Mapping 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change in India Using Global Land Survey Landsat Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Global Land Survey Surface Reflectance Datasets
2.3. Impervious Surface Mapping for 2010
2.4. Impervious Surface Mapping for 2000
2.4.1. Overall Algorithm Design
2.4.2. Algorithm Initialization
2.4.3. No Change Mask Generation
2.4.4. Iterative Training and Prediction (ITP)
2.5. Quantification of 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change
2.6. Validation of 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change
- The 500 most populous Indian cities were classified into seven groups: more than 5 million, 1~5 million, 500~1000 thousand, 250~500 thousand, 100~250 thousand, 50~100 thousand, and less than 50 thousand. From each group, two cities were selected. In total, 14 cities were selected that distribute across different regions of India;
- Eighteen Landsat scene covering these 14 cities were identified;
- For every Landsat scene, randomly select 50 pixels from each of these four groups:, ,,.
- The difference between Google Earth™ and Landsat image acquisition dates is within two years (730 days) for both 2000 and 2010. This constrain could be relaxed if multiple Google Earth™ images with the same ISC were found before, during, and after the date range between GLS-2000 and GLS-2010;
- There are no clouds/shadows in Google Earth™ image for both dates;
- There are no apparent misregistration errors between two Google Earth™ images.
3. Results
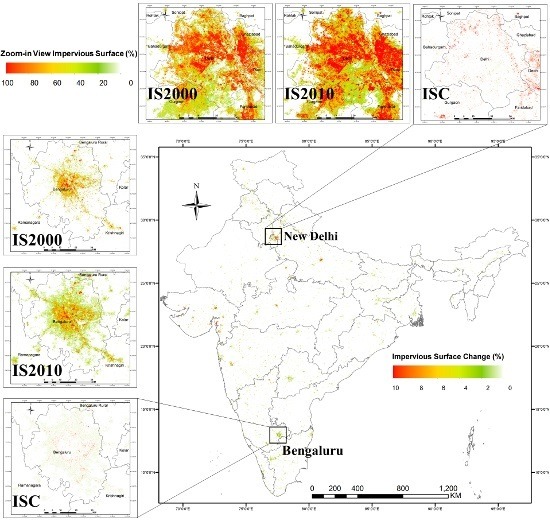
3.1. Visual Assessments of the IS and ISC Products
3.2. Accuracies of IS and ISC Products
3.3. ISC in India and Relationships between ISC and Socio-Economic Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2015); World Urbanization Prospects: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Shepherd, J.M. Global urban land-use trends and climate impacts. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2009, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, J.P.; Groffman, P.M.; Grimm, N.B.; Baker, L.A.; Pouyat, R.V. A distinct urban biogeochemistry? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. A new map of global urban extent from modis satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Global population distribution and urban land use in geophysical parameter space. Earth Interact. 2004, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Land use transitions: Socio-ecological feedback versus socio-economic change. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Sohlberg, R. Global land cover classification at 1 km spatial resolution using a classification tree approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. Modis collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Belward, A.S. The igbp-dis global 1 km land cover data set, discover: First results. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 3291–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIESIN (Center for International Earth Science Information Network). Global Rural-Urban Mapping Project, Version 1 (grumpv1): Urban Extents. 2011. Available online: http://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/grump-v1 (accessed on 15 May 2016).
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Howard, A.T.; Milesi, C.; Bhaduri, B.; Nemani, R. Global distribution and density of constructed impervious surfaces. Sensors 2007, 7, 1962–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with landsat tm and etm+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A pok-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R.; Cowen, D.C. Remote sensing of urban suburban infrastructure and socio-economic attributes. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1999, 65, 611–622. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.M.; Huang, C.; Homer, C.G.; Wylie, B.K.; Coan, M.J. An approach for mapping large-area impervious surfaces: Synergistic use of landsat-7 etm+ and high spatial resolution imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.S.; Li, G.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Moran, E. Methods to extract impervious surface areas from satellite images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, D. Extracting impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery: A comparison. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3209–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.T. Subpixel urban land cover estimation: Comparing cubist, random forests, and support vector regression. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Homer, C. Updating the 2001 national land cover database impervious surface products to 2006 using landsat imagery change detection methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wu, C.S.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of spectral analysis techniques for impervious surface estimation using landsat imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yuan, F. Seasonal sensitivity analysis of impervious surface estimation with satellite imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Baker, M.E.; Townshend, J.R. Urban growth of the washington, D.C.-baltimore, md metropolitan region from 1984 to 2010 by annual, landsat-based estimates of impervious cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-P.; Sexton, J.O.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Townshend, J.R. Characterizing the magnitude, timing and duration of urban growth from time series of landsat-based estimates of impervious cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerts, E.; Pumain, D.; Denis, E. The future of india’s urbanization. Futures 2014, 56, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner of Inida. Provisional Population Totals Paper 2 of 2011. 2011. Available online: http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/census2011_paper2.html (accessed on 20 November 2016).
