Associations of Weekday and Weekend Sleep with Children’s Reported Eating in the Absence of Hunger
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
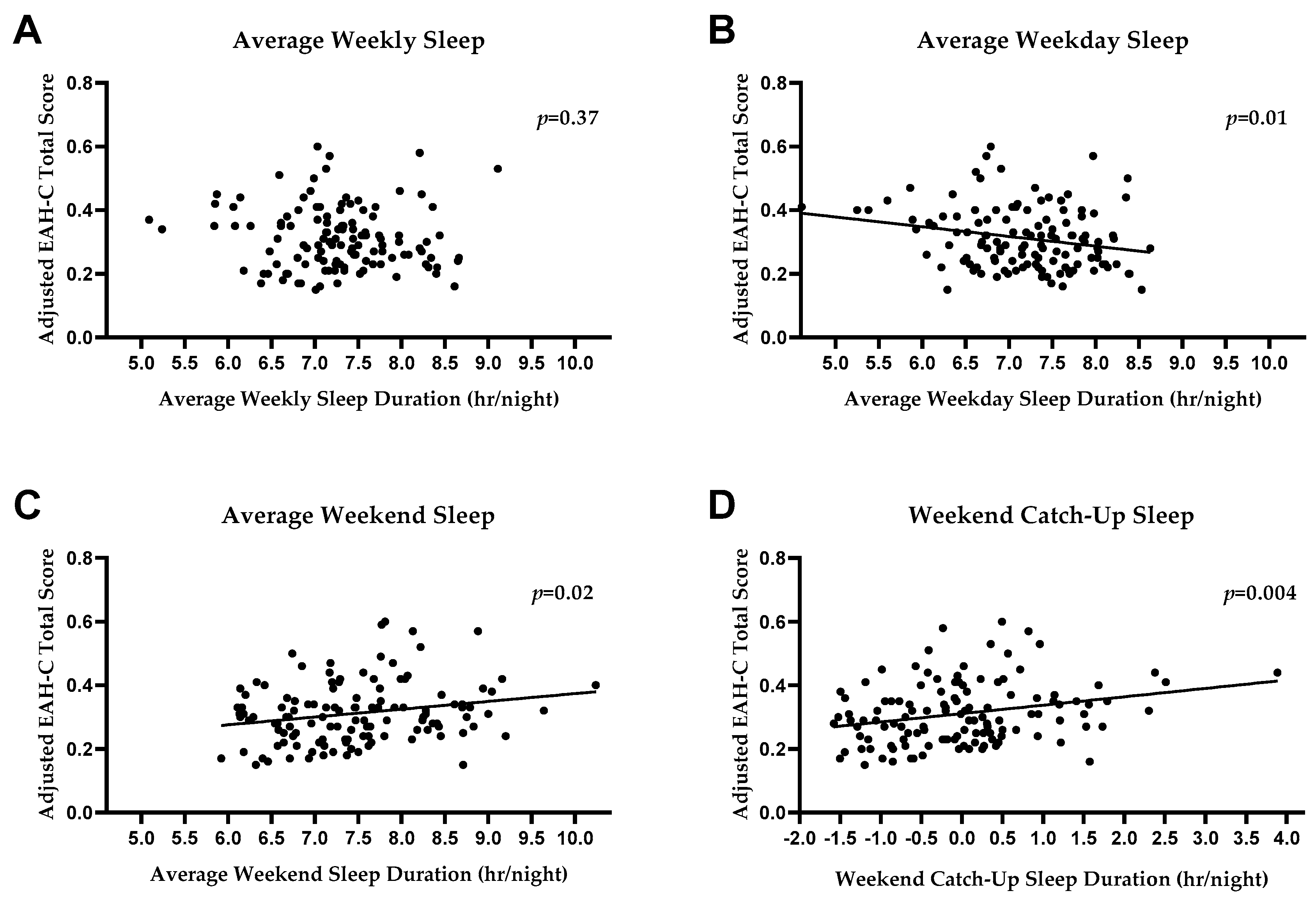
3. Results
3.1. EAH
3.2. Fat Mass
3.3. Exploratory Mediation Analyses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hales, C.M.; Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity among Adults and Youth: United States, 2015–2016; NCHS Data Brief, no 288; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8.
