Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua Atmospheric Correction and Chlorophyll Products of Western North American Coastal Waters Based on 13 Years of Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Set and Analysis
2.2.1. Satellite Data and Image Processing
Atmospheric Correction Approach
chla Retrievals
Processing Flags
2.2.2. In Situ Data for Method Validation
In Situ Radiometric Measurements
In Situ Chlorophyll Data
2.2.3. Match-Up Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Atmospheric Correction
3.1.1. AERONET Match-Ups
3.1.2. In Situ above Water Match-Ups
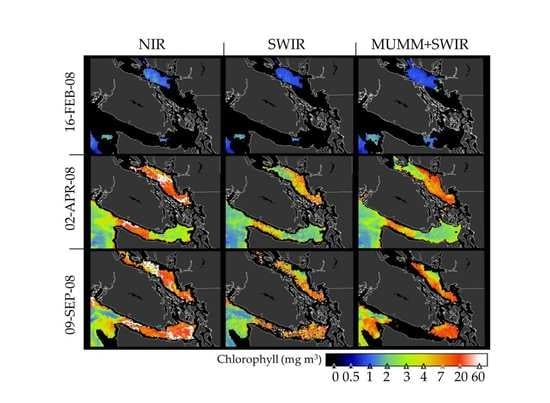
3.2. OC3M Chlorophyll Retrievals
4. Discussion
4.1. Atmospheric Correction
4.2. Chlorophyll Retrievals
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perry, R.I.; Masson, D. An integrated analysis of the marine social–ecological system of the Strait of Georgia, Canada, over the past four decades, and development of a regime shift index. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.; Fuentes-Yaco, C.; Frank, K.T. Marine ecology: Spring algal bloom and larval fish survival. Nature 2003, 423, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweigert, J.F.; Thompson, M.; Fort, C.; Hay, D.E.; Therriault, T.W.; Brown, L.N. Factors linking pacific herring (clupea pallasi) productivity and the spring plankton bloom in the strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.; Sathyendranath, S.; Müller, D.; Brockmann, C.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Devred, E.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.; Grant, M.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: III. A round-robin comparison on in-water bio-optical algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attila, J.; Koponen, S.; Kallio, K.; Lindfors, A.; Kaitala, S.; Ylöstalo, P. MERIS Case II water processor comparison on coastal sites of the northern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. Estimation of ocean contribution at the MODIS near-infrared wavelengths along the east coast of the US: Two case studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New aerosol models for the retrieval of aerosol optical thickness and normalized water-leaving radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS sensors over coastal regions and open oceans. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Woerd, H.; Pasterkamp, R. Mapping of the North Sea turbid coastal waters using SeaWiFS data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Brewin, R.J.; Jackson, T.; Mélin, F.; Platt, T. Ocean-colour products for climate-change studies: What are their ideal characteristics? Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W. Alkane and PAH depositional history, sources and fluxes in sediments from the Fraser River Basin and Strait of Georgia, Canada. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 1429–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, S.C.; Macdonald, R.W.; Paton, D.W. A sediment and organic carbon budget for the greater Strait of Georgia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gargett, A.; Denman, K. What Determines Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton in Strongly Estuarine Systems? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 50, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, E.A.; Costa, M. Inherent optical properties and optical mass classification of the waters of the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Prog. Oceanogr. 2010, 87, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, S.C.; Masson, D.; Macdonald, R.W. Distribution and cycling of suspended particles inferred from transmissivity in the strait of Georgia, ham strait and Juan de Fuca Strait. Atmos. Ocean 2006, 44, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, J.N.; Johannessen, S.C.; Macdonald, R.W. A nitrogen budget for the strait of Georgia, British Columbia, with emphasis on particulate nitrogen and dissolved inorganic nitrogen. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7179–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.K.; Allen, S.E.; Pawlowicz, R. The role of wind in determining the timing of the spring bloom in the Strait of Georgia. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1597–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J.; Fulton, J.D.; Taylor, F.J.R.; Parsons, T.R. Review of the biological oceanography of the Strait of Georgia: pelagic environment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1983, 40, 1064–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.E.; Wolfe, M.A. Hindcast of the timing of the spring phytoplankton bloom in the Strait of Georgia, 1968–2010. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Statham, S.; Fox, R.; Young, E. The Malaspina Dragon: A newly-discovered pattern of the early spring bloom in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospelova, V.; Esenkulova, S.; Johannessen, S.C.; O’Brien, M.C.; Macdonald, R.W. Organic-walled dinoflagellate cyst production, composition and flux from 1996 to 1998 in the central Strait of Georgia (BC, Canada): A sediment trap study. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2010, 75, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.D.; Goldblatt, R.H.; Harrison, P.J.; St. John, M.; Clifford, P.J.; Beamish, R.J. Importance of wind and river discharge in influencing nutrient dynamics and phytoplankton production in summer in the central Strait of Georgia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 161, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokoye, A.I.; Royer, A.; O’Neil, N.T.; Cliche, P.; Fedosejevs, G.; Teillet, P.M.; McArthur, L.J.B. Characterization of atmospheric aerosols across Canada from a ground-based sunphotometer network: AEROCAN. Atmos. Ocean 2001, 39, 429–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowicz, R.; Riche, O.; Halverson, M. The circulation and residence time of the Strait of Georgia using a simple mixing-box approach. Atmos. Ocean 2007, 45, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingarzan, R.; Thomson, B. Temporal variation in daily concentrations of ozone and acid-related substances at Saturna Island, British Columbia. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, T.; Okamoto, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Numaguti, A.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Global three-dimensional simulation of aerosol optical thickness distribution of various origins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 17853–17873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D.; Werdell, J.; Franz, B.; Ahmad, Z.; Bailey, S. Atmospheric Correction for Satellite Ocean Color Radiometry; Technical Report for Lockheed, NASA/TM-2016-217551, GSFC-E-DAA-TN35509; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1 June 2016.
- Fraser, R.S.; Kaufman, Y.J. The Relative Importance of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption in Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. The Rayleigh lookup tables for the SeaWiFS data processing: accounting for the effects of ocean surface roughness. Intern. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Castaño, D.J. Aerosol analysis with the Coastal Zone Color Scanner: a simple method for including multiple scattering effects. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R.; Voss, K.J. MODIS Normalized Water-Leaving Radiance Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Technical Report, NAS5-31363; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 30 April 1999. Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/atbd/atbd_mod17.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Goyens, C.; Jamet, C.; Schroeder, T. Evaluation of four atmospheric correction algorithms for MODIS-Aqua images over contrasted coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Wang, M.; Maritorena, S.; Robinson, W. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery: the black pixel assumption. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, G.M.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the 200-nm to 200-µm wavelength region. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, D.; Peña, A. Chlorophyll distribution in a temperate estuary: The Strait of Georgia and Juan de Fuca Strait. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komick, N.M.; Costa, M.P.F.; Gower, J. Bio-optical algorithm evaluation for MODIS for western Canada coastal waters: An exploratory approach using in situ reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Tang, J. Water property monitoring and assessment for China’s inland Lake Taihu from MODIS-Aqua measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.R.; Ainsworth, E.J.; Barnes, R.A.; Eplee, R.E.; Patt, F.S.; Robinson, W.D.; Wang, M.; Bailey, S.W. SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses, Part 1; Technical Report, 2000-206892; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2000. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/SeaWiFS/TECH_REPORTS/PLVol9.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B. Chlorophyll aalgorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; O’Brien, M.C.; Siegel, D.A.; Toole, D.; Menzies, D.; Smith, R.C.; Mueller, J.L.; Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; et al. SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses, Part 3. Technical Report, 2000-206892; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwimq4f5-vPWAhWENpQKHQ04BJwQFggpMAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Foceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov%2FSeaWiFS%2FTECH_REPORTS%2FPLVol11.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0WKlJsGtDgk0MG9Y7b-I2P (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Ding, K.; Gordon, H.R. Atmospheric correction of ocean-color sensors: effects of the Earth’s curvature. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 7096–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; McClain, C.R. Point-spread function of the ocean color bands of the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer on Aqua. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Carlund, T.; Holben, B.N.; Stefan, S. Validation of SeaWiFS and MODIS Aqua/Terra aerosol products in coastal regions of European marginal seas. Oceanologia 2013, 55, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. (1984–2012) 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, S.; Firestone, E.R.; Patt, F.S.; Barnes, R.A.; Eplee, R.E., Jr.; Franz, B.A.; Robinson, W.D.; Feldman, G.C.; Bailey, S.W. Algorithm Updates for the Fourth SeaWiFS Data Reprocessing. Technical Report, 2003-206892; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1 May 2003. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/technical/seawifs_reports/postlaunch/post_vol22_abs/ (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Bidigare, R.R.; Trees, C.; Balch, W.M.; Dore, J.; Drapeau, D.T.; Karl, D.; Van Heukelem, L.; Perl, J. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, Revision 5: Biogeochemical and Bio-Optical Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols; Mueller, J.L., Fargion, G.S., McClain, C.R., Eds.; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, December 2003; Volume 5, pp. 1–43. Available online: https://seabass.gsfc.nasa.gov/wiki/System_Description/Protocols_Ver5_VolV.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Arar, E.J. Determination of Chlorophylls a and B and Identification of Other Pigments of Interest in Marine and Freshwater Algae Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Visible Wavelength Detection; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1997; pp. 1–20.
