Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
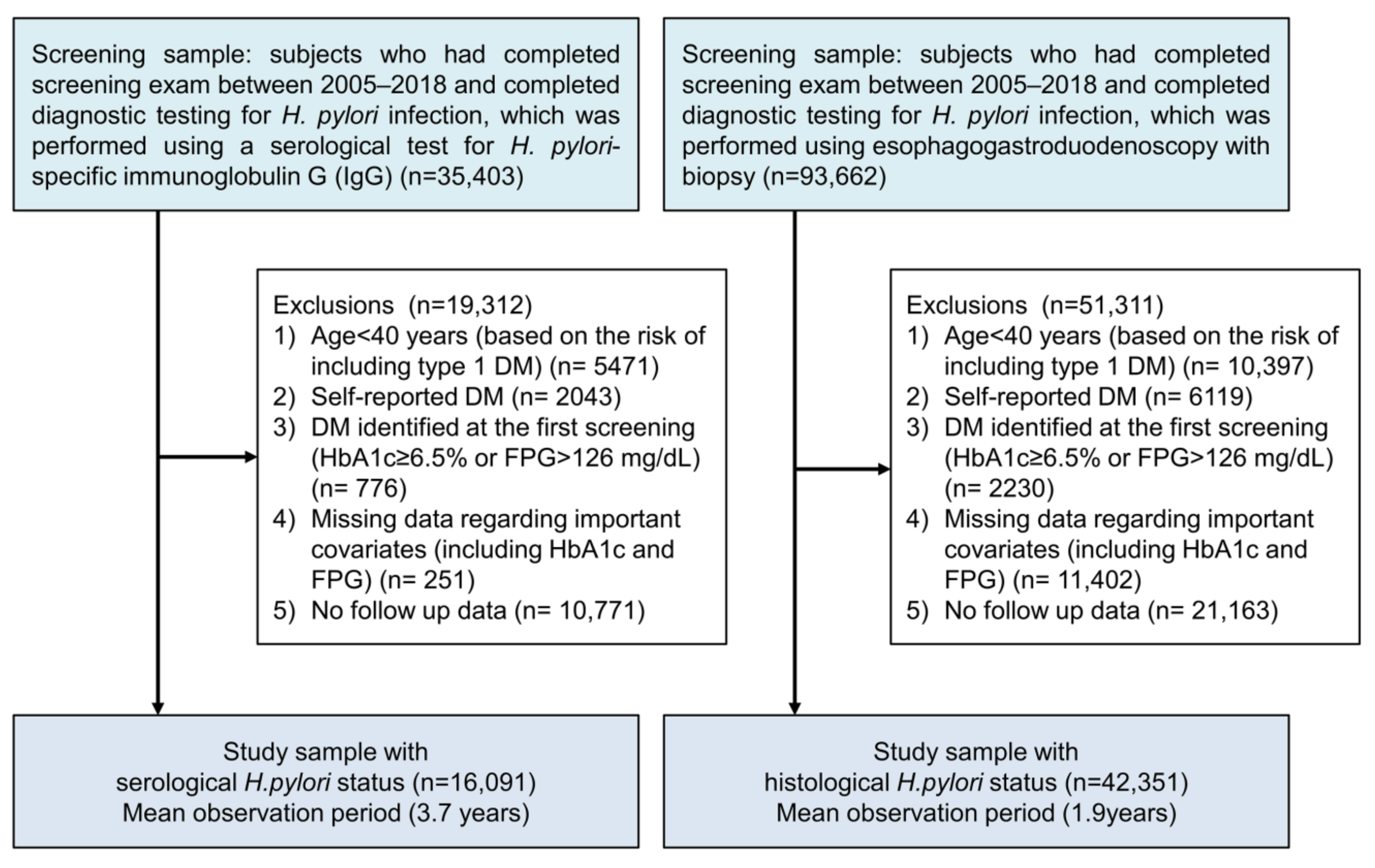
2.1. Study Cohorts
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Diagnosis of H. pylori Infection
2.4. Diagnoses of DM and Diabetic Nephropathy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Incidences of DM, IGT, and Diabetic Nephropathy
3.3. Serological H. pylori Status and DM
3.4. Histological H. pylori Status and DM
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyle, F.A. Helicobacter pylori: Current perspectives. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1991, 13 (Suppl. 1), S114–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, P. Review article: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 13 (Suppl. 1), 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiewicz, J.J. Current insights in the pathogenesis of helicobacter pylori infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 7, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsay, F.W.; Hsu, P.I.H. Pylori infection and extra-gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Franceschi, F.; Nishizawa, T.; Gasbarrini, A. Extragastric manifestations of helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2011, 16 (Suppl. 1), 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Kwon, H.T.; Kang, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.C.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Son, K.Y.; Cho, B. Association between metabolic syndrome and helicobacter pylori infection diagnosed by histologic status and serological status. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubaud Baudron, C.; Franceschi, F.; Salles, N.; Gasbarrini, A. Extragastric diseases and helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2013, 18 (Suppl. 1), 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razuka-Ebela, D.; Giupponi, B.; Franceschi, F. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Helicobacter 2018, 23 (Suppl. 1), e12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunji, T.; Matsuhashi, N.; Sato, H.; Fujibayashi, K.; Okumura, M.; Sasabe, N.; Urabe, A. Helicobacter pylori infection is significantly associated with metabolic syndrome in the japanese population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogru, I.; Kalay, N.; Dogan, A.; Inanc, M.T.; Kaya, M.G.; Topsakal, R.; Gul, I.; Kutukoglu, I.; Kilic, H.; Eryol, N.K. The relationship between helicobacter pylori igg titre and coronary atherosclerosis. Acta Cardiol. 2007, 62, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Sinn, D.H.; Min, Y.W.; Son, H.J.; Kim, J.J.; Chang, Y.; Baek, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, H.; Ryu, S. A cohort study on helicobacter pylori infection associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunji, T.; Matsuhashi, N.; Sato, H.; Fujibayashi, K.; Okumura, M.; Sasabe, N.; Urabe, A. Helicobacter pylori infection significantly increases insulin resistance in the asymptomatic japanese population. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghian, A.; Hashemi, S.A.; Hamidian Jahromi, A.; Eshraghian, H.; Masoompour, S.M.; Davarpanah, M.A.; Eshraghian, K.; Taghavi, S.A. Helicobacter pylori infection as a risk factor for insulin resistance. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Haan, M.N.; Cheng, C.; Clayton, E.R.; Mayeda, E.R.; Miller, J.W.; Aiello, A.E. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with an increased rate of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Blaser, M.J. Association between gastric helicobacter pylori colonization and glycated hemoglobin levels. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senmaru, T.; Fukui, M.; Kuroda, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ushigome, E.; Sakabe, K.; Nakanishi, N.; Mineoka, Y.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Serum pepsinogen i/ii ratio is correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fu, Y.; Lv, Z. Association of helicobacter pylori infection with diabetic complications: A meta-analysis. Endocr. Res. 2014, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z. Association of helicobacter pylori infection with diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis of 39 studies involving more than 20,000 participants. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.N.; Yu, W.L.; Zhu, H.T.; Ding, J.X.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.M. Is helicobacter pylori infection associated with glycemic control in diabetics? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, J.; Yamada, T.; Saito, T.; Ishigaki, Y.; Hinokio, Y.; Kotake, H.; Oka, Y.; Katagiri, H. Eradication of insulin resistance. Lancet 2009, 374, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, C.; Kodama, S.; Fujihara, K.; Hirasawa, R.; Yachi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Hanyu, O.; Shimano, H.; Sone, H. High risk of failing eradication of helicobacter pylori in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 106, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, H.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.H.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, H.J.; Rhee, P.L.; et al. Helicobacter pylori is associated with dyslipidemia but not with other risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Pankow, J.S.; Bertoni, A.G.; Szklo, M.; Folsom, A.R. Serological evidence of infections and type 2 diabetes: The multiethnic study of atherosclerosis. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2009, 26, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Hamamoto, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Honjo, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Tatsuoka, H.; Matsuoka, A.; Ikeda, H.; Fujikawa, J.; Koshiyama, H. The eradication of helicobacter pylori does not affect glycemic control in japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Jpn. Clin. Med. 2013, 4, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jun, J.K.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, E.C. Overview of the national cancer screening programme and the cancer screening status in korea. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2011, 12, 725–730. [Google Scholar]
- Standards of medical care in diabetes—2010. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (Suppl. 1), S11–S61.
