A Robust Inversion Algorithm for Surface Leaf and Soil Temperatures Using the Vegetation Clumping Index
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inversion Algorithm
2.1. Inversion Method
2.2. Component Effective Emissivity
2.3. Vegetation Clumping Index
3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.1. Simulated Dataset
3.2. Inversion by the FR97 and NDVI Algorithms
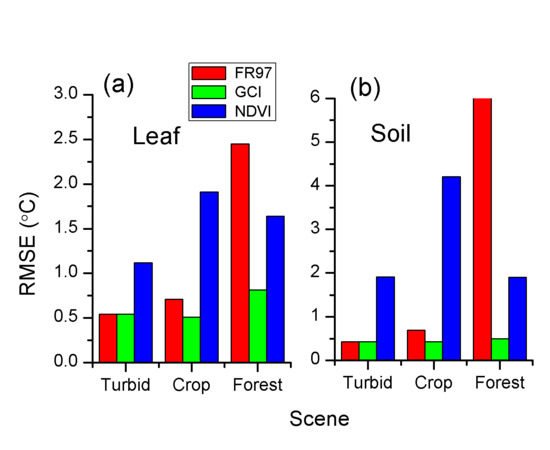
3.3. Results
3.4. Effect of the Clumping Index Error
3.5. Effect of the LAI Error
4. Inversion Validation
4.1. Experimental Campaign
4.2. Measured Dataset
4.3. Results
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Molden, D.J.; Makin, I.W. Remote sensing for irrigated agriculture: Examples from research and possible applications. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 46, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelan, S.K.; Laguette, S.; Casady, G.M.; Seielstad, G.A. Remote sensing applications for precision agriculture: A learning community approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.-L. A physics-based algorithm for retrieving land-surface emissivity and temperature from eos/modis data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, A.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A temperature and emissivity separation algorithm for advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (aster) images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, B.H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hughes, C.G.; Hook, S.J. Quantifying uncertainties in land surface temperature and emissivity retrievals from aster and modis thermal infrared data. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, B. Evaluation of the viirs and modis lst products in an arid area of northwest China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, D.S. Effects of vegetation canopy structure on remotely sensed canopy temperatures. Remote Sens. Environ. 1980, 10, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Yu, T. Modeling directional brightness temperature of the winter wheat canopy at the ear stage. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3721–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Gu, X.F.; Guoliang, G.L.; LeGrand, M.; Baret, F.; Hanocq, J.F.; Bosseno, R.; Zhang, Y. Modeling directional brightness temperature over a maize canopy in row structure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2290–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. A two-source approach for estimating turbulent fluxes using multiple angle thermal infrared observations. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. A two-source energy balance approach using directional radiometric temperature observations for sparse canopy covered surfaces. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, S.; Kustas, W.P.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.; Xia, T.; Li, M. Application of remote sensing-based two-source energy balance model for mapping field surface fluxes with composite and component surface temperatures. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, J.; Verhoef, W.; van der Tol, C.; Su, Z. Retrieval of canopy component temperatures through bayesian inversion of directional thermal measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M.; Jia, L.; Li, Z.L.; Djepa, V.; Wang, J.; Stoll, M.P.; Su, Z.; Rast, M. Estimation of soil and vegetation temperatures with multiangular thermal infrared observations: Imgrass, heife, and sgp 1997 experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 11997–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, Z.L.; Menenti, M.; Su, Z.; Verhoef, W.; Wan, Z. A practical algorithm to infer soil and foliage component temperatures from bi-angular atsr-2 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4739–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Stoll, M.; Renhua, Z.; Li, J.; Zhongbo, S. On the separate retrieval of soil and vegetation temperatures from atsr data. Sci. China Ser. D 2001, 44, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kimes, D. Remote sensing of row crop structure and component temperatures using directional radiometric temperatures and inversion techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 1983, 13, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, C.; Ottle, C.; Prevot, L. Analytical parameterization of canopy directional emissivity and directional radiance in the thermal infrared. Application on the retrieval of soil and foliage temperatures using two directional measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2587–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; O’Shaughnessy, S.; Gowda, P.; Evett, S.; Howell, T.; Kustas, W.; Anderson, M. Radiometer footprint model to estimate sunlit and shaded components for row crops. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Thermal infrared inverse model for component temperatures of mixed pixels. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, T. A theoretical analysis of the frequency of gaps in plant stands. Agric. Meteorol. 1971, 8, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.; Kustas, W.P.; Li, F.; Prueger, J.H.; Mecikalski, J.R. Effects of vegetation clumping on two-source model estimates of surface energy fluxes from an agricultural landscape during smacex. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qin, W.; Liu, Q. Rapid: A radiosity applicable to porous individual objects for directional reflectance over complex vegetated scenes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Li, Z.L.; Liu, Q.H.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, B. Definition of component effective emissivity for heterogeneous and non-isothermal surfaces and its approximate calculation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fan, W.; Chen, L. Matrix expression of thermal radiative characteristics for an open complex. Sci. China Ser. D 2002, 45, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, S.