Emerging Role of Vitamins D and K in Modulating Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Aspect of Passive Calcification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Traditional Aspect: Active Uremic Vascular Calcification Induced by Hyperphosphatemia and Uremic Toxin Accumulation
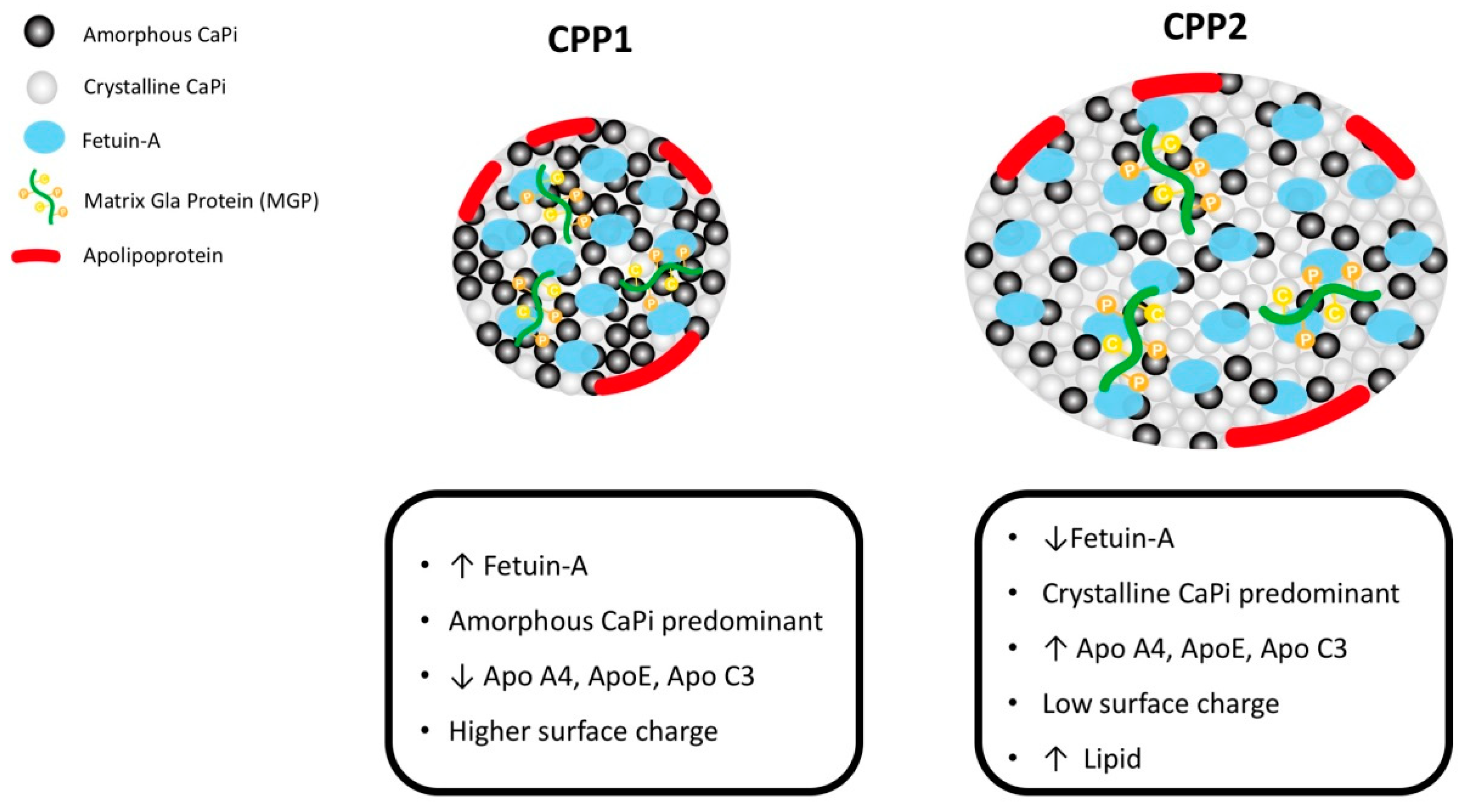
1.2. The New Aspect: Passive Calcification through Interaction between CPPs and MVs
1.3. Vitamin D and K Deficiencies in CKD as an Etiology of Vascular Calcification
Metabolism of Vitamin K in CKD
1.4. Vitamin D Supplementation as a Potential Target for Salvaging Uncarboxylated MGP
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CPP | calciprotein particle |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| ER | endothelial reticular |
| EV | extracellular vesicles |
| FGF23 | fibroblast growth factor 23 |
| HD | hemodialysis |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| MGP | matrix Gla protein |
| MV | matrix vesicle |
| PBUT | protein binding uremic toxin |
| PD | peritoneal dialysis |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| VSMC | vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Inker, L.A.; Astor, B.C.; Fox, C.H.; Isakova, T.; Lash, J.P.; Peralta, C.A.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Feldman, H.I. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narula, N.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Olin, J.W.; Bhatt, D.L.; Johnson, K.W.; Nadkarni, G.; Min, J.; Torii, S.; Poojary, P.; Anand, S.S.; et al. Pathology of peripheral artery disease in critical limb ischemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuiri, S.; Nishizawa, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Mizuno, K.; Ishine, M.; Doi, S.; Masaki, T.; Shigemoto, K. Coronary artery calcification score and common iliac artery calcification score in non-dialysis CKD patients. Nephrology 2018, 23, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, C.E.; Desai, C.S.; Dardari, Z.A.; Al-Mallah, M.H.; Miedema, M.D.; Ouyang, P.; Budoff, M.J.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Nasir, K.; Blaha, M.J. The association of coronary artery calcium with noncardiovascular disease: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorriz, J.L.; Molina, P.; Cerveron, M.J.; Vila, R.; Bover, J.; Nieto, J.; Barril, G.; Martinez-Castelao, A.; Fernandez, E.; Escudero, V.; et al. Vascular calcification in patients with nondialysis CKD over 3 years. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, Y.S.; Ting, K.T.; Chi, W.C.; Lin, C.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Chuang, W.L. Aortic arch calcification predicts patency loss of arteriovenous fistula in end-stage renal disease patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.O.; Bangalore, S.; Lavelle, M.P.; Pellikka, P.A.; Sidhu, M.S.; Boden, W.E.; Asif, A. Diagnosis and management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease: A review. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.S.; Evans, C.V.; Johnson, E.; Redmond, N.; Coppola, E.L.; Smith, N. Nontraditional risk factors in cardiovascular disease risk assessment: Updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2018, 320, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruderman, I.; Holt, S.G.; Hewitson, T.D.; Smith, E.R.; Toussaint, N.D. Current and potential therapeutic strategies for the management of vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease including those on dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.C.; Liu, W.C. Role of vitamin D in uremic vascular calcification. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2803579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, M.; Schafer, C.; Heiss, A.; Graber, S.; Kinkeldey, A.; Buscher, A.; Schmitt, M.M.; Bornemann, J.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Clearance of fetuin-A—Containing calciprotein particles is mediated by scavenger receptor-A. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.X.; O’Neill, K.D.; Moe, S.M. Matrix vesicles induce calcification of recipient vascular smooth muscle cells through multiple signaling pathways. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, C.S.B.; Santos, L.; Macedo, A.L.; Matos, A.A.; Silva, A.P.; Neves, P.L.; Staes, A.; Gevaert, K.; Morais, R.; Vermeer, C.; et al. Chronic kidney disease circulating calciprotein particles and extracellular vesicles promote vascular calcification: A role for GRP (Gla-rich protein). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, S. Phosphate metabolism and vitamin D. Bonekey Rep. 2014, 3, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.C.; Lu, C.L.; Lu, K.C. Mineral bone disorders in chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2018, 23 (Suppl. 4), 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, N.M.; Sanchez, C.P.; Lindsey, R.C.; Watt, H.; Mohan, S. Cortical and trabecular bone are equally affected in rats with renal failure and secondary hyperparathyroidism. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, S.; Jiang, S.; Ouyang, H.; Shi, Y.; Shen, H. The effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on intact parathyroid hormone levels in peritoneal dialysis patients. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldost. Syst. 2015, 16, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.D.; Gomez, L.M.; Marchioni, D.M.L.; Dos Anjos, F.S.N.; Molina, M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Bensenor, I.J.M.; Titan, S.M.O. Association between dietary intake and coronary artery calcification in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease: The progredir study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Wu, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Indoxyl sulfate: A novel cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Tomino, Y.; Lu, K.C. Impacts of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresol sulfate on chronic kidney disease and mitigating effects of ast-120. Toxins 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.; Mao, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W. Indoxyl sulfate potentiates endothelial dysfunction via reciprocal role for reactive oxygen species and RhoA/ROCK signaling in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Arake, R.; Sugimoto, R.; Imafuku, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Ishima, Y.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate potentiates skeletal muscle atrophy by inducing the oxidative stress-mediated expression of myostatin and atrogin-1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.J. The effects of indoxyl sulfate-induced endothelial microparticles on neointimal hyperplasia formation in an ex vivo model. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2017, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Ji, S.; Dong, W.; Qi, Y.; Song, W.; Cui, D.; Shi, J. Indolic uremic solutes enhance procoagulant activity of red blood cells through phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle release. Toxins 2015, 7, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Huang, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Tsai, T.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Huang, P.H.; Tarng, D.C. Indoxyl sulfate suppresses endothelial progenitor cell-mediated neovascularization. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirich, T.L.; Meyer, T.W.; Gondouin, B.; Brunet, P.; Niwa, T. Protein-bound molecules: A large family with a bad character. Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervloet, M.; Cozzolino, M. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: Different bricks in the wall? Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlieper, G.; Schurgers, L.; Brandenburg, V.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Floege, J. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: An update. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Schafer, C.; Ketteler, M.; McKee, M.D. Mineral chaperones: A role for fetuin-A and osteopontin in the inhibition and regression of pathologic calcification. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Heiss, A.; Schafer, C.; Ketteler, M. Fetuin-A regulation of calcified matrix metabolism. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 1494–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppert, S.; Buscher, A.; Babler, A.; Ghallab, A.; Buhl, E.M.; Latz, E.; Hengstler, J.G.; Smith, E.R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Cellular clearance and biological activity of calciprotein particles depend on their maturation state and crystallinity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Anokhina, V.; Dieudonne, G.; Abramowitz, M.K.; Kashyap, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, T.T.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Miller, B.L.; Bushinsky, D.A. Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease and vascular calcification have a large hydrodynamic radius of secondary calciprotein particles. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Tokumoto, M.; Tsuruya, K.; Tatsumoto, N.; Noguchi, H.; Kitazono, T.; Ooboshi, H. Fetuin-A decrease induced by a low-protein diet enhances vascular calcification in uremic rats with hyperphosphatemia. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2015, 309, F744–F754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasch, A.; Block, G.A.; Bachtler, M.; Smith, E.R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Arampatzis, S.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.; Ma, X.; Floege, J. Blood calcification propensity, cardiovascular events, and survival in patients receiving hemodialysis in the evolve trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruderman, I.; Smith, E.R.; Toussaint, N.D.; Hewitson, T.D.; Holt, S.G. Longitudinal changes in bone and mineral metabolism after cessation of cinacalcet in dialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzer, P.; Boehm, M.; Sorribas, V.; Thiriet, M.; Janzen, J.; Zeller, T.; St Hilaire, C.; Shanahan, C. Medial vascular calcification revisited: Review and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, S.E.; Aikawa, E. Role of extracellular vesicles in de novo mineralization: An additional novel mechanism of cardiovascular calcification. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Thadhani, R.; Brandenburg, V.M. Calciphylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.; Li, Q.; Pfeifer, A.; Werner, N. Endothelial- and immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the regulation of cardiovascular health and disease. JACC 2017, 2, 790–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, J.A. Vascular calcification: Mechanisms of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shearer, M.J.; Okano, T. Key pathways and regulators of vitamin k function and intermediary metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, D.; Zhelev, Z.; Getsov, P.; Nikolova, B.; Aoki, I.; Higashi, T.; Bakalova, R. Vitamin K: Redox-modulation, prevention of mitochondrial dysfunction and anticancer effect. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Rotondi, S.; Bover, J.; Goldsmith, D.; Pasquali, M. News on biomarkers in ckd-mbd. Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, J.; Dhondt, A. The role of vitamin k in vascular calcification of patients with chronic kidney disease. Acta Clin. Belg. 2016, 71, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzantian, H.; Akers, S.R.; Oldland, G.; Javaid, K.; Miller, R.; Ge, Y.; Ansari, B.; Lee, J.; Suri, A.; Hasmath, Z.; et al. Circulating dephospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla-protein is associated with kidney dysfunction and arterial stiffness. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardana, M.; Vasim, I.; Varakantam, S.; Kewan, U.; Tariq, A.; Koppula, M.R.; Syed, A.A.; Beraun, M.; Drummen, N.E.; Vermeer, C.; et al. Inactive matrix Gla-protein and arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Beulens, J.W. The Role of Vitamin K Status in Cardiovascular Health: Evidence from Observational and Clinical Studies. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2017, 6, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.F.; Drummen, N.E.; Schutte, A.E.; Thijs, L.; Jacobs, L.; Petit, T.; Yang, W.Y.; Smith, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Gu, Y.M.; et al. Vitamin K dependent protection of renal function in multi-ethnic population studies. EBioMedicine 2016, 4, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupisti, A.; D’Alessandro, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Cosola, C.; Gallieni, M.; Egidi, M.F.; Fusaro, M. Non-traditional aspects of renal diets: Focus on fiber, alkali and vitamin K1 intake. Nutrients 2017, 9, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple, J.D.; Greene, T.; Chumlea, W.C.; Hollinger, D.; Maroni, B.J.; Merrill, D.; Scherch, L.K.; Schulman, G.; Wang, S.R.; Zimmer, G.S. Relationship between nutritional status and the glomerular filtration rate: Results from the MDRD study. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1688–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, W.F.; Tomassini, J.E.; Neff, D.R. Lipid abnormalities in patients with chronic kidney disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 171, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; D’Alessandro, C.; Noale, M.; Tripepi, G.; Plebani, M.; Veronese, N.; Iervasi, G.; Giannini, S.; Rossini, M.; Tarroni, G.; et al. Low vitamin k1 intake in haemodialysis patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, K.M.; Booth, S.L.; Fu, X.; Ward, E.; Adams, M.A.; Holden, R.M. Vitamin K metabolism in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Bloch, D.B.; Nazarian, R.M.; Vermeer, C.; Booth, S.L.; Xu, D.; Thadhani, R.I.; Malhotra, R. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla protein influences the risk of calciphylaxis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaesler, N.; Magdeleyns, E.; Herfs, M.; Schettgen, T.; Brandenburg, V.; Fliser, D.; Vermeer, C.; Floege, J.; Schlieper, G.; Kruger, T. Impaired vitamin k recycling in uremia is rescued by vitamin K supplementation. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxma, P.Y.; van den Berg, E.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Laverman, G.D.; Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C.; Kema, I.P.; Muskiet, F.A.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.; et al. Vitamin K intake and plasma desphospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla-protein levels in kidney transplant recipients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, K.S.; Bots, M.L.; Vermeer, C.; Witteman, J.C.; Grobbee, D.E. Vitamin K intake and osteocalcin levels in women with and without aortic atherosclerosis: A population-based study. Atherosclerosis 1995, 116, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleijnse, J.M.; Vermeer, C.; Grobbee, D.E.; Schurgers, L.J.; Knapen, M.H.; van der Meer, I.M.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C. Dietary intake of menaquinone is associated with a reduced risk of coronary heart disease: The rotterdam study. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3100–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattazzi, M.; Faggin, E.; Bertacco, E.; Nardin, C.; Pagliani, L.; Plebani, M.; Cinetto, F.; Guidolin, D.; Puato, M.; Pauletto, P. Warfarin, but not rivaroxaban, promotes the calcification of the aortic valve in ApoE−/− mice. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 36, e12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Long, X.; Yan, J. Vitamin K2 can suppress the expression of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4, and inhibit calcification of aortic intima in ApoE−/− mice as well as smooth muscle cells. Vascular 2018, 26, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Zhao, S.; Wenger, J.; Hymes, J.L.; Maddux, F.W.; Thadhani, R.I.; Chan, K.E. A nationally representative study of calcific uremic arteriolopathy risk factors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragatski, E.; Grommes, J.; Schurgers, L.J.; Langer, S.; Kennes, L.; Tamm, M.; Koeppel, T.A.; Kranz, J.; Hackhofer, T.; Arakelyan, K.; et al. Vitamin K antagonism aggravates chronic kidney disease-induced neointimal hyperplasia and calcification in arterialized veins: Role of vitamin K treatment? Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenfeld, R.; Krueger, T.; Schlieper, G.; Cranenburg, E.C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Heidenreich, S.; Holzmann, S.; Vermeer, C.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M.; et al. Effect of vitamin K2 supplementation on functional vitamin K deficiency in hemodialysis patients: A randomized trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, R.M.; Booth, S.L.; Day, A.G.; Clase, C.M.; Zimmerman, D.; Moist, L.; Shea, M.K.; McCabe, K.M.; Jamal, S.A.; Tobe, S.; et al. Inhibiting the progression of arterial calcification with vitamin K in HemoDialysis patients (iPACK-HD) trial: Rationale and study design for a randomized trial of vitamin K in patients with end stage kidney disease. Canadian J Kidney Health Disease 2015, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Ortiz-Arduan, A.; Lorenzo-Sellares, V. Vitamin D and proteinuria: A critical review of molecular bases and clinical experience. Nefrologia 2013, 33, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R. Vitamin D, proteinuria, diabetic nephropathy, and progression of CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.P.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Lim, C.S. Prevalence of vitamin d deficiency and effects of supplementation with cholecalciferol in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Renal Nutr. 2014, 24, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Paricalcitol attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3382–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, E.; Nishizawa, Y.; Inaba, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Emoto, M.; Kawagishi, T.; Shoji, S.; Okuno, S.; Kim, M.; Miki, T.; et al. Serum levels of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D in nondialyzed patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briese, S.; Wiesner, S.; Will, J.C.; Lembcke, A.; Opgen-Rhein, B.; Nissel, R.; Wernecke, K.D.; Andreae, J.; Haffner, D.; Querfeld, U. Arterial and cardiac disease in young adults with childhood-onset end-stage renal disease-impact of calcium and vitamin D therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 375. [Google Scholar]
- Legarth, C.; Grimm, D.; Wehland, M.; Bauer, J.; Kruger, M. The impact of vitamin d in the treatment of essential hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murni, I.K.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Oktaria, V. Association of vitamin D deficiency with cardiovascular disease risk in children: Implications for the Asia pacific region. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 25, s8–s19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.D.; Price, P.A. Induction of matrix Gla protein synthesis during prolonged 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment of osteosarcoma cells. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1990, 46, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, N.; Hoshi, K.; Sano, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Tadano, K.; Koshihara, Y. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes vitamin K2 metabolism in human osteoblasts. Osteoporos. Int. 2001, 12, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, P.A.; Baukol, S.A. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases serum levels of the vitamin K-dependent bone protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1981, 99, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Bruge, F.; Cecconi, S.; Manzotti, S.; Littarru, G.P.; Tiano, L. Vitamin MK-7 enhances vitamin D3-induced osteogenesis in hMSCs: Modulation of key effectors in mineralization and vascularization. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.C.; Li, R.W.; Seto, S.W.; Kong, S.K.; Ho, H.P.; Hoi, M.P.; Lee, S.M.; Ngai, S.M.; Chan, S.W.; Leung, G.P.; et al. In vitro vitamin K(2) and 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) combination enhances osteoblasts anabolism of diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 767, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyama, Y.; Horiuch, M.; Hayashi, M.; Kanke, Y. Effect of vitamin K2 on experimental calcinosis induced by vitamin D2 in rat soft tissue. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1996, 66, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bostrom, K.I. Cell differentiation in vascular calcification. Z. Kardiol. 2000, 89, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farzaneh-Far, A.; Weissberg, P.L.; Proudfoot, D.; Shanahan, C.M. Transcriptional regulation of matrix gla protein. Z. Kardiol. 2001, 90, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Cepelis, A.; Visser, M.; Brouwer, I.A.; van Schoor, N.M.; Beulens, J.W. Joint Association of Low Vitamin D and Vitamin K Status With Blood Pressure and Hypertension. Hypertension 2017, 69, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, E.; Molgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Jakobsen, J.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.J.; Cashman, K.D. Serum percentage undercarboxylated osteocalcin, a sensitive measure of vitamin k status, and its relationship to bone health indices in Danish girls. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, O., Jr.; Seidlerova, J.; Wohlfahrt, P.; Filipovsky, J.; Cifkova, R.; Cerna, V.; Kucerova, A.; Pesta, M.; Fuchsova, R.; Topolcan, O.; et al. Synergistic effect of low k and d vitamin status on arterial stiffness in a general population. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 46, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asemi, Z.; Raygan, F.; Bahmani, F.; Rezavandi, Z.; Talari, H.R.; Rafiee, M.; Poladchang, S.; Darooghegi Mofrad, M.; Taheri, S.; Mohammadi, A.A.; et al. The effects of vitamin D, K and calcium co-supplementation on carotid intima-media thickness and metabolic status in overweight type 2 diabetic patients with CHD. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Giannini, S.; Gallieni, M.; Noale, M.; Tripepi, G.; Rossini, M.; Messa, P.; Rigotti, P.; Pati, T.; Barbisoni, F.; et al. Calcimimetic and vitamin D analog use in hemodialyzed patients is associated with increased levels of vitamin K dependent proteins. Endocrine 2016, 51, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C. The use of bone turnover markers in chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorders. Nephrology 2017, 22 (Suppl. 2), 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massy, Z.; Drueke, T. Adynamic bone disease is a predominant bone pattern in early stages of chronic kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguineti, R.; Monacelli, F.; Parodi, A.; Furfaro, A.L.; Borghi, R.; Pacini, D.; Pronzato, M.A.; Odetti, P.; Molfetta, L.; Traverso, N. Vitamins D3 and K2 may partially counterbalance the detrimental effects of pentosidine in ex vivo human osteoblasts. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ussif, A.; Pihlstrom, H.; Pasch, A.; Holdaas, H.; Hartmann, A.; Smerud, K.; Asberg, A. Paricalcitol supplementation during the first year after kidney transplantation does not affect calcification propensity score. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Zheng, C.-M.; Chen, R.-M.; Lin, Y.-F.; Liu, W.-C.; Yen, T.-H.; Chen, R.; Lu, K.-C. Emerging Role of Vitamins D and K in Modulating Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Aspect of Passive Calcification. Nutrients 2019, 11, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010152
Hou Y-C, Lu C-L, Zheng C-M, Chen R-M, Lin Y-F, Liu W-C, Yen T-H, Chen R, Lu K-C. Emerging Role of Vitamins D and K in Modulating Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Aspect of Passive Calcification. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010152
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yi-Chou, Chien-Lin Lu, Cai-Mei Zheng, Ruei-Ming Chen, Yuh-Feng Lin, Wen-Chih Liu, Tzung-Hai Yen, Remy Chen, and Kuo-Cheng Lu. 2019. "Emerging Role of Vitamins D and K in Modulating Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Aspect of Passive Calcification" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010152
APA StyleHou, Y. -C., Lu, C. -L., Zheng, C. -M., Chen, R. -M., Lin, Y. -F., Liu, W. -C., Yen, T. -H., Chen, R., & Lu, K. -C. (2019). Emerging Role of Vitamins D and K in Modulating Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Aspect of Passive Calcification. Nutrients, 11(1), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010152




