Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Observation
2.2. Inversion of Backscatter Coefficient by Lidar
2.3. Inversion of Planetary Boundary Layer Height
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison between Three PBLH Calculation Methods
3.2. PBL Statistical Characteristics
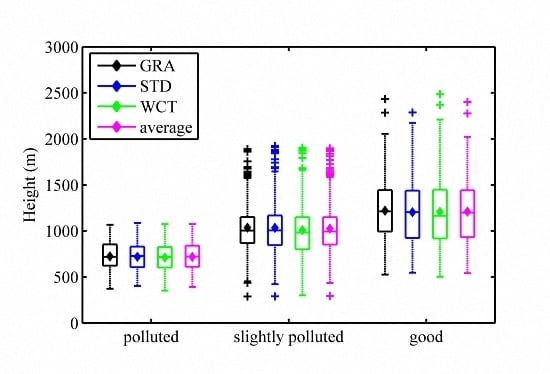
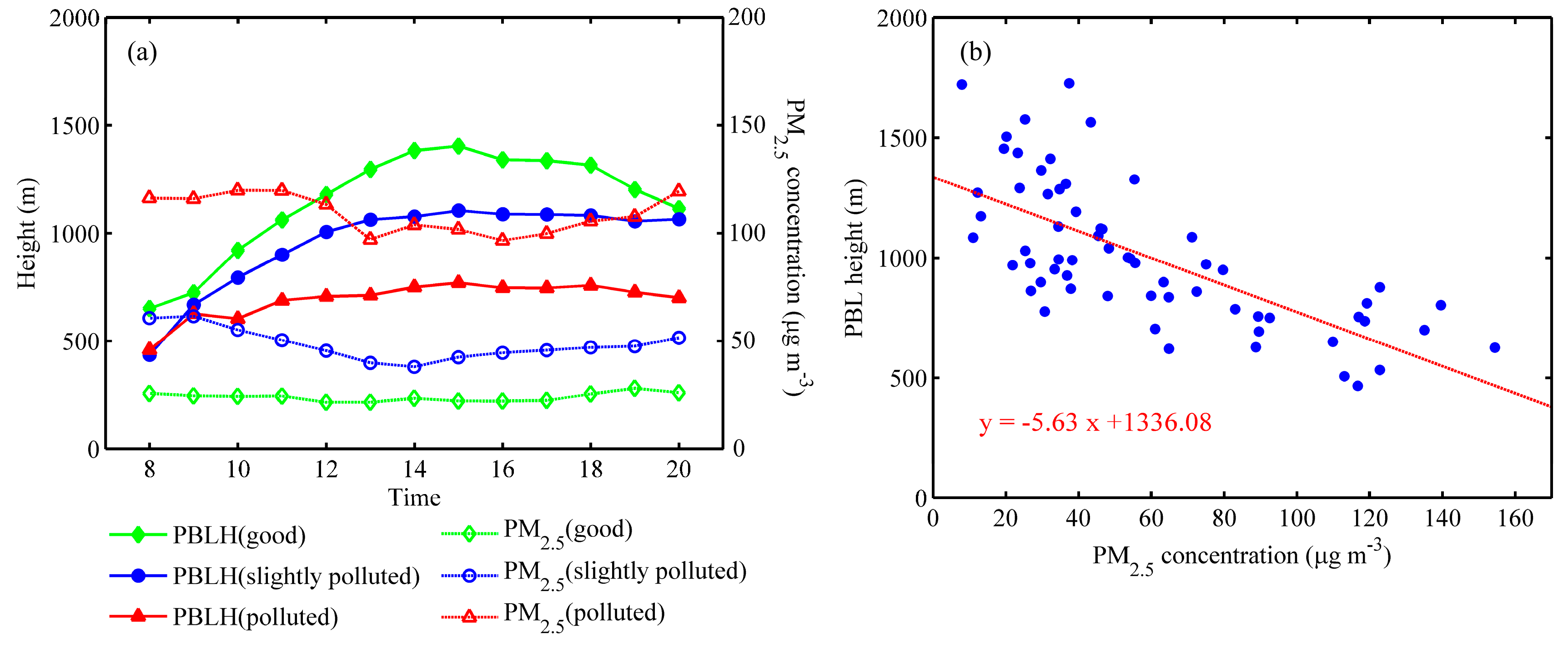
3.3. PBLH Variation Properties under Different Particulate Pollution Conditions
3.4. Case Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.; Wang, T.; Lu, X.; Yu, Y.; Kasoar, M.; Xie, M.; Zhuang, B. Source apportionment of size-fractionated particles during the 2013 Asian Youth Games and the 2014 Youth Olympic Games in Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.F.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.B.; Wang, W.Q. National-scale estimates of ground-level PM2.5 concentration in China using geographically weighted regression based on 3 km resolution MODIS aod. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; Rasch, P.; Satheesh, S.K.; et al. Cloud and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 614–623. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, H.D.; London, S.J.; Chen, G.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Song, G.X.; Zhao, N.Q.; Jiang, L.L.; Chen, B.H. Season, sex, age, and education as modifiers of the effects of outdoor air pollution on daily mortality in Shanghai, China: The public health and air pollution in Asia (PAPA) study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.J.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, F. Modeling heterogeneous chemical processes on aerosol surface. Particuology 2010, 8, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.G. Spectral dependence on the correction factor of erythemal UV for cloud, aerosol, total ozone, and surface properties: A modeling study. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, M.A. The radiation budget for polluted layers of the urban environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1971, 10, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; Tao, M.; Zhu, L. Modeling the feedback between aerosol and meteorological variables in the atmospheric boundary layer during a severe fog-haze event over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Deng, J.J.; Xie, M. Investigations on direct and indirect effect of nitrate on temperature and precipitation in China using a regional climate chemistry modeling system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, A.R.; Washenfelder, R.A.; Brock, C.A.; Hu, W.; Baumann, K.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Day, D.A.; Edgerton, E.S.; Murphy, D.M.; Palm, B.B.; et al. Trends in sulfate and organic aerosol mass in the Southeast U.S.: Impact on aerosol optical depth and radiative forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7701–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Park, S.; Zeng, J.; Ge, C.; Yang, K.; Carn, S.; Krotkov, N.; Omar, A.H. Modeling of 2008 kasatochi volcanic sulfate direct radiative forcing: Assimilation of omi SO2 plume height data and comparison with MODIS and CALIOP observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Jiang, F.; Wang, T.J.; Li, S.; Zhu, B. Investigation on the direct radiative effect of fossil fuel black-carbon aerosol over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Huang, R.J.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Cao, J.J.; Ni, H.Y.; Tie, X.X.; Zhao, S.Y.; Su, X.L.; Han, Y.M.; Shen, Z.X.; et al. Physicochemical characteristics of black carbon aerosol and its radiative impact in a polluted urban area of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12505–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Solmon, F.; Zhuang, B.L.; Wu, H.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.M. Impact of aerosols on regional climate in southern and northern China during strong/weak East Asian summer monsoon years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4069–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Wang, T.J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Talbot, R.; Mao, H.T.; Yang, X.Q.; Fu, C.B.; Yin, C.Q.; Zhu, J.L.; et al. Optical properties and radiative forcing of urban aerosols in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yin, C.Q.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Yang, X.Q.; et al. Absorption coefficient of urban aerosol in Nanjing, west Yangtze River delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13633–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Xu, X.B.; Zhao, C.S.; Yan, P. A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1006–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.H.; Chen, L.F.; Xiong, X.Z.; Zhang, M.G.; Ma, P.F.; Tao, J.H.; Wang, Z.F. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over Northern China in january 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynard, A.; Clerbaux, C.; Clarisse, L.; Safieddine, S.; Pommier, M.; Van Damme, M.; Bauduin, S.; Oudot, C.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; et al. First simultaneous space measurements of atmospheric pollutants in the boundary layer from IASI: A case study in the North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology (Vol. 13); Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Petaja, T.; Jarvi, L.; Kerminen, V.M.; Ding, A.J.; Sun, J.N.; Nie, W.; Kujansuu, J.; Virkkula, A.; Yang, X.Q.; Fu, C.B.; et al. Enhanced air pollution via aerosol-boundary layer feedback in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilitinkevich, S.S.; Tyuryakov, S.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I.; Mareev, E.A. Theoretical models of the height of the atmospheric boundary layer and turbulent entrainment at its upper boundary. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2012, 48, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Tiwari, S.; Mishra, A.; Singh, S.; Hopke, P.K.; Singh, S.; Attri, S.D. Characteristics of absorbing aerosols during winter foggy period over the national capital region of Delhi: Impact of planetary boundary layer dynamics and solar radiation flux. Atmos. Res. 2017, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventidou, E.; Zanis, P.; Balis, D.; Giannakaki, E.; Pytharoulis, I.; Amiridis, V. Factors affecting the comparisons of planetary boundary layer height retrievals from CALIPSO, ECMWF and radiosondes over Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Huang, J.P.; Chen, B.; Zhou, T.; Yan, H.R.; Jin, H.C.; Huang, Z.W.; Zhang, B.D. Comparisons of PBL heights derived from CALIPSO and ECMWF reanalysis data over China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 153, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Wilczak, J.M. Convective boundary layer depth: Improved measurement by doppler radar wind profiler using fuzzy logic methods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkel, C.; Schafer, K.; Emeis, S. Adding confidence levels and error bars to mixing layer heights detected by ceilometer. In Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XVI; Kassianov, E.I., Comeron, A., Picard, R.H., Schafer, K., Eds.; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 8177. [Google Scholar]
- Lotteraner, C.; Piringer, M. Mixing-height time series from operational ceilometer aerosol-layer heights. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 161, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, L.; Egert, S.; Alpert, P. Ceilometer evaluation of the eastern mediterranean summer boundary layer height—First study of two Israeli sites. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasanta, G.; Pietroni, I.; Petenko, I.; Argentini, S. Observed and modelled convective mixing-layer height at Dome C, Antarctica. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 151, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petenko, I.; Argentini, S.; Casasanta, G.; Kallistratova, M.; Sozzi, R.; Viola, A. Wavelike structures in the turbulent layer during the morning development of convection at Dome C, Antarctica. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 161, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tomasi, F.; Perrone, M.R. PBL and dust layer seasonal evolution by Lidar and radiosounding measurements over a peninsular site. Atmos. Res. 2006, 80, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S. Monitoring depth of shallow atmospheric boundary layer to complement Lidar measurements affected by partial overlap. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8468–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Deng, X.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, G. Study on aerosol optical properties and radiative effect in cloudy weather in the Guangzhou region. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.Y.; Pan, Z.X. An improved iterative fitting method to estimate nocturnal residual layer height. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; GuiseBagley, L.; Staebler, R.M.; Wiebe, H.A.; Brook, J.; Georgi, B.; Dusterdiek, T. Lidar, nephelometer, and in situ aerosol experiments in Southern Ontario. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 19199–19209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H.; Durand, P. Lidar determination of the entrainment zone thickness at the top of the unstable marine atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1997, 83, 247–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennemuth, B.; Lammert, A. Determination of the atmospheric boundary layer height from radiosonde and Lidar backscatter. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 120, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeron, A.; Sicard, M.; Rocadenbosch, F. Wavelet correlation transform method and gradient method to determine aerosol layering from Lidar returns: Some comments. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, W.P.; Eloranta, E.W. Lidar measurements of wind in the planetary boundary-layer—The method, accuracy and results from joint measurements with radiosonde and kytoon. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H. Urban boundary-layer height determination from Lidar measurements over the Paris area. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, S.A.; Angevine, W.M. Boundary layer height and entrainment zone thickness measured by Lidars and wind-profiling radars. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Munoz, M.J.; Navas-Guzman, F.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Lyamani, H.; Fernandez-Galvez, J.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Automatic determination of the planetary boundary layer height using Lidar: One-year analysis over Southeastern Spain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Wu, D.; Deng, X.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Liao, B. A vertical sounding of severe haze process in Guangzhou area. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2650–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, D.G.; Boldi, M.; Hoff, R.M. The detection of mixed layer depth and entrainment zone thickness from Lidar backscatter profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägeli, P.; Steyn, D.G.; Strawbridge, K.B. Spatial and temporal variability of mixed-layer depth and entrainment zone thickness. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 97, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter extinction ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Yu, X.; Li, X.M.; Chen, C.; Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Z.P.; Wang, F.Q. Urban boundary layer height characteristics and relationship with particulate matter mass concentrations in Xi’an, central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Eixmann, R. Three years of routine raman Lidar measurements of tropospheric aerosols: backscattering, extinction, and residual layer height. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2002, 2, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, V.; Bosenberg, J. Aerosol climatology for the planetary boundary layer derived from regular Lidar measurements. Atmos. Res. 2002, 63, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kamp, D.; McKendry, I. Diurnal and seasonal trends in convective mixed-layer heights estimated from two years of continuous ceilometer observations in Vancouver, BC. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2010, 137, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawbridge, K.; Travis, M.; Harwood, M. Preliminary results from scanning Lidar measurements of stack plumes during winter/summer. In Proceedings of the SPIE 4546 Laser Radar: Ranging and Atmospheric Lidar Techniques III, Toulouse, France, 17 September 2017; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) and General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine (AQISQ) of the People’s Republic of China. Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB 3095-2012); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Batchvarova, E.; Gryning, S.-E. Applied model for the growth of the daytime mixed layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1991, 56, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.J.; Wang, T.J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Xie, M.; Zhang, R.J.; Huang, X.X.; Zhu, J.L. Characterization of visibility and its affecting factors over Nanjing, China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.J.T.; Prenni, A.J.; Palm, B.B.; Day, D.A.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Winkler, P.M.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; DeMott, P.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Smith, J.N. Size-resolved aerosol composition and its link to hygroscopicity at a forested site in Colorado. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, P.; Wang, T. Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070668
Qu Y, Han Y, Wu Y, Gao P, Wang T. Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070668
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Yawei, Yong Han, Yonghua Wu, Peng Gao, and Tijian Wang. 2017. "Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070668
APA StyleQu, Y., Han, Y., Wu, Y., Gao, P., & Wang, T. (2017). Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070668