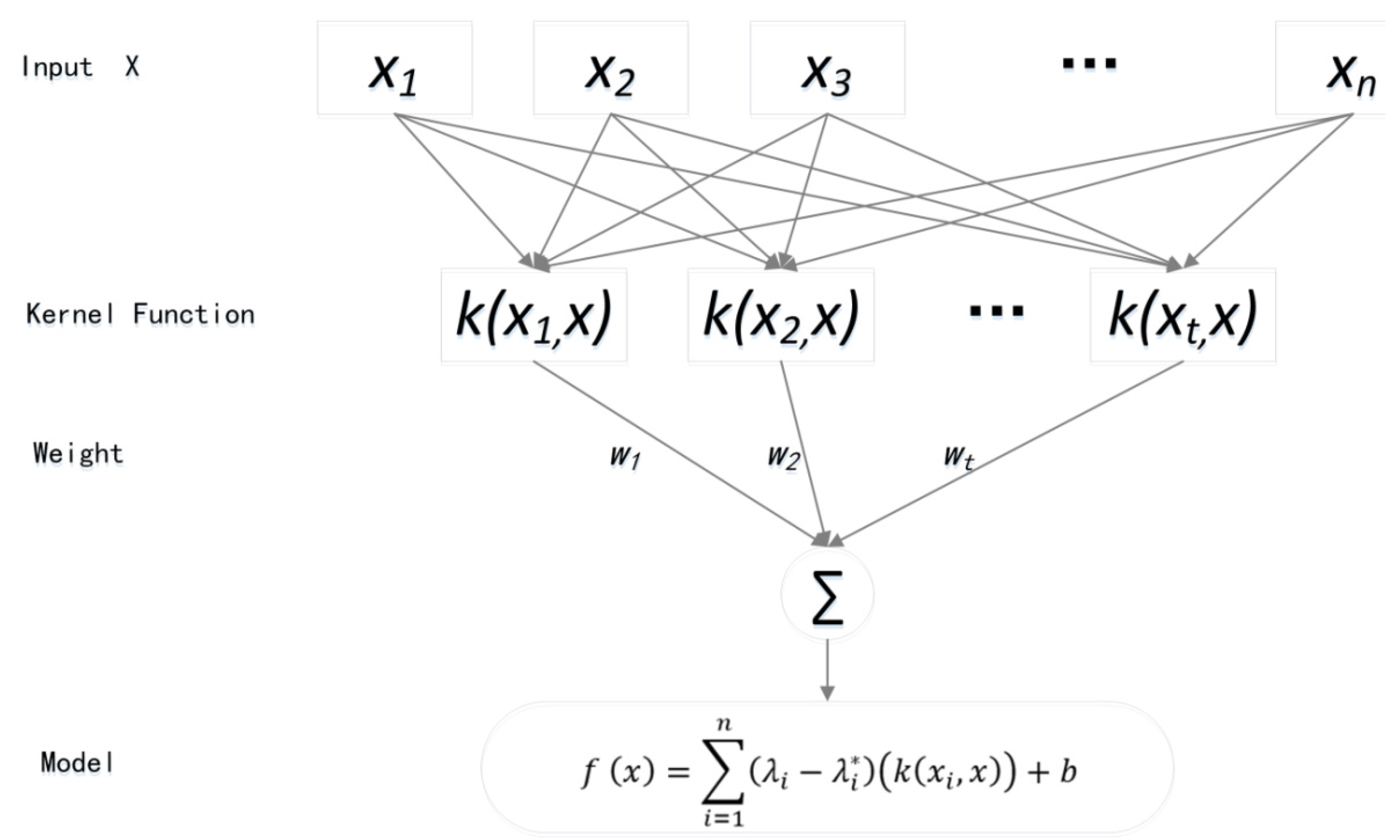
3.3. Biomass Estimation Model: Support Vector Machine Algorithm
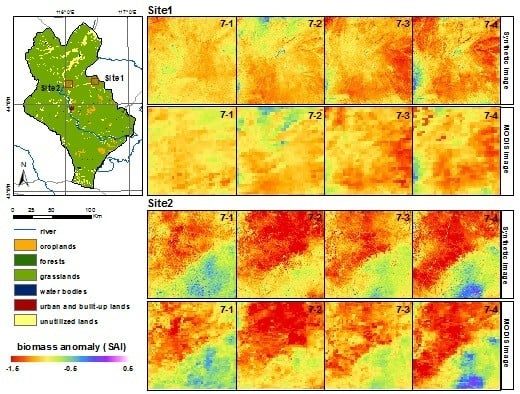
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Assessment of Synthetic NDVI Based on STARFM

| Type | Mean | Standard Deviation | Entropy | Average Gradient | Mean Absolute Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM_NDVI | 0.240 | 0.049 | 3.619 | 0.014 | / |
| Pre_NDVI_Scheme1 | 0.244 | 0.053 | 3.653 | 0.013 | 0.019 |
| Pre_NDVI_Scheme2 | 0.245 | 0.045 | 3.566 | 0.012 | 0.018 |
| Pre_NDVI_Scheme3 | 0.247 | 0.060 | 3.725 | 0.016 | 0.022 |
4.2. Prediction of Time-Series Synthetic NDVI

4.3. Development of the AGB Estimation Model
| AGB Model | Regression Equation | Training Set | Testing Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | RMSEr | R2 | RMSE | RMSEr | ||
| (g/m2) | (g/m2) | ||||||
| Linear regression model | 0.71 | 31.40 | 42.6% | 0.79 | 26.48 | 34.6% | |
| Power function model | 0.68 | 33.62 | 44.6% | 0.84 | 28.03 | 38.0% | |
| Exponential model | 0.67 | 34.14 | 45.1% | 0.84 | 28.60 | 38.8% | |
| SVM-AGB | / | 0.77 | 17.22 | 24.8% | 0.83 | 22.60 | 31.3% |
| AGB Model | Regression Equation | Training Set | Testing Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | RMSEr | R2 | RMSE | RMSEr | ||
| (g/m2) | (g/m2) | ||||||
| Linear regression model | 0.66 | 34.13 | 46.3% | 0.64 | 34.19 | 42.1% | |
| Power function model | 0.68 | 33.21 | 44.8% | 0.69 | 31.23 | 40.9% | |
| Exponential model | 0.68 | 33.36 | 44.9% | 0.69 | 31.24 | 41.1% | |
| SVM-AGB | / | 0.73 | 30.61 | 43.0% | 0.72 | 22.89 | 37.1% |
4.4. Drought Condition Monitoring with Time-Series Biomass Maps




5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, P. Zoning grassland protection area using remote sensing and cellular automata modeling—A case study in Xilingol steppe grassland in northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbagy, E.G.; Sala, O.E. Controls of grass and shrub aboveground production in the Patagonian steppe. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, M.L.; Evertson, J. Monitoring change in mountainous dry-heath vegetation at a regional scale using multitemporal Landsat TM data. Ambio 2003, 32, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. How unique are spectral signatures. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P. Cloud cover in Landsat observations of the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, P.V. Determination of cloud coverage over Denmark using Landsat MSS/TM and NOAA–AVHRR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3363–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.C.; Roy, D.P. The availability of cloud-free Landsat ETM plus data over the conterminous United States and globally. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1196–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, E.; Zalevsky, Z. Resolution-enhanced remote sensing via multi spectral and spatial data fusion. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2011, 2, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carper, W.J.; Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W. The use of intensity-hue-saturation transformations for merging SPOT panchromatic and multispectral image data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 1990, 56, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Shettigara, V.K. A generalized component substitution technique for spatial enhancement of multispectral images using a higher resolution data set. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 1992, 58, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Yocky, D.A. Multiresolution wavelet decomposition image merger of Landsat thematic mapper and SPOT panchromatic data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 1996, 62, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.J.; Chen, B.Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.L.; Hilker, T. An improved image fusion approach based on enhanced spatial and temporal the adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6346–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.L.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.H.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Seitz, N.; White, J.C.; Gao, F.; Masek, J.G.; Stenhouse, G. Generation of dense time series synthetic Landsat data through data blending with MODIS using a spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.J.; de Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Y.J.; Fensholt, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y. Mapping and evaluation of NDVI trends from synthetic time series obtained by blending Landsat and MODIS data around a coalfield on the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4255–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Udelhoven, T.; Gill, T.; Roder, A. Long term data fusion for a dense time series analysis with MODIS and Landsat imagery in an Australian savanna. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063512. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, J.D.; Powell, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Hilker, T. Improved classification of conservation tillage adoption using high temporal and synthetic satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D. Generation and evaluation of gross primary productivity using Landsat data through blending with MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2011, 13, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D. Evaluation of long-term NDVI time series derived from Landsat data through blending with MODIS data. Atmosfera 2012, 25, 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, S.; Phinn, S.; Gill, T. Preparing Landsat image time series (LITS) for monitoring changes in vegetation phenology in Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1856–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Leitao, P.J.; Pflugmacher, D.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Mapping land cover in complex Mediterranean landscapes using Landsat: Improved classification accuracies from integrating multi-seasonal and synthetic imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Song, H.H. Spatiotemporal reflectance fusion via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.F.; Wu, P.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Ai, T.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.P. A spatial and temporal reflectance fusion model considering sensor observation differences. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4367–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.H.; Du, X.; Wu, B.F. Generation of high spatial and temporal resolution NDVI and its application in crop biomass estimation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, H.K. Spatio-temporal reflectance fusion via unmixing: Accounting for both phenological and land-cover changes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6213–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.L.; Liu, D.S. Blending MODIS and Landsat images for urban flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanova, I.V.; McVicar, T.R.; van Niel, T.G.; Li, L.T.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Assessing the accuracy of blending Landsat-MODIS surface reflectances in two landscapes with contrasting spatial and temporal dynamics: A framework for algorithm selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.C.; Jin, Y.X.; Ma, H.L.; Li, J.Y.; Yu, H.D. Using MODIS time series data to estimate aboveground biomass and its spatio-temporal variation in Inner Mongolia’s grassland between 2001 and 2011. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7796–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomppo, E.; Nilsson, M.; Rosengren, M.; Aalto, P.; Kennedy, P. Simultaneous use of Landsat-TM and IRS-1C WIFS data in estimating large area tree stem volume and aboveground biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.C.; Sha, Z.Y.; Yu, M.; Bai, Y.F.; Zhang, L. A comparison of two models with Landsat data for estimating above ground grassland biomass in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Model 2009, 220, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Liu, C. Biomass retrieval from high-dimensional active/passive remote sensing data by using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Prasher, S.O.; Lacroix, R.; Goel, P.K.; Karimi, Y.; Viau, A.; Patel, R.M. Artificial neural networks to predict corn yield from compact airborne spectrographic imager data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 47, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yool, S.R. Land cover classification in rugged areas using simulated moderate-resolution remote sensor data and an artificial neural network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.F. Synergy of multitemporal ERS-1 SAR and Landsat TM data for classification of agricultural crops. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbek, F.S.; Ozkan, C.; Taberner, M. Comparison of maximum likelihood classification method with supervised artificial neural network algorithms for land use activities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Govil, R. Detecting temporal changes in satellite imagery using ANN. In Proceedings of the RAST 2005 2nd International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2005; pp. 645–647.
- Balabin, R.M.; Lomakina, E.I. Support vector machine regression (SVR/lS-SVM)—An alternative to neural networks (ANN) for analytical chemistry? Comparison of nonlinear methods on near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy data. Analyst 2011, 136, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Hay, G.J.; Zhou, Y.L. Estimation of forest height, biomass and volume using support vector regression and segmentation from Lidar transects and Quickbird imagery. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4.
- Gleason, C.J.; Im, J. Forest biomass estimation from airborne LiDAR data using machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachowski, N.R.A.; Quak, M.S.Y.; Friess, D.A.; Duangnamon, D.; Webb, E.L.; Ziegler, A.D. Mangrove biomass estimation in southwest Thailand using machine learning. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 45, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. Based on Meteorological Data of Drought Disaster Forecast Study in Pastoral Area of Xilingol League. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.X.; Yang, X.C.; Qiu, J.J.; Li, J.Y.; Gao, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Ma, H.L.; Yu, H.D.; Xu, B. Remote sensing-based biomass estimation and its spatio-temporal variations in temperate grassland, northern china. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1496–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Peng, D.L.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, Q.J.; Liu, L.L. Monitoring the distribution of C3 and C4 grasses in a temperate grassland in northern China using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer normalized difference vegetation index trajectories. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.K. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Han, X.G.; Wu, J.G.; Chen, Z.Z.; Li, L.H. Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature 2004, 431, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermonte, E.F.; Kotchenova, S.Y.; Ray, J.P. MODIS Surface Reflectance User’s Guide, Version 1.4. Available online: http://modis-sr.ltdri.org/guide/MOD09_UserGuide_v1_3.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2015).
- Makela, H.; Pekkarinen, A. Estimation of forest stand volumes by Landsat TM imagery and stand-level field-inventory data. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.W.; Glantz, M.H. Anatomy of a rainfall index. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarihani, A.A.; McVicar, T.R.; van Niel, T.G.; Emelyanova, I.V.; Callow, J.N.; Johansen, K. Blending Landsat and MODIS data to generate multispectral indices: A comparison of “Index-then-blend”and “Blend-then-index” approaches. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9213–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.W.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. A Practical Guide to Support Vector Classification. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2015).
- Rembold, F.; Atzberger, C.; Savin, I.; Rojas, O. Using low resolution satellite imagery for yield prediction and yield anomaly detection. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1704–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, K.; Akiyama, T.; Yokota, H.; Tsutsumi, M.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, O.; Wang, S.P. Quantifying grazing intensities using geographic information systems and satellite remote sensing in the Xilingol steppe region, Inner Mongolia, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, F.; Li, C.L.; Bao, Y.H. The wavelet analysis of average temperature and precipitation in Xilinhot during 57 years. J. Inner Mong. Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 42, 47–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Farmer's Daily. Available online: http://szb.farmer.com.cn/nmrb/html/2011–04/13/nw.D110000nmrb_20110413_1–03.htm?div=-1 (accessed on 4 September 2015).
- Hang, Y.L.; Bao, G.; Bao, Y.H.; Burenjirigala; Altantuya, D. Spatiotemporal changes of vegetation coverage in Xilingol grassland and its responses to climate change during 2000–2010. Acta Agres. Sin. 2014, 22, 1194–1204. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.D.; Yang, X.C.; Xu, B.; Jin, Y.X.; Gao, T.; Li, J.Y. Changes of grassland vegetation growth in Xilingol league over 10 years and analysis on the influence factors. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2013, 15, 270–279. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xilinhaote News. Available online: http://xilinhaote.nmgnews.com.cn/system/2009/07/20/010253966.shtml (accesed on 4 September 2015).
- Liu, C.L.; Fan, R.H.; Wu, J.J.; Yan, F. Temporal lag of grassland vegetation growth response to precipitation in Xilinguolemeng. Arid Land Geogr. 2009, 32, 512–518. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Xie, D.; Yin, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Application of Synthetic NDVI Time Series Blended from Landsat and MODIS Data for Grassland Biomass Estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010010
Zhang B, Zhang L, Xie D, Yin X, Liu C, Liu G. Application of Synthetic NDVI Time Series Blended from Landsat and MODIS Data for Grassland Biomass Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Binghua, Li Zhang, Dong Xie, Xiaoli Yin, Chunjing Liu, and Guang Liu. 2016. "Application of Synthetic NDVI Time Series Blended from Landsat and MODIS Data for Grassland Biomass Estimation" Remote Sensing 8, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010010
APA StyleZhang, B., Zhang, L., Xie, D., Yin, X., Liu, C., & Liu, G. (2016). Application of Synthetic NDVI Time Series Blended from Landsat and MODIS Data for Grassland Biomass Estimation. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010010