Spatially and Temporally Complete Satellite Soil Moisture Data Based on a Data Assimilation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Data
2.1. Soil Moisture Model
2.2. Cost Function and Optimization Method
2.3. Data
2.3.1. Meteorological Data
2.3.2. Soil Moisture Data
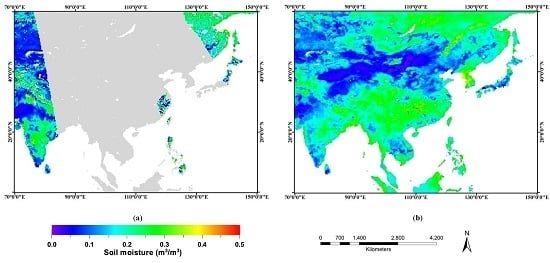
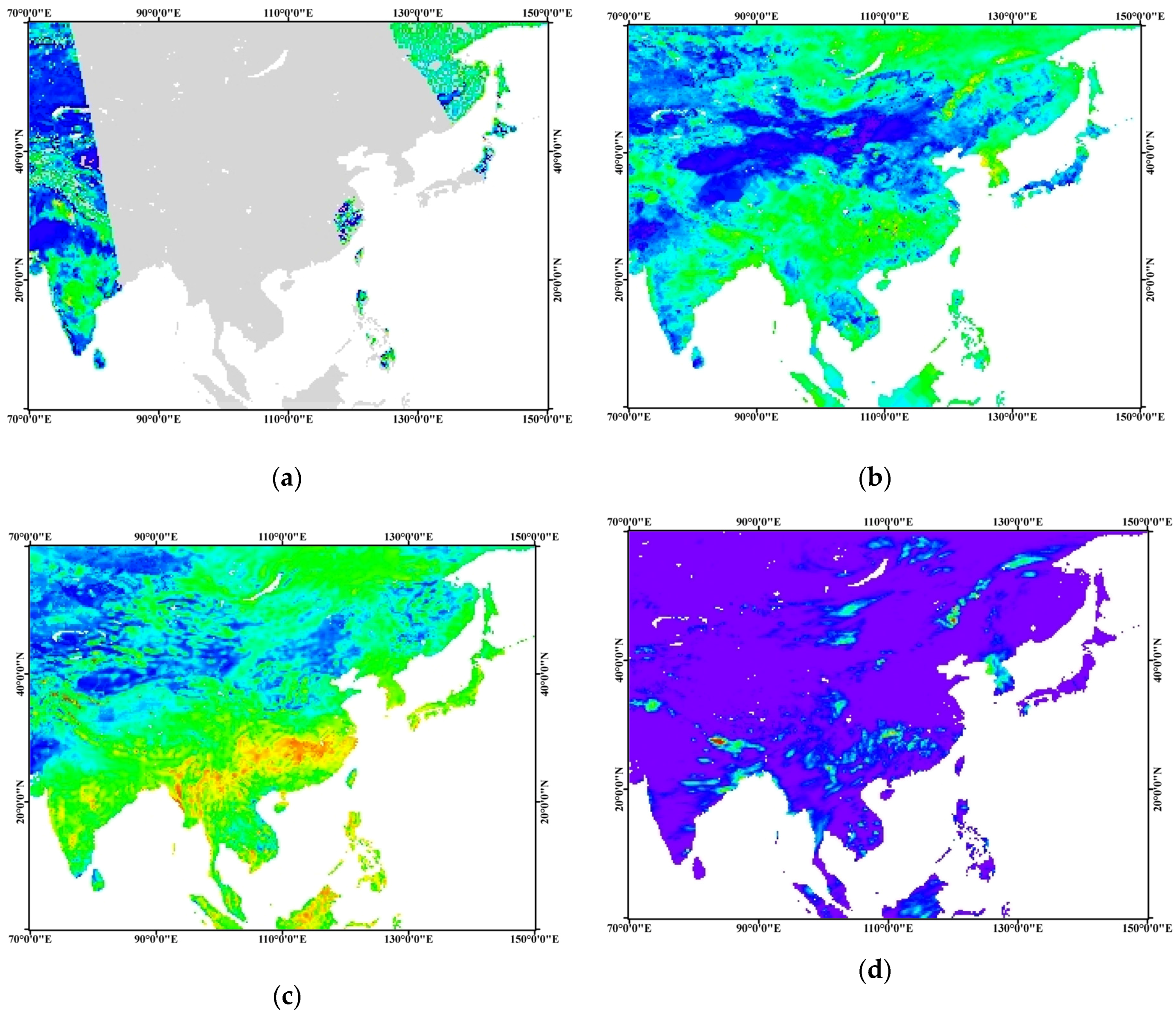
3. Result Analysis
3.1. Comparison in Space



3.2. Comparison against Soil Moisture Measurements from Multi-Scale Networks


| Area | Product | Ascending Orbit | Descending Orbit | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | Bias | N | R2 | RMSE | Bias | N | ||
| Medium network | TCRM | 0.339 | 0.079 | −0.056 | 124 | 0.479 | 0.075 | −0.056 | 123 |
| DARM | 0.378 | 0.078 | −0.058 | 124 | 0.476 | 0.078 | −0.061 | 123 | |
| Large network | TCRM | 0.357 | 0.068 | −0.042 | 107 | 0.473 | 0.068 | −0.049 | 70 |
| DARM | 0.373 | 0.072 | −0.046 | 107 | 0.437 | 0.059 | −0.032 | 70 | |



4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Martinuzzi, J.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalis, Z.; Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Hasenauer, S.; Scipal, K.; Bonekamp, H.; Figa, J.; Anderson, C. Initial soil moisture retrievals from the METOPA Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, T.; Sezai, T.; Ito, Y.; Imaoka, K.; Takeshima, T.; Ishido, Y.; Shibata, A.; Miura, M.; Inahata, H.; Spencer, R.W. The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for the Earth Observing System (AMSR-E), NASDA’s contribution to the EOS for global energy and water cycle studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kaihotsu, I.; Davva, G.; Matsuura, N.; Tamagawa, K.; Fujii, H. Development of an Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR-E) algorithm of soil moisture and vegetation water content. Annu. J. Hydraul. Eng. Jpn. Soc. Civil Eng. 2004, 48, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris Anguela, T.; Zribi, M.; Habets, F.; Hasenauer, S.; Loumagne, C. Analysis of surface and root soil moisture dynamics with ERS scatterometer and the hydrometeorological model SAFRAN-ISBA-MODCOU at Grand Morin watershed (France). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 5, 1903–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, R.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Wagner, W.; Hauesner, S. Analysis of ASCAT-C band scatterometer estimations derived over a semi-arid region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Scipal, K.; Pathe, C.; Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Rudolf, B. Evaluation of the agreement between the first global remotely sensed soil moisture data with model and precipitation data. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, C.; Calvet, J.; Gruhier, C.; Holmes, T.; de Jeu, R.; Wagner, W. An intercomparison of ERS-Scat and AMSR-E soil moisture observations with model simulations over France. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jeu, R.; Wagner, W.; Holmes, T.; Dolman, A.; van de Giesen, N.; Friesen, J. Global soil moisture patterns observed by space borne microwave radiometers and scatterometers. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Cosh, M.; Bindlish, R.; Starks, P.; Bosch, D.; Seyfried, M.; Goodrich, D.; Moran, S.; Du, J. Validation of advanced microwave scanning radiometer soil moisture products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4256–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.; Zhao, T.; Starks, P.; Bosch, D.; Seyfried, M.; Moran, M.; Goodrich, D.; Kerr, Y.; et al. Validation of Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) soil moisture over watershed networks in the U.S. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitar, A.; Leroux, D.; Kerr, Y.; Merlin, O.; Richaume, P.; Sahoo, A.; Wood, E. Evaluation of SMOS soil moisture products over continental U.S. using the SCAN/SNOTEL network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1572–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Hasenauerb, S.; Lacavac, T.; Melonea, F.; Moramarcoa, T.; Wagnerb, W.; Dorigob, W.; Matgend, P.; Martínez-Fernándeze, J.; Llorensf, P.; et al. Soil moisture estimation through ASCAT and AMSR-E sensors: An intercomparison and validation study across Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3390–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.; Walker, J.; Steinle, P.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. An evaluation of AMSR-E derived soil moisture over Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wen, J.; Dente, L.; van der Velde, R.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z. The Tibetan Plateau observatory of plateau scale soil moisture and soil temperature (Tibet-Obs) for quantifying uncertainties in coarse resolution satellite and model products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Garcia, D.; Liu, Y.; Jeu, R.D.; Dolman, A.J. A three-dimensional gap filling method for large geophysical datasets: Application to global satellite soil moisture observations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 30, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varella, H.; Guérif, M.; Buis, S. Global sensitivity analysis measures the quality of parameter estimation: The case of soil parameters and a crop model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viovy, N.; Arino, O.; Belward, A.S. The Best Index Slope Extraction (BISE)—A method for reducing noise in NDVI time-series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, J.F. Stabilizing high-order, non-classical harmonic analysis of NDVI data for average annual models by damping model roughness. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2801–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A.; Verhoef, W. Changes in land surface temperatures and NDVI values over Europe between 1982 and 1999. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q. Reconstruction of satellite-retrieved land-surface reflectance based on temporally-continuous vegetation indices. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9844–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time—Series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.; Tucker, C.; Collatz, G.; Los, S.; Justice, C.; Dazlich, D.; Randall, D. A global 1 by 1 NDVI data set for climate studies. Part 2: The generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from the NDVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3519–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Menenti, M.; Verhoef, W. Reconstructing cloud free NDVI composites using Fourier analysis of time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liang, S.; Townshend, J.; Dickinson, R. Spatially and temporally continuous LAI data sets based on an integrated filtering method: Examples from North America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, E.G.; King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F. Spatially complete global spectral surface albedos: Value-add datasets derived from Terra MODIS land products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, W.; Han, M. Evaluation of AMSR-E retrievals and GLDAS simulations against observations of a soil moisture network on the central Tibetan plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4466–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, C.R.; Crow, W.T.; Anderson, M.C.; Mecikalski, J.R. An ensemble Kalman filter dual assimilation of thermal infrared and microwave satellite observations of soil moisture into the Noah land surface model. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Wood, E.F. The assimilation of remotely sensed soil brightness temperature imagery into a land surface model using ensemble Kalman filtering: A case study based on ESTAR measurements during SGP97. Adv. Water Resour. 