- Ko, S.H.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, D.J.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Shim, K.H.; Woo, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, J.T.; et al. 2011 clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in korea. Diabetes Metab. J. 2011, 35, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, I.J. Current challenges in diabetic nephropathy: Early diagnosis and ways to improve outcomes. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, C.; Kodama, S.; Fujihara, K.; Yachi, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Suzuki, A.; Hanyu, O.; Shimano, H.; Sone, H. Association of helicobacter pylori infection with glycemic control in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 250620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, D.I.; Cho, Y.K.; Sung, I.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Kim, B.I.; Keum, D.K. Helicobacter pylori eradication has no effect on metabolic and inflammatory parameters. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2005, 97, 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, S.O.; Btaiche, I.F.; Alaniz, C. Relationship between hyperglycemia and infection in critically ill patients. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Pyo, J.H.; Lee, H.; Baek, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, H.J.; Rhee, P.L.; et al. Lack of association between helicobacter pylori infection and various markers of systemic inflammation in asymptomatic adults. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 72, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J.; Francois, F.; Mathew, J.P.; Ye, X.Y.; Goldberg, J.D.; Bini, E.J. Helicobacter pylori and overweight status in the united states: Data from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelli, M.; Rigante, D.; Marietti, G.; Nista, E.C.; Crea, F.; Schiavino, A.; Cammarota, G.; Pignataro, G.; Petrucci, S.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication rate and glycemic control in young patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanuma, M.; Yanai, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Hirata, Y.; Yamaji, Y.; Kawazu, S.; Maeda, S. Influence of helicobacter pylori eradication on the management of type 2 diabetes. Hepato Gastroenterol. 2012, 59, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Cordero, J.M.; Caballero, C.; Boixeda, D.; Aller, R.; Canton, R.; De la Calle, H. Effect of the treatment of helicobacter pylori infection on gastric emptying and its influence on the glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2001, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| All (n = 16091) | H. pylori (−) (n = 6700, 41.6%) | H. pylori (+) (n = 9391, 58.4%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 51.3 | 51.2 ± 7.6 | 51.4 ± 7.4 | 0.003 |
| Sex (male, %) | 60.2 | 59.1 | 61.0 | 0.015 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 114.1 | 113.8 ± 15.2 | 114.3 ± 15.5 | 0.069 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 69.9 | 69.6 ± 10.2 | 70.0 ± 10.4 | 0.016 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 | 23.8 ± 2.7 | 23.8 ± 2.7 | 0.309 |
| Current smoker (%) | 19.9 | 21.2 | 19.1 | 0.002 |
| Heavy drinker (%) | 14.9 | 14.9 | 14.9 | 0.917 |
| Regular exercise (%) | 44.8 | 45.5 | 44.3 | 0.146 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl) | 192.2 | 191.2 ± 31.7 | 192.9 ± 31.9 | 0.004 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dl) | 127.7 | 126.1 ± 29.5 | 127.6 ± 29.6 | <0.001 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dl) | 57.3 | 57.9 ± 14.2 | 56.8 ± 13.9 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dl) | 74.7 | 128.6 ± 81.0 | 127.0 ± 75.0 | 0.577 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dl) | 89.2 | 89.4 ± 9.5 | 89.1 ± 9.5 | 0.038 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.3 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 0.346 |
| Insulin (µIU/mL) | 9.0 | 9.1 ± 3.9 | 9.0 ± 3.9 | 0.075 |
| C-peptide (ng/mL) | 1.8 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Urinary microalbumin (mg/g Cr) | 2.6 | 2.6 ± 18.5 | 2.6 ± 8.8 | 0.443 |
| Estimated GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 87.9 | 88.4 ± 12.2 | 87.6 ± 12.2 | <0.001 |
| Cases/n (%) | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | ||
| DM | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 569/6700 (8.5) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 769/9391 (8.2) | 0.98 (0.88–0.10) | 0.97 (0.87–1.08) | 1.01 (0.89–1.16) | 1.01 (0.88–1.16) |
| P value | 0.763 | 0.578 | 0.863 | 0.854 | |
| IGT | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 3460/6700 (51.6) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 4791/9391 (51.0) | 1.00 (0.96–1.05) | 0.98 (0.94–1.03) | 0.99 (0.94-1.04) | 0.98 (0.93–1.04) |
| P value | 0.930 | 0.476 | 0.628 | 0.566 | |
| DM nephropathy | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 300/569 (52.7) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 400/769 (52.0) | 0.99 (0.85–1.15) | 0.99 (0.85–1.15) | 1.00 (0.83–1.21) | 0.99 (0.82–1.21) |
| P value | 0.875 | 0.871 | 0.990 | 0.952 | |
| Poor DM control | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 446/568 (78.5) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 621/768 (80.9) | 1.05 (0.93–1.18) | 1.06 (0.94–1.20) | 1.06 (0.91–1.23) | 1.05 (0.90–1.22) |
| P value | 0.479 | 0.352 | 0.465 | 0.535 |
| Cases/n (%) | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | ||
| DM | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 2578/36283 (7.1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 453/6068 (7.5) | 0.93 (0.84–1.03) | 0.94 (0.85–1.04) | 0.93 (0.82–1.07) | 0.93 (0.81–1.07) |
| P value | 0.157 | 0.247 | 0.313 | 0.311 | |
| IGT | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 19075/36283 (52.6) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 3219/6068 (53.0) | 0.94 (0.91–0.98) | 0.95 (0.91–0.98) | 0.93 (0.89–0.98) | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) |
| P value | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| DM nephropathy | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 1172/2578 (45.5) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 212/452 (46.9) | 1.03 (0.89–1.19) | 1.03 (0.89–1.19) | 0.97 (0.80–1.18) | 0.99 (0.81–1.20) |
| P value | 0.677 | 0.701 | 0.772 | 0.888 | |
| Poor DM control | |||||
| H. pylori (−) | 2020/2578 (78.4) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H. pylori (+) | 352/453 (77.7) | 0.99 (0.88–1.11) | 1.00 (0.90–1.13) | 1.01 (0.86–1.18) | 1.00 (0.86–1.17) |
| P value | 0.854 | 0.940 | 0.947 | 0.989 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyo, J.H.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.C.; Cho, S.J.; Choi, Y.-H.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Kim, K.; et al. Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081874
Pyo JH, Lee H, Choi SC, Cho SJ, Choi Y-H, Min YW, Min B-H, Lee JH, Yoo H, Kim K, et al. Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081874
Chicago/Turabian StylePyo, Jeung Hui, Hyuk Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Soo Jin Cho, Yoon-Ho Choi, Yang Won Min, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Heejin Yoo, Kyunga Kim, and et al. 2019. "Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081874
APA StylePyo, J. H., Lee, H., Choi, S. C., Cho, S. J., Choi, Y.-H., Min, Y. W., Min, B.-H., Lee, J. H., Yoo, H., Kim, K., & Kim, J. J. (2019). Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study. Nutrients, 11(8), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081874






