A Satellite-Based Sunshine Duration Climate Data Record for Europe and Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. SARAH-2
2.2. Station-Based Sunshine Duration Data
3. Approach
3.1. Weighting of Sunny Slots
4. Evaluation Results
4.1. Evaluation of Daily Data
4.2. Evaluation of Monthly Data
4.3. Discussion
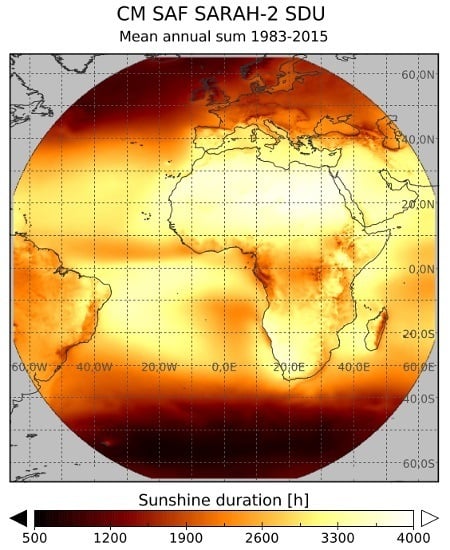
5. Applications
Trend in Sunshine Duration
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pallé, E.; Butler, C.J. Sunshine records from Ireland: Cloud factors and possible links to solar activity and cosmic rays. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Kalimeris, A.; Pierros, F. Multi annual variability and climatic signal analysis of sunshine duration at a large urban area of Mediterranean (Athens). Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandirmaz, H.M. A model for the estimation of the daily global sunshine duration from meteorological geostationary satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5061–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, E. Estimating daily sunshine duration over the UK from geostationary satellite data. Weather 2010, 65, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, M.A.; Remesan, R.; Han, D. An improved technique for global daily sunshine duration estimation using satellite imagery. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2012, 13, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journée, M.; Demain, C.; Bertrand, C. Sunshine duration climate maps of Belgium and Luxembourg based on Meteosat and in-situ observations. Adv. Sci. Res. 2013, 10, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. Solar and terrestrial radiation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, J.A. Evaporation from water surface in relation to solar radiation. Trans. R. Soc. Aust. 1940, 64, 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kothe, S.; Good, E.; Obregón, A.; Ahrens, B.; Nitsche, H. Satellite-based sunshine duration for Europe. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2943–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation, 7th ed.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, M.; Yan, N.; Xing, Q. A method to estimate sunshine duration using cloud classification data from a geostationary meteorological satellite (FY-2D) over the Heihe River Basin. Sensors 2016, 16, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothe, S.; Dobler, A.; Beck, A.; Ahrens, B. The radiation budget in a regional climate model. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katragkou, E.; García-Díez, M.; Vautard, R.; Sobolowski, S.; Zanis, P.; Alexandri, G.; Cardoso, R.M.; Colette, A.; Fernandez, J.; Gobiet, A.; et al. Regional climate hindcast simulations within EURO-CORDEX: Evaluation of a WRF multi-physics ensemble. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiacchio, M.; Solmon, F.; Giorgi, F.; Stackhouse, P.; Wild, M. Evaluation of the radiation budget with a regional climate model over Europe and inspection of dimming and brightening. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 1951–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, G.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Zanis, P.; Katragkou, E.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Kourtidis, K.; Meleti, C. On the ability of RegCM4 regional climate model to simulate surface solar radiation patterns over Europe: An assessment using satellite-based observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13195–13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.R.K. Crop growth modeling and its applications in agricultural meteorology. Satell. Remote Sens. GIS Appl. Agric. Meteorol. 2011, 1, 235–261. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M. Modeling regional vegetation NPP variations and their relationships with climatic parameters in Wuhan, China. Earth Interact. 2013, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Montenegro, A.; Zhu, X. NDVI and vegetation phenology dynamics under the influence of sunshine duration on the Tibetan plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifroth, U.; Kothe, S.; Müller, R.; Cremer, R.; Trentmann, J.; Hollmann, R. Surface solar radiation data set—Heliosat (SARAH)—Edition 2. Satell. Appl. Facil. Clim. Monit. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.; Heinemann, D.; Hoyer, C.; Kuhlmann, R.; Lorenz, E.; Müller, R.; Beyer, H.G. Solar energy assessment using remote sensing technologies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.; Trentmann, J.; Träger-Chatterjee, C.; Posselt, R.; Stöckli, R. The Role of the effective cloud albedo for climate monitoring and analysis. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2305–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.; Behrendt, T.; Hammer, A.; Kemper, A. A New algorithm for the satellite-based retrieval of solar surface irradiance in spectral bands. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 622–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skartveit, A.; Olseth, J.; Tuft, M. An hourly diffuse fraction model with correction for variability and surface albedo. Sol. Energy 1998, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.; Pfeifroth, U.; Träger-Chatterjee, C.; Trentmann, J.; Cremer, R. Digging the METEOSAT treasure—3 decades of solar surface radiation. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8067–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CM SAF Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document, Meteosat Solar Surface Radiation and effective Cloud Albedo Climate Data Records—Heliosat, SARAH-2 2017. Under Preparation. Available online: http://www.cmsaf.eu/EN/Documentation/Documentation/ATBD/ATBD_node.html (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Riihelä, A.; Thomas Carlund, T.; Trentmann, J.; Müller, R.; Lindfors, A.V. Validation of CM SAF surface solar radiation datasets over Finland and Sweden. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6663–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žák, M.; Mikšovský, J.; Pišoft, P. CMSAF radiation data: New possibilities for climatological applications in the Czech Republic. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14445–14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A.; Peng, J.; Borsche, M. High-resolution land surface fluxes from satellite and reanalysis data (HOLAPS v1.0): Evaluation and uncertainty assessment. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2499–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, G.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Meleti, C.; Balis, D.; Kourtidis, K.A.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Trentmann, J.; Zanis, P. A high resolution satellite view of surface solar radiation over the climatically sensitive region of Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Res. 2017, 188, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CM SAF Validation Report, Meteosat Solar Surface Radiation and Effective Cloud Albedo Climate Data Record. Under Preparation. 2017. Available online: http://www.cmsaf.eu/EN/Documentation/Documentation/ValidationRep/ValidationReports_node.html (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Wijngaard, J.B.; Konnen, G.P.; Bohm, R.; Demaree, D.; Gocheva, A.; Mileta, M.; Pashiardis, S.; Hejklik, L.; Kern-Hansen, C.; et al. Daily dataset of 20th-century surface air temperature and precipitation series for the European climate assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 22, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECA&D Project Team. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD). 2013. Available online: http://www.ecad.eu/documents/atbd.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2017). version 10.7.
