Abstract
It has been suggested that in doubtful cases of coeliac disease, a high CD3+ T-cell receptor gamma delta+ (TCRγδ+) intraepithelial lymphocyte count increases the likelihood of coeliac disease. Aim: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of both an isolated increase of TCRγδ+ cells and a coeliac lymphogram (increase of TCRγδ+ plus decrease of CD3− intraepithelial lymphocytes) evaluated by flow cytometry in the diagnosis of coeliac disease. Methods: The literature search was conducted in MEDLINE and EMBASE. The inclusion criteria were: an article that allows for the construction of a 2 × 2 table of true and false positive and true and false negative values. A diagnostic accuracy test meta-analysis was performed. Results: The search provided 49 relevant citations, of which 6 were selected for the analysis, which represented 519 patients and 440 controls. Coeliac lymphogram: The pooled S and Sp were 93% and 98%, without heterogeneity. The area under the SROC curve (AUC) was 0.98 (95% CI, 0.97–0.99). TCRγδ+: Pooled S and Sp were both 95%, with significant heterogeneity. The AUC was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.95–0.98). Conclusions: Both TCRγδ+ count and coeliac lymphogram assessed by flow cytometry in duodenal mucosal samples are associated with a high level of diagnostic accuracy for and against coeliac disease.
1. Introduction
Coeliac disease (CD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder elicited by the ingestion of gluten in genetically susceptible individuals. The pooled global prevalence of CD based on serological test results is 1.4% and based on biopsy results is 0.7% [1]. CD is characterized by the presence of a varied array of gluten-dependent clinical manifestations, CD-specific antibodies, HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 haplotypes, and enteropathy [2,3,4,5]. Generally speaking, CD diagnosis presents no difficulties when the biopsy shows severe villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia. In clinical practice, however, diagnosis is often less straightforward. Diagnostic difficulties arise especially when biopsy findings are borderline. In such cases, there exists the risk of both under- and over-diagnosis.
Tissue transglutaminase IgA class autoantibodies (anti-tTG2) are the serological markers of choice for the detection of CD [3,4,5]. Serological tests have a high specificity and sensitivity, but can fluctuate in cases with mild intestinal damage and a low gluten intake [6,7]. Moreover, serology seems to have a lower sensitivity and specificity in adults [8].
In addition, the overlap between patients with non-coeliac gluten sensitivity and CD patients with a Marsh type I lesion becomes evident and makes differential diagnosis quite difficult [9,10]. Increasingly, clinicians face the challenge of making a diagnosis of patients who choose to live without gluten, without a previous diagnosis of CD. This is challenging, since both the serology and histology of the small intestine are normalized in patients with CD on a gluten-free diet (GFD). In these circumstances, HLA genotyping is of value, since CD is extremely improbable in patients who are HLA-DQ2/8 negative, though it is insufficient in HLA-DQ2/8 positive patients, since 30–40% of the healthy population are also positive.
Other diagnostic approaches beyond conventional histology and serology have been introduced for the diagnosis of CD [11]. The European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guidelines suggest that in doubtful cases, a high CD3+ T-cell receptor gamma delta+ (TCRγδ+) intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) count increases the likelihood of CD diagnosis [4,5]. IELs are increased in the mucosa of untreated coeliac patients. In general, these IELs are CD3+αβ+ T-cell-receptor-bearing cells. However, 20–30% of CD3+ IELS are γδ+ T-cell-receptor-bearing cells in CD, which comprise fewer than 10% of the IELs in non-coeliac subjects [12]. TCRγδ+ IELs are considered to be highly sensitive and specific for CD, and, furthermore, remain elevated despite a GFD [13,14,15]. Non-T-cell CD3− IELs are the second most abundant IEL subset in healthy mucosa. CD3− IELs comprise heterogeneous phenotypes, of which the functions are not clearly elucidated and which are decreased in untreated coeliac patients [16,17].
The assessment of the density of TCRγδ+ IELs is, in general, performed with immunohistochemistry techniques in frozen biopsy samples [13]. This is a user-dependent, laborious technique in well-orientated, high-quality samples, but sampling is often compromised and conclusions may be difficult to draw. The assessment of TCRγδ+ IELs by flow cytometry allows for a more accurate quantification. Flow cytometry is a powerful analytical tool for the study of small intestinal immune cells, and, in particular, of IEL cells, and is therefore of value in the diagnosis of CD [18]. Using this technique, an IEL pattern that is typical of CD (coeliac lymphogram) has been defined, consisting of both an increase in TCRγδ+ IELs and a decrease in CD3− IELs [18,19].
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of both an isolated increase of TCRγδ+ IELs and a coeliac lymphogram assessed by flow cytometry in duodenal mucosal samples for CD diagnosis by performing a systematic review and meta-analysis of the current literature.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
Bibliographical searches were performed in the MEDLINE and EMBASE electronic databases according to the following search strategy: (celiac OR coeliac OR gluten-sensitive*) AND (gamma delta* OR lymphogram OR T-cell receptor* OR intraepithelial lymphocyte* OR flow cytometry). Limits: English and Spanish languages (English abstracts of articles written in other languages were also reviewed); humans; from January 1990 to July 2019. Inclusion criteria were: (1) Any article with people of any sex, age, and race that allowed for the construction of a two-way table, extracting true positive, false positive, true negative, and false negative values for TCRγδ+ IEL counting and/or coeliac lymphogram for the diagnosis of CD; (2) TCRγδ+ and CD3− IELs assessed by flow cytometry; and (3) A clear description of how the diagnosis of CD had been performed. CD was defined as the presence of a positive coeliac serology (antiendomysium antibody and/or anti-tissue transglutaminase antibody), a compatible duodenal biopsy, and a positive clinical and serological response to a GFD. We excluded articles not fulfilling the inclusion criteria, duplicated articles, letters to the editor, editorials, case series, narrative reviews, and those not related to the object of our study after title and/or abstract reading. Bibliographies of all identified eligible studies were also comprehensively searched for studies not identified using the initial search strategy. Where data were missing from the publication, the first and/or senior author was contacted for further information. According to these criteria, two independent reviewers, reaching a consensus when discrepancies appeared, carried out the identification and selection of the studies (F.F-B. and M.E.). The selection process was documented in line with PRISMA recommendations [20].
2.2. Outcome Assessment
2.2.1. Data Extraction
The name of the first author, year of publication, publication country, number of subjects and controls, definition of CD, flow cytometry methodology, cut-offs of TCRγδ+ IEL and CD3− IEL, mean or median TCRγδ+ IEL count, mean or median CD3− IEL count, and true positive, false positive, true negative, and false negative values for TCRγδ+ IEL and/or coeliac lymphogram were recorded in a standardized fashion.
