Abstract
Spaceborne Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Interferometry (MT-InSAR) has been a valuable tool in mapping motion phenomena in different scenarios. Recently, the capabilities of MT-InSAR for risk monitoring and preventive analysis of heritage sites have increasingly been exploited. Considering the limitations of conventional MT-InSAR techniques, in this study a two-step Tomography-based Persistent Scatterers (PS) Interferometry (Tomo-PSInSAR) approach is proposed for monitoring ground deformation and structural instabilities over the Ancient City Walls (Ming Dynasty) in Nanjing city, China. For the purpose of this study we utilized 26 Stripmap acquisitions from TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X missions, spanning from May 2013 to February 2015. As a first step, regional-scale surface deformation rates on single PSs were derived (ranging from −40 to +5 mm/year) and used for identifying deformation hotspots as well as for the investigation of a potential correlation between urbanization and the occurrence of surface subsidence. As a second step, structural instability parameters of ancient walls (linear motion rates, non-linear motions and material thermodynamics) were estimated by an extended four-dimensional Tomo-PSInSAR model. The model applies a two-tier network strategy; that is, the detection of most reliable single PSs in the first-tier Delaunay triangulation network followed by the detection of remaining single PSs and double PSs on the second-tier local star network referring to single SPs extracted in the first-tier network. Consequently, a preliminary phase calibration relevant to the Atmospheric Phase Screen (APS) is not needed. Motion heterogeneities in the spatial domain, either caused by thermal kinetics or displacement trends, were also considered. This study underlines the potential of the proposed Tomo-PSInSAR solution for the monitoring and conservation of cultural heritage sites. The proposed approach offers a quantitative indicator to local authorities and planners for assessing potential damages as well as for the design of remediation activities.
1. Introduction
As irreplaceable sources of life and inspiration, heritage is the witness to past civilizations and past social evolution, and can hold lessons for modern society. Nowadays, the sustainability of heritage is facing challenges induced, in the long-term, by natural degradation (e.g., erosion under environmental change) and in the short-term by deterioration due to anthropogenic activities (e.g., urbanization) and geohazards (e.g., earthquake). Spatio-temporal changes in motion patterns, either at a regional scale or instabilities at a structural level, could be typical precursors implying the potential vulnerability of heritage sites.
Apart from point-based measurements, like precise leveling and GPS surveys, Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Interferometry (MT-InSAR) technique [1], including Persistent Scatterers (PS) SAR interferometry (PSInSAR) [2,3,4,5], Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) [6] and SqueeSAR [7], have been proved effective tools for the monitoring of regional displacements with up to few millimeters accuracy. The development of MT-InSAR approaches was led by the technological advancements of satellite SAR sensors, moving from the first generation SAR missions, with medium spatial resolution and monthly revisit cycles in around 2000 (e.g., Envisat ASAR, ALOS PALSAR, Radarsat-1), to the second generation SAR missions like TerraSAR/TanDEM-X, Cosmo-SkyMed constellation, Radarsat-2 and ALOS PALSAR-2, with high resolution and weekly-to-daily revisit cycles in around 2010. Generally, the accumulation of long time series of SAR data hastened a new era of MT-InSAR for risk monitoring and preventive diagnosis of monuments as well as their surroundings, such as the Historic Centre of Rome, Italy [8,9], Angkor site, Cambodia [10], Mexico City, Mexico [11] and the Summer Palace, China [12]. Those pilot studies are beneficial for the conservation of heritage sites; nonetheless, further investigation is required considering the following aspects: first, the feasibility of MT-InSAR approaches introduced for the assessment of monuments and heritage sites are not systematically exploited and, second, the capabilities of high-resolution spaceborne SAR data for the structural instability of monuments are not fully estimated, particularly when the spatial density of measuring points overlaid on monuments are low.
In this study, a heritage-monitoring-oriented Tomography-based Persistent Scatterers Interferometry (Tomo-PSInSAR) approach is proposed, based on a two-step estimation scheme. A tradeoff between the monitoring capability (from regional to monument scale) and the computation efficiency of Tomo-PSInSAR was resolved. Owing to the two-tier network strategy applied, the phase calibration related to the Atmospheric Phase Screen (APS) in the Tomo-PSInSAR procedure is not required. Generally, Tomo-PSInSAR outperforms PSInSAR in the detection of PS points by jointly analyzing SAR amplitude and phase information [13], which is also essential for structural instability monitoring, taking advantage of the increased observation samples in vertical. The performance of the proposed approach was then evaluated over the Ming Dynasty City Walls (dating back to 600 B P) in Nanjing City, China, exploiting multi-temporal TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X data.
2. Study Site and Data Used
2.1. Study Site
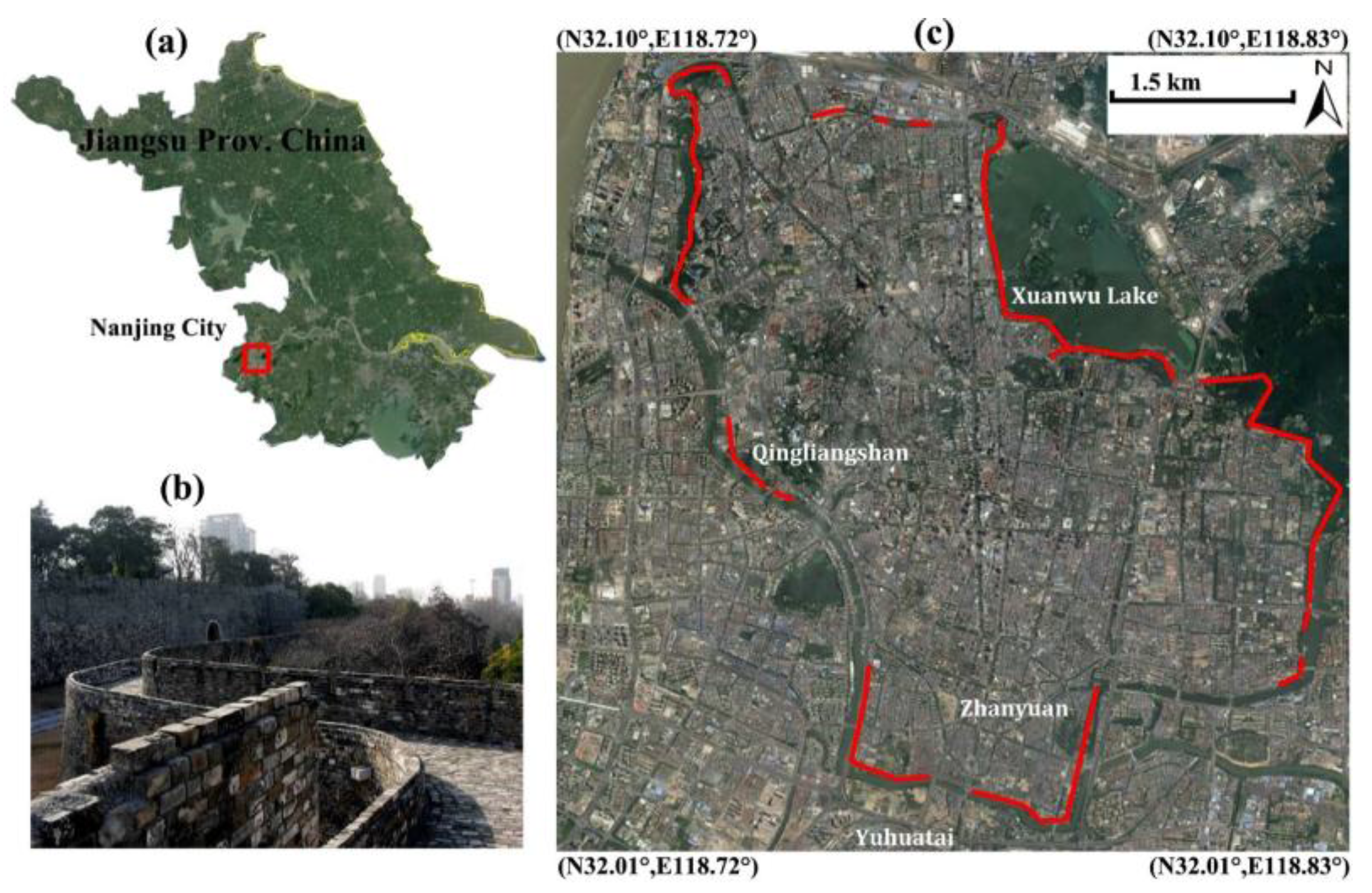
As the capital city of Jiangsu province, Nanjing is the second largest city in the lower Yangtze River region of China. Influenced by the East Asian monsoon, a humid subtropical climate prevails with average annual rainfall of 1090 millimeters and average temperature ranging from 2.7 °C in January to 28.1 °C in July. Due to its strategic location and the surrounding fertile land, Nanjing served as the capital of ten Chinese political regimes for 1800 years, including Eastern Wu (one of the three major states in the Three Kingdoms period, 211–280 AD), the Eastern Jin and the Southern Dynasties (Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang and Chen, 317–589 AD), the Southern Tang of the Ten Kingdoms (937–976 AD), the empire of Ming Dynasty (1368–1421 AD) and finally the Republic of China (1927–1937, 1945–1949). The splendid history of Nanjing left us various sites of cultural heritage, such as the World Heritage of Ming Xiaoling Mausoleum and the well-known Ming Dynasty City Walls. This ancient city wall, totally 48 km long, was constructed by the first emperor of the Ming Dynasty (Zhu Yuanzhang, Hongwu Emperor) in 1368. At present, the well preserved part of the wall is about 25.1 km (Figure 1) and is considered to be the longest surviving city wall in China.
