Abstract
Bariatric surgery remains the most effective option for achieving important and sustained weight loss. We explored the effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) on the circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin, and the adiponectin/leptin (Adpn/Lep) ratio in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Twenty-five T2D volunteers undergoing RYGB were included in the study, and further subclassified as patients that responded or not to RYBG, regarding remission of T2D. Anthropometric and biochemical variables were evaluated before and after RYGB. Obese patients with T2D exhibited an increase (p < 0.0001) in the Adpn/Lep ratio after RYGB. Changes in the Adpn/Lep ratio correlated better with changes in anthropometric data (p < 0.001) than with the variations of adiponectin or leptin alone. Multiple regression analysis revealed that the change in the Adpn/Lep ratio in patients with T2D was an independent predictor of the changes in body mass index (p < 0.001) and body fat percentage (p = 0.022). However, the Adpn/Lep ratio did not differ between individuals with or without T2D remission after RYGB. In summary, the current study demonstrated that after weight and body fat loss following RYGB, the Adpn/Lep ratio increased in patients with obesity and T2D.
1. Introduction
The prevalence of overweight and obesity is increasing worldwide, reaching epidemic proportions and emerging as a major public health challenge [1,2]. Trends are alarming because obesity affects the function of different organ systems, shortening life span, and conferring an increased risk for multiple serious conditions, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), cardiovascular diseases, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and different types of cancers [3]. The management of obesity is often difficult or unsuccessful due to its multifactorial nature [4]. Treatment options involve lifestyle interventions (caloric restriction, reduction of sedentary behaviors, and increased physical activity), pharmacotherapy as well as surgical procedures [5,6]. Conventional treatments have little effect on weight loss and are relatively inefficient in treating obesity in the long-term [7,8,9]. By contrast, bariatric surgery has rapidly expanded, due to its capacity to induce sustained long-term weight loss, ameliorate obesity-related comorbidities, and reduce mortality, constituting an effective option for individuals with severe obesity [6,10].
Even though bariatric surgery leads to the improvement of T2D, differences related to the resolution of the obesity-related conditions exist [11]. Therefore, the identification of prediction factors of T2D remission after bariatric surgery is an important topic [12,13]. Factors such as the preoperative duration of T2D, the use of insulin, as well as a high percentage of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and lower weight loss after surgery can influence the remission of T2D [14,15]. Among these factors, different studies have described the potential role of adipokines in weight loss and T2D remission after surgery [16,17,18]. Adiponectin has strong anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing functions and their plasma levels have been clearly demonstrated to be decreased as the body mass index (BMI) increases being oppositely correlated with insulin resistance [19,20]. Increased adiponectin levels after bariatric surgery are associated with metabolic benefits and with a higher rate of T2D remission [21,22]. By contrast leptin, another adipocyte-derived factor, parallels the degree of adiposity and is associated with insulin resistance [23,24]. After bariatric surgery, leptin concentrations decrease in proportion to post-operatively achieved weight loss [25]. The balance between these adipose tissue-derived hormones has a pivotal role in evaluating the metabolic outcome of bariatric surgery. We proposed the adiponectin/leptin (Adpn/Lep) ratio as a marker of adipose tissue dysfunction and inflammation [26,27], being better correlated with insulin resistance than adiponectin or leptin alone [28]. Furthermore, we found a decreased Adpn/Lep ratio in patients with the metabolic syndrome [28] and a gradual reduction with increasing number of risk factors for metabolic syndrome has been also reported [29,30]. Patients with obesity and type 1 diabetes (T1D) also exhibited a significantly lower Adpn/Lep ratio compared to non-obese T1D patients [31]. Moreover, the Adpn/Lep ratio has shown to estimate insulin sensitivity [32,33] and the risk of cardiovascular diseases in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome [34,35]. In this regard, new cutoffs to assess metabolic risk based on the Adpn/Lep ratio have been proposed [26]. An Adpn/Lep ratio higher than 1.0 can be considered as normal whereas a ratio below 0.5 may indicate an increase in the metabolic risk (with adiponectin concentrations measured in μg/mL and leptin levels in ng/mL) [26].