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Severe Obesity among Children and Adolescents Aged 2–19 Years: United States, 1963–1965 through 2015–2016. 2018. National Center for Health Statistics, September 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/obesity_child_15_16/obesity_child_15_16.htm (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Ebbeling, C.B.; Pawlak, D.B.; Ludwig, D.S. Childhood obesity: Public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 2002, 360, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Must, A.; Strauss, R. Risks and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity. Int. J. Obes. 1999, 23, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgaron, E.R. Childhood Obesity: A Review of Increased Risk for Physical and Psychological Co-morbidities. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, A18–A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, Y.; Doi, S.A.R.; Mamun, A.A. Longitudinal impact of sleep on overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and bias-adjusted meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Kruisbrink, M.; Wallace, J.; Ji, C.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sleep duration and incidence of obesity in infants, children, and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep 2018, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Schvey, N.A.; Olsen, C.H.; Gustafson, J.; Yanovski, J.A. A Prospective Study of Loss of Control Eating for Body Weight Gain in Children at High Risk for Adult Obesity. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2009, 42, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.E.; Austin, S.B.; Taylor, C.B.; Malspeis, S.; Rosner, B.; Rockett, H.R.; Gillman, M.W.; Colditz, G. Relation Between Dieting and Weight Change Among Preadolescents and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneville, K.R.; Horton, N.J.; Micali, N.; Crosby, R.D.; Swanson, S.A.; Solmi, F.; Field, A.E. Longitudinal associations between binge eating and overeating and adverse outcomes among adolescents and young adults: Does loss of control matter? JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E.; Agras, W.S.; Hammer, L.D. Risk factors for the emergence of childhood eating disturbances: A five-year prospective study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1999, 25, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Cohen, M.L.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Cox, C.; Theim, K.R.; Keil, M.; Reynolds, J.C.; Yanovski, J.A. A Prospective Study of Psychological Predictors of Body Fat Gain Among Children at High Risk for Adult Obesity. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Sonneville, K.R.; Micali, N.; Crosby, R.D.; Swanson, S.A.; Laird, N.M.; Treasure, J.; Solmi, F.; Horton, N.J. Prospective Association of Common Eating Disorders and Adverse Outcomes. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e289–e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, C.E.; Poitras, V.J.; Gruber, R.; Olds, T.; Weiss, S.K.; Kho, M.E.; Sampson, M.; Belanger, K.; Eryuzlu, S.; Callender, L.; et al. Systematic review of the relationships between sleep duration and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S266–S282. [Google Scholar]
- Maslowsky, J.; Ozer, E.J. Developmental trends in sleep duration in adolescence and young adulthood: Evidence from a national United States sample. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 54, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for Pediatric Populations: A Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knell, G.; Durand, C.P.; Kohl, H.W.; Wu, I.H.; Gabriel, K.P. Prevalence and Likelihood of Meeting Sleep, Physical Activity, and Screen-Time Guidelines among US Youth. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricciani, L.; Olds, T.; Petkov, J. In search of lost sleep: Secular trends in the sleep time of school-aged children and adolescents. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.E.; Goodwin, J.L.; Parthasarathy, S.; Sherrill, D.L.; Vana, K.D.; Drescher, A.A.; Quan, S.F. Longitudinal Association between Short Sleep, Body Weight, and Emotional and Learning Problems in Hispanic and Caucasian Children. Sleep 2011, 34, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storfer-Isser, A.; Patel, S.R.; Babineau, D.C.; Redline, S. Relation between sleep duration and BMI varies by age and sex in youth age 8–19. Pediatr Obes. 2012, 7, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Taheri, S. Associations among late chronotype, body mass index and dietary behaviors in young adolescents. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrin, D.C.; McGrath, J.J.; Drake, C.L. Beyond sleep duration: Distinct sleep dimensions are associated with obesity in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, V.; Petit, D.; Falissard, B.; Vitaro, F.; Tremblay, R.E.; Montplaisir, J.; Touchette, E. Short Sleep Duration and Body Mass Index: A Prospective Longitudinal Study in Preadolescence. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, L.A.; Murray, D.M.; Laska, M.N.; Pasch, K.E.; Anderson, S.E.; Farbakhsh, K. Examining the longitudinal relationship between change in sleep and obesity risk in adolescents. Health Educ. Behav. 