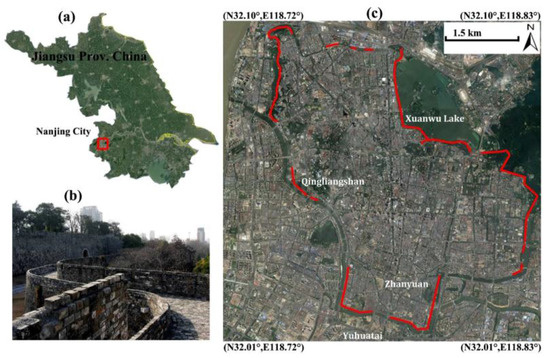
Figure 1.
(a) Location of Nanjing City indicated by the red rectangle; (b) Photograph of city wall remains and (c) the preserved sections marked by red lines overlayed on Google Earth imagery.
2.2. TerraSAR-X and Other Complimentary Data
TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X (TerraSAR-X add-on for Digital Elevation Measurement, the name of TerraSAR-X’s twin satellite), are second-generation spaceborne SAR missions from the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Airbus Defence and Space (former EADS Astrium). They are capable of acquiring high-resolution and wide-area radar images in five main image modes (Staring Spotlight, High resolution Spotlight, Stripmap, ScanSAR and Wide ScanSAR), independent of the weather conditions in X-band (3.1 cm wavelength). For the purpose of the study, 26 ascending Stripmap SAR acquisitions (in HH polarization), acquired from May 2013 to February 2015 (Table 1), were utilized for monitoring the Ming Dynasty City Walls. The swath coverage of the SAR data extends over 30 × 50 sq. km. Pixel samplings in azimuth and range direction are 2.04 m and 0.91 m respectively, approximately equal to a ground resolution of 3 m considering a central incidence angle of 37.3°.

Table 1.
Interferometric parameters of TerraSAR/TanDEM-X acquisitions in conjunction with the corresponding temperature data. The acquisition of 2014-01-28 (indicated by ‘*’ symbol) was selected as the reference imagery for the interferogram generation to minimize spatial-temporal decorrelation.
The 3-arcsecond (~90 m) resolution Digital Elevation Model (DEM) from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) of the United States Geological Survey (USGS) were initially used for topographic phase simulation and removal. SRTM data were further used for geocoding of InSAR products, namely the transformation from Range-Doppler SAR imaging coordinates to the Universal Transverse Mercator mapping coordinate system. Daily maximum temperature data (http://lishi.tianqi.com/Nanjing/index.html), collocated to SAR acquisitions, were obtained (Table 1) for the calculation of thermodynamics of wall materials using the extended Tomo-PSInSAR model [14].
3. Principles and Methodology
3.1. Rational Basis
The Tomo-PSInSAR [15,16] technique integrates merits from PSInSAR [3] and SAR tomography [17,18]. Interferograms were generated using the star-graph approach based on the reference imagery selected. Orbit parameters (disseminated with SAR data) and SRTM DEM data were applied for the removal of flat-Earth and topographic phase, resulting in differential interferograms whose phase comprises four components:
where is the residual height contribution, is the deformation contribution we are interested, is the atmospheric phase delay contribution, is the sum of all decorrelation noises including errors from data processing (e.g., co-registration and phase unwrapping), and is the phase unwrapping operator. In Equation (1), can be formulated by:
where is the normal baseline with respect to the reference imagery, is the wavelength, is the slant range between target and sensor, and is the slant elevation (vertical height with the incidence angle of ). in Equation (1) can be expressed by Formulas (3) and (4), when a linear motion [13,15,19] or an extended motion (linear motion plus thermal expansion) model [14,20,21] is applied, respectively:
where and are temporal and thermal baseline, respectively; and are linear deformation rate and thermal amplitude respectively.
For a given range-azimuth pixel exhibiting ideal scattering from one or more point targets, the mathematical model for the extended 4-dimentional (space-velocity-temperature) Tomo-PSInSAR [22] can be formulated as [23]:
where is the Single Look Complex (SLC) pixel value in the nth layer of N coregistered interferometric stacks, for . is the target reflectivity profile in the space of (s, v, k). , , is the range of the expected elevation, linear motion and phase-to-temperature sensitivity value respectively. In contrast to PSInSAR, Tomo-PSInSAR synergistically analyzes the amplitude and phase of points based on the assumption of more than one PS in one pixel. Consequently, the ensemble coherence of PSInSAR (Formula (6)) can be modified into Formula (7) [21] to reconstruct the tomography for the motion, height and thermal amplitude parameters calculation using spectral estimators. It should be mentioned that the module of the maximum value of the normalized beamforming can be equivalent to the Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test (GLRT) [13]:
where is the complex values of pixels after the differential interferometry, is the transpose and conjugate operation, is the amplitude removal operation, and is the repeat-pass of SAR acquisitions.
3.2. Two-Step Tomo-PSInSAR Approach
For optimization between computation efficiency and observation/analysis extent, a two-step Tomo-PSInSAR processing scheme was implemented; elaborated initially at a regional-scale for wide surface area deformation monitoring, followed by a monument-scale analysis for structural instability assessment.
As a first step, a linear motion model (Formula (3)) was applied for the surface deformation monitoring. Single PS candidates were initially selected using the amplitude dispersion criterion [3], e.g., a threshold of 0.22 in this study. Then, a Delaunay triangulation was applied to connect point candidates for the estimation of relative parameters (height and linear motion rates) at arcs based on the combination of beamforming and an M-estimator [24]. An advantage of such an approach is that atmospheric artifacts can be ignored. After that, the motion and height estimates were integrated through network adjustment to refer measurements to a common reference point. For the potentially ill-adjusted regulate problem of the matrix consisting of −1, 0 and 1, a ridge estimator [21] was introduced to the regional-scale Tomo-PSInSAR method; where −1 at one row of the matrix represents the starting single PS candidate of one arc and 1 represents the end single PS candidate of the arc. The ensemble coherence threshold of 0.78 was further applied for the finalization of single PS points.
As a second step, the extended Tomo-PSInSAR model with a two-tier network was introduced for height and motion estimation (linear rates and thermal amplitudes, see Formula (4), as well as for retrieving deformation time series of PS points. In the first-tier Delaunay triangulation network, the core algorithms described in the first step were applied (ensemble coherence threshold of 0.78 for single PS). The Tomo-PSInSAR is capable of separating overlaid PS in the same location, minimizing the unfavorable layover effects of slant-range imaging in SAR data. Thus, in the second-tier local star network, double PS (overlaying PS) and the remaining single PS points were extracted using the local maximum ratio [21] and amplitude dispersion criterion [3] respectively, referring to single PSs extracted from the first-tier network. An enhanced PS density (double PSs and remaining single PSs with ensemble coherence threshold of 0.60 and 0.75 respectively) was derived especially on monuments of interest. Owing to the two-tier network applied, the removal of the Atmospheric Phase Screen (APS) is no longer needed. Following analysis involved temporal high-pass filtering (a Gaussian filter with a temporal threshold of 0.1-year) to compensate for residual phases in the time series at each arc after subtraction of height and motion components. This approach is convenient for separating atmospheric artifacts from un-modeled non-linear motions before their integrations. Finally, the accumulated deformation time series were derived on a monument-scale, with reference to the first SAR acquisition, allowing the monitoring and analysis of potential structural risks.