Since bariatric surgery induces sustained weight and fat loss and improves the resolution of T2D together with an increase of adiponectin concentrations and a reduction in leptin levels, we aim to investigate the Adpn/Lep ratio in patients with T2D before and after weight loss achieved by bariatric surgery. In addition, we analyzed whether the Adpn/Lep ratio varies among groups of patients with different outcomes of T2D improvement after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
A group of 25 patients with obesity and T2D (11 males and 14 females) recruited from patients visiting the Departments of Endocrinology & Nutrition and Surgery for weight loss treatment at the Clínica Universidad de Navarra was used to analyze the effect of RYGB on the Adpn/Lep ratio one year after surgery. The clinical assessment was performed by a multidisciplinary consultation team. Individuals with severe systemic disease not related to obesity, infectious disease, cancer, liver disease or severe nephropathy, pregnancy or lactation, patients with serious eating disorders, and people whose freedom is under legal or administrative requirement were excluded. The experimental design was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Navarra (protocol 2017.126) and the study followed the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All volunteers signed the informed consent to participate in the study.
Obese patients were diagnosed as patients with T2D following the criteria of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes [36]. In order to be able to identify potential differences among patients as regards T2D remission, volunteers were studied one year after RYGB. To make sure that the improvement in their glucose metabolism was consistent, the classification of the same patients as responders or non-responders was made upon the analytical values obtained 3 years after RYGB. The volunteers maintained the classification after the 3 years. Remission of T2D in obese patients was defined according to the American Diabetes Association criteria [36]. Specifically, remission was defined by HbA1c < 6.0%, fasting glucose < 100 mg/dL, and no use of antidiabetic medication for at least 12 months. The novel scoring system (DiaRem score) to estimate the probability of T2D remission after RYGB was also calculated based on age, preoperative HbA1c, as well as the use of metformin, sulfonylurea, glitazones, and/or insulin, as previously reported [12]. BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms (kg) divided by the height in meters squared and body fat (BF) was estimated by air-displacement-plethysmography (Bod-Pod®, Life Measurements, Concord, CA, USA) as previously described [37]. The waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) was calculated as the ratio of waist circumference (at the midpoint between the margin of the last palpable rib and the top of the iliac crest) to hip circumference (at the widest trochanters).
2.2. Analytical Procedures
Plasma samples were obtained by venipuncture after an overnight fast. Glucose was analyzed by an automated analyzer (Roche Cobas 8000, Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Insulin was measured by an automated enzyme immunoassay (IMMULITE® 2000 XPi, Siemens, Malvern, PA, USA) with intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation of 4.2% and 5.7%, respectively. Insulin sensitivity and resistance were calculated using the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI) and homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) indices, respectively. Fasting C-peptide levels and 6-min after an intravenous injection of 1 mg of glucagon were measured by an automated enzyme immunoassay (IMMULITE® 2000 XPi, Siemens). Total cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations were determined by enzymatic spectrophotometric methods (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany). High-density lipoprotein (HDL-cholesterol) was quantified by a colorimetric method in a Beckman Synchron® CX analyzer (Beckman Instruments, Ltd., Bucks, UK) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-cholesterol) was calculated using the Friedewald formula as previously described [27]. Uric acid, creatinine, and the hepatic enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT) were analyzed in an automated analyzer (Roche/Hitachi Modular P800). Fibrinogen, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) and von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF) levels were measured as previously reported [27]. Leptin levels were quantified by a double-antibody radioimmunoassay method (Linco Research, Inc., St. Charles., MO, USA) as previously described [38]. The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were 5.0% and 4.5%, respectively. Adiponectin was determined by a commercially available ELISA kit (Biovendor, Brno, Czech Republic) with intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation being 3.9% for the former and 4.2% for the latter. The Adpn/Lep ratio was calculated with adiponectin concentrations expressed in μg/mL and leptin levels in ng/mL [26].