2.2.2. Study Methodological Quality
The quality of the studies identified was assessed using the QUADAS-2 (Quality Assessment of Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy included in Systematic Reviews) tool [21], which assesses both the risk of bias and applicability of a study. It comprises four domains: patient selection, index test, reference standard, and flow and timing. Each domain is assessed in terms of risk of bias, and the first three domains are also assessed in terms of concerns regarding applicability. Both reviewers also made this assessment, reaching a consensus when discrepancies appeared.
The methodological quality of the flow cytometry methods was assessed following the MIFlowCyt guidelines [22].
2.2.3. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
The software STATA 16.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA) was used to perform the meta-analysis, using the “midas” command [23]. A diagnostic accuracy test meta-analysis was performed using a multi-level, bivariate mixed-effects model to synthesize evidence. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (LRP), negative likelihood ratio (LRN), and a hierarchical summary receiver operator characteristics (SROC) curve were calculated from accuracy data, and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were further obtained if necessary. The Cochran-Q method and inconsistency index (I2) were adopted to investigate and quantify heterogeneity among the studies.
Fagan’s nomogram and the likelihood matrix were used to evaluate the clinical utility of both TCRγδ+ IEL and coeliac lymphogram [23].
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
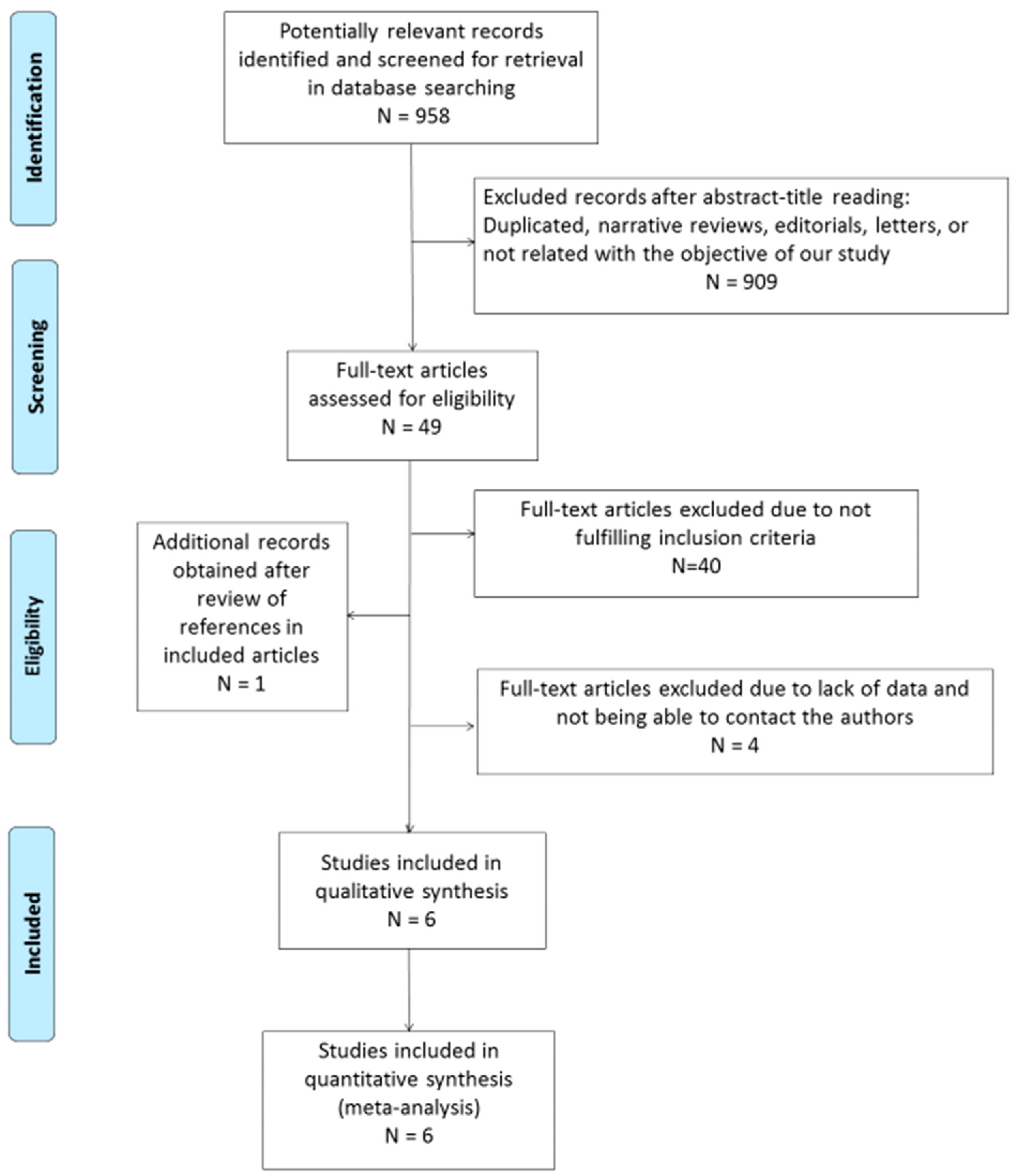
The search strategy returned 958 citations, of which 49 appeared to be relevant. Full texts were subsequently retrieved for detailed assessment. Forty studies were excluded as they did not meet the inclusion criteria of the systematic review. One additional study was identified in the bibliography search of the eligible studies. Among the 10 eligible articles, there were 6 potentially appropriate articles with insufficient data, for which we tried to contact the authors. In the case of two citations, we successfully contacted the senior author, who provided the number of true positive, false positive, true negative, and false negative values. Finally, four potentially appropriate studies were excluded since important information for the systematic review was lacking in two of them and the authors could not be contacted, while two others were excluded because the diagnosis of CD was not clearly described and generated important doubts for the two reviewers. Thus, a total of six eligible studies, including 519 patients and 440 controls, were selected for the analysis (Figure 1) [14,15,24,25,26,27].
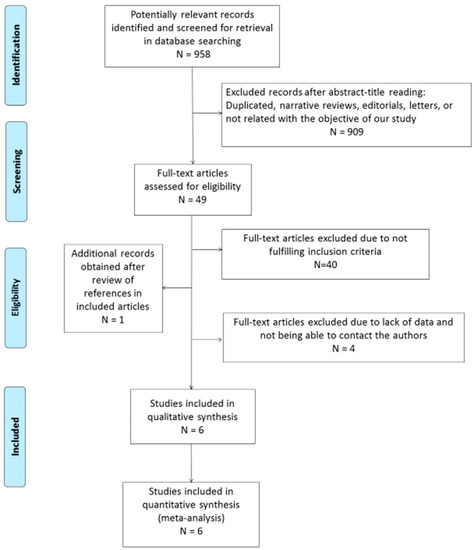
Figure 1.
Flow diagram describing the study selection process.
3.2. Description of the Included Studies
Table 1 summarizes the six selected cross-sectional studies, all of which were focused on European populations, all except one having been carried out in Spain. One of them studied children and adult populations separately [25], and these were included separately in the analysis. For two studies, only the coeliac lymphogram, and for one study, only TCRγδ+ IEL were described; thus, there were five eligible studies for the analysis of coeliac lymphogram (in one of them, separately for children and adults), and four eligible studies for the analysis of TCRγδ+ IEL diagnostic accuracy.