3.3. Technology Improvements
The scientific improvement of the proposed two-step Tomo-PSInSAR can be summarized into three aspects. First, a coarse-to-fine observation strategy (large-scale hotspot identification followed by detailed monument-scale monitoring) was introduced for the optimization of computation efficiency in detection motion anomalies coupled with understanding kinetics of monuments. Second, contrary to current two-step approaches [23,25], the preliminary removal of APS in this study can be avoided due to the applied two-tier network in the detection of single and double PS points using the extend Tomo-PSInSAR model with two sequential sub-procedures. Finally, the robustness of parameter estimation at arcs and the network adjustment of the Tomo-PSInSAR approach can be guaranteed owing to the combination of beamforming, M-estimator and ridge estimator.
4. Results and Interpretation
In order to understand the impact of urbanization (e.g., subways construction) and the thermodynamics of materials on the vulnerability of Ming Dynasty City Walls in Nanjing, the developed two-step Tomo-PSInSAR approach was utilized to quantitatively assess motion trends on the monument itself, as well as its surroundings.
The acquisition of 2014-01-28 (stable weather conditions) was selected as the reference scene to minimize the spatio-temporal decorrelation and atmospheric artifacts. The time series of SAR data were co-registered using the amplitude-based cross-correlation approach, resulting in a high accuracy of up to 0.08 pixels in azimuth and 0.09 pixels in range direction. Differential interferograms were then generated following commonly applied procedure of flattening, DEM simulation and topographic phase.
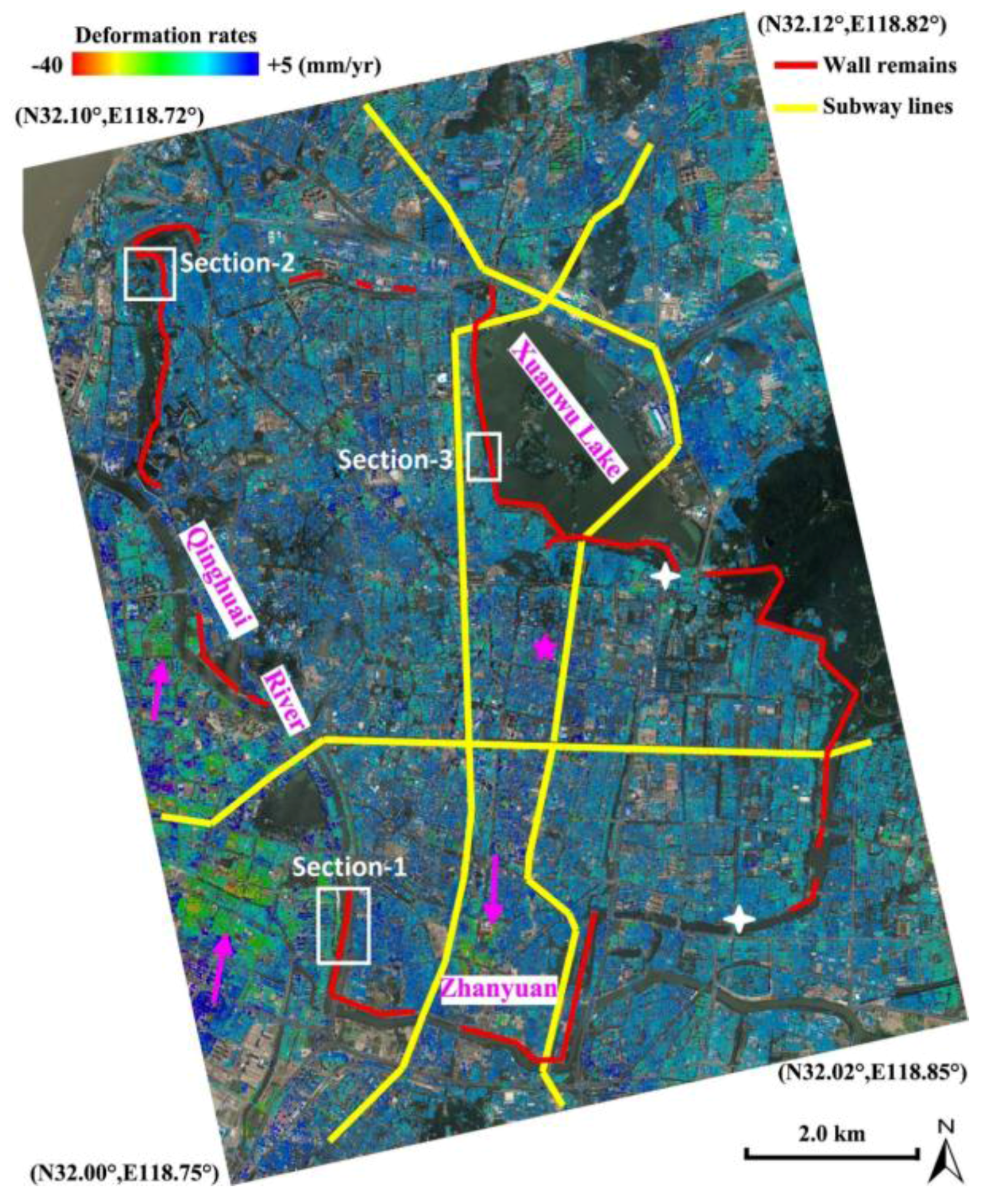
A reference point located at Southeast University’s Sipailou Campus (pink star in Figure 2) was selected for the calibration of InSAR-derived motion measurements. The stability of the local reference is ensured since it is located over a mature residential zone, and consequently the potential impact from construction instability is negligible. In addition, the geological background [26] indicates its distance from Quaternary deposits of thick soft sediments, such as Xuanwu Lake and Zhanyuan (Figure 1).
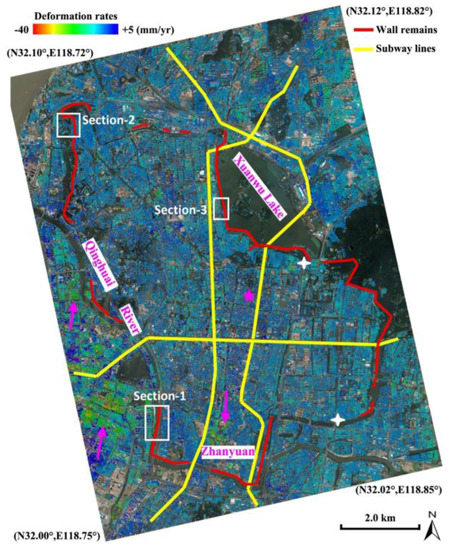
Figure 2.
Surface motion rates at the surroundings of Nanjing city downtown, derived from region-scale Tomo-PSInSAR. City-wall remains (red lines) and the current subway lines (yellow lines) are shown. Local land subsidence patterns are indicated (pink arrows). Cross-section-1, 2 and 3 (white rectangles), were applied for the monument-scale Tomo-PSInSAR investigation. Precise leveling data from two observation points were indicated by white crosses.