2003, 26, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D. Global assimilation of satellite surface soilmoisture retrievals into the NASA catchment land surface model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Nandagiri, L.; Purandara, B.K.; Reddy, V.B. Modelling soil moisture under different land covers in a sub-humid environment of Western Ghats. India J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 120, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T. On the estimation of antecedent wetness conditions in rainfall-runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, L. Evaluation des besoins en eau d’irrigation, évapotranspiration potentielle. Ann. Agron. 1961, 12, 13–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Estimating potential evapotranspiration. J. Irrig. Drain. E-Asce 1982, 108, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration. In Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Irrigation Drainage Paper No.56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V.K. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xie, Z.; Qian, H.; Liang, M.; Yang, X. China land soil moisture EnKF data assimilation based on satellite remote sensing data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, A.; Sang, J.; Pan, N. Atmospheric Physics; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.; Wigneron, J.P.; Chanzy, A. A parameterized multifrequency-polarization surface emission model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Du, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, L.M. Analysis of spatial distribution and multi-year trend of the remotely sensed soil moisture on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Kimball, J.S.; Shi, J.; Jones, L.A.; Wu, S.; Sun, R.; Yang, H. Inter-calibration of satellite passive microwave land observations from AMSR-E and AMSR2 using overlapping FY3B-MWRI sensor measurements. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8594–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, L.; Qi, Y.; Du, J.; Tao, J. Comparison of satellite soil moisture products with field observations and model simulation in the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Njoku, E.; Chan, S. Vegetation and surface roughness effects on AMSR-E land observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, F01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. Available online: http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/hydrology/data-holdings (accessed on 19 September 2015).
- Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Han, M.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Lv, N.; Ding, B.H.; et al. A multi-scale soil moisture and freeze-thaw monitoring network on the Third Pole. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Liang, S.; Sun, R. Estimating the fractional vegetation cover from GLASS leaf area index product. Remote Sens. 2015. under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandagiri, L.; Kovoor, G. Performance evaluation of reference evapotranspiration equations across a range of Indian climates. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, J. Spatially and Temporally Complete Satellite Soil Moisture Data Based on a Data Assimilation Method. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010049
Xiao Z, Jiang L, Zhu Z, Wang J, Du J. Spatially and Temporally Complete Satellite Soil Moisture Data Based on a Data Assimilation Method. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Zhiqiang, Lingmei Jiang, Zhongli Zhu, Jindi Wang, and Jinyang Du. 2016. "Spatially and Temporally Complete Satellite Soil Moisture Data Based on a Data Assimilation Method" Remote Sensing 8, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010049
APA StyleXiao, Z., Jiang, L., Zhu, Z., Wang, J., & Du, J. (2016). Spatially and Temporally Complete Satellite Soil Moisture Data Based on a Data Assimilation Method. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010049