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Differences in the proportion of subjects within groups regarding gender were assessed by the Chi-square test. Differences between groups were assessed by two-tailed paired or unpaired Student’s t tests as appropriate. Correlations between two variables were computed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r). The calculations were performed using the SPSS/Windows version 15.0 statistical package (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
Anthropometric and biochemical characteristics of the subjects enrolled in the study are summarized in Table 1. All the subjects included in the study were classified as patients with obesity and T2D. From the whole cohort, 44% were males and 56% were females, with no differences in gender distribution (p = 0.549). As expected, after an average post-surgical period of one year, patients experienced a significant decrease (p < 0.0001) in all anthropometric measurements (BMI, body adiposity, waist circumference, and WHR). Furthermore, insulin resistance improved as evidenced by the decrease in fasting glucose (p < 0.05) and insulin concentrations (p < 0.001), together with a decrease (p < 0.001) in the HOMA as well as an increase (p < 0.001) in the QUICKI indices. After the first postoperative year, the HbA1c mean values decreased significantly (p < 0.01). Volunteers also had improved lipid metabolism supported by a significant reduction (p < 0.01) in circulating triglycerides, total- and LDL-cholesterol as well as an increase (p < 0.01) in HDL-cholesterol concentrations. Noteworthy, a decrease in the circulating concentrations of the inflammatory markers CRP (p < 0.05) and uric acid (p < 0.001), as well as in the levels of γ-GT (p < 0.01), a marker of hepatobiliary injury, after weight loss, were detected.

Table 1.
Anthropometric and metabolic effects in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB).
RYGB was associated with an increase (p < 0.0001) in adiponectin together with a decrease (p < 0.0001) in leptin concentrations. Importantly, the Adpn/Lep ratio increased significantly after weight loss (from 0.21 ± 0.03 to 1.20 ± 0.19; p < 0.0001) (Figure 1). According to the cutoff points defining cardiometabolic risk previously proposed by our group [26], following bariatric surgery, patients with T2D showed an increase in the Adpn/Lep ratio from below 0.5 (indicative of a severe increase in their cardiometabolic risk) to over 1.0 (considered as normal).
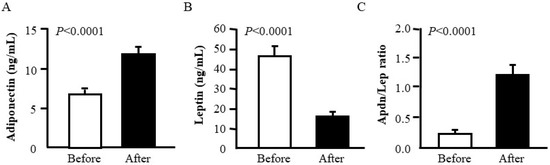
Figure 1.
Comparison of serum adiponectin (A) and leptin (B) concentrations as well as the Adiponectin/Leptin (Adpn/Lep) ratio (C) before and after Roux-en Y gastric bypass in patients with obesity and T2D (n = 25). Statistical differences were analyzed by two-tailed paired Student’s t test.
We also detected a highly positive correlation between post-operative values of the Adpn/Lep ratio and changes in anthropometric characteristics (Table 2). To further strengthen the reliability of the Adpn/Lep ratio as an important marker of weight and body fat loss after RYBG, we compared the degree of correlation between changes in the Adpn/Lep ratio and the variations in body composition-related variables as opposed to each adipokine separately (Table 3). Interestingly, changes in Adpn/Lep ratio provided better correlations with differences in BMI (r = −0.64, p < 0.001), body fat (r = −0.80, p < 0.001), waist circumference (r = −0.76, p < 0.001), and WHR (r = −0.52, p = 0.011), compared with the associations of the leptin and adiponectin concentration changes alone.

Table 2.
Univariate analysis of the correlations between the adiponectin/leptin ratio before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) with changes in anthropometric characteristics.

Table 3.
Univariate analysis of the correlations between the differences in adiponectin and leptin concentrations as well as in the adiponectin/leptin ratio with changes in anthropometric characteristics after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB).
