Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports
Abstract
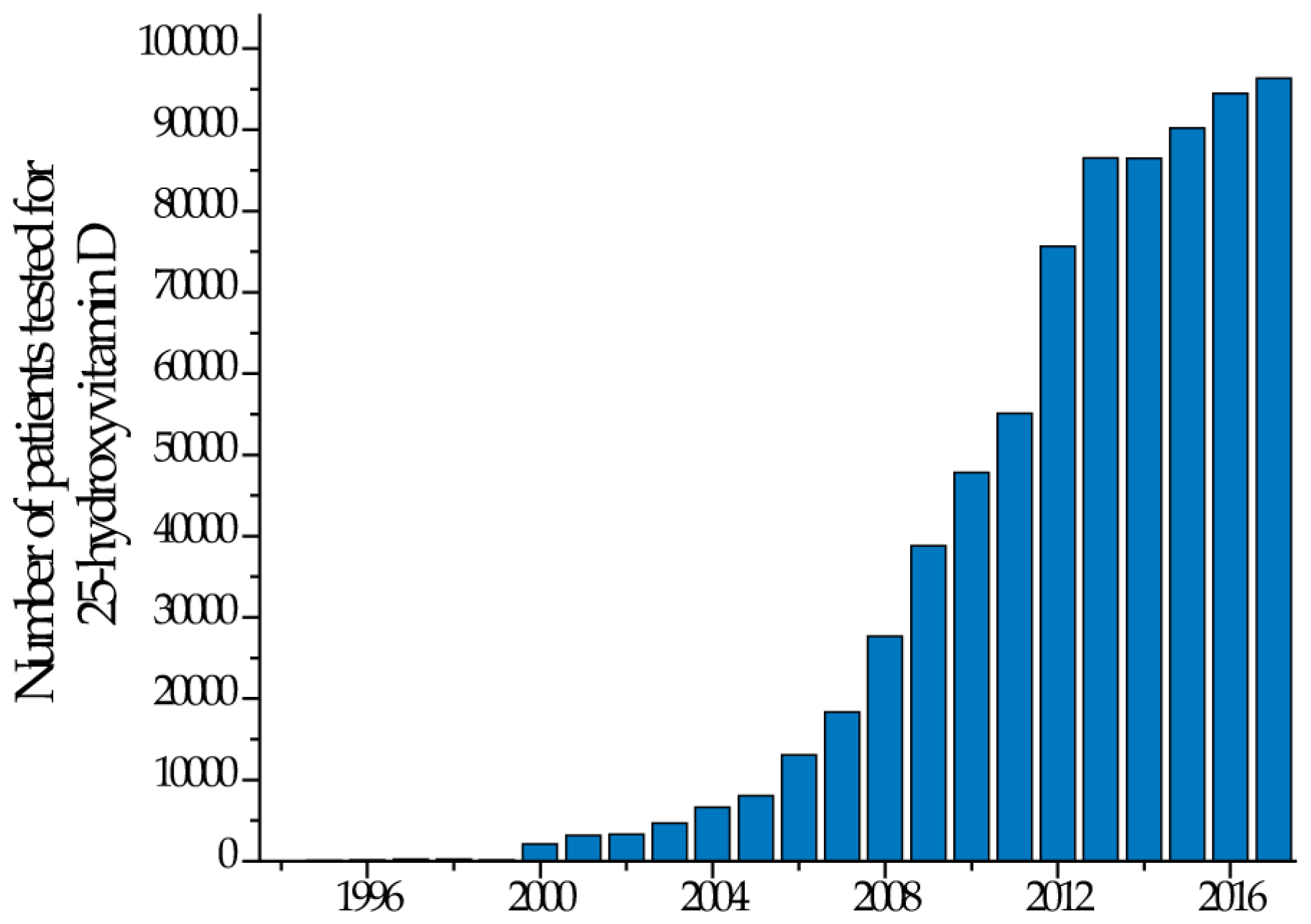
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Manufacturing Errors
3.2. Inappropriate Administration
3.3. Incorrect Prescribing by Physicians
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delvin, E.; Souberbielle, J.C.; Viard, J.P.; Salle, B. Role of vitamin D in acquired immune and autoimmune diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2014, 51, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, L.C.; Michos, E.D.; Reis, J.P. Vitamin D in atherosclerosis, vascular disease, and endothelial function. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, R. Nutritional aspects of bone health. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glade, M.J. A 21st century evaluation of the safety of oral vitamin D. Nutrition 2012, 28, 344–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathcock, J.N.; Shao, A.; Vieth, R.; Heaney, R. Risk assessment for vitamin D. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieth, R. Why the optimal requirement for Vitamin D3 is probably much higher than what is officially recommended for adults. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 8, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M.; Endocrine, S. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.P.; Alagiakrishnan, K.; Sadowski, C. The cure of ageing: Vitamin D—magic or myth? Postgrad. Med. J. 2010, 86, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahangian, S.; Alspach, T.D.; Astles, J.R.; Yesupriya, A.; Dettwyler, W.K. Trends in laboratory test volumes for Medicare Part B reimbursements, 2000-2010. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Deficiency of sunlight and vitamin D. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2008, 336, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galior, K.; Ketha, H.; Grebe, S.; Singh, R.J. 10 years of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D testing by LC-MS/MS-trends in vitamin-D deficiency and sufficiency. Bone Rep. 2018, 8, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, U.; Gjessing, H.R.; Hirche, F.; Mueller-Belecke, A.; Gudbrandsen, O.A.; Ueland, P.M.; Mellgren, G.; Lauritzen, L.; Lindqvist, H.; Hansen, A.L.; et al. Efficacy of fish intake on vitamin D status: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, R.J.; Lu, Z.; Bogusz, J.M.; Williams, J.E.; Holick, M.F. Photobiology of vitamin D in mushrooms and its bioavailability in humans. Dermatoendocrinol 2013, 5, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.P.; Tansey, M.; Jetton, J.G.; Krasowski, M.D. Vitamin D Toxicity: A 16-Year Retrospective Study at an Academic Medical Center. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, H.A.; Good, T.F.; Spiller, N.E.; Aleguas, A. Vitamin D exposures reported to US poison centers 2000-2014: Temporal trends and outcomes. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.N.; Davies, J.S. A review of the growing risk of vitamin D toxicity from inappropriate practice. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Hashiba, K. Reliability of QT intervals as indicators of clinical hypercalcemia. Clin. Cardiol. 1988, 11, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minisola, S.; Pepe, J.; Piemonte, S.; Cipriani, C. The diagnosis and management of hypercalcaemia. BMJ 2015, 350, h2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahrani, F.; Aljohani, N. Vitamin D: Deficiency, sufficiency and toxicity. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3605–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A. Optimal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels for multiple health outcomes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anik, A.; Catli, G.; Abaci, A.; Dizdarer, C.; Bober, E. Acute vitamin D intoxication possibly due to faulty production of a multivitamin preparation. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kara, C.; Gunindi, F.; Ustyol, A.; Aydin, M. Vitamin D intoxication due to an erroneously manufactured dietary supplement in seven children. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e240–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, T.; Holick, M.F.; Alfonso, B.D.; Charlap, E.; Romero, C.M.; Rizk, D.; Newman, L.G. Vitamin D intoxication with severe hypercalcemia due to manufacturing and labeling errors of two dietary supplements made in the United States. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3603–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutkia, P.; Chen, T.C.; Holick, M.F. Vitamin D intoxication associated with an over-the-counter supplement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketha, H.; Wadams, H.; Lteif, A.; Singh, R.J. Iatrogenic vitamin D toxicity in an infant--a case report and review of literature. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 148, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbao, N.A. Vitamin D Toxicity in Young Breastfed Infants: Report of 2 Cases. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2017, 4, 2333794X17731695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, P.N.; Santos, C.S.; Avila, M.O.; Neves, C.L.; Bahiense-Oliveira, M. Hypercalcemia and acute kidney injury caused by abuse of a parenteral veterinary compound containing vitamins A, D, and E. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2011, 33, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Mithal, A. Vitamin D toxicity resulting from overzealous correction of vitamin D deficiency. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, P.A.; Ahmad, S.H.; Ahmad, F.; Jan, R.A.; Shah, S.U.; Khan, U.H. Vitamin d toxicity in adults: A case series from an area with endemic hypovitaminosis d. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, R.K.; Tyagi, P.; Sharma, P.; Singla, V.; Arora, V.; Bansal, N.; Kumar, A.; Arora, A. Iatrogenic hypervitaminosis D as an unusual cause of persistent vomiting: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandita, K.K.; Razdan, S.; Kudyar, R.P.; Beigh, A.; Kuchay, S.; Banday, T. “Excess gooD can be Dangerous”. A case series of iatrogenic symptomatic hypercalcemia due to hypervitaminosis D. Clin. Cases. Miner. Bone Metab. 2012, 9, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdry, A.M.; Azad, H.; Najar, M.S.; Mir, I. Acute kidney injury due to overcorrection of hypovitaminosis D: A tertiary center experience in the Kashmir Valley of India. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2017, 28, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Stephens, L.D.; Fitzgerald, R.L. How much is too much? Two contrasting cases of excessive vitamin D supplementation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 473, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age (years) | Vitamin D dose | Form of Intake | Reason | Vitamin D, Serum (ng/m) | Total Ca, Serum (mg/dL) | Symptoms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4–4.2 (n = 7) | 260,000–800,000 IU/day | Fish oil supplements | Labeling errors | 340–962 | 13.4–18.8 | Weakness, loss of appetite, vomiting | [23] |