- Deutscher Wetterdienst. Global Climate Data. Available online: http://www.dwd.de/EN/ourservices/climat/climat.html (accessed on 9 March 2017).
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Wild, M. Decadal variations in estimated surface solar radiation over Switzerland since the late 19th century. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 8635–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, T. Comparison of daily sunshine duration recorded by Campbell-Stokes and Kipp and Zonen sensors. Weather 2014, 69, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszko, D. A comparison of sunshine duration records from the Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder and CSD3 sunshine duration sensor. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Romero, A.; González, J.; Calbó, J.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A. Using digital image processing to characterize the Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder and to derive high-temporal resolution direct solar irradiance. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Wild, M.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; de Laat, A.T.J. Relationship between sunshine duration and temperature trends across Europe since the second half of the twentieth century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10823–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeder, J.; Good, E.; Kothe, S.; Trentmann, J. Comparison of in-situ and spaceborne derived monthly sunshine duration grids over the United Kingdom. Unpublished work. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hannak, L.; Knippertz, P.; Fink, A.H.; Kniffka, A.; Pante, G. Why do global climate models struggle to represent low-level clouds in the West African summer monsoon? Clim. Dyn. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifroth, U.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Manara, V.; Trentmann, J. Trends and variability of surface solar radiation in Europe based on CM SAF satellite data records. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Enriquez-Alonso, A.; Wild, M.; Trentmann, J.; Vincente-Serrano, S.M.; Sanchez-Romero, A.; Posselt, R.; Hakuba, M. Trends in downward surface solar radiation from satellites and ground observations over Europe during 1983–2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Bias (h) | MAD (h) | Correlation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.41 | 1.33 | 0.91 |
| MAM | 0.32 | 1.38 | 0.92 |
| JJA | 0.41 | 1.43 | 0.93 |
| SON | 0.53 | 1.26 | 0.88 |
| DJF | 0.37 | 1.23 | 0.81 |
| Bias (h) | MAD (h) | Correlation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 7.5 | 18.4 | 0.96 |
| Mean NH | 6.4 | 17.4 | 0.97 |
| Mean SH | −2.2 | 15.2 | 0.95 |
| MAM | 7.8 | 20.1 | 0.92 |
| MAM NH | 4.7 | 18.6 | 0.94 |
| MAM SH | −0.4 | 14.6 | 0.95 |
| JJA | 8.6 | 20.6 | 0.93 |
| JJA NH | 6.9 | 20.5 | 0.93 |
| JJA SH | −3.2 | 13.6 | 0.97 |
| SON | 10.3 | 18.0 | 0.96 |
| SON NH | 10.3 | 17.0 | 0.97 |
| SON SH | −3.8 | 15.0 | 0.95 |
| DJF | 9.1 | 20.2 | 0.96 |
| DJF NH | 6.8 | 18.5 | 0.94 |
| DJF SH | 0.9 | 17.6 | 0.93 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kothe, S.; Pfeifroth, U.; Cremer, R.; Trentmann, J.; Hollmann, R. A Satellite-Based Sunshine Duration Climate Data Record for Europe and Africa. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050429
Kothe S, Pfeifroth U, Cremer R, Trentmann J, Hollmann R. A Satellite-Based Sunshine Duration Climate Data Record for Europe and Africa. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(5):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050429
Chicago/Turabian StyleKothe, Steffen, Uwe Pfeifroth, Roswitha Cremer, Jörg Trentmann, and Rainer Hollmann. 2017. "A Satellite-Based Sunshine Duration Climate Data Record for Europe and Africa" Remote Sensing 9, no. 5: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050429
APA StyleKothe, S., Pfeifroth, U., Cremer, R., Trentmann, J., & Hollmann, R. (2017). A Satellite-Based Sunshine Duration Climate Data Record for Europe and Africa. Remote Sensing, 9(5), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050429