Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Sampling
2.2. Hypocaloric Diet Plus Physical Exercise Program (HPP)
2.3. Anthropometric and Biochemical Measurements
2.4. DNA Extraction and Screening of the ADIPOQ Gene
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. A Hypocaloric Diet Plus Physical Exercise Program Ameliorates Biochemical Parameters of People with Severe Obesity and Increase Acpr30 Levels
3.2. High-Molecular Weight Oligomers of Adiponectin Increase at the End of a 4-Week HPP
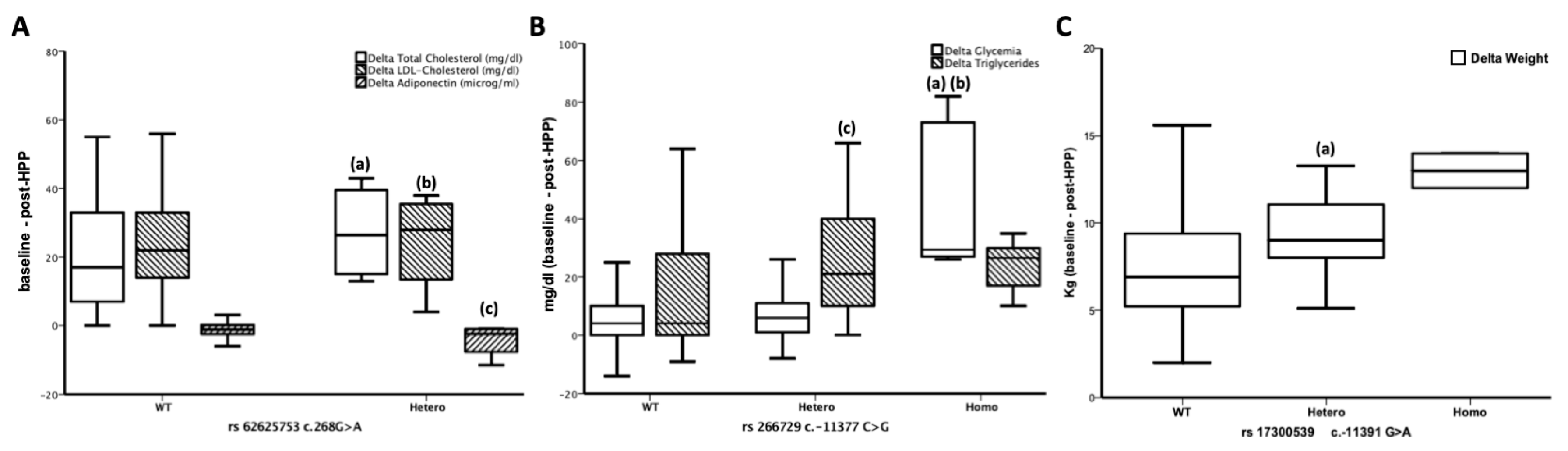
3.3. ADIPOQ Polymorphisms are Related to the Effects of a 4-week HPP
3.4. rs62625753 Predicts Δ Adiponectin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheikh, A.B.; Nasrullah, A.; Haq, S.; Akhtar, A.; Ghazanfar, H.; Nasir, A.; Afzal, R.; Bukhari, M.M.; Chaudhary, A.Y.; Naqvi, S.W. The Interplay of Genetics and Environmental Factors in the Development of Obesity. Cureus 2017, 7, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.; Nigro, E.; Monaco, M.L.; Matera, M.G.; Scudiero, O.; Mazzarella, G.; Daniele, A. The burden of obesity in asthma and COPD: Role of adiponectin. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 43, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 11, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.; Mazzarella, G.; Turchiarelli, V.; Nigro, E.; Corbi, G.; Scudiero, O.; Sofia, M.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin: An attractive marker for metabolic disorders in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Nutrients 2013, 5, 4115–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; Palmieri, A.; Mazzarella, G.; Costagliola, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. New insight into adiponectin role in obesity and obesity-related diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 658913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Sugiura, E.; Abe, H.; Kagawa, T.; Goto, M.; Takahashi, R.I.; Akimoto, T.; Suemizu, H. Adiponectin deficiency-induced diabetes increases TNFα and FFA via downregulation of PPARα. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirbu, A.E.; Buburuzan, L.; