Characterization of Turbulence in Wind Turbine Wakes under Different Stability Conditions from Static Doppler LiDAR Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement Campaign
2.2. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. General Flow Field Characterization
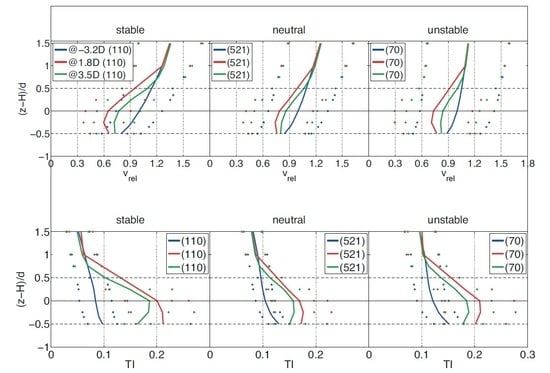
3.2. Average Wake Profiles
3.3. Case Study of the Spectral Signature of a Turbine Wake
3.4. Effects of Stability on Turbulence Spectra in Wakes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| D | Rotor Diameter |
| DBS | Doppler Beam Swing |
| FINO | Forschungsplattform in Nord- und Ostsee |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| RaDAR | Radio Detection and Ranging |
| SoDAR | Sonic Detection and Ranging |
| TI | Turbulence Intensity |
| TKE | Turbulent Kinetic Energy |
| WINTWEX-W | WINd Turbine Wake EXperiment Wieringermeer |
References
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Larsen, G.C.; Frandsen, S.T.; Folkerts, L.; Rados, K.; Pryor, S.C.; Lange, B.; Schepers, G. Comparison of Wake Model Simulations with Offshore Wind Turbine Wake Profiles Measured by Sodar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungo, G.; Porté-Agel, F. Volumetric scans of wind turbine wakes performed with three simultaneous wind LiDARs under different atmospheric stability regimes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 524, 012164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombe, P.J.; Pinson, P.; Vincent, C.; Bøvith, T.; Cutululis, N.A.; Draxl, C.; Giebel, G.; Hahmann, A.N.; Jensen, N.E.; Jensen, B.P.; et al. Weather radars—The new eyes for offshore wind farms? Wind Energy 2014, 17, 1767–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smalikho, I.N.; Banakh, V.A.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.M.; Lundquist, J.K.; Kelley, N.D. Lidar Investigation of Atmosphere Effect on a Wind Turbine Wake. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2554–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.; Smalikho, I. Coherent Doppler Wind Lidars in a Turbulent Atmosphere; Artech House: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Frehlich, R.; Meillier, Y.; Jensen, M.L.; Balsley, B.; Sharman, R. Measurements of boundary layer profiles in an urban environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Calhoun, R.; Billings, B.; Doyle, J. Wind turbulence estimates in a valley by coherent Doppler LiDAR. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Crippa, P.; Wang, H.; Smith, C.M.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Choukulkar, A.; Calhoun, R.; Valyou, D.; Marzocca, P.; Matthiesen, D.; et al. 3D wind and turbulence characteristics of the atmospheric boundary layer. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirocha, J.D.; Rajewski, D.A.; Marjanovic, N.; Lundquist, J.K.; Kosović, B.; Draxl, C.; Churchfield, M.J. Investigating wind turbine impacts on near-wake flow using profiling LiDAR data and large-eddy simulations with an actuator disk model. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 043143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.L.; Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Lundquist, J.K. Quantifying Wind Turbine Wake Characteristics from Scanning Remote Sensor Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 765–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.L.; Lundquist, J.K. Utility-scale wind turbine wake characterization using nacelle-based long-range scanning LiDAR. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, F.; Mann, J.; Larsen, G.C. Light detection and ranging measurements of wake dynamics part I: One-dimensional scanning. Wind Energy 2010, 13, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Banta, R.M.; Pauscher, L.; Vogstad, K.; Schlipf, D.; Wylie, S. Estimating Turbulence Statistics and Parameters from Ground- and Nacelle-Based Lidar Measurements: IEA Wind Expert Report; DTU Wind Energy: Roskilde, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumer, V.M.; Reuder, J.; Dorninger, M.; Zauner, R.; Grubisic, V. Turbulent kinetic energy estimates from profiling wind LiDAR measurements and their potential for wind energy applications. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Cariou, J.P.; Courtney, M.S.; Parmentier, R.; Mikkelsen, T.; Wagner, R.; Lindelöw, P.; Sjöholm, M.; Enevoldsen, K. Comparison of 3D turbulence measurements using three staring wind LiDARs and a sonic anemometer. Meteorol. Z. 2009, 18, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, F.C.; Iungo, G.V.; Porte-Agel, F. 3D turbulence measurements using three synchronous wind LiDARs: Validation against sonic anemometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, M.E.; Lundquist, J.K. The Effect of Wind-Turbine Wakes on Summertime US Midwest Atmospheric Wind Profiles as Observed with Ground-Based Doppler Lidar. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 149, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumer, V.M.; Reuder, J.; Svardal, B.; Sætre, C.; Eecen, P. Characterisation of Single Wind Turbine Wakes with Static and Scanning WINTWEX-W LiDAR Data. Energy Procedia 2015, 80, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.K.; Churchfield, M.J.; Lee, S.; Clifton, A. Quantifying error of LiDAR and sodar Doppler beam swinging measurements of wind turbine wakes using computational fluid dynamics. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StatOil. Hywind Scotland Pilot Park–Executive Summary of the Environmental Statement; Technical Report; StatOil: Stavanger, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schepers, J.G.; Obdam, T.S.; Prospathopoulos, J. Analysis of wake measurements from the ECN Wind Turbine Test Site Wieringermeer, EWTW. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikill, R. An Investigation of Single Wind Turbine Wakes with Static LiDAR Wind Profilers. Master’s Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Gottschall, J.; Courtney, M.S. Can Wind Lidars Measure Turbulence? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadillas, B.; Bégué, A.; Neumann, T. Comparison of turbulence spectra derived from LiDAR and sonic measurements at the offshore platform FINO1. In Proceedings of the 10th German Wind Energy Conference (DEWEK 2010), Bremen, Germany, 17–18 November 2010; pp. 18–21.