Table 1.
Summary of selected studies
Table 2 describes the flow cytometry technique used in the selected studies, showing some differences, mainly in the definition of the CD3− IEL subsets.

Table 2.
Summary of flow cytometry technique characteristics in selected studies
3.3. Qualitative Analysis of Included Studies
The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated using the QUADAS-2 tool (Table 3). In two studies, the risk of bias about patient selection was high, since they enrolled non-consecutive patients with known disease and a control group without the condition, which may exaggerate diagnostic accuracy [14,15]. There was also a high risk that the conduct of the index test had introduced a bias in one study [15], since the test threshold was not pre-specified, and a multiple logistic regression was developed to calculate the probability of having CD using both TCRγδ + and CD3− counts, which could lead to overoptimistic estimates of test performance. In three other studies, the test threshold was not described in the paper but was provided by the authors after contacting them and was the threshold pre-specified for clinical use in their labs [14,25,26]. There were no concerns regarding test applicability.

Table 3.
Results of Quality Assessment of Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy included in Systematic Reviews (QUADAS-2) checklist.
The methodological quality of the flow cytometry methods is summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Included Studies
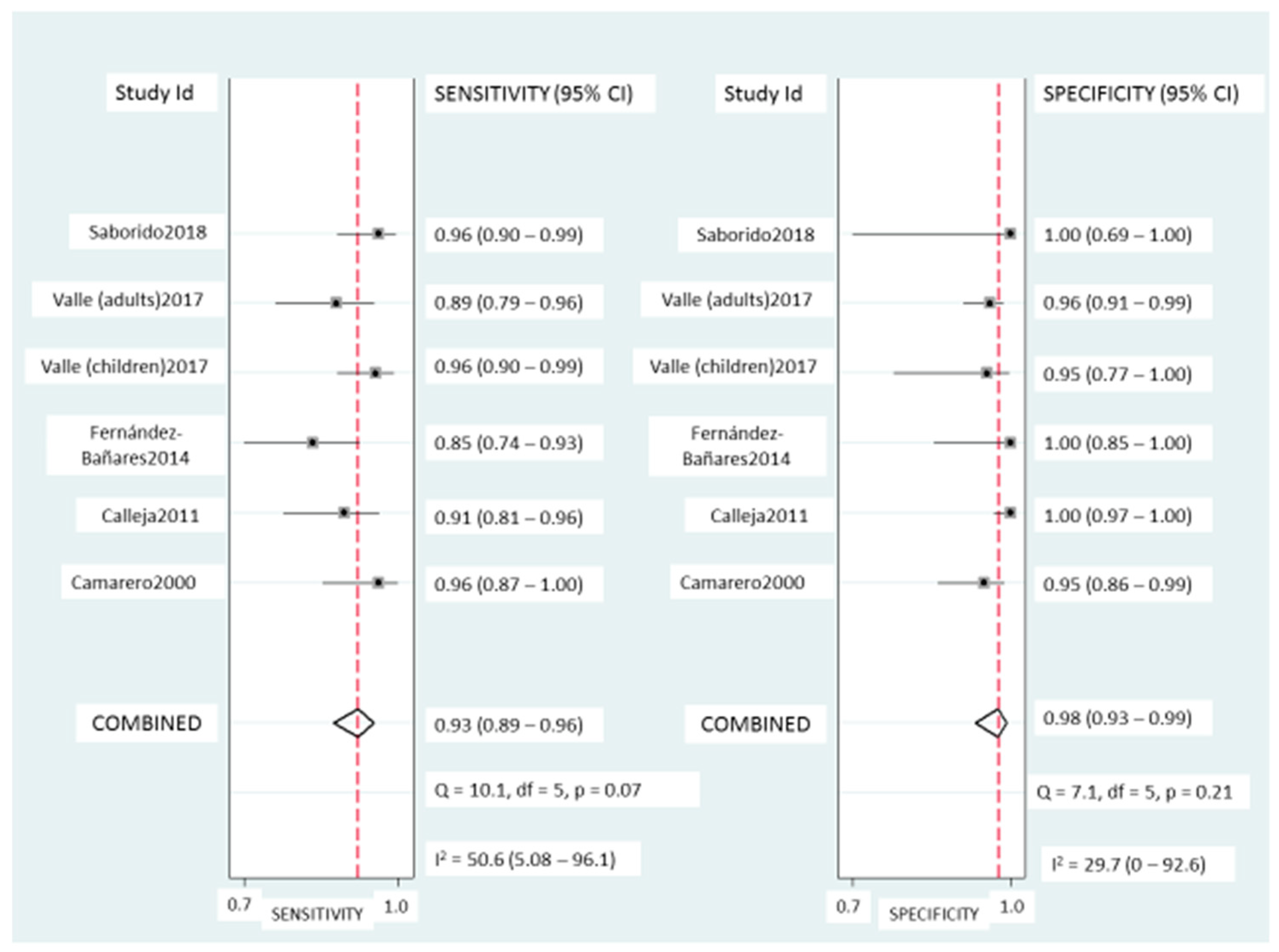
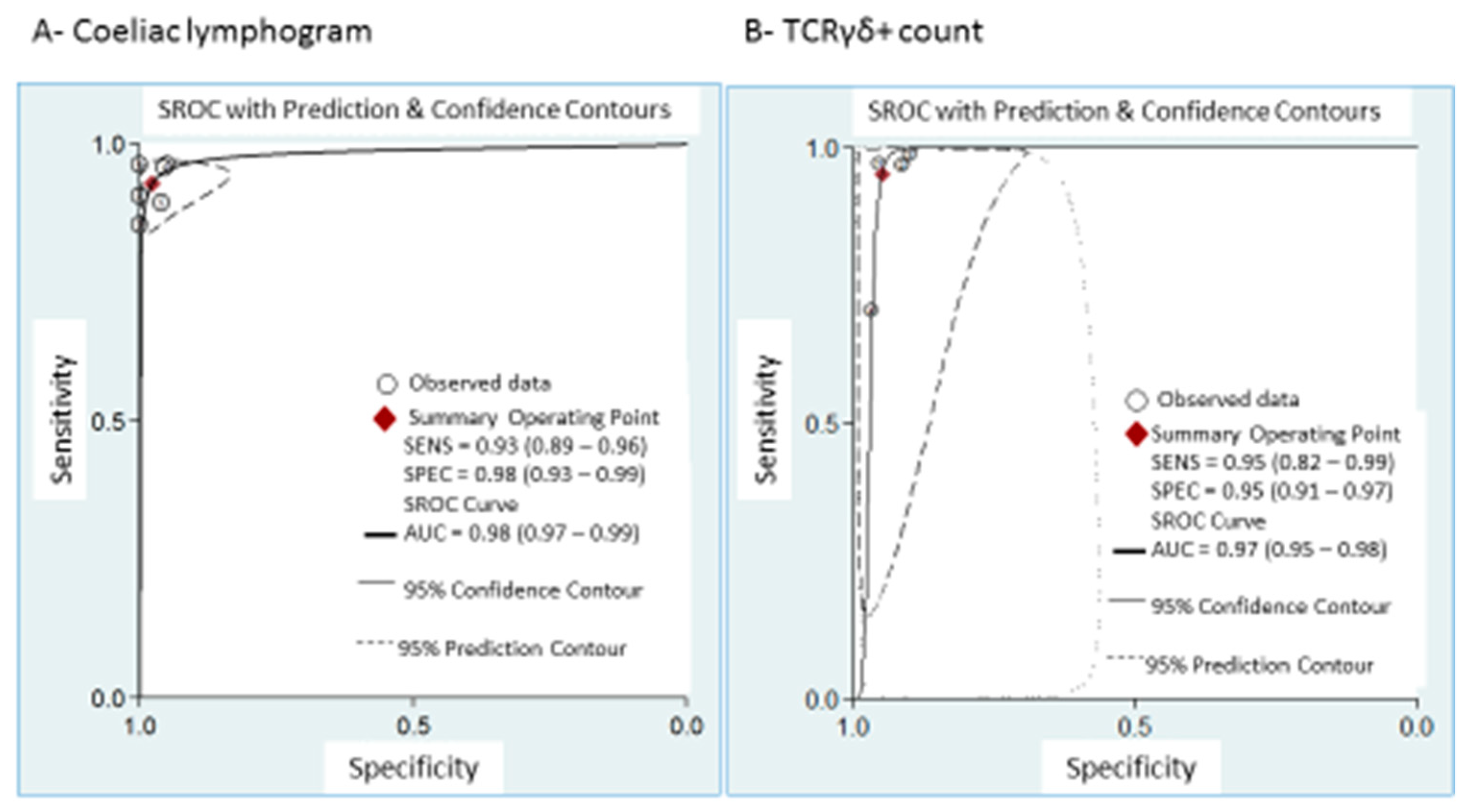
Coeliac lymphogram: As mentioned, a coeliac lymphogram consists of both an increase in TCRγδ+ IEL and a decrease in CD3− IEL. Pooled sensitivity and specificity (Figure 2) were 93% (95% CI, 89–96%) and 98% (95% CI, 93–99%), respectively. The SROC curve is described in Figure 3A, being the area under the curve (AUROC) of 0.98 (95%, 0.97–0.99), which implies a high diagnostic accuracy for diagnosing CD. There was no significant heterogeneity.
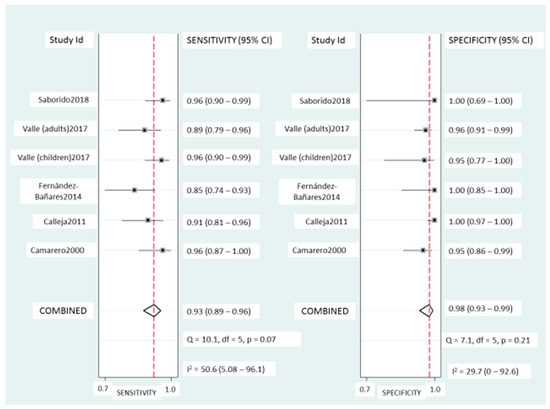
Figure 2.
Forest plots showing the pooled sensitivity and specificity of coeliac lymphogram (defined as an increase in TCRγδ+ IEL plus a decrease in CD3− IEL) for coeliac disease diagnos.
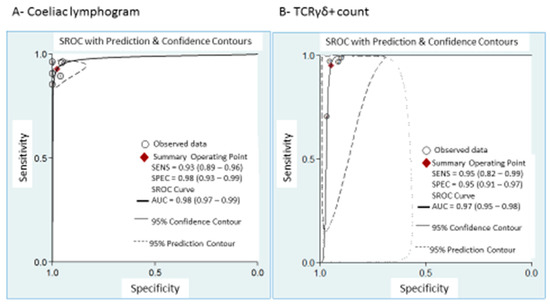
Figure 3.
Summary ROC curve (SROC) with confidence and prediction regions around mean operating sensitivity and specificity point of: (A) coeliac lymphogram (increase in TCRγδ+ IEL plus decrease in CD3– IEL); (B) TCRγδ+ count.
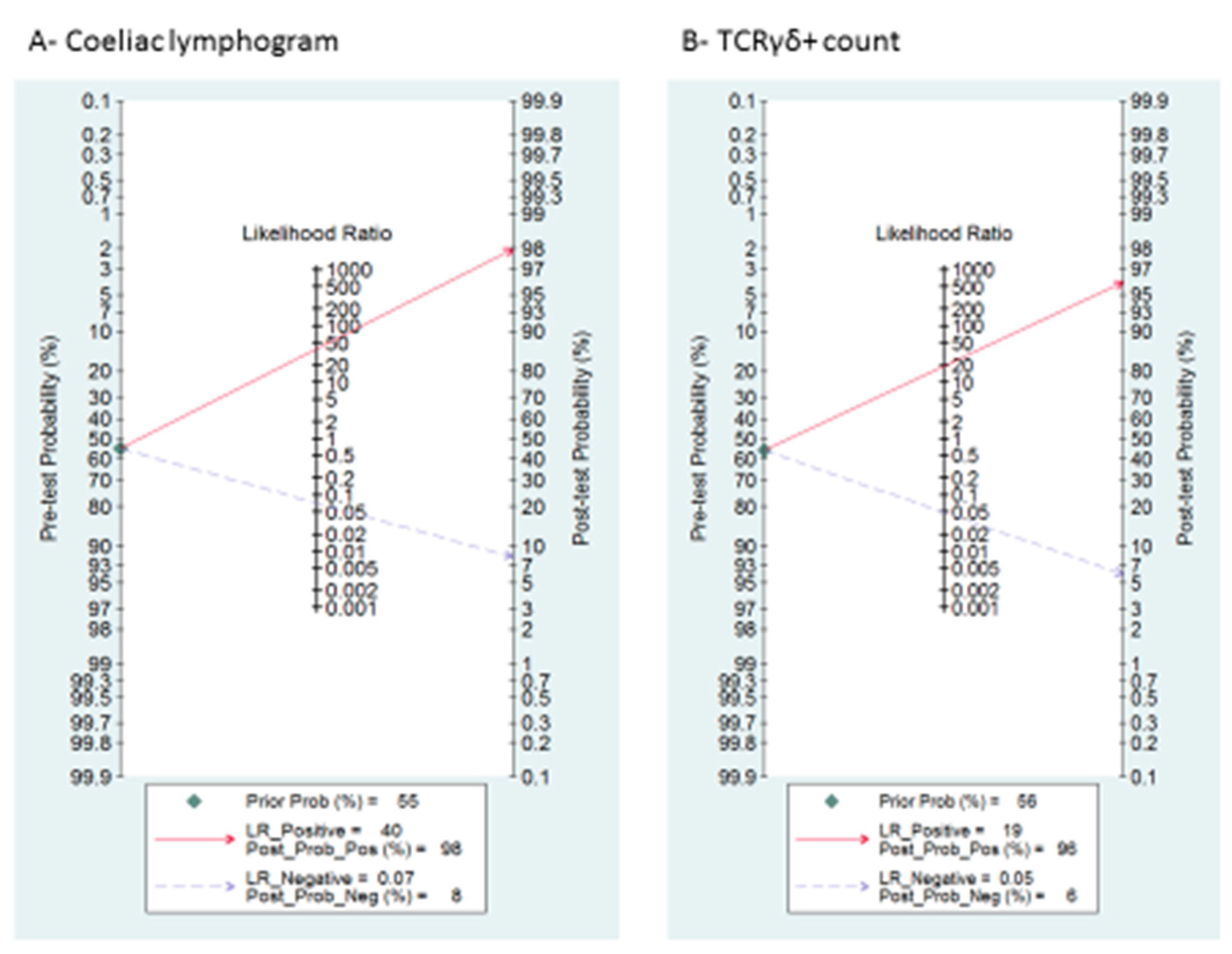
A summary of LRP and LRN with 95% CIs is described in Supplementary Figure S1, suggesting that the test is useful for confirmation (when positive) and exclusion (when negative) of CD. Fagan’s nomogram is presented in Figure 4A. Among patients with a pre-test coeliac disease probability of 55%, post-test probabilities were 98% and 8% for positive and negative coeliac lymphogram, respectively.
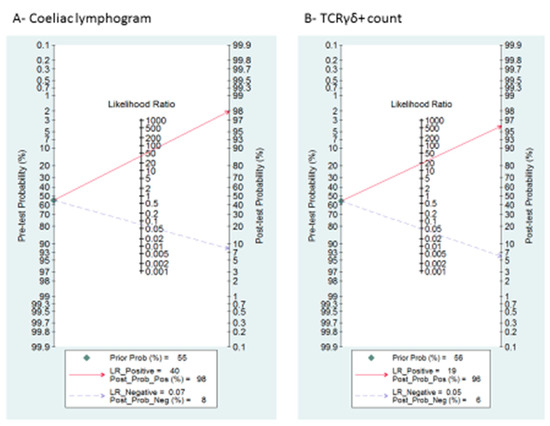
Figure 4.
Fagan’s nomogram for the elucidation of post-test probabilities. With a pre-test probability of CD of 55%, the post-test probabilities of CD, given positive and negative index test, were: (A) coeliac lymphogram: 98% and 8%, respectively; and (B) TCRγδ+: 96% and 6%, respectively.
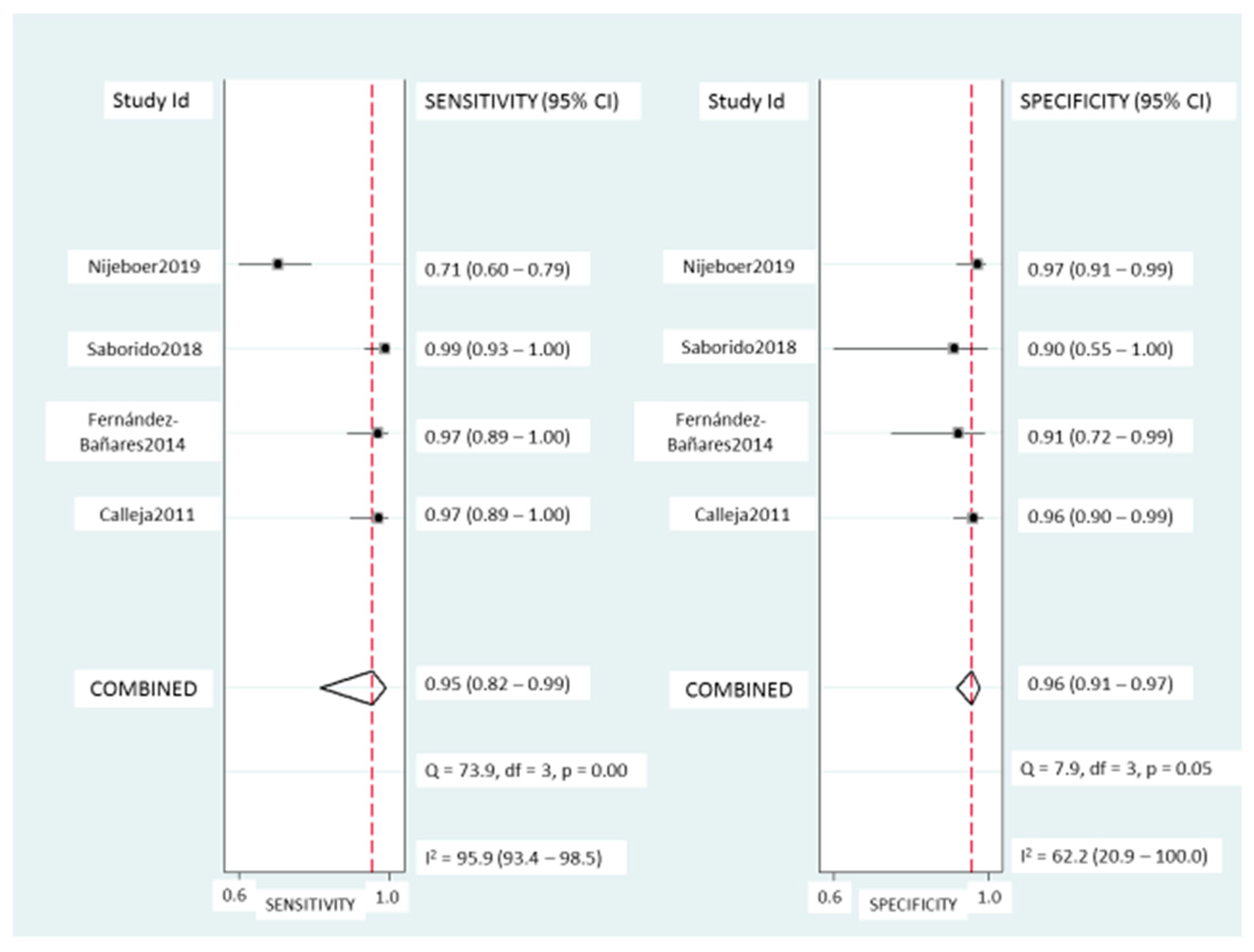
TCRγδ+ IEL: Pooled sensitivity (Figure 5) was 95% (95% CI, 82–99%) with significant heterogeneity (I2 = 95.6%; p < 0.001). Pooled specificity (Figure 5) was 95% (95% CI, 91–97%), with heterogeneity (I2 = 62%; p = 0.05). The SROC curve is described in Figure 3B, being the AUROC of 0.97 (95%, 0.95–0.98), which implies a high diagnostic accuracy for diagnosing CD.
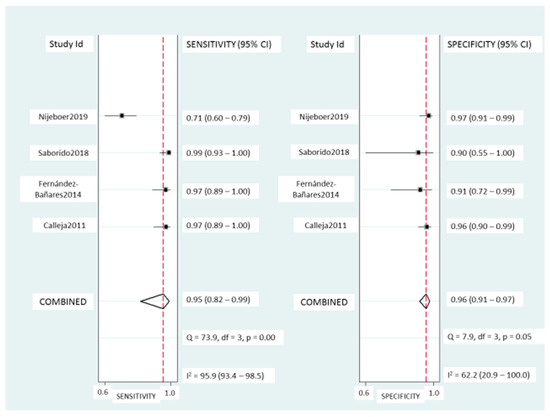
Figure 5.
Forest plots showing the pooled sensitivity and specificity of the TCRγδ+ count for coeliac disease diagnosis.
Supplementary Figure S1 and Figure 4B describe the likelihood ratio matrix and the Fagan’s nomogram, respectively. It is suggested that the test is useful for confirmation (when positive) and exclusion (when negative) of CD. Among patients with a pre-test coeliac disease probability of 55%, post-test probabilities were 96% and 6% for positive and negative TCRγδ+, respectively.
3.5. TCRγδ+ IEL in Diseased Controls with Non-Coeliac Atrophy
Two studies included a control group of patients, all suffering from villous atrophy by any cause other than CD (including malignant immunoproliferative diseases (n = 5), olmesartan use (n = 5), collagenous sprue (n = 2), autoimmune disease-associated enteropathy (n = 8), Crohn’s disease (n = 1), or idiopathic villous atrophy (n = 10)) [24,27]. These patients (n = 30), displayed a negative TCRγδ+ count in 93.3% (95% CI, 78.6–98.1).
3.6. TCRγδ+ IEL Evolution after a Gluten-Free Diet
Four of the selected studies described the percentage of TCRγδ+ IEL in patients on a GFD [14,15,26,27]. One of them prospectively assessed the evolution of this percentage after 1 year on a GFD [14]. In addition, we added data from our series, published only as an abstract [28], also prospectively evaluating the changes in TCRγδ+ IEL after a GFD. Ultimately, 201 patients were evaluated (Table 4). Results demonstrated the persistence of the increased values of this intraepithelial T lymphocyte subset after long-term follow-up on a GFD in both children and adults. Regrettably, it was not possible to perform a meta-analysis of these data.

Table 4.
TCRγδ+ cells in CD patients following a long-term GFD.
4. Discussion
Recent ESsCD guidelines for CD diagnosis states in the “areas of future research” section that studies are needed to evaluate T-cell flow cytometry and make it widely available for clinical use [5]. The results reported herein suggest that both coeliac lymphogram (an increase in TCRγδ+ IEL plus a decrease in CD3− IEL) and the isolated increase in TCRγδ+ IEL, assessed by flow cytometry in duodenal specimens, would be appropriate tests for CD diagnosis, since they were associated with an AUROC of 0.97–0.98 and LR values representing strong evidence both in favor of and against CD. Coeliac lymphogram was associated with a higher specificity than the assessment of isolated TCRγδ+ cells, whereas an isolated TCRγδ+ cell count was associated with a higher sensitivity.
The advantages of the use of flow cytometry to assess TCRγδ+ cells are considerable compared to other user-dependent techniques [18]. Results are obtained in an objective, quantitative, reproducible way, allowing for the analysis of a greater number of cells than with immunohistochemistry. The concomitant measurement of CD3− IEL adds specificity to the assay, as has been demonstrated in the present and previous studies [18]. Although the analysis of IEL subpopulations is, in general, not needed for CD diagnosis in seropositive patients, it may have high diagnostic value in doubtful cases that involve differentiating between CD and non-CD atrophy, those in which the mucosal lesion is equivocal [29], when HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ8 are negative [30], or when serum tTG levels are negative or with low titers (mainly those associated with negative EmA) [31]. The World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines for CD diagnosis recommend second biopsies to be performed in patients in whom the first biopsies and serological tests have been inconclusive (e.g., seronegative enteropathy) [32], but this strategy implies a second invasive procedure and a considerable delay in the final diagnosis. Finally, it may be useful in HLA-DQ2/8+ patients presenting with a grade 1 mucosal lesion since it is a non-specific lesion [10,24,33], which is caused by CD in around 5–15% of cases [34], and serology is positive in only 20–30% of them [35]. In this sense, subjecting a patient to an invasive procedure like gastroscopy with biopsies should involve trying to get as much information as possible from the procedure in order to achieve an accurate diagnosis. Taking an additional biopsy for flow cytometry is an easy procedure and may yield substantial information. Most labs in tertiary and even secondary hospitals have a flow cytometer for diagnostic purposes and analyzing the lymphocyte subpopulations in the duodenal mucosa is an affordable technique.
From the 958 articles selected in this systematic review, only 6 of the 49 references that were classified as potentially relevant were finally included in the meta-analysis. Some of the excluded studies had a high methodological quality, but did not meet the inclusion criteria and, consequently, were not useful for the aim of our meta-analysis, since most of them used immunohistochemistry instead of flow cytometry to assess TCRγδ+ cells. Other reasons for excluding studies were reasonable doubts on how CD diagnosis was achieved or on how CD was ruled out in the control group, and the absence of the data required to construct the 2 × 2 tables. The six studies included in the present meta-analysis comprised 959 individuals. Most of them were cross-sectional studies carried out in Spain, where the intraepithelial lymphogram technique was first described and is widely utilized, and has been recently included in the Ministry of Health guidelines for the early diagnosis of CD [36]. Two studies included only pediatric patients, three evaluated a mix of pediatric and adult populations, one of them studied children and adults separately, and one included only adults. Since there were only two studies independently assessing an adult population, a meta-regression analysis could not be performed. In addition, the median age of included patients in the study performed only in adults was 55 years, much higher than in other ones; a TCRγδ+ IEL count resulted in 66% sensitivity for CD diagnosis in that study [27], likely being a reason for the heterogeneity observed in meta-analysis. It is noteworthy that the CD patients with normal TCRγδ+ IEL in that study were significantly older than those with abnormal values [27]. The authors argued that advanced age may be a factor preventing the characteristic increase of TCRγδ+ IEL in CD for unknown reasons, and thus might explain the lower sensitivity found in that study. In the validation cohort of the cut-off for TCRγδ+ established in our laboratory, we did not find differences in TCRγδ+ sensitivity (≈94%) for CD diagnosis between different age groups, but the patients included were under 50 years of age [37]. It is possible that some subjects with suspected CD who are over 50 years of age could have a negative coeliac lymphogram; thus, further studies will be required to assess the TCRγδ+ sensitivity in these patients. Specificity, in contrast, was very high regardless of age.