4.1. Regional-Scale Monitoring
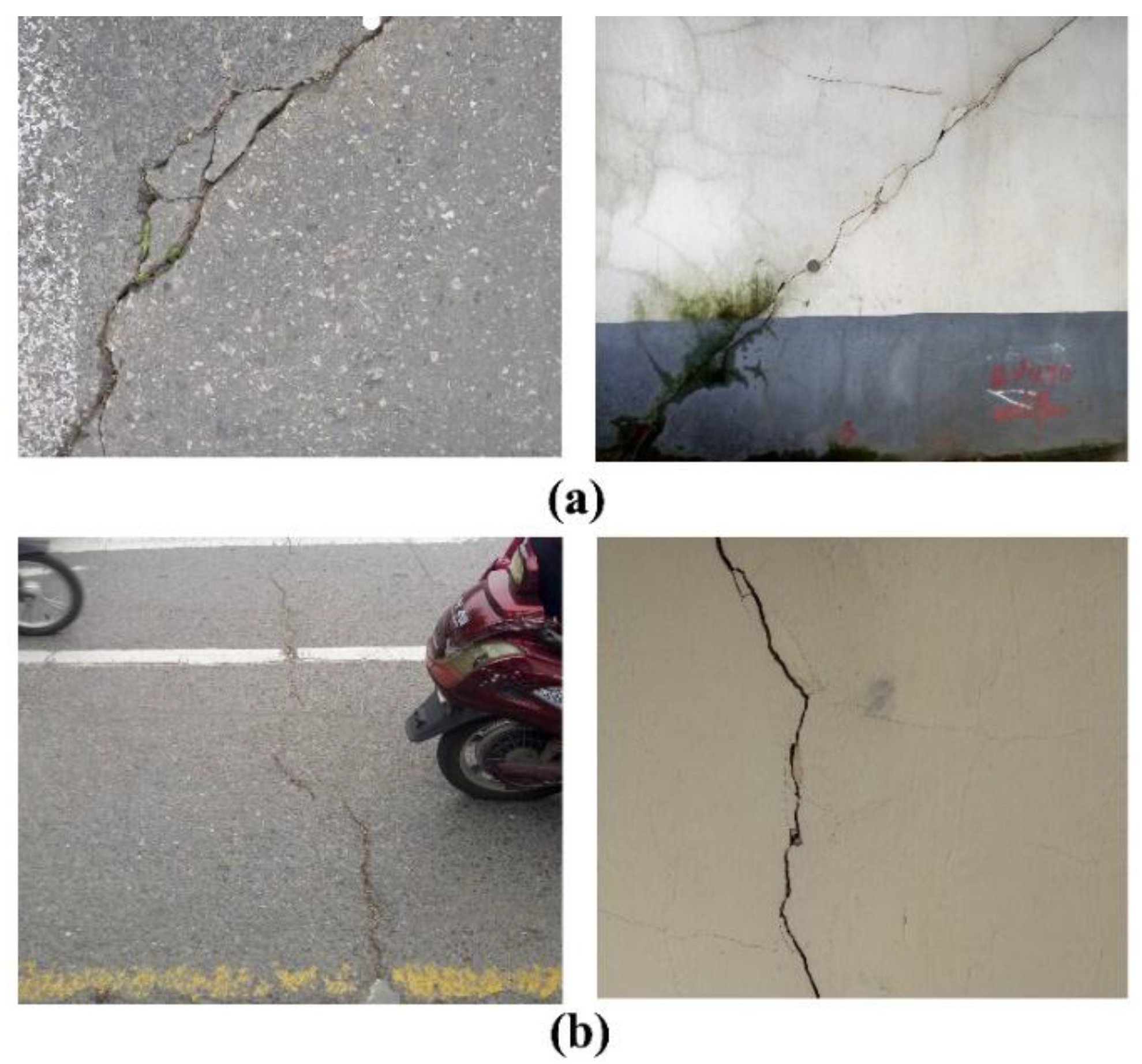
Concerning the regional-scale monitoring, the estimated deformation rates over Nanjing city downtown were primary in the range of −40.0 mm/year to +5.0 mm/year. Overall, the core urban area (enclosed by the ancient city walls in Figure 2) is relatively stable, with deformation ranging from −10.0 mm/year to +5.0 mm/year. However, a local subsidence pattern was observed in the Zhanyuan zone, with deformation rates larger than −20.0 mm/year. Moreover, several subsidence patterns, with rates larger than −20.0 mm/year, were also recognized West of the Qinghai River. A previous study from Shi et al. [27] indicated that the soft soil deposits within the city walls of Nanjing were predominately formed in the Holocene. Drill core data revealed that the near surface geology in the downtown area is a substrate of bedrock overlaid by a varying thickness (approximately 20 to 40 m) of silt sand and clay. Generally, the shallowest depths of bedrock are located at the middle regions of Qingliangshan and the southern regions surrounding Yuhuatai, whereas thickest deposits are located in north basin of Xuanwu Lake and south basin of Zhanyuan [26] (Figure 1). The subsidence pattern centered in Zhanyuan could be attributed to the local differences in geological condition. A thicker soft soil deposit results in an aggravated surface subsidence due to physical soil consolidation and creeping, particularly triggered by construction works such as the subways. Cracks and/or fissures were observed on the ground and buildings surrounding the above-mentioned area during field campaigns, as illustrated in Figure 3a. In contrast, recent floodplain soft soil deposits, with a thickness of up to 60–90 m, are well developed and spread along the lower reaches of the Yangtze River in the western Nanjing. During the last two decades, this region was heavily developed, including the construction of residential zones and underground space facilities (subway lines, tunnels below rivers, etc.), indicating high susceptibility to damages. The regional-scale InSAR observations indicate that this specific zone is still vulnerable to surface subsidence (Figure 2). Those motion anomalies could be caused by the heterogeneity of soft soil consolidations triggered by civil construction and urban expansion. Analogously, fissures and cracks were observed on the ground as well as on buildings during in-situ field observations (Figure 3b).
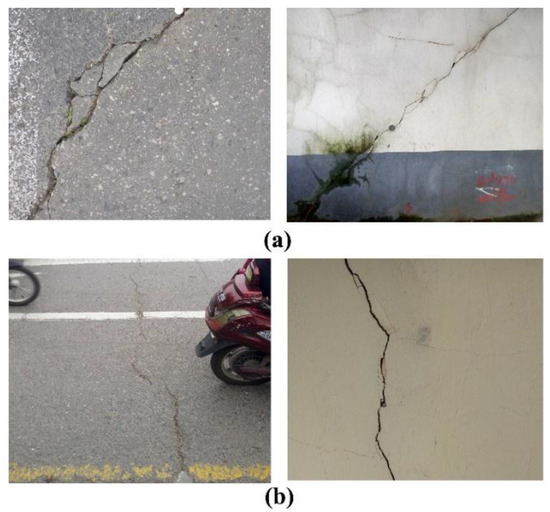

Figure 3.
Cracks and fissures observed during field campaign undertaken in November 2016, (a) Zhanyuan area and (b) local subsidence pattern west of Qinghuai River.
As illustrated in Figure 2, there are four cross sections between city wall remains (red lines) and subway lines (yellow lines). The subway system in Nanjing city is comprised of Line 1, 2 and 3; in operation since 2005, 2010 and 2015 respectively. Fortunately, no evident surface motions were observed in those sections except the one in the south dike of Xuanwu Lake, indicating a regional moderate-subsidence ranging from −12.0 mm/year to −8.0 mm/year (interpreted based on local geological conditions, such as the occurrence of a thick soft-soil deposit). However, several future subway lines have already been designed, and some of them would definitely run beneath the wall remains. Thus, the impact of civil construction such as subways on the sustainability of ancient city walls needs to be deliberately assessed using geotechnical studies, aided by Earth observation measurements such as the InSAR monitoring system presented herein.
4.2. Monument-Scale Monitoring
For the detailed monitoring of structural instability in city walls, the extended Tomo-PSInSAR model was applied. Three cross-sections along selected wall remains were investigated, as indicated by white rectangles in Figure 2. The selection of the specific cross-sections was based mainly on the degree of exposure to the sensor’s line-of-sight geometry, that is, the monument wall’s direction being parallel to satellite flight paths.
4.2.1. Section-1
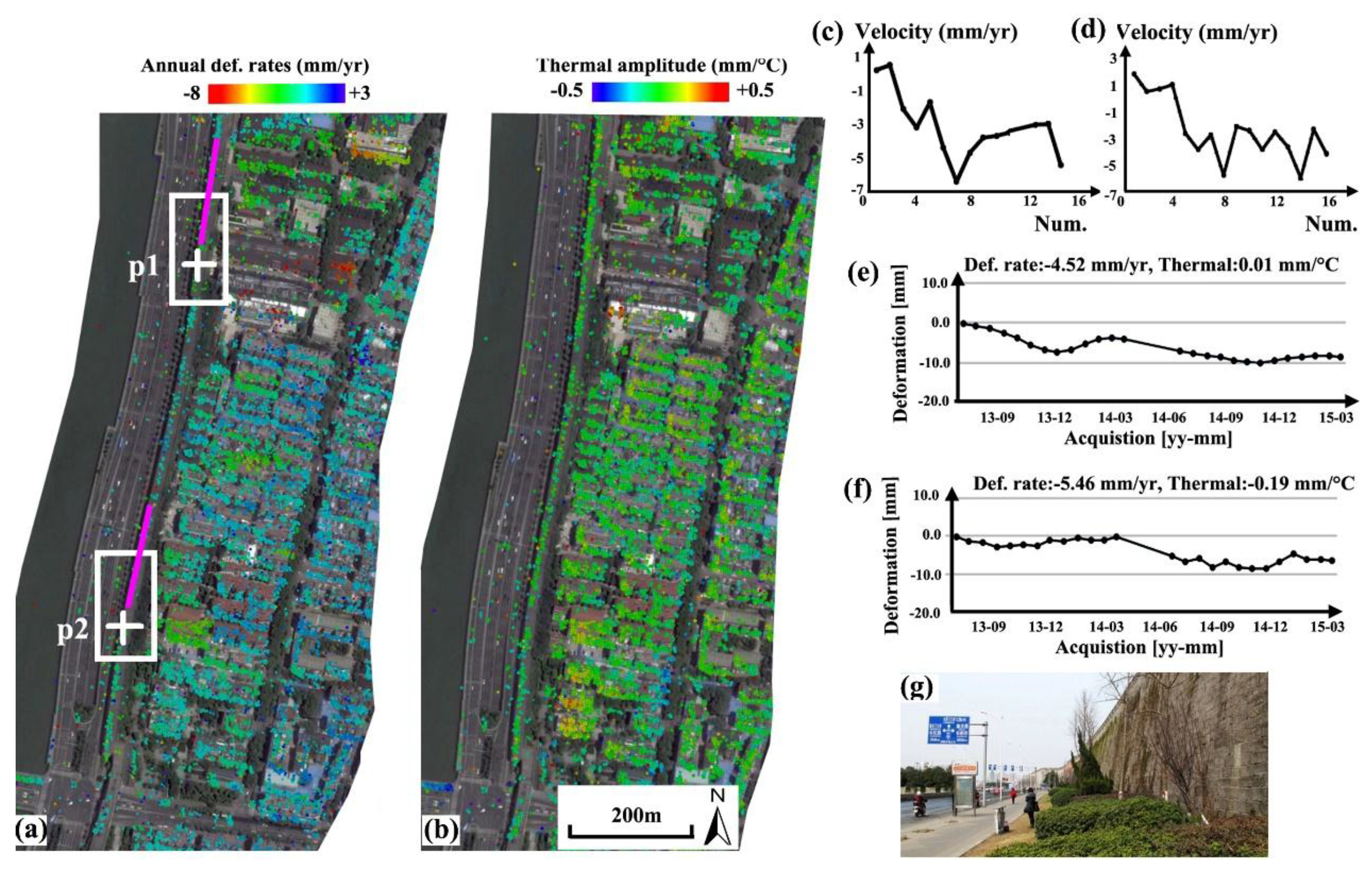
As illustrated in Figure 2, terrain in this region is relatively stable. Separated by the Qinhuai River, the geology of this region is different from the core subsidence 1.2–1.4 km to the West. Apart from surface subsidence, the heterogeneity of structural motions could be another factor that influences the monuments’ susceptibility. In the monument-scale observation, physical parameters of motion, height and material thermodynamics were estimated simultaneously using the extended Tomo-PSInSAR model. The derived linear deformation rates and thermal amplitudes of monuments in the Section-1 was illustrated in Figure 4. Non-linear motions were separated from atmospheric artifacts, resulting in the deformation time series of targets observed. Both deformation rates (Figure 4a) and thermal amplitudes (Figure 4b) indicate that the ancient city walls in Section-1 are stable compared with the surrounding surface and buildings, with values primarily in the range of −6.0 to +3.0 mm/year and −0.15 to 0.15 mm/°C (corresponding to a contraction-expansion thermodynamics with values range from −4.5 to +4.5 mm in case for a seasonal temperature variation up to 30 °C). Nonetheless, two mild-sinking subzones (−2.0 to −5.0 mm/year) were also observed, as indicated by white rectangles, which were probably triggered by the subsidence phenomena (with values up to −8.0 mm/year) in their east vicinities. Two velocity profiles measuring PS points along the wall remains were shown in Figure 4c,d; and their corresponding velocity values (first profile with 14 measuring points and the other with 16 measuring points) were listed in Table 2. In general, a declining motion trend (approximately −3.0 mm/year) can be observed from normal sections (−1.5 to +1.5 mm/year), shifting into sinking subzones (−3.0 to −6.0 mm/year). Motion time series of two PS points (p1 and p2, Figure 4e,f) indicate that linear motion is dominant complimentary with seasonal non-linear components (particularly evident in Figure 4e) that could be contributed by the thermodynamics of the materials. Field observations (Figure 4g) indicate that the biological deterioration can be ignored due to the absence of trees along this section.
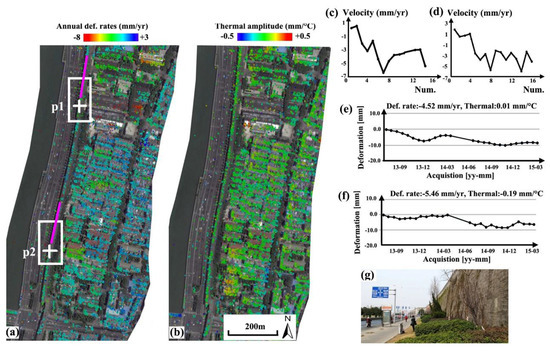
Figure 4.
Section-1 (highlighted by the white rectangle in Figure 2) of wall remains. (a) Deformation rates and (b) thermal amplitude along the linear wall remains; (c,d) motion velocities of PS points along two profiles (highlighted by pink lines); (e,f) motion time series of PS points “p1 and p2, indicated by white crosses” located in mild sinking subzones (indicated by white rectangles); (g) Photo obtained from field visits.

Table 2.
Measuring points along two profiles (the first one with 14 observations and the second with 16 observations) indicated by pink lines in Figure 4.
4.2.2. Section-2
The derived annual deformation rates and material thermodynamics of the Section-2 city wall monuments were illustrated in Figure 5. Analogously to Section-1, a steady condition of monuments was also observed, with motion rates in the range of −3.0 to +3.0 mm/year (Figure 5a), although the eastern side of the wall is accompanied by trees (see background imagery on the courtesy of Google Earth in Figure 5). It implies that the biological deterioration of the wall’s susceptibility is limited to short terms. Due to the disturbance from the canopy cover, the distribution of PS points along the linear monument was uneven. Furthermore, an anomaly of thermal amplitudes was detected on the Yifeng Gate, as indicated by the white rectangle in Figure 5b. The heterogeneity of thermodynamics was generally along with the two stores of the gate (Figure 5b); that is, the lower store indicating mild amplitudes (e.g., absolute values within 0.1 mm/°C) versus the second-high store indicating an expansion trend (e.g., with values around 0.2 mm/°C). This phenomenon can be interpreted two-fold: first, the architectural materials of these two stores are different and the second one indicates larger coefficient of linear thermal expansion; second, thermal amplitudes measured on the second store is the accumulation value from the foundation and higher architecture, resulting in magnified values. Note that, whatever the cause of this anomaly, the heterogeneity of thermal amplitude (0.1 mm/°C, corresponding to an expansion difference of 3 mm in a seasonal cycle) could be destructive for the sustainability of the gate monument in the medium-long term. The impact of thermodynamics from two different stores can also be observed from the PS time series, as illustrated in Figure 5c,d, p1 from the first and p2 from the higher-second store. The measuring point from the higher stores (e.g., p2) indicates a more distinctive non-linear seasonal trend, primarily attributed to thermal kinetics.
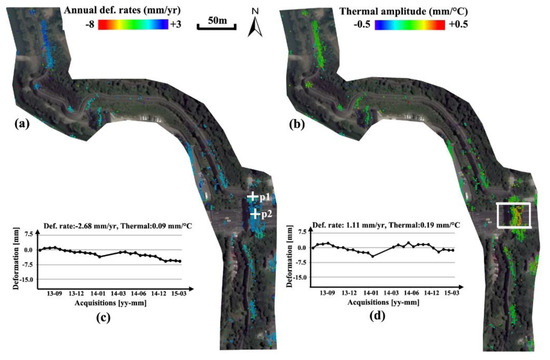
Figure 5.
Section-2 (see Figure 2) of wall remains showing (a) annual deformation rates; (b) thermal amplitudes with difference values on Yifeng Gate (white rectangle); (c,d) are the motion time series of PS points “p1 and p2” on Yifeng Gate (white crosses).