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Harding, L.W., Jr.; Feldman, G.C.; McClain, C.R. Regional and seasonal variability of chlorophyll-a in Chesapeake Bay as observed by SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.W.; Blaisdell, J.M.; Darzi, M. Level-3 SeaWiFS Data Products: Spatial and Temporal Binning Algorithms; Technical Report, 104566; Hooker, S.B., Firestone, E.R., Acker, J.G., Eds.; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1995; Volume 32, pp. 1–80. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/technical/seawifs_reports/prelaunch/vol32_abs/ (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Tilstone, G.H.; Angel-Benavides, I.M.; Pradhan, Y.; Shutler, J.D.; Groom, S.; Sathyendranath, S. An assessment of chlorophyll-a algorithms available for SeaWiFS in coastal and open areas of the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2277–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaeps, E.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Raymaekers, D.; Ruddick, K.; Sterckx, S. In situ evidence of non-zero reflectance in the OLCI 1020nm band for a turbid estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Ocean reflectance spectra at the red, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared from highly turbid waters: A study in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014b, 59, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Cherukuru, N.; Lavender, S.J. Apparent and inherent optical properties of turbid estuarine waters: measurements, empirical quantification relationships, and modeling. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of near-infrared water-leaving reflectance for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Meister, G.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Ahmad, Z.; McClain, C.R. MODIS land bands for ocean remote sensing applications. In Proceedings of the Ocean Optics XVIII, Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–13 October 2006; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Barnes, W.L. Early on-orbit calibration results from Aqua MODIS. In Proceedings of the SPIE 4881, Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites VI, Crete, Greece, 23–27 September 2003; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Advantages of high quality SWIR bands for ocean colour processing: Examples from Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W. Remote sensing of water optical property for China’s inland Lake Taihu using the SWIR atmospheric correction with 1640 and 2130 nm bands. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. Sensor Noise Effects of the SWIR Bands on MODIS-Derived Ocean Color Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3280–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W. Evaluation of shortwave infrared atmospheric correction for ocean color remote sensing of Chesapeake Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, T.; Wen, Z. A review of some important technical problems in respect of satellite remote sensing of chlorophyll-a concentration in coastal waters. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2275–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR atmospheric correction algorithms using SeaBASS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Meister, G.; Werdell, P.J. Quality and consistency of the NASA ocean color data record. In Proceedings of the Ocean Optics XXI, Glasgow, UK, 8–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eck, T.F. Columnar aerosol optical properties at AERONET sites in central eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical mid-Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D06202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Clerici, M.; Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.N.; Smirnov, A. Validation of SeaWiFS and MODIS aerosol products with globally distributed AERONET data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.B.; Bélanger, S.; Larouche, P. Evaluation of ocean color algorithms in the southeastern Beaufort Sea, Canadian Arctic: New parameterization using SeaWiFS, MODIS, and MERIS spectral bands. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.; Mélin, F.; D’Alimonte, D.; Berthon, J.-F.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D. AERONET-OC: An overview. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, C.; Hooker, S.; Feldman, G.; Bontempi, P. Satellite data for ocean biology, biogeochemistry, and climate research. Eos. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2006, 87, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.P.; Voß, D.; Wollschläger, J.; Zielinski, O. Modern approaches to shipborne ocean color remote sensing. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Phillips, S.; Wang, Z.; Vandenberg, N. A road map for autonomous, continuous in situ above-water hyperspectral reflectance data from ferry platforms: Ferry Ocean Colour Observations System (FOCOS). In Proceedings of the International Ocean Optics Conference, Victoria, BC, Canada, 7–12 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brewin, R.J.; Raitsos, D.E.; Pradhan, Y.; Hoteit, I. Comparison of chlorophyll in the Red Sea derived from MODIS-Aqua and in vivo fluorescence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Ouillon, S.; Ngoc, D.D.; Herrmann, M.; Tran, V.; Mériaux, X.; Dessailly, D.; Jamet, C.; Duhaut, T.; et al. Assessment and analysis of the chlorophyll-a concentration variability over the Vietnamese coastal waters from the MERIS ocean color sensor (2002–2012). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gower, J.F.R.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Brando, V.E. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volpe, G.; Santoleri, R.; Vellucci, V.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Marullo, S.; D’Ortenzio, F. The colour of the Mediterranean Sea: Global versus regional bio-optical algorithms evaluation and implication for satellite chlorophyll estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Lotliker, A.A.; Miller, P.I.; Ashraf, P.M.; Kumar, T.S.; Suresh, T.; Ragavan, B.R.; Menon, H.B. Assessment of MODIS-Aqua chlorophyll-a algorithms in coastal and shelf waters of the eastern Arabian Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 65, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.; Costa, M. Spatial-temporal bio-optical classification of dynamic semi-estuarine waters in the Salish Sea, Western North America. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczuk, P.; Olszewski, J.; Darecki, M.; Kaczmarek, S. Empirical relationships between coloured dissolved organic matter (CDOM) absorption and apparent optical properties in Baltic Sea waters. Intern. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Donaghay, P.L. Separating in situ and terrigenous sources of absorption by dissolved materials in coastal waters. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans (1978–2012) 2001, 106, 2545–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S. Validation of chlorophyll fluorescence derived from MERIS on the west coast of Canada. Intern. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 28, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R.; Brown, L.; Borstad, G.A. Observation of chlorophyll fluorescence in west coast waters of Canada using the MODIS satellite sensor. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.; Zhou, J.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Fluorescence Component in the Reflectance Spectra from Coastal Waters. II. Performance of retrieval algorithms. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Madriñán, M.J.; Fischer, A.M. Performance of the MODIS FLH algorithm in estuarine waters: A multi-year (2003–2010) analysis from Tampa Bay, Florida (USA). Intern. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6467–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Gilerson, A.; Zhou, J.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Jerez, W.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F. Impact of scattering and absorption of photosynthetic pigments on fluorescence retrieval algorithms for coastal waters. In Proceedings of the SPIE 6743 Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, and Large Water Regions, Florence, Italy, 8 October 2007; p. 674307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Mitchell, B.G.; van Dijken, G.L.; Arrigo, K.R. Regional chlorophyll a algorithms in the Arctic Ocean and their effect on satellite-derived primary production estimates. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2016, 130, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, W.J.; Ackleson, S.G.; Hair, J.W.; Hostetler, C.A.; Miller, W.D. Spatial scales of optical variability in the coastal ocean: Implications for remote sensing and in situ sampling. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 4194–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mouw, C.B.; Yoder, J.A. Primary production calculations in the Mid-Atlantic Bight, including effects of phytoplankton community size structure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Source | Period | N | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institute of Ocean Sciences | 2002–2014 | 618 | chla |