We next addressed whether the Adpn/Lep ratio differed between patients with T2D that responded or not to RYGB regarding remission of T2D. For both groups of T2D obese patients, follow-up data beyond the third postoperative year were available (Table 4). Overall, we categorized the 25 patients with T2D who underwent RYGB surgery as non-responders (n = 7, 28%) and responders (n = 18, 72%). As expected, non-responders showed a significantly higher DiaRem score compared to those classified as responders (10.30 ± 1.72 vs. 4.27 ± 0.86; p = 0.008). Although fasting C-peptide levels were higher in responders (4.22 ± 0.27 ng/mL) compared to non-responders (3.21 ± 0.69 ng/mL), differences did not reach statistical significance. C-peptide levels 6-min after intravenous injection of 1 mg of glucagon followed the same trend, being increased in patients with T2D remission (responders: 6.79 ± 0.56 ng/mL vs. non-responders: 5.86 ± 0.46 ng/mL). However, differences were not statistically significant. Both groups of patients exhibited an increased Adpn/Lep ratio but no significant differences between individuals who experienced a T2D remission or not after RYGB were found.

Table 4.
Effects of weight loss one year after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) in obese patients with T2D classified as responders and non-responders.
4. Discussion
A huge body of knowledge supports the surgical management as the most effective treatment for severe obesity, being associated with a significant reduction of mortality [6]. The Adpn/Lep ratio might represent a useful biomarker of dysfunctional adipose tissue because it is negatively correlated with markers of low-grade chronic inflammation [26,27,28]. In this regard, we designed the present study to determine changes in the Adpn/Lep ratio after RYGB in obese patients with T2D. Indeed, obese patients with T2D exhibited an increase in the Adpn/Lep ratio after RYGB. Consistently, we also found that changes in the Adpn/Lep ratio correlated better with changes in anthropometric data than the variations of adiponectin or leptin alone. However, there was no difference in the Adpn/Lep ratio between individuals who experienced a remission or not of T2D after RYGB.
Adipose tissue constitutes an active and potent endocrine organ capable of releasing a large number of adipokines involved in the pathophysiological link between increased adiposity and its associated metabolic alterations [23]. Among these factors, important studies have shown increased and decreased circulating levels of leptin and adiponectin, respectively, in the obese state as well as their significant role in the regulation of weight loss and glycaemic control [23,39,40]. The usefulness of the combination of both adipocyte-derived hormones in the Adpn/Lep ratio has been clearly demonstrated, concluding that it could be a better marker for insulin resistance rather than these adipokines individually [26,27,33,41,42]. In this sense, we have recently described that a low Adpn/Lep ratio is associated with a dysfunctional adipose tissue [26,27]. In this study, subjects with obesity and T2D showed an increase in the Adpn/Lep ratio after RYGB. Reportedly, low-to-moderate weight loss in adolescents after conventional treatment (diet, physical exercise, and clinical support) promoted a significant increase in the Adpn/Lep ratio, with changes in lean body mass constituting an independent predictor of changes in this ratio [43]. Moreover, the Mediterranean diet led to increased Adpn/Lep ratio, mainly associated to its efficacy in reducing abdominal fat [41].
The reduction in anthropometric measurements, specifically in visceral fat, after RYGB may underlie the increase of the Adpn/Lep ratio in our patients with T2D, being associated with important and positive health consequences. Consequently, we also determined that changes in the Adpn/Lep ratio were better associated with changes in BMI, body fat, and waist circumference than the changes in individual levels of leptin and adiponectin. The Adpn/Lep ratio has been also correlated with insulin resistance more closely than both hormones alone or even the HOMA index [33]. These results reinforce the importance of RYGB for the treatment of obesity targeting a reduction of body fat, mainly the visceral depot. Furthermore, the Adpn/Lep ratio better predicts the risk of cardiovascular diseases, as compared to the individual leptin and adiponectin concentrations [44,45]. We recently found that a low Adpn/Lep ratio is associated with an increased cardiometabolic risk, evidenced by elevated systemic inflammation and oxidative stress [28]. In addition, the Adpn/Lep ratio negatively correlates with the markers of inflammation SAA and CRP, suggesting that this marker may reflect the systemic inflammation in the context of obesity [27,46].