4.2.3. Section-3
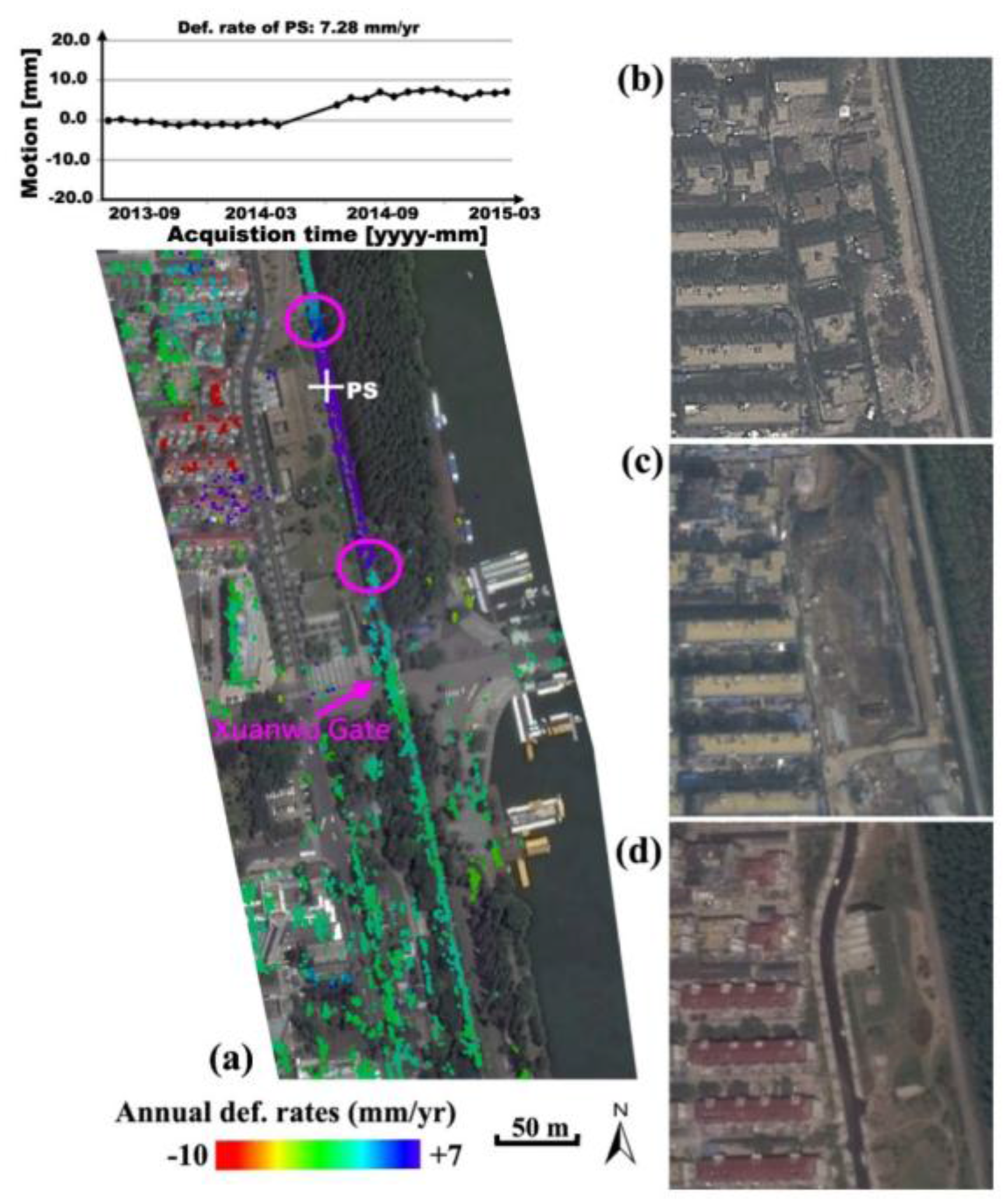
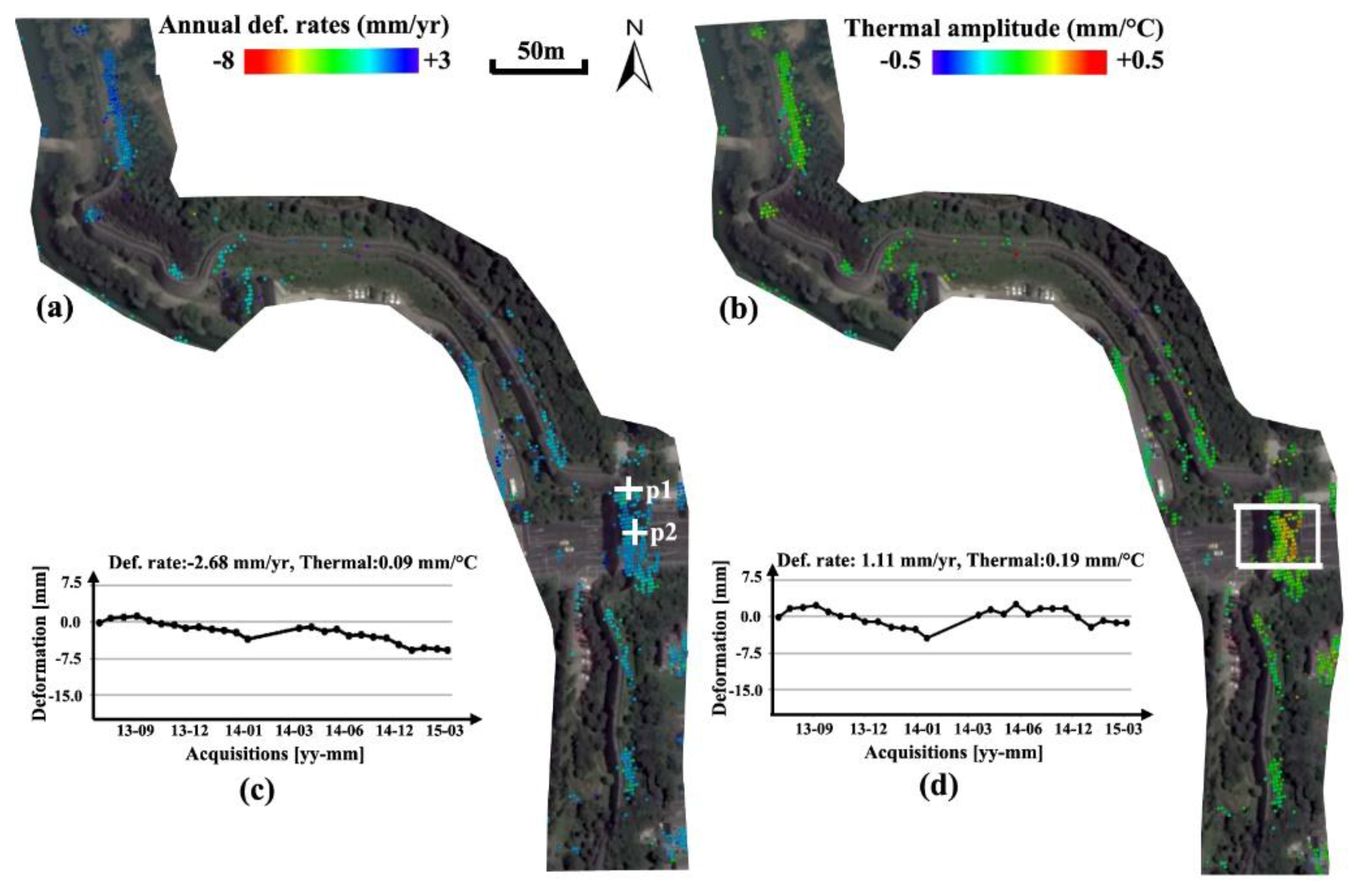
The annual deformation rates along Section-3 city wall remains were derived, as illustrated in Figure 6. Although other components are stable (within ±2.0 mm/year), a heterogeneous uplifting motion trend (with values up to 7.0 mm/year) along the linear remains (immediately in the north of Xuanwu Gate) can be observed. The estimated thermal amplitudes along the entire feature were consistent (primarily in the range of −0.1 to 0.1 mm/°C), implying negligible impact from the thermal kinetics of monument materials. The length of motion anomalies along the wall monument is approximately 180 m. In addition, various motion values (lower than −10.0 mm/year or larger than +5.0 mm/year) overlaid on residential buildings were detected in the western vicinity of this anomaly section, implying the negative impact of anthropogenic activities began in March 2014 as shown by the motion time series of a PS point in Figure 6a. For verification, multi-temporal optical images (overlapped observation time with SAR data acquisitions) from Google Earth were applied for the change detection, as illustrated in Figure 6b–d. It was clear that behaviors of demolition and construction were implemented in the period from April 2013 to October 2014, triggering a motion anomaly detected by the Tomo-PSInSAR. Generally, the motion heterogeneity has a close link to the structural instability and/or future collapses of monuments. In this study, cracks were found in field visits to two hotspots where maximum motion gradients occurred along the wall remains, as indicated by pink circles in Figure 6a. These defects are required to be remedied as a priority to prevent potential collapse, along with other countermeasures for motion mitigation.

Figure 6.
Section-3 (see Figure 2) of wall remains showing, annual deformation rates with heterogeneous motions and the displacement time series of a PS target marked by white cross (a). Triggering factors of demolition and construction activities are shown using a series of multi-temporal Google Earth images acquired on (b) April 2013, (c) March 2014 and (d) October 2014. Cracks were found on hotspots with maximum motion gradients (pink circles).