-B. Genetic algorithm based surface component temperatures retrieval by integrating modis tir data from terra and aqua satellites. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2012, 31, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Cao, B.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q. Retrieval of leaf, sunlit soil, and shaded soil component temperatures using airborne thermal infrared multiangle observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Xu, X. Integrative inversion of land surface component temperature. Sci. China Ser. D 2005, 48, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Black, T. Foliage area and architecture of plant canopies from sunfleck size distributions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1992, 60, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, R.; Yan, G.; Li, Z.-L.; Qin, Q.; Liu, Q.; Nerry, F. Performance evaluation of four directional emissivity analytical models with thermal sail model and airborne images. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A346–A360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoef, W.; Jia, L.; Xiao, Q.; Su, Z. Unified optical-thermal four-stream radiative transfer theory for homogeneous vegetation canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1808–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, J.M.; Pisek, J.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. Global clumping index map derived from the modis brdf product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Peng, J.; Xu, X. Estimating savanna clumping index using hemispherical photographs integrated with high resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Xu, X.; Fan, W. A unified canopy bidirectional reflectance (BRDF) model for row ceops. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (hiwater): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Peng, J.J.; Li, B. Image processing method of airborne widas sensor in water campaign. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2010, 25, 797–804. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, L.S.; Acharya, P.K.; Dothe, H.; Matthew, M.W.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Pukall, B. Modtran 4 Radiative Transfer Modeling for Atmospheric Correction; SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, C.C. Surface emissivity and temperature retrieval for a hyperspectral sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 1998, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 546–549. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, M. Estimating and validating soil evaporation and crop transpiration during the hiwater-musoexe. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Q. Modeling directional brightness temperature over mixed scenes of continuous crop and road: A case study of the heihe river basin. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.C.T.; Privette, J.L.; Mahoney, R.; Tucker, C.J. Directional effects in a daily avhrr land surface temperature dataset over africa. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, C.; Berruti, B.; Buongiorno, A.; Ferreira, M.-H.; Féménias, P.; Frerick, J.; Goryl, P.; Klein, U.; Laur, H.; Mavrocordatos, C. The global monitoring for environment and security (gmes) sentinel-3 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Unit | Value or Range |
|---|---|---|
| Scene | -- | Turbid, Crop, Forest |
| LAI | -- | 0.5, 1,0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5 |
| LIDF | -- | Spherical |
| (red) | -- | 0.057 |
| (red) | -- | 0.042 |
| (red) | -- | 0.164 |
| (NIR) | -- | 0.460 |
| (NIR) | -- | 0.462 |
| (NIR) | -- | 0.244 |
| -- | 0.99, 0.97 | |
| -- | 0.97, 0.93 | |
| VZA | ° | [0, 60] |
| °C | 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 |
| Date | Beijing Time | Type | LAI | LIDF | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 August 2012 | 14:00–14:30 | Orchard | 2.4 | Spherical | Row planted; a = 2.5 m; c = 6.0 m; H = 5.0 m; |
| 17 June 2014 | 12:00–14:00 | Maize | 1.2 | Plagiophile | Regularly planted; Spacing = 0.5 m; |
| Wheat | 1.5 | Row plated; a = 0.1 m; c = 0.2 m; H = 0.65 m |
| Leaf (°C) | Soil (°C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene | Toward Angle (°) | Measured | FR97 | GCI | Measured | FR97 | GCI |
| maize | 180 | 29.3 | 31.7 | 30.3 | 41.2 | 42.5 | 42.4 |
| 0 | 29.4 | 31.3 | 29.0 | 48.2 | 48.5 | 48.1 | |
| 90 | 31.2 | 35.5 | 34.1 | 45.9 | 47.4 | 47.2 | |
| 270 | 32.8 | 34.5 | 32.9 | 46.0 | 46.7 | 46.6 | |
| wheat | 180 | 28.4 | 22.4 | 24.4 | 33.9 | 39.3 | 35.2 |
| 0 | 30.9 | 29.3 | 30.2 | 36.2 | 38.2 | 36.3 | |
| 90 | 32.0 | 32.7 | 31.3 | 42.2 | 41.3 | 41.8 | |
| 270 | 29.1 | 31.0 | 30.1 | 37.7 | 37.2 | 37.5 | |
| orchard | 300 | 29.3 | 26.3 | 28.7 | 46.0 | 46.1 | 45.4 |
| 120 | 30.3 | 27.2 | 29.0 | 48.7 | 45.1 | 45.5 | |
| RMSE | 3.0 | 1.7 | 2.3 | 1.2 | |||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, Z.; Cao, B.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Song, L.; Fan, W.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q. A Robust Inversion Algorithm for Surface Leaf and Soil Temperatures Using the Vegetation Clumping Index. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080780
Bian Z, Cao B, Li H, Du Y, Song L, Fan W, Xiao Q, Liu Q. A Robust Inversion Algorithm for Surface Leaf and Soil Temperatures Using the Vegetation Clumping Index. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080780
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Zunjian, Biao Cao, Hua Li, Yongming Du, Lisheng Song, Wenjie Fan, Qing Xiao, and Qinhuo Liu. 2017. "A Robust Inversion Algorithm for Surface Leaf and Soil Temperatures Using the Vegetation Clumping Index" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080780
APA StyleBian, Z., Cao, B., Li, H., Du, Y., Song, L., Fan, W., Xiao, Q., & Liu, Q. (2017). A Robust Inversion Algorithm for Surface Leaf and Soil Temperatures Using the Vegetation Clumping Index. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080780