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J. Measurement of turbulence spectra using scanning pulsed wind LiDARs. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. (1984–2012) 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, A.C.; Olson, J.B.; Lundquist, J.K.; Dudhia, J.; Gupta, A.K.; Michalakes, J.; Barstad, I. Local and Mesoscale Impacts of Wind Farms as Parameterized in a Mesoscale NWP Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 3017–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungo, G.V.; Porté-Agel, F. Measurement procedures for characterization of wind turbine wakes with scanning Doppler wind LiDARs. Adv. Sci. Res. 2013, 10, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S. Wind Energy Meteorology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 99, pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Højstrup, J. Spectral coherence in wind turbine wakes. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 80, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, Y.A.; Aubrun, S.; Masson, C. Determination of real-time predictors of the wind turbine wake meandering. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Barlas, T.; Bierbooms, W.; van Bussel, G.J.W. Influence of atmospheric stability on wind turbine loads. Wind Energy 2013, 16, 1013–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Martin, C.M.; Lundquist, J.K.; Clifton, A.; Poulos, G.S.; Schreck, S.J. Wind turbine power production and annual energy production depend on atmospheric stability and turbulence. Wind Energ. Sci. 2016, 1, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Instrument | Shadow | Distance (D) | Direction () | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mast Shadow | 0 | 180 | ||
| M3 | WT5 | 3.5 | 315 | |
| WT6 | 2.5 | 31 | ||
| WT7 | 5.4 | 71 | ||
| WT8 | 9.0 | 81 | ||
| WT9 | 12.7 | 85 | ||
| wls67 | M3 | 0.8 | 357 | |
| WT5 | 4.2 | 322 | ||
| WT6 | 3.2 | 23 | ||
| WT7 | 5.7 | 63 | ||
| WT8 | 9.1 | 76 | ||
| WT9 | 12.8 | 81 | ||
| wls37 | WT 5 | 5.2 | 260 | |
| WT6 | 1.8 | 228 | ||
| WT7 | 2.9 | 123 | ||
| WT8 | 6.6 | 107 | ||
| WT9 | 10.3 | 103 | ||
| wls65 | WT 5 | 6.7 | 252 | |
| WT6 | 3.5 | 227 | ||
| WT7 | 3.0 | 156 | ||
| WT8 | 5.9 | 121 | ||
| WT9 | 9.5 | 111 | ||
| Stability Class | Temperature Difference | Data Share | Average Wind Speed at 108 m |
|---|---|---|---|
| stable | 27% | 9.1 s | |
| neutral | 55% | 9.8 s | |
| unstable | 18% | 8.9 s |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumer, V.-M.; Reuder, J.; Oftedal Eikill, R. Characterization of Turbulence in Wind Turbine Wakes under Different Stability Conditions from Static Doppler LiDAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030242
Kumer V-M, Reuder J, Oftedal Eikill R. Characterization of Turbulence in Wind Turbine Wakes under Different Stability Conditions from Static Doppler LiDAR Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(3):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030242
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumer, Valerie-Marie, Joachim Reuder, and Rannveig Oftedal Eikill. 2017. "Characterization of Turbulence in Wind Turbine Wakes under Different Stability Conditions from Static Doppler LiDAR Measurements" Remote Sensing 9, no. 3: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030242
APA StyleKumer, V.-M., Reuder, J., & Oftedal Eikill, R. (2017). Characterization of Turbulence in Wind Turbine Wakes under Different Stability Conditions from Static Doppler LiDAR Measurements. Remote Sensing, 9(3), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030242