4.3. Validation
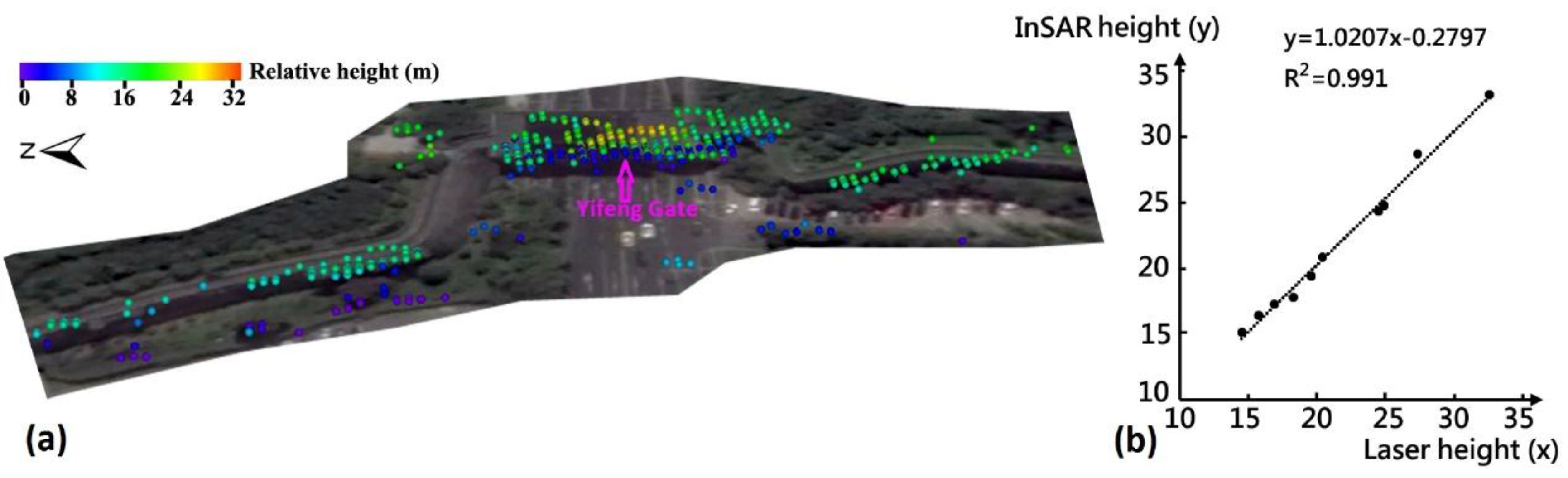
Tomo-PSInSAR derived results, both in regional and monumental-scale, were validated both qualitatively and quantitatively. From the qualitative aspect, it is evident that there is a close relationship between the local geological conditions and the spatial distribution of surface subsidence. Cracks or fissures on buildings or the ground were observed in regions with significant subsidence (Figure 3). Assuming the downward pressure from building weights and traffic overloads is common for the observed scenario (uniform dense-urbanized landscapes), the heterogeneity of surface motions can be caused by the creeping and consolidation of soft soil deposits. Geophysical process indicates that the extent of soil creeping and consolidation phenomena are proportional to the thickness of sediments. The concurrence of sediment basins (with the thickest soft soils) and surface subsidence holds this regulation. Residual heights (relative to the reference DEM) and motion components (linear, non-linear and thermodynamic components) are both unknown parameters of the Tomo-PSInSAR models that need to be resolved. Consequently, from the quantitative aspect, the validation of height estimates can, to some extent, be used to validate the motion contribution [2] in the absence of ground-truth motion measurements (e.g., GPS and precise leveling). On the Section-2 wall remains, low-to-high multi-terrace height values (Figure 7a), as estimated by the Tomo-PSInSAR model, were observed; that is from the ground (0–2 m), to wall remains (14–21 m) and finally to the Yifeng Gate including minstrel gallery (24–34 m). The InSAR estimated and ground-based measured heights (determined using a laser handheld distance-meter, analogously to the work of Tapete et al. [28]) were cross-compared once their coordinates were transforming into the uniform WGS84 reference system. Note that the repetition of laser-distance is recommended to guarantee the accuracy (e.g., decimeters) of heights measured compared to the precision of InSAR estimates, at the order of 1 m [29]. Using 10 selected PS points, the scatter plot (Figure 7b) indicates that consistent InSAR-height estimates were obtained by comparisons to in-situ architecture height measurements using the linear regression coupled with the height dispersion less than 1 m. Precise leveling measurements of two observation points (indicated by white crosses in Figure 2) for the period of 2009–2015 were used for the cross-validation of Tomo-PSInSAR-derived motions, after transformation into the WGS84 reference system. The nearest neighbor approach was applied for the selection of PS points in case two different measurements were not overlaid precisely. The displacement rates of leveling were 0.0 and 1.0 mm/year, respectively, compared to 1.8 and –1.4 mm/year of Tomo-PSInSAR estimates, respectively. A good agreement can be observed with discrepancy values of 1.0 to 2.0 mm/year.
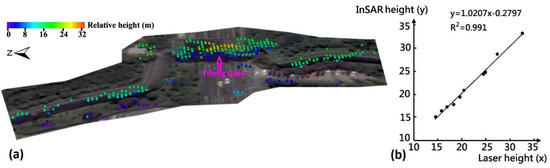
Figure 7.
(a) Calculated heights (relative to the ground) of wall remains as well as the Yifeng Gate by Tomo-PSInSAR; (b) scatter plot of measured heights from InSAR and laser distance-meter.
5. Discussion
The MT-InSAR technique has been an essential tool for the monitoring and assessment of risk to cultural heritage sites, delivering deformation measurements with accuracy at a millimeter level. Given the availability of data from high resolution SAR missions of frequent repeat cycles, presently the MT-InSAR approach can be applied as a diagnostic tool for identification of potential structural instability of monuments.
As a complementary source of information, the heights of PS targets estimated by MT-InSAR are of significant importance in solving uncertainties related to the geolocation of scattering objects, especially for spatially overlapping targets, as well as separating structural deformation components (e.g., thermal dilatation) from ground deformation signals. As illustrated in Figure 5, the difference in thermal amplitudes of the Yifeng Gate (including the Minstrel Gallery) for different scattering heights were successfully separated, demonstrating the added-value concerning the detailed monitoring of the monument’s stability. Moreover, the spatio-temporal analysis of PS motions helps to locate deformation hotspots as well as to prevent erroneous misinterpretations due to misleading deformation velocity rates, such as for a mild motion rate (assumed to be steady), coupled with an accelerating trend (which should be identified as an anomaly).
It is worth noting that the spatial heterogeneity of detected deformation either on a local-scale or structural-scale is considered more destructive than of a uniform displacement pattern, due to the maximization of shearing forces (highlighted by pink lines in Figure 4 and pink circles in Figure 6) resulting in the occurrence of cracks. Moreover, the time series of MT-InSAR measurements points out changes to motion trends, facilitating the detection of imperceptible defect-behaviors on monuments and/or surrounding landscapes triggered by human activities, mainly construction works (began in March 2014 as shown in Figure 6), and/or due to geohazard events, particularly when PS measurements indicate steady deformation velocity rates.
Although the capacity of the proposed approach for two-scale monitoring of monuments is well-underlined, further investigation is required in order to assess the feasibility of the MT-InSAR approach (including Tomo-PSInSAR, as proposed herein) and understand possible limitations in its applicability to different environmental settings.