No differences in the Adpn/Lep ratio at one year between individuals who experienced a T2D remission or not three years after RYGB existed in our study. Of note, age is a common denominator of diabetes remission across multiple studies, despite different surgical types and remission criteria [12,47]. In this sense, patients from this study, not experiencing a remission in T2D, were older and exhibited a deteriorated pancreatic β-cell function with insulinopenia. This finding is being probably related to their impaired diabetes remission after bariatric surgery. C-peptide is considered an important determinant of T2D remission since it constitutes a direct measure of insulin production and provides an accurate measure of pancreatic β-cell reserve [48,49]. Higher C-peptide levels have been described in subjects with T2D remission compared to those without remission suggesting that preoperative C-peptide determination may be a useful estimator of T2D remission after bariatric surgery [50]. Although differences were not statistically significant, we found that fasting C-peptide and C-peptide levels 6-min after intravenous injection of 1 mg of glucagon were higher in responders compared to non-responders. Patients without diabetes remission at three years after RYGB included in the study suffered from NAFLD, which could explain the higher ratio of the Adpn/Lep ratio without T2D remission. Further studies with a larger number of patients would clarify the involvement of the Adpn/Lep ratio in the prediction of T2D remission after bariatric surgery. The potential impact of other factors known to be changed following bariatric surgery like fibroblast growth factors, caveolin-1, or aquaporins [51,52,53] as well as their plausible influence on relevant aspects of adipobiology such as lipolysis [54,55] should not be discarded.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we showed that the increase in the Adpn/Lep ratio after RYGB might constitute a significant factor for the body composition and metabolic benefits after bariatric procedures. The ratio, however, does not represent a predictive factor for the remission of T2D. Due to the complex regulation of hormonal and body composition alteration involved in weight loss, the balance between the anti-inflammatory adipokine, adiponectin, and its inflammatory counterpart, leptin, may be of great importance in determining the postoperative weight and fat loss as well as the metabolic outcome of bariatric surgery. Further prospective studies will assess the involvement of the Adpn/Lep ratio after bariatric surgery in the prevention of serious obesity-related complications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G.-A., G.F., and V.C.; data curation, X.U., M.I., P.P., G.F., and V.C.; formal analysis, X.U., M.I., J.G.-A., A.R., B.R., S.B., C.S., and J.S.; funding acquisition, J.G.-A., G.F., and V.C.; methodology, X.U., M.I., B.R., V.V., R.M., and V.C.; writing—original draft, X.U., G.F., and V.C.; writing—review & editing, M.I., J.G.-A., A.R., B.R., S.B., V.V., R.M., C.S., J.S., P.P., G.F., and V.C. All authors read and approved the final version of the article.