| 1–2 (n = 2) 1 | 200 IU/day (2–4weeks) 200 IU/day (1 month) | Oral preparation Oral preparation | Labeling errors Labeling errors | >160 760 | 13.7–19.3 19.4 | Abdominal pain, vomiting Poor appetite, vomiting | [22] |
| 58 40 | 1,864,000 IU (2 months) 970,000 IU (1 month) | Oral supplements Oral supplements | Labeling errors Labeling errors | 1220 645 | 15 13.2 | Fatigue, thirst, polyuria Nausea, vomiting, thirst, polyuria, muscle aches | [24] |
| 42 | 156,000–2,604,000 IU/day (2 years) | Oral supplements | Labeling errors | 487.3 | 15 | Dehydration, fatigue, loss of apetite | [25] |
| 0.3 | 50,000 IU/day (2 months) | Oral supplements | Inappropriate administration | 294 | 18.7 | Vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration | [26] |
| 0.3–0.2 (n = 2) | 20,000 IU/day (1.5 weeks) | Oral supplements | Inappropriate administration | 644 680 | 15 L 21 L | Poor appetite, lethargy, crying | [27] |
| 19 | 15,000,000 IU (1 year) | Injection | Inappropriate administration | 150 | 14.8 | Anorexia, nausea, vomiting | [28] |
| 42–86 (n = 16) | 2,220,000–6,360,000 IU (1–3 months) | Injection or oral sachets | Iatrogenic (body aches and fatigue) | 175–1161 | 11.1–15.7 | Nausea, vomiting, constipation | [29] |
| 48–75 (n = 0) | 3,000,000–60,000,000 IU (1–4 months) | Injection or oral sachets | Iatrogenic (various indications) | 164–306 | 12–13.98 | Vomiting, polyuria, anorexia | [30] |
| 45 | 6,000,000 IU (2 weeks) | Injection | Iatrogenic (knee surgery) | 150 | 23.1 | Anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain | [31] |
| 42–85 (n = 15) | 600,000 IU (1 month–3 years) | Oral supplements + injections | Iatrogenic (improve health) | 103–164 | 10.9–15.2 | Altered sensorium, dehydration, vomiting, anorexia | [32] |
| 45–89 (n = 19) | 4,200,000–9,000,000 IU (1–5 months) | Oral tablets or injections | Iatrogenic (bone pain, aches, fatigue) | 190–988 | 11.9–15.2 | Vomiting, altered sensorium, AKI, constipation, | [33] |
| 75 | 50,000 IU/day (1 year) | Oral supplements | Iatrogenic (hypoparathyroidism) | 243 | 15.3 | Altered mental status | [34] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galior, K.; Grebe, S.; Singh, R. Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports. Nutrients 2018, 10, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080953
Galior K, Grebe S, Singh R. Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports. Nutrients. 2018; 10(8):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080953
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalior, Kornelia, Stefan Grebe, and Ravinder Singh. 2018. "Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports" Nutrients 10, no. 8: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080953
APA StyleGalior, K., Grebe, S., & Singh, R. (2018). Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports. Nutrients, 10(8), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080953




