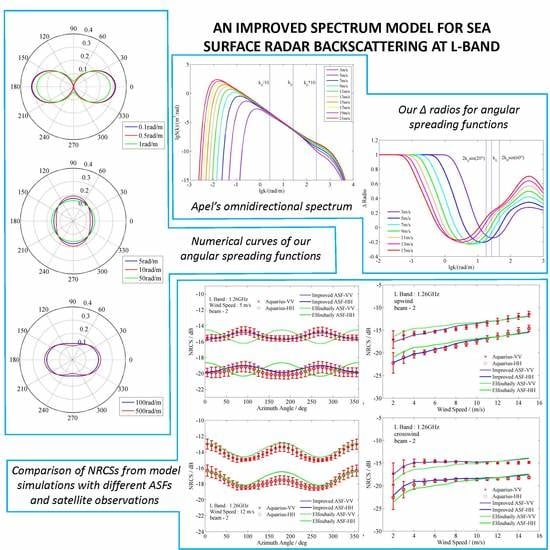
An Improved Spectrum Model for Sea Surface Radar Backscattering at L-Band
Abstract
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, K.-S.; Ma, W.; Li, Z. An Improved Spectrum Model for Sea Surface Radar Backscattering at L-Band. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080776
Du Y, Yang X, Chen K-S, Ma W, Li Z. An Improved Spectrum Model for Sea Surface Radar Backscattering at L-Band. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080776
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yanlei, Xiaofeng Yang, Kun-Shan Chen, Wentao Ma, and Ziwei Li. 2017. "An Improved Spectrum Model for Sea Surface Radar Backscattering at L-Band" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080776
APA StyleDu, Y., Yang, X., Chen, K.-S., Ma, W., & Li, Z. (2017). An Improved Spectrum Model for Sea Surface Radar Backscattering at L-Band. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080776