Funding
This research was supported by Plan Estatal I+D+I from the Spanish Instituto de Salud Carlos III–Subdirección General de Evaluación y Fomento de la investigación–FEDER (grants number PI16/01217, PI17/02183 and PI17/02188), by the Gobierno de Navarra (10/2018) and by CIBEROBN, ISCIII, Spain.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the valuable collaboration of all the members of the Nutrition Unit for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Catalán, V. Precision medicine: Diagnosis and management of obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Frühbeck, G.; Ryan, D.H.; Wilding, J.P. Management of obesity. Lancet 2016, 387, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G. Bariatric and metabolic surgery: A shift in eligibility and success criteria. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The science of obesity management: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloy, V.L.; Briel, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kashyap, S.R.; Schauer, P.R.; Mingrone, G.; Bucher, H.C.; Nordmann, A.J. Bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2013, 347, f5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikramuddin, S.; Korner, J.; Lee, W.J.; Connett, J.E.; Inabnet, W.B.; Billington, C.J.; Thomas, A.J.; Leslie, D.B.; Chong, K.; Jeffery, R.W.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: The Diabetes Surgery Study randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cummings, D.E. Mechanisms of diabetes improvement following bariatric/metabolic surgery. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.W.; Efird, J.T.; Guidry, C.A.; Penn, R.I.; Sawyer, R.G.; Schirmer, B.D.; Hallowell, P.T. Long-term diabetic response to gastric bypass. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 190, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Still, C.D.; Wood, G.C.; Benotti, P.; Petrick, A.T.; Gabrielsen, J.; Strodel, W.E.; Ibele, A.; Seiler, J.; Irving, B.A.; Celaya, M.P.; et al. Preoperative prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Borisenko, O.; Telegina, I.; Hargreaves, J.; Ahmed, A.R.; Sanchez Santos, R.; Pring, C.; Funch-Jensen, P.; Dillemans, B.; Hedenbro, J.L. Systematic review of risk prediction models for diabetes after bariatric surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Almulaifi, A.; Tsou, J.J.; Ser, K.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.C. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: Predicting the success by ABCD score. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, G.C.; Mirshahi, T.; Still, C.D.; Hirsch, A.G. Association of DiaRem Score with cure of type 2 diabetes following bariatric surgery. JAMA Surg. 2016, 151, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, G.F.; Scopinaro, N.; Cordera, R. Adipokine pattern after bariatric surgery: Beyond the weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Ramírez, B.; Rotellar, F.; Pastor, C.; Silva, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Frühbeck, G. Proinflammatory cytokines in obesity: Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus and gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G. Adipokines in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and obesity. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2009, 10, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linscheid, P.; Christ-Crain, M.; Stoeckli, R.; Reusch, C.E.; Lutz, T.A.; Muller, B.; Keller, U. Increase in high molecular weight adiponectin by bariatric surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Control of body weight: A physiologic and transgenic perspective. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, G.F.; Gradaschi, R.; Andraghetti, G.; Scopinaro, N.; Cordera, R. Serum leptin and adiponectin concentration in type 2 diabetes patients in the short and long term following biliopancreatic diversion. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: A promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio is a functional biomarker of adipose tissue inflammation. Nutritents 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Portincasa, P.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Involvement of the leptin-adiponectin axis in inflammation and oxidative stress in the metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.M. Metabolic risk susceptibility in men is partially related to adiponectin/leptin ratio. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 409679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Rhee, E.J.; Choi, J.H.; Bae, J.C.; Yoo, S.H.; Kim, W.J.; Park, C.Y.; Mok, J.O.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, W.Y.; et al. The relationship of adiponectin/leptin ratio with homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance index and metabolic syndrome in apparently healthy korean male adults. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, F.; Blaha, V.; Ticha, A.; Hyspler, R.; Haluzik, M.; Lesna, J.; Smahelova, A.; Sobotka, L. Effects of body weight reduction on plasma leptin and adiponectin/leptin ratio in obese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Maehata, E.; Yano, M.; Taniyama, M.; Suzuki, S. Correlation between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2005, 54, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Yano, M.; Yamakado, M.; Maehata, E.; Suzuki, S. Relationship between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in subjects without hyperglycemia. Metabolism 2006, 55, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigouroux, C.; Maachi, M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Coussieu, C.; Gharakhanian, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Rozenbaum, W.; Capeau, J.; et al. Serum adipocytokines are related to lipodystrophy and metabolic disorders in HIV-infected men under antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2003, 17, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiliscan, C.; Arama, V.; Mihailescu, R.; Munteanu, D.; Iacob, D.G.; Popescu, C.; Catana, R.; Negru, A.; Lobodan, A.; Arama, S.S. Association of adiponectin/leptin ratio with carbohydrate and lipid metabolism parameters in HIV-infected patients during antiretroviral therapy. Endocr. Res. 2018, 43, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Andrada, P.; Ramírez, B.; Ibañez, P.; Vila, N.; Romero, S.; Margall, M.A.; Gil, M.J.; et al. Increased cardiometabolic risk factors and inflammation in adipose tissue in obese subjects classified as metabolically healthy. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruzábal, F.J.; Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Archanco, M.; Burrell, M.A. Immunocytochemical detection of leptin in non-mammalian vertebrate stomach. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 128, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancha, A.; Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Peripheral signalling involved in energy homeostasis control. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2012, 25, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Ezquerro, S.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G. Revisiting the adipocyte: A model for integration of cytokine signaling in the regulation of energy metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E691–E714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, A.; Miranda, J.; Bullo, M.; Casas, R.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Larretxi, I.; Estruch, R.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Portillo, M.P. Comparative effect of two Mediterranean diets versus a low-fat diet on glycaemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, N.; Iniamura, S.; Fujita, T.; Uchida, Y.; Inagaki, K.; Kakizawa, H.; Hayakawa, N.; Suzuki, A.; Takeda, J.; Horikawa, Y.; et al. The ratio of leptin to adiponectin can be used as an index of insulin resistance. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2008, 57, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masquio, D.C.; de Piano, A.; Sanches, P.L.; Corgosinho, F.C.; Campos, R.M.; Carnier, J.; da Silva, P.L.; Caranti, D.A.; Tock, L.; Oyama, L.M.; et al. The effect of weight loss magnitude on pro-/anti-inflammatory adipokines and carotid intima-media thickness in obese adolescents engaged in interdisciplinary weight loss therapy. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 79, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norata, G.D.; Raselli, S.; Grigore, L.; Garlaschelli, K.; Dozio, E.; Magni, P.; Catapano, A.L. Leptin:adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of intima media thickness of the common carotid artery. Stroke 2007, 38, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, N.; Naruse, M.; Usui, T.; Tagami, T.; Suganami, T.; Yamada, K.; Kuzuya, H.; Shimatsu, A.; Ogawa, Y. Leptin-to-adiponectin ratio as a potential atherogenic index in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2488–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J.; Rotellar, F.; Silva, C.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gil, M.J.; Frühbeck, G. Increased serum amyloid A concentrations in morbid obesity decrease after gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Prediction of Diabetes Remission in Morbidly Obese Patients After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannipieri, M.; Mari, A.; Anselmino, M.; Baldi, S.; Barsotti, E.; Guarino, D.; Camastra, S.; Bellini, R.; Berta, R.D.; Ferrannini, E. The role of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in the remission of type 2 diabetes after gastric bypass surgery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1372–E1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallipedhi, A.; Min, T.; Prior, S.L.; MacIver, C.; Luzio, S.D.; Dunseath, G.; Bracken, R.M.; Islam, S.; Barry, J.D.; Caplin, S.; et al. Association between the preoperative fasting and postprandial C-peptide AUC with resolution of type 2 diabetes 6 months following bariatric surgery. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, W.J.; Chong, K.; Ser, K.H.; Chen, J.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.C.; Su, Y.H.; Tsai, M.H. C-peptide predicts the remission of type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Silva, C.; Rotellar, F.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G. Expression of caveolin-1 in human adipose tissue is upregulated in obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus and related to inflammation. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G. Obesity: Aquaporin enters the picture. Nature 2005, 438, 436–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalán, V.; Domingo, P.; Giralt, M.; Frühbeck, G.; Villarroya, F. Opposite alterations in FGF21 and FGF19 levels and disturbed expression of the receptor machinery for endocrine FGFs in obese patients. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Modulation of the leptin-induced white adipose tissue lipolysis by nitric oxide. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Salvador, J. Leptin-induced lipolysis opposes the tonic inhibition of endogenous adenosine in white adipocytes. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).