- Pandey, B.; Joshi, P.K.; Seto, K.C. Monitoring urbanization dynamics in india using dmsp/ols night time lights and spot-vgt data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. Urbanization and agricultural land loss in india: Comparing satellite estimates with census data. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 148, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagendra, H.; Sudhira, H.S.; Katti, M.; Schewenius, M. Sub-regional assessment of india: Effects of urbanization on land use, biodiversity and ecosystem services. In Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities: A Global Assessment; Elmqvist, T., Fragkias, M., Goodness, J., Güneralp, B., Marcotullio, P.J., McDonald, R.I., Parnell, S., Schewenius, M., Sendstad, M., Seto, K.C., et al., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Q.; Banger, K.; Bo, T.; Dadhwal, V.K. History of land use in india during 1880–2010: Large-scale land transformations reconstructed from satellite data and historical archives. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 121, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, B.N.; Solomon, E.K.; Bechdol, M.A.; Herold, N.D. Radar and optical data comparison/integration for urban delineation: A case study. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Rulequest Research Data Mining with Cubist. 2016. Available online: https://www.rulequest.com/cubist-info.html (accessed on 16 December 2016).
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Feng, M.; Noojipady, P.; Anand, A.; Huang, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Collins, K.M.; Channan, S.; DiMiceli, C.; et al. Global, 30-m resolution continuous fields of tree cover: Landsat-based rescaling of modis vegetation continuous fields with lidar-based estimates of error. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Homer, C.; Demitz, J.; Fry, J.; Hossain, N.; Wickham, J. Change of impervious surface area between 2001 and 2006 in the conterminous united states. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 758–762. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Huang, C.; Chander, G.; Noojipady, P.; Masek, J.G. Assessment of the NASA–USGS global land survey (GLS) datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Administrative Areas (GADM) Dataset Version 2.8. 2015. Available online: http://gadm.org (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Planning Commission of India. Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) at Current Prices. 2014. Available online: http://planningcommission.nic.in/data/datatable/0306/table%20168.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2016).
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using modis 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Peng, Y.; Lang, M.G.; Yeo, I.Y.; McCarty, G. Wetland inundation mapping and change monitoring using landsat and airborne lidar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| State/Union Territory | GSDP Change (Billion Rupees) | Population Change (Million People) | ISCA (km2) | STD (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar | 36.64 | 0.02 | 0.77 | 0.18 |
| Andhra Pradesh | N/A | N/A | 55.32 | 0.81 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 85.15 | 0.28 | 3.29 | 0.58 |
| Assam | 875.07 | 4.53 | 34.97 | 0.57 |
| Bihar | 1896.61 | 20.93 | 42.17 | 0.62 |
| Chandigarh | 177.21 | 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.02 |
| Chhattisgarh | 1033.33 | 4.71 | 34.71 | 0.75 |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | N/A | N/A | 2.80 | 0.05 |
| Daman and Diu | N/A | N/A | 1.09 | 0.02 |
| Goa | 289.28 | 0.11 | 4.79 | 0.12 |
| Gujarat | 4709.9 | 9.79 | 307.72 | 0.88 |
| Haryana | 2364.54 | 4.67 | 65.23 | 0.43 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 478.09 | 0.78 | 14.44 | 0.48 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | 477.2 | 2.48 | 30.18 | 0.66 |
| Jharkhand | 1088.22 | 6.02 | 48.09 | 0.57 |
| Karnataka | 3423.65 | 8.40 | 167.59 | 0.89 |
| Kerala | 2299.82 | 1.55 | 27.40 | 0.39 |
| Lakshadweep | N/A | N/A | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 2249.25 | 12.21 | 134.25 | 1.13 |
| Maharashtra | 9263.6 | 15.62 | 304.42 | 1.23 |
| Manipur | 71.35 | 0.43 | 1.84 | 0.30 |
| Meghalaya | 119.34 | 0.66 | 6.05 | 0.30 |
| Mizoram | 52.51 | 0.20 | 1.69 | 0.29 |
| Nagaland | 92.31 | −0.01 | 4.97 | 0.26 |
| NCT of Delhi | 2319.3 | 2.90 | 36.37 | 0.08 |
| Odisha | 1678.27 | 5.24 | 61.23 | 0.80 |
| Puducherry | 103.71 | 0.27 | 1.49 | 0.05 |
| Punjab | 1768.19 | 3.42 | 73.52 | 0.46 |
| Rajasthan | 3116.51 | 12.15 | 67.60 | 1.18 |
| Sikkim | 74.8 | 0.07 | 1.76 | 0.17 |
| Tamil Nadu | 5164.51 | 10.03 | 148.64 | 0.73 |
| Telangana | N/A | N/A | 73.43 | 0.69 |
| Tripura | 146.12 | 0.48 | 13.17 | 0.21 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 4887.38 | 33.53 | 388.78 | 1.09 |
| Uttarakhand | 825.52 | 1.63 | 48.18 | 0.47 |
| West Bengal | 3810.65 | 11.13 | 65.56 | 0.59 |
| Total India | 62,939.65 | 181.99 | 2274.62 | 3.92 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Brown de Colstoun, E.C. Mapping 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change in India Using Global Land Survey Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040366
Wang P, Huang C, Brown de Colstoun EC. Mapping 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change in India Using Global Land Survey Landsat Data. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(4):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040366
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Panshi, Chengquan Huang, and Eric C. Brown de Colstoun. 2017. "Mapping 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change in India Using Global Land Survey Landsat Data" Remote Sensing 9, no. 4: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040366
APA StyleWang, P., Huang, C., & Brown de Colstoun, E. C. (2017). Mapping 2000–2010 Impervious Surface Change in India Using Global Land Survey Landsat Data. Remote Sensing, 9(4), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040366