| Pacific Biological Station | 2012, 2013 | 192/194 | chla/Rrs |
| [39] | 2006 | 15 | Rrs |
| Parameter | NIR | SWIR | MUMM + SWIR |
|---|---|---|---|
| τa (443 nm) | |||
| |ψ| (%) | 93.57 | 168.18 | 71.34 |
| ψ (%) | +93.57 | +168.18 | +70.45 |
| |δ| | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.06 |
| τa (675 nm) | |||
| |ψ| (%) | 123.40 | 200.00 | 110.88 |
| ψ (%) | +123.40 | +200.00 | +52.58 |
| |δ| | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| τa (865 nm) | |||
| |ψ| (%) | 91.76 | 150.00 | 88.90 |
| ψ (%) | +91.76 | +150.00 | +88.90 |
| |δ| | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Å (440, 870 nm) | |||
| |ψ| (%) | 24.48 | 24.33 | 27.51 |
| ψ (%) | −3.27 | +11.65 | −13.79 |
| |δ| | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.34 |
| Method | (λ) | % Negative | Count (N) | MAD% | MRD% | RMSE | rlinear | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIR | Rrs(412) | 62 | 14 | 404 | 321 | 0.002 | 0.30 | 0.18 |
| Rrs(443) | 15 | 29 | 99 | −4 | 0.002 | 0.30 | 0.16 | |
| Rrs(488) | 0 | 34 | 58 | −31 | 0.002 | 0.82 | 0.69 | |
| Rrs(531) | 0 | 34 | 54 | −9 | 0.002 | 0.84 | 1.07 | |
| Rrs(547) | 0 | 34 | 38 | −21 | 0.002 | 0.89 | 1.00 | |
| Rrs(667) | 12 | 30 | 54 | −35 | 0.002 | 0.84 | 0.31 | |
| SWIR | Rrs(412) | 64 | 9 | 587 | 550 | 0.003 | 0.24 | 0.27 |
| Rrs(443) | 56 | 11 | 151 | 107 | 0.003 | 0.35 | 0.34 | |
| Rrs(488) | 56 | 11 | 74 | 16 | 0.003 | 0.36 | 0.43 | |
| Rrs(531) | 40 | 15 | 54 | −20 | 0.004 | 0.63 | 0.51 | |
| Rrs(547) | 28 | 17 | 53 | −32 | 0.004 | 0.57 | 0.46 | |
| Rrs(667) | 40 | 13 | 70 | −32 | 0.002 | 0.37 | 0.29 | |
| MUMM + SWIR | Rrs(412) | 52 | 13 | 42 | −13 | 0.002 | 0.69 | 0.85 |
| Rrs(443) | 37 | 16 | 48 | −6 | 0.002 | 0.66 | 0.66 | |
| Rrs(488) | 19 | 22 | 56 | −22 | 0.002 | 0.67 | 0.61 | |
| Rrs(531) | 11 | 23 | 44 | −10 | 0.002 | 0.74 | 0.61 | |
| Rrs(547) | 4 | 23 | 37 | −14 | 0.019 | 0.78 | 0.62 | |
| Rrs(667) | 22 | 21 | 43 | −38 | 0.019 | 0.82 | 0.61 |
| Method | Parameters | Count (N) | MAD% | MRD% | logRMSE | rlinear | Slope | rlog |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIR | chla 8 h | 54 | 481 | 453 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 2.07 | 0.59 |
| chla 6 h | 38 | 510 | 483 | 0.67 | 0.25 | 2.75 | 0.59 | |
| chla 4 h | 32 | 394 | 368 | 0.63 | 0.41 * | 2.87 | 0.61 | |
| chla 2 h | 23 | 489 | 472 | 0.69 | 0.44 * | 3.24 | 0.58 | |
| chla 1 h | 12 | 460 | 438 | 0.69 | −0.10 | −0.31 | 0.34 | |
| SWIR | chla 8 h | 35 | 508 | 452 | 0.60 | −0.09 | −0.49 | 0.23 |
| chla 6 h | 26 | 667 | 611 | 0.70 | −0.15 | −1.04 | 0.16 | |
| chla 4 h | 23 | 741 | 688 | 0.70 | −0.16 | −1.18 | 0.09 | |
| chla 2 h | 16 | 529 | 482 | 0.65 | −0.10 | −0.84 | 0.10 | |
| chla 1 h | 9 | 82 | 31 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.37 | |
| MUMM+SWR | chla 8 h | 82 | 64 | 18 | 0.34 | 0.81 * | 0.79 | 0.74 |
| chla 6 h | 52 | 62 | 14 | 0.35 | 0.76 * | 0.69 | 0.70 | |
| chla 4 h | 46 | 62 | 15 | 0.34 | 0.77 * | 0.71 | 0.72 | |
| chla 2 h | 34 | 67 | 27 | 0.33 | 0.80 * | 0.75 | 0.73 | |
| chla 1 h | 16 | 62 | 21 | 0.33 | 0.83 * | 0.89 | 0.74 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carswell, T.; Costa, M.; Young, E.; Komick, N.; Gower, J.; Sweeting, R. Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua Atmospheric Correction and Chlorophyll Products of Western North American Coastal Waters Based on 13 Years of Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101063
Carswell T, Costa M, Young E, Komick N, Gower J, Sweeting R. Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua Atmospheric Correction and Chlorophyll Products of Western North American Coastal Waters Based on 13 Years of Data. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101063
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarswell, Tyson, Maycira Costa, Erika Young, Nicholas Komick, Jim Gower, and Ruston Sweeting. 2017. "Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua Atmospheric Correction and Chlorophyll Products of Western North American Coastal Waters Based on 13 Years of Data" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101063
APA StyleCarswell, T., Costa, M., Young, E., Komick, N., Gower, J., & Sweeting, R. (2017). Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua Atmospheric Correction and Chlorophyll Products of Western North American Coastal Waters Based on 13 Years of Data. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101063