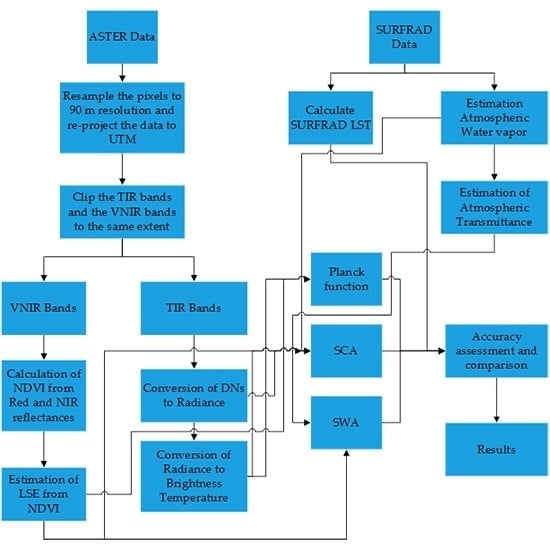
Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Terra ASTER Data: A Comparison of Three Algorithms
Abstract
Share and Cite
Ndossi, M.I.; Avdan, U. Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Terra ASTER Data: A Comparison of Three Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120993
Ndossi MI, Avdan U. Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Terra ASTER Data: A Comparison of Three Algorithms. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(12):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120993
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdossi, Milton Isaya, and Ugur Avdan. 2016. "Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Terra ASTER Data: A Comparison of Three Algorithms" Remote Sensing 8, no. 12: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120993
APA StyleNdossi, M. I., & Avdan, U. (2016). Inversion of Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Terra ASTER Data: A Comparison of Three Algorithms. Remote Sensing, 8(12), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120993