As mentioned, it has been suggested that TCRγδ+ values remain elevated in CD patients despite a GFD. The present systematic analysis included 200 patients supporting this observation. The persistence of the increased TCRγδ+ cell values after a long-term GFD (1 year to a mean of 5 years) opens up the possibility of using this biomarker to confirm CD in patients who were started on a GFD, and for whom serology and histology may have yielded misleading results. In addition, it may prove useful for distinguishing between CD and non-coeliac gluten sensitivity in patients who are symptom-free after a GFD and reluctant to undergo a gluten challenge. Further studies are required to evaluate the persistence of the increased TCRγδ+ cell populations after longer follow-up.
There were small differences in the flow cytometry technique used between the six studies. Aspects of the sampling, the number of biopsies used, and the sampling locations differed between studies or were not appropriately described. However, unlike histopathological analyses, the IEL pattern is uniformly distributed in the distal duodenum and the duodenal bulb in healthy donors and coeliac patients [38], and the sampling location is therefore not a critical factor. All of the six studies used calcium chelation and shaking for the isolation of IEL, with minor differences between them (time, temperature, and buffer). The number of isolated IELs, the viability of the obtained cell suspension and the amount of starting material were not always reported, which is not critical due to the high efficiency of the isolation protocols [18]. The major differences between the six papers were in the staining panel, gating strategy, and IEL subset definition. Only one of the six papers excluded dead cells in its gating strategy, which is an essential step for reducing nonspecific stained cells that would interfere in the results. Of particular importance is the definition of the CD3− subset, given the heterogeneous nature of this subset and its importance in defining the “coeliac lymphogram”: a consensus regarding the most adequate definition should be reached to reduce confusion in the field. In fact, the CD3− subset evaluated by Nijeboer et al. was completely different from that in the rest of studies (Table 2); it corresponded to a small proportion of IELs lacking surface CD3 but expressing intracellular CD3, which was massively expanded in refractory CD type II [39]. The aforementioned differences in analysis strategy might explain, at least in part, the differences in the cut-off, which might not be transferable from lab to lab. In fact, four different cut-off values for TCRγδ+ were used in the six studies. All these differences could account for the heterogeneity observed in the present meta-analysis. Heterogeneity is to be expected in meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy, and for this reason, a random effects model was used for the present analysis.
None of the papers fulfilled the criteria to be considered reproducible according to the MIFlowCyt guidelines [22]. Considering the proven clinical usefulness of the IEL pattern, an effort should be made by all researchers to report methodologies at a sufficient level of detail to allow other groups to implement them in a standardized manner.
A limitation of the present study was the heterogeneity of the control group (a small number of patients with non-coeliac atrophy or other enteropathies, and a majority with functional bowel disease patients, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, Helicobacter pylori gastritis, parasitic infections, etc., all with normal small bowel histology). In this sense, the absence of a subgroup of seronegative CD among cases and a subgroup with enough non-CD atrophy patients among controls was a drawback, since these are the patient subgroups in which coeliac lymphogram has the highest diagnostic interest. However, two of the included studies provided data on a small sample of non-coeliac villous atrophy patients, suggesting that TCRγδ+ count may be useful to rule out CD in this setting. Finally, since all included articles except one were carried out in Spain, it could be argued whether the results might be extrapolated to other populations. However, the increase of TCRγδ+ in patients with CD has been described in studies from other countries around the world [13,40,41,42,43,44].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, both TCRγδ+ count and coeliac lymphogram assessed by flow cytometry in duodenal mucosal samples have been associated with a high level of diagnostic accuracy for and against coeliac disease. Further studies are warranted to confirm the diagnostic value of the technique in cases in which diagnosis is not straightforward.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/9/1992/s1, Figure S1: Likelihood matrix for the overall distribution of the studies: (A) Coeliac lymphogram; (B) TCRγδ+. Each point corresponds to a study. The summary positive likelihood ratio (LRP) and negative likelihood ratio (LRN) for index test are found on the left upper quadrant of the matrix, and showed a high accuracy for both exclusion and confirmation of CD., Table S1: Methodological quality of the flow cytometry methods
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.F.-B., A.C. and M.E.; Data curation, A.C.; Formal analysis, F.F.-B.and A.C.; Investigation, F.F.-B.and A.C.; Methodology, F.F.-B., A.C., A.M. and M.E.; Project administration, F.F.-B.; Resources, F.F.-B.and A.M.; Software, A.C.and A.M.; Supervision, F.F.-B.; Validation, A.C.; Visualization, F.F.-B.and M.E.; Writing—original draft, F.F.-B.; Writing—review & editing, F.F.-B., A.C., A.M. and M.E.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The ‘Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas’ (CIBERehd) is an initiative of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Madrid, Spain. This institution played no role in the study design, acquisition, or analysis nor in the interpretation of the data or the report writing. The authors thank the statistical advice provided by ‘Simplifying Research Institute’ (www.simplifying-research.eu).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, K.E.A.; Qiao, S.-W.; Snir, O.; Sollid, L.M. Coeliac disease – from genetic and immunological studies to clinical applications. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Bai, J.C.; Biagi, F.; Card, T.R.; Ciacci, C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Green, P.H.R.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Holdoway, A.; Van Heel, D.; et al. Diagnosis and management of adult coeliac disease: Guidelines from the British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut 2014, 63, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Mearin, M.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, J.A.; Diamond, B.; Rotterdam, H.; Green, P.H.R. Seronegative Celiac Disease: Increased Prevalence with Lesser Degrees of Villous Atrophy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, W.; Hughes, D.F.; McMillan, S.A. Dissapearance of endomysial antibodies in treated celiac disease does not indicate histological recovery. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 712–714. [Google Scholar]
