Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Datasets
2.2. The Role of External DEM in StaMPS-PS
2.3. Processing and Accuracy
3. External DEM Effects in Simulated Experiment
3.1. Simulated Parameters
3.2. Deformation Rate Difference of the Three Platforms
3.3. The Deformation Time-Series Difference in the Three Platforms
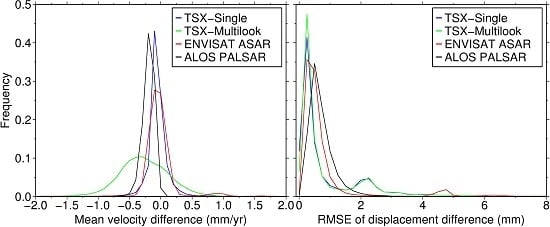
4. Comparative Studies in Real Data Experiment
4.1. PS Selection
4.2. Mean Deformation Rate
4.3. Deformation Time-Series
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of PS Selection
5.2. Analysis of Parameter Estimation
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, B07407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangcai, F.; Zhiwei, L.; Xinjian, S.; Bing, X.; Yanan, D. Source parameters of the 2014 Mw 6.1 South Napa earthquake estimated from the Sentinel 1A, COSMO-SkyMed and GPS data. Tectonophysics 2015, 655, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Hu, J.; Feng, G. Deriving dynamic subsidence of coal mining areas using InSAR and logistic model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Jónsson, S.; Klinger, Y. Which fault segments ruptured in the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and which did not? New evidence from near—Fault 3d surface displacements derived from sar image offsets. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2017, 107, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J. Geodetic model of the 2015 April 25 Mw 7.8 Gorkha Nepal Earthquake and Mw 7.3 aftershock estimated from InSAR and GPS data. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Feng, G.; Wang, T.; Bürgmann, R. Toward full exploitation of coherent and incoherent information in Sentinel-1 TOPS data for retrieving surface displacement: Application to the 2016 Kumamoto (Japan) earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D. InSAR Imaging of Aleutian Volcanoes. In InSAR Imaging of Aleutian Volcanoes; Springer Praxis Books; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 87–345. ISBN 978-3-642-00347-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 978-1-4020-4576-9. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z. Modeling PSInSAR time series without phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.P.; Guillaso, S.; Jolivet, R.; Lasserre, C.; Lodge, F.; Ducret, G. Presentation of the small baseline NSBAS processing chain on a case example: The Etna deformation monitoring from 2003 to 2010 using Envisat data. In Proceedings of the European Space Agency Symposium “Fringe”, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducret, G.; Doin, M.P.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Guillaso, S. DEM corrections before unwrapping in a small baseline strategy for InSAR time series analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Schmidt, D.; Simoni, A. The influence of external digital elevation models on PS-InSAR and SBAS results: Implications for the analysis of deformation signals caused by slow moving landslides in the Northern Apennines (Italy). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S. Topographic correction for ALOS PALSAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3020–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantianuparp, P.; Balz, T.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. Analyzing the topographic influence for the PS-INSAR processing in the Three Gorges region. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3843–3846. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J. Characterizing sudden geo-hazards in mountainous areas by D-InSAR with an enhancement of topographic error correction. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. DEM error correction in InSAR time series. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4249–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, G.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Q. On the accuracy of topographic residuals retrieved by MTInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.J.; Fernández, J. Error estimation in multitemporal InSAR deformation time series, with application to Lanzarote, Canary Islands. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Ruiz, A.M.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bastos, L.; Gil, A.J.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; Sanz de Galdeano, C. PS-InSAR processing methodologies in the detection of field surface deformation—Study of the Granada basin (Central Betic Cordilleras, southern Spain). J. Geodyn. 2010, 49, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bastos, L.C.; Ruiz, A.M. Persistent Scatterer InSAR: A comparison of methodologies based on a model of temporal deformation vs. spatial correlation selection criteria. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, S.N.; Schmidt, D.A.; Deligne, N.I. An analysis of terrain properties and the location of surface scatterers from persistent scatterer interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-F.; Chang, K.-J.; Angelier, J.; Chan, Y.-C.; Deffontaines, B.; Lee, C.-T.; Lin, M.-L. Topographical changes revealed by high-resolution airborne LiDAR data: The 1999 Tsaoling landslide induced by the Chi–Chi earthquake. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A.; Fiedler, H.; Hajnsek, I.; Werner, M.; Younis, M.; Zink, M. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3317–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samadzadegan, F.; Hahn, M.; Bigdeli, B. Automatic road extraction from LIDAR data based on classifier fusion. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, R.B.; Frazier, P.S. High-resolution remote sensing of upland swamp boundaries and vegetation for baseline mapping and monitoring. Wetlands 2010, 30, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perroy, R.L.; Bookhagen, B.; Asner, G.P.; Chadwick, O.A. Comparison of gully erosion estimates using airborne and ground-based LiDAR on Santa Cruz Island, California. Geomorphology 2010, 118, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Astrup, R.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E.; Weydahl, D.J. Estimating spruce and pine biomass with interferometric X-band SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfle, B.; Vetter, M.; Pfeifer, N.; Mandlburger, G.; Stötter, J. Water surface mapping from airborne laser scanning using signal intensity and elevation data. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Pan, K. Gravity anomalies of arbitrary 3D polyhedral bodies with horizontal and vertical mass contrasts up to cubic order. GEOPHYSICS 2017, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xie, R. Coastal subsidence monitoring associated with land reclamation using the point target based SBAS-InSAR method: A case study of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Q. Deformation behavior of Shenzhen soft clay and post-construction settlement. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2002, 24, 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.N.; Feng, G.C.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Peng, X. Generation of high precision DEM from TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 3089–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, R.-F.; Lin, C.-W. Recent landslide movement in Tsaoling, Taiwan tracked by TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X DEM time series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 90-73235-43-X. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to InSAR time series. JOSA A 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagliani, A.; Mosconi, A.; Marzorati, D.; Cremonesi, A.; Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Tamburini, A. Use of satellite radar data for surface deformation monitoring: A wrap-up after 10 years of experimentation. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 19–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Feng, G.C. Modeling minimum and maximum detectable deformation gradients of interferometric SAR measurements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Xie, R.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J. Generalized functional model of maximum and minimum detectable deformation gradient for PALSAR interferometry. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, F.J. The kolmogorov-smirnov test for goodness of fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, M.; Wolfe, D.A.; Chicken, E. Nonparametric Statistical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-470-38737-5. [Google Scholar]
















| SRTM-1arc DEM Single-Look Geocoding | SRTM-1arc DEM Multi-Look Geocoding | TanDEM-X DEM Single-Look Geocoding | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS | DPS | TPS | CPS | DPS | TPS | CPS | DPS | TPS | |
| TerraSAR-X | 238,548 | 123,523 | 362,071 | 198,215 | 125,311 | 323,526 | 198,215 | 162,530 | 360,745 |
| ASAR | 58,740 | 12,895 | 71,635 | 58,740 | 16,075 | 74,815 | |||
| ALOS/PALSAR1 | 150,606 | 15,232 | 165,838 | 150,606 | 15,796 | 166,402 | |||
| SRTM-1arc DEM Single-Look Geocoding | SRTM-1arc DEM Multi-Look Geocoding | SRTM-1arc DEM Single-Look Geocoding | SRTM-1arc DEM Multi-Look Geocoding | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate difference: Mean/Std (mm/year) | Displacement difference: Mean (mm) | |||
| TerraSAR-X | −0.05/0.38 | −0.22/0.54 | 0.88 | 0.86 |
| ASAR | −0.02/0.30 | 0.94 | ||
| ALOS/PALSAR | −0.20/0.10 | 1.47 | ||
| SRTM-1arc DEM Single-Look Geocoding | SRTM-1arc DEM Multi-Look Geocoding | TanDEM-X DEM Single-Look Geocoding | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | 2290 | 2354 | 2409 |
| Area 2 | 7373 | 6982 | 7366 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Z. Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111115
Du Y, Feng G, Li Z, Peng X, Zhu J, Ren Z. Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(11):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111115
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yanan, Guangcai Feng, Zhiwei Li, Xing Peng, Jianjun Zhu, and Zhengyong Ren. 2017. "Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 11: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111115
APA StyleDu, Y., Feng, G., Li, Z., Peng, X., Zhu, J., & Ren, Z. (2017). Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sensing, 9(11), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111115