2013, 40, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ievers-Landis, C.E.; Kneifel, A.; Giesel, J.; Rahman, F.; Narasimhan, S.; Uli, N.; O’Riordan, M. Dietary Intake and Eating-Related Cognitions Related to Sleep Among Adolescents Who Are Overweight or Obese. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016, 41, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, J.S.; Hjorth, M.F.; Andersen, R.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Tetens, I.; Astrup, A.; Chaput, J.P.; Sjödin, A. Short sleep duration and large variability in sleep duration are independently associated with dietary risk factors for obesity in Danish school children. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2014, 38, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thivel, D.; Isacco, L.; Aucouturier, J.; Pereira, B.; Lazaar, N.; Ratel, S.; Doré, E.; Duché, P. Bedtime and Sleep Timing but not Sleep Duration Are Associated With Eating Habits in Primary School Children. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2015, 36, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Kong, A.P.S.; Wing, Y.K.; Li, S.X.; Kong, A.P.S. The Effect of Weekend and Holiday Sleep Compensation on Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 994–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Hasler, B.P.; Dahl, R.E.; Holm, S.M.; Jakubcak, J.L.; Ryan, N.D.; Silk, J.S.; Phillips, M.L.; Forbes, E.E. Weekend—Weekday advances in sleep timing are associated with altered reward-related brain function in healthy adolescents. Boil. Psychol. 2012, 91, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinska, A.J.; Yasuda, M.; Burant, C.F.; Gregor, N.; Khatri, S.; Sweet, M.; Falk, E.B. Impulsivity and inhibitory control deficits are associated with unhealthy eating in young adults. Appetite 2012, 59, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansigan, R.K.; Emond, J.A.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. Understanding eating in the absence of hunger among young children: A systematic review of existing studies. Appetite 2015, 85, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, N.R.; Shomaker, L.B.; Pickworth, C.K.; Brady, S.M.; Courville, A.B.; Bernstein, S.; Schvey, N.A.; Demidowich, A.P.; Galescu, O.; Yanovski, S.Z.; et al. A Prospective Study of Adolescent Eating in the Absence of Hunger and Body Mass and Fat Mass Outcomes. Obesity 2015, 23, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Ranzenhofer, L.M.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Schvey, N.A.; Faith, M.; Gustafson, J.; Yanovski, J.A. Psychometric Properties of a New Questionnaire to Assess Eating in the Absence of Hunger in Children and Adolescents. Appetite 2008, 51, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.O.; Birch, L.L. Eating in the absence of hunger and overweight in girls from 5 to 7 y of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.L.; Fisher, J.O.; Davison, K.K. Learning to overeat: Maternal use of restrictive feeding practices promotes girls’ eating in the absence of hunger. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.A.; Birch, L.L. Maternal weight status modulates the effects of restriction on daughters’ eating and weight. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, N.F.; Cai, G.; Cole, S.A.; Wilson, T.A.; Fisher, J.O.; Zakeri, I.F.; Ellis, K.J.; Comuzzie, A.G. Metabolic and behavioral predictors of weight gain in Hispanic children: The Viva la Familia Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Bixler, E.O.; Liao, J.; Berg, A.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Liao, D. Habitual sleep variability, mediated by nutrition intake, is associated with abdominal obesity in adolescents. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.F.; Balantekin, K.N.; Altman, M.; Wilfley, D.E.; Taylor, C.B.; Williams, J. Sleep Patterns and Quality Are Associated with Severity of Obesity and Weight-Related Behaviors in Adolescents with Overweight and Obesity. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Després, J.-P.; Bouchard, C.; Tremblay, A. The Association between Short Sleep Duration and Weight Gain Is Dependent on Disinhibited Eating Behavior in Adults. Sleep 2011, 34, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiatrault, M.-L.; Chaput, J.-P.; Drapeau, V.; Tremblay, A. Eating behavior traits and sleep as determinants of weight loss in overweight and obese adults. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, B.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, Y.J. The Association between Self-reported Sleep Duration and Body Mass Index among Korean Adolescents. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrimmon, A.W.; Smith, A.D. Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence, 2nd edition (WASI-II). J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 2013, 31, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, R.J. 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: Methods and Development; Vital and Health Statistics Series 11; National Center for Health Statistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–190.
- Daniels, S.R. The Use of BMI in the Clinical Setting. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.J.; Kelly, N.R.; Brychta, R.J.; Grammer, A.C.; Jaramillo, M.; Chen, K.Y.; Fletcher, L.A.; Bernstein, S.B.; Courville, A.B.; Shank, L.M.; et al. Associations of sleep patterns with metabolic syndrome indices, body composition, and energy intake in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, A.; Sharkey, M.; Carskadon, M.A. Activity-Based Sleep-Wake Identification: An Empirical Test of Methodological Issues. Sleep 1994, 17, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, C.A.; Chang, A.; Gadkary, C.; Guilleminault, C.; Carrillo, O.; Dement, W.C. Comparison of actigraphic, polysomnographic, and subjective assessment of sleep parameters in sleep-disordered patients. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauri, P.J.; Kripke, D.F.; Lavie, P.; Sadeh, A. The Role of Actigraphy in the Evaluation of Sleep Disorders. Sleep 1995, 18, 288–302. [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer, L.J.; Wong, P.; Biggs, S.N.; Traylor, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Narang, I.; Marcus, C.L. Validation of Actigraphy in Middle Childhood. Sleep 2016, 39, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, M. The Children’s Depression, Inventory (CDI). Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1985, 21, 995–998. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, M. Children’s Depression Inventory 2nd Edition Technical Manual; Multi-Health Systems, Inc.: Ontario, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, M.; Beck, A.T. An empirical-clinical approach toward a definition of childhood depression. In Depression in Childhood: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Conceptual Models; Schulterbrandt, J.G., Raskin, A., Eds.; Raven: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Saylor, C.F.; Finch, A.J.; Spirito, A.; Bennett, B. The Children’s Depression Inventory: A systematic evaluation of psychometric properties. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1984, 52, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golley, R.K.; Maher, C.A.; Matricciani, L.; Olds, T.S. Sleep duration or bedtime? Exploring the association between sleep timing behaviour, diet and BMI in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-López, N.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M.; Pico, Y.; Livianos-Aldana, L.; Llopis-González, A. Nutrient Intake and Depression Symptoms in Spanish Children: The ANIVA Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2016, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Cha, H.S. Retrospective cohort study on Korean adolescents’ sleep, depression, school adjustment, and life satisfaction. Nurs. Heal. Sci. 2018, 20, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, J.P.; Preacher, K.J. Mediation Models for Longitudinal Data in Developmental Research. Res. Hum. Dev. 2009, 6, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suglia, S.F.; Kara, S.; Robinson, W.R. Sleep duration and obesity among adolescents transitioning to adulthood: Do results differ by sex? J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, A.; Janson, C.; Lindberg, E. The impact of obesity and weight gain on development of sleep problems in a population-based sample. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.A.; Caputi, P.; Iverson, D.C. Patterns of health behaviours predict obesity in Australian children. J. Paediatr. Child Heal. 2013, 49, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Lambert, M.; Gray-Donald, K.; McGrath, J.J.; Tremblay, M.S.; O’Loughlin, J.; Tremblay, A. Short Sleep Duration Is Independently Associated With Overweight and Obesity in Quebec Children. Can. J. Public Heal. 2011, 102, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, S.W.; Filtness, A.; Phillips, C.L.; Anderson, C. Enhanced preference for high-fat foods following a simulated night shift. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Heal. 2015, 41, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depner, C.M.; Melanson, E.L.; Eckel, R.H.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Perreault, L.; Bergman, B.C.; Higgins, J.A.; Guerin, M.K.; Stothard, E.R.; Morton, S.J.; et al. Ad libitum Weekend Recovery Sleep Fails to Prevent Metabolic Dysregulation during a Repeating Pattern of Insufficient Sleep and Weekend Recovery Sleep. Curr. Boil. 2019, 29, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.N.; Carskadon, M.A.; Considine, R.V.; Fava, J.L.; Lawton, J.; Raynor, H.A.; Jelalian, E.; Owens, J.; Wing, R. Changes in Children’s Sleep Duration on Food Intake, Weight, and Leptin. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHill, A.W.; Melanson, E.L.; Higgins, J.; Connick, E.; Moehlman, T.M.; Stothard, E.R.; Wright, K.P. Impact of circadian misalignment on energy metabolism during simulated nightshift work. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17302–17307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Wright, K.P., Jr. Influence of weeks of circadian misalignment on leptin levels. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2010, 2, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Hilton, M.F.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Shea, S.A. Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeke, C.E.; Storfer-Isser, A.; Redline, S.; Taveras, E.M. Childhood Sleep Duration and Quality in Relation to Leptin Concentration in Two Cohort Studies. Sleep 2014, 37, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Wright, H.R.; Lack, L.C. Sleeping-in on the weekend delays circadian phase and increases sleepiness the following week. Sleep Boil. Rhythm. 2008, 6, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, N.R.; Shomaker, L.B.; Radin, R.M.; Thompson, K.A.; Cassidy, O.L.; Brady, S.; Mehari, R.; Courville, A.B.; Chen, K.Y.; Galescu, O.A.; et al. Associations of Sleep Duration and Quality with Disinhibited Eating Behaviors in Adolescent Girls At-Risk for Type 2 Diabetes. Eat. Behav. 2016, 22, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, S.R.; Miranda, A.M.; Coelho, R.; Monteiro, A.C.; Bragança, G.; Loureiro, H.C. Overweight in youth and sleep quality: Is there a link? Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, J.L.; Van Cauter, E. Disturbances of sleep and circadian rhythms: Novel risk factors for obesity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2016, 23, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.J.; Hasler, B.P. Chronotype and Mental Health: Recent Advances. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madowitz, J.; Liang, J.; Peterson, C.B.; Rydell, S.; Zucker, N.L.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Harnack, L.; Boutelle, K.N. Concurrent and convergent validity of the eating in the absence of hunger questionnaire and behavioral paradigm in overweight children. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Mooreville, M.; Shomaker, L.B.; A Reina, S.; Courville, A.B.; E Field, S.; E Matheson, B.; Brady, S.M.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A.; et al. Links of adolescent- and parent-reported eating in the absence of hunger with observed eating in the absence of hunger. Obesity 2013, 21, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristic a | Sample with Overweight (n = 38) | Sample without Overweight (n = 85) | Total Sample (n = 123) | Total Sample Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) Sex (% female) Race/Ethnicity (%) * Hispanic or Latino Asian Black or African American Multiple Races White Unknown Fat Mass (kg) * Overweight/Obesity (85th percentile, %) BMIz Score * Average Weekly Sleep Duration (hr/night) Weekday Sleep Duration (hr/night) Weekend Sleep Duration (hr/night) Weekend “Catch-Up” Sleep Duration (hr/night) Eating in the Absence of Hunger | 12.4 ± 2.5 58.0 7.9 0.0 47.4 10.5 31.6 2.6 24.9 ± 9.4 1.7 ± 0.4 7.1 ± 0.8 7.0 ± 0.8 7.3 ± 1.0 0.2 ± 0.9 1.1 ± 0.5 | 12.9 ± 2.6 49.0 7.1 16.5 21.1 5.9 49.4 0.0 11.2 ± 4.4 0.0 ± 0.7 7.3 ± 0.7 7.2 ± 0.8 7.6 ± 1.0 0.3 ± 1.0 1.1 ± 0.5 | 12.7 ± 2.6 52.0 7.3 11.4 29.3 7.3 43.9 0.8 15.5 9.0 30.9 0.5 ± 1.0 7.3 ± 0.7 7.2 ± 0.8 7.5 ± 1.0 0.3 ± 1.0 1.1 ± 0.5 | 8.0–17.9 4.0–54 −1.6–2.8 −1.6–2.8 4.9–8.8 4.6–8.7 5.3–9.6 −1.5–4.5 0.5–3.0 |
| Facet of Sleep | Direct Effect (c’ Path) | Indirect Effect (ab Path) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Value | SE | p-Value | 95% CI | R2 | SE | |
| Average Weekly Sleep Weekday Sleep Weekend Sleep Weekend Catch-up Sleep | −1.33 −1.30 −0.90 0.02 | 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 | 0.19 0.20 0.37 0.85 | −0.004–0.009 −0.005–0.01 −0.005–0.004 −0.009–0.007 | 0.01 0.01 0.007 0.004 | 0.003 0.004 0.002 0.004 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LeMay-Russell, S.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Schvey, N.A.; Kelly, N.R.; Shank, L.M.; Mi, S.J.; Jaramillo, M.; Ramirez, S.; Altman, D.R.; Rubin, S.G.; et al. Associations of Weekday and Weekend Sleep with Children’s Reported Eating in the Absence of Hunger. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071658
LeMay-Russell S, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Schvey NA, Kelly NR, Shank LM, Mi SJ, Jaramillo M, Ramirez S, Altman DR, Rubin SG, et al. Associations of Weekday and Weekend Sleep with Children’s Reported Eating in the Absence of Hunger. Nutrients. 2019; 11(7):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071658
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeMay-Russell, Sarah, Marian Tanofsky-Kraff, Natasha A. Schvey, Nichole R. Kelly, Lisa M. Shank, Sarah J. Mi, Manuela Jaramillo, Sophie Ramirez, Deborah R. Altman, Sarah G. Rubin, and et al. 2019. "Associations of Weekday and Weekend Sleep with Children’s Reported Eating in the Absence of Hunger" Nutrients 11, no. 7: 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071658
APA StyleLeMay-Russell, S., Tanofsky-Kraff, M., Schvey, N. A., Kelly, N. R., Shank, L. M., Mi, S. J., Jaramillo, M., Ramirez, S., Altman, D. R., Rubin, S. G., Byrne, M. E., Burke, N. L., Davis, E. K., Broadney, M. M., Brady, S. M., Yanovski, S. Z., & Yanovski, J. A. (2019). Associations of Weekday and Weekend Sleep with Children’s Reported Eating in the Absence of Hunger. Nutrients, 11(7), 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071658