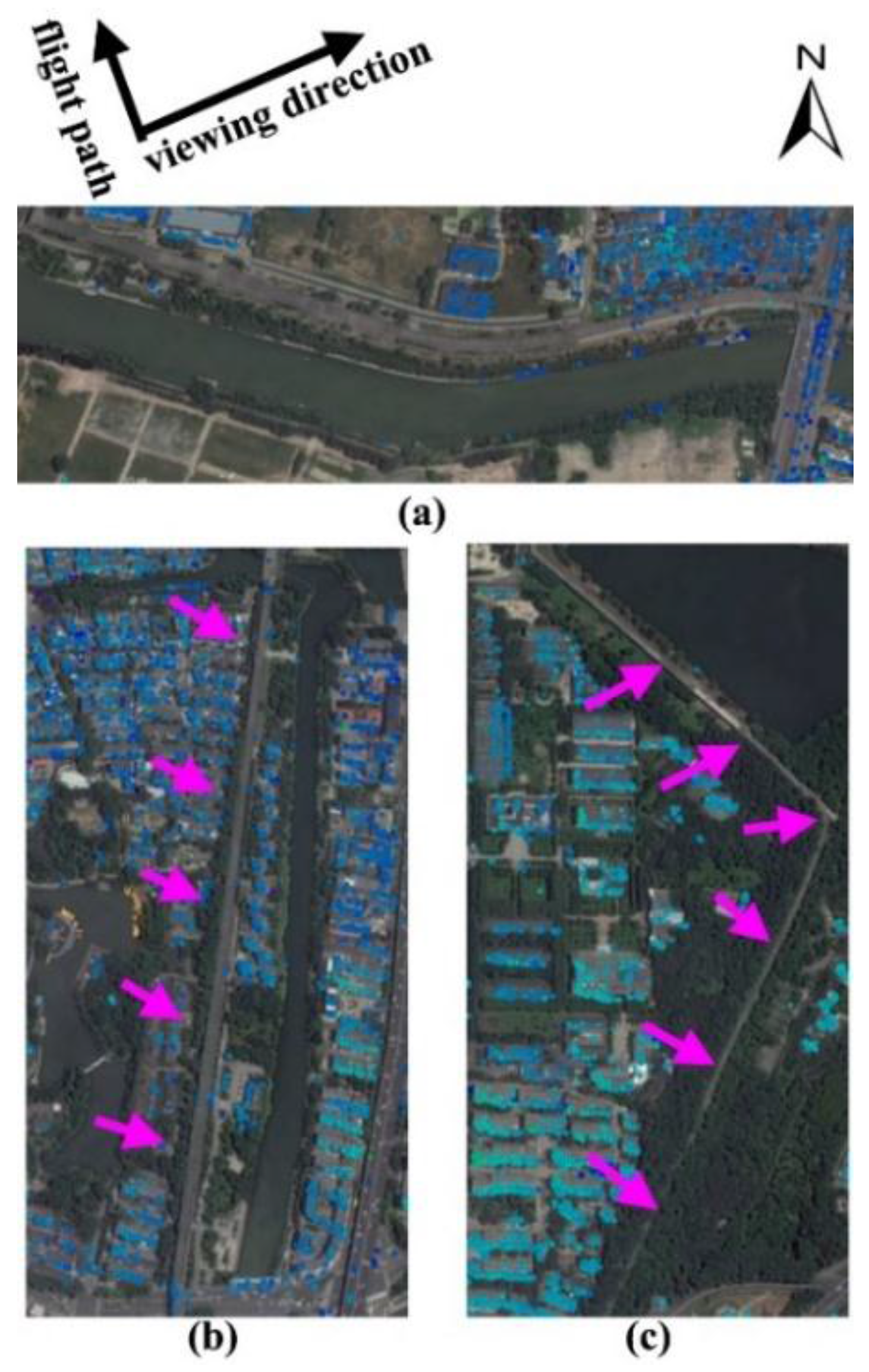
In principal, Tomo-PSInSAR approach outperforms PSInSAR in detection PS points, however, the geometric distortions caused by slant-range radar imaging hampers its utilization for monuments monitoring (Figure 8). Generally, object orientation parallel to the satellite flight direction results in strong backscatter echoes and, vice versa, suppressed ones (e.g., the E-W direction wall monuments in Figure 8a). Furthermore, the application of MT-InSAR and/or Tomo-PSInSAR models can be severely constrained over vegetated landscapes due to the spatio-temporal decorrelation. As demonstrated, tree barriers along the western side of the wall remnants filter out PS points along the monument (Figure 8b,c). This unfavorable condition can be partly mitigated utilizing SAR acquisition from a different orbital pass (in our case a descending orbit) considering the absence of vegetation along the eastern side of the monument.

Figure 8.
Unfavorable observation sections of ancient city walls constrained by (a) SAR viewing geometry and the occurrence of vegetation, e.g., relics sheltered by trees indicated by pink arrows in (b,c).
Taking advantage of the regional observation capability of the spaceborne SAR, MT-InSAR is definitely a cost-effective tool for the sustainable conservation of cultural heritage sites, especially when they extend tens to hundreds of square kilometres over the landscape. On the contrary, ground-based SAR systems are recommended as an alternative for the surveillance of a single monument. Furthermore, high-resolution SAR data are preferable (e.g., in Spotlight mode), in particular for the structural instability of the architecture. High resolution systems detect such spatial details that allow enhanced separation of overlaid PS points, of particular interest when applying Tomo-PSInSAR models to extend the MT-InSAR approach for risk monitoring of a single monument.
6. Conclusions
To assess the vulnerability of cultural heritage sites, jointly induced by geological change and anthropogenic activities, a two-step Tomo-PSInSAR approach was developed in the present study to extract motion anomalies at regional-to-monumental observation scales. By analyzing 26 scenes of multi-temporal TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X SAR data, the performance and feasibility of Tomo-PSInSAR models were investigated. The regional InSAR-derived results demonstrate that there is a positive correlation between the spatial occurrence of surface subsidence and the local geological conditions. Although no evidence for surface deformation due to subway construction, anomalies of thermodynamics on Section 4.2.2 (the Yifeng Gate with an expansion difference of 3 mm in a seasonal cycle) or motion trends on Section 4.2.3 of the city wall remains (an uplift with rates up to +7 mm/year, in the northern vicinity of Xuanwu Gate) were observed using the monument-scale Tomo-PSInSAR model. The above findings underline the negative impact of natural processes on relic materials, and of disturbances from municipal construction works on the conservation of monuments.
Benefitting from developments in Earth observation technologies, today Tomo-PSInSAR can act as a non-invasive tool in risk monitoring and prevention for heritage sites. Improvement of the proposed approach could be achieved by the integration of ascending and descending high resolution SAR data on the Ming Dynasty City Walls.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge support and funding from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0501502), Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. Y5YR0300QM), CAS-TWAS Centre of Excellence on Space Technology for Disaster Mitigation “Joint Program on Space Technology for Disaster Mitigation for Belt and Road Initiative”. TerraSAR-X data in this study were provided by Deutschen Zentrums für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) under the AO TSX-Archive project (CAL3304).
Author Contributions
Fulong Chen, Yuhua Wu, Yimeng Zhang, Issaak Parcharidis conceived and designed the experiments; Fulong Chen, Peifeng Ma, Wei Zhou and Panpan Tang performed the InSAR data processing and results analysis; Ruya Xiao and Jia Xu contributed InSAR results validation; Fulong Chen, Issaak Parcharidis and Michael Foumelis wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Hu, X. Slope superficial displacement monitoring by small baseline SAR interferometry using data from L-band ALOS PALSAR and X-band TerraSAR: A case study of Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1564–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B07407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. A New algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapete, D.; Fanti, R.; Cecchi, R. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring and early-stage warning of structural instability in archaeological sites. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N.; Milillo, P.; Tapete, D. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Processing of COSMO-SkyMed StripMap HIMAGE Time Series to Depict Deformation of the Historic Centre of Rome, Italy. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12593–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jiang, A.; Ishwaran, N. Angkor site monitoring and evaluation by radar remote sensing. Proceedings of Land Surface Remote Sensing II, Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Symposium 2014, Beijing, China, 13–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, W. Monitoring cultural heritage sites with advanced multi-temporal InSAR technique: The case study of the Summer Palace. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A.; Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A. Detection of single scatterers in multidimensional SAR imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2284–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Lan, H.; Chen, F. Multi-dimensional SAR tomography for monitoring the deformation of newly built concrete buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Serafino, F.; Reale, D. 4-D SAR imaging: the case study of Rome. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Montazeri, S.; Gisinger, C.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bamler, R. Geodetic SAR Tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Balz, T.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. A novel fast approach for SAR tomography: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M.; Shahzad, M.; Zhu, X.X. Reconstruction of individual trees from multi-aspect TomoSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F. Differential tomography: A new framework for SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Luzi, G.; Crippa, B. Measuring thermal expansion using X-band persistent scatter interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 100, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Lin, H. Robust detection of single and double persistent scatterers in urban built environments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2124–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F.; Viviani, F. New development of 4D+ differential SAR tomography to probe complex dynamic scenes. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2014, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 3362–3365. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.A.; Wegmüller, U.; Hajnsek, I.; Frey, O. Single-look SAR tomography as an add-on to PSI for improved deformation analysis in urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6119–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J. Robust estimation of a location parameter. Ann. Math. Stat. 1964, 35, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Lombardini, F.; Pauciullo, A.; Reale, D.; Viviani, F. Tomographic Processing of Interferometric SAR Data: Developments, applications, and future research perspectives. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yan, C.; Sun, Y. Environmental geological problems of urban underground engineering. J. Eng. Geol. 2003, 11, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.Q.; Pan, F.Y.; Miao, B.Z. Old channel and its influence on municipal construction in Nanjing city. Jiangsu Geol. 1990, 1, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tapete, D.; Morelli, S.; Fanti, R.; Casagli, N. Localising deformation along the elevation of linear structures: An experiment with spaceborne InSAR and RTK GPS on the Roman Aqueducts in Rome, Italy. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 58, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. Detection of cavity migration and sinkhole risk using radar interferometric time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).