- Vivas, S.; De Morales, J.M.R.; Fernandez, M.; Hernando, M.; Herrero, B.; Casqueiro, J.; Gutierrez, S. Age-Related Clinical, Serological, and Histopathological Features of Celiac Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2360–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, P.D.; Aziz, I.; Sanders, D.S. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: Clinical relevance and recommendations for future research. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bañares, F.; Carrasco, A.; Rosinach, M.; Arau, B.; García-Puig, R.; González, C.; Tristán, E.; Zabana, Y.; Esteve, M. A Scoring System for Identifying Patients Likely to Be Diagnosed with Low-Grade Coeliac Enteropathy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bañares, F.; Farré, C.; Carrasco, A.; Marine, M.; Esteve, M. New tools for the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease. In Advances in the Understanding of Gluten related Pathology and the Evolution of Gluten-Free Foods; Omnia Publisher SL: Barcelona, Spain, 2015; Volume 25, pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg, P.; Halstensen, T.; Kett, K.; Krajči, P.; Kvale, D.; Rognum, T.; Scott, H.; Sollid, L. Immunobiology and immunopathology of human gut mucosa: Humoral immunity and intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology 1989, 97, 1562–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.T.; Kaukinen, K.; Laurila, K.; Kyrönpalo, S.; Rasmussen, M.; Mäki, M.; Korhonen, H.; Reunala, T.; Collin, P. Intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleja, S.; Vivas, S.; Santiuste, M.; Arias, L.; Hernando, M.; Nistal, E.; Casqueiro, J.; De Morales, J.G.R. Dynamics of Non-conventional Intraepithelial Lymphocytes—NK, NKT, and γδ T—In Celiac Disease: Relationship with Age, Diet, and Histopathology. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2042–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarero, C.; Eiras, P.; Asensio, A.; Leon, F.; Olivares, F.; Escobar, H.; Roy, G. Intraepithelial lymphocytes and coeliac disease: Permanent changes in CD3−/CD7+ and T cell receptor γβ subsets studied by flow cytometry. Acta Paediatr. 2000, 89, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, G. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes contain a CD3-CD7+ subset expressing natural killer markers and a singular pattern of adhesion molecules. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- León, F.; Roldán, E.; Sanchez, L.; Camarero, C.; Bootello, A.; Roy, G. Human small-intestinal epithelium contains functional natural killer lymphocytes. Gastroenterology. 2003, 125, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, F. Flow cytometry of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease. J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 363, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, F.; Eiras, P.; Roy, G.; Camarero, C. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and anti-transglutaminase in a screening algorithm for coeliac disease. Gut 2002, 50, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bossuyt, P.M. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies FREE. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Spidlen, J.; Boyce, K.; Cai, J.; Crosbie, N.; Dalphin, M.; Furlong, J.; Gasparetto, M.; Goldberg, M.; Goralczyk, E.M.; et al. MIFlowCyt: The Minimum Information about a Flow Cytometry Experiment. Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwamena, B.A. MIDAS: Stata module for meta-analytical integration of diagnostic test accuracy studies. In Statistical Software Components S456880; Boston College Department of Economics: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Bañares, F.; Carrasco, A.; Garcia-Puig, R.; Rosinach, M.; González, C.; Alsina, M.; Loras, C.; Salas, A.; Viver, J.M.; Esteve, M. Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Cytometric Pattern Is More Accurate than Subepithelial Deposits of Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase IgA for the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease in Lymphocytic Enteritis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.; Morgado, J.M.T.; Ruiz-Martín, J. Flow cytometry of duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytes improves diagnosis of celiac disease in difficult cases. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saborido, R.; Martinón, N.; Regueiro, A.; Crujeiras, V.; Eiras, P.; Leis, R. Intraepithelial lymphocyte immunophenotype: A useful tool in the diagnosis of celiac disease. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijeboer, P.; Van Gils, T.; Reijm, M.; Ooijevaar, R.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; Bontkes, H.J.; Mulder, C.J.; Bouma, G. Gamma-Delta T Lymphocytes in the Diagnostic Approach of Coeliac Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, e208–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinach, M.; Carrasco, A.; Gonzalo, V. Evolución del linfograma intraepithelial celíaco después de la dieta sin gluten en pacientes con enteritis linfocítica (abstract). Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 40, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Ravelli, A.; Villanacci, V. Tricks of the trade: How to avoid histological Pitfalls in celiac disease. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2012, 208, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bañares, F.; Arau, B.; Dieli-Crimi, R.; Rosinach, M.; Nuñez, C.; Esteve, M. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Show 3% of Patients With Celiac Disease in Spain to be Negative for HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ8. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Peerally, M.F.; Barnes, J.H.; Kandasamy, V.; Whiteley, J.C.; Partridge, D.; Sanders, D.S. The clinical and phenotypical assessment of seronegative villous atrophy; a prospective UK centre experience evaluating 200 adult cases over a 15-year period (2000-2015). Gut 2017, 66, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.C.; Fried, M.; Corazza, G.R.; Schuppan, D.; Farthing, M.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines: Celiac Disease. 2016. Available online: http://www.worldgastroenterology.org/guidelines/global-guidelines/celiac-disease (accessed on 15 August 2019).
- Rosinach, M.; Fernández-Bañares, F.; Carrasco, A.; Ibarra, M.; Temiño, R.; Salas, A.; Esteve, M. Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial: Gluten versus Placebo Rechallenge in Patients with Lymphocytic Enteritis and Suspected Celiac Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voort JL, V.; Murray, J.A.; Lahr, B.D.; Van Dyke, C.T.; Kroning, C.M.; Moore, S.B.; Wu, T.T. Lymphocytic duodenosis and the spectrum of coeliac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santaolalla, R.; Fernández-Bañares, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Alsina, M.; Rosinach, M.; Marine, M.; Farre, C.; Salas, A.; Forné, M.; Loras, C.; et al. Diagnostic value of duodenal antitissue transglutaminase antibodies in gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupo de Trabajo del Protocolo Para el Diagnóstico Precoz de la Enfermedad Celíaca. Protocolo Para el Diagnóstico Precoz de la Enfermedad Celíaca. Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. Servicio de Evaluación del Servicio Canario de la Salud (SESCS). 2018. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/prestacionesSanitarias/publicaciones/DiagnosticoCeliaca.htm (accessed on 15 August 2019).
- Fernández-Bañares, F.; Esteve, M. Gamma-delta T lymphocytes in the diagnostic approach of celiac disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andrés, A.; Camarero, C.; Roy, G. Distal duodenum versus duodenal bulb: Intraepithelial lymphocytes have something to say in celiac disease diagnosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wanrooij, R.L.; Müller, D.M.; Neefjes-Borst, E.A. Optimal strategies to identify aberrant intra-epithelial lymphocytes in refractory coeliac disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahlot GP, S.; Das, P.; Baloda, V.; Singh, A.; Vishnubhatla, S.; Gupta, S.D.; Makharia, G.K. Duodenal mucosal immune cells in treatment-naive adult patients with celiac disease having different histological grades and controls. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2019, 62, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Steenholt, J.V.; Nielsen, C.; Baudewijn, L.; Staal, A.; Rasmussen, K.S.; Sabir, H.J.; Barington, T.; Husby, S.; Toft-Hansen, H. The composition of T cell subtypes in duodenal biopsies are altered in coeliac disease patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosco, A.; Maglio, M.; Paparo, F.; Greco, L.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, R. Discriminant Score for Celiac Disease Based on Immunohistochemical Analysis of Duodenal Biopsies. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, G.; Naiyer, A.J.; Shah, J.G.; Harper, J.; Jabri, B.; Wang, T.C.; Manavalan, J.S. Small intestinal CD8+TCRgammadelta+NKG2A+ intraepithelial lymphocytes have attributes of regulatory cells in patients with celiac disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; Adames, K.; Castillo-Rodal, A.I.; Ramírez, T.; Barreto-Zuñiga, R.; López-Vidal, Y.; Uscanga, L.F. Intraepithelial gammadelta+ lymphocytes: A comparative study between celiac disease, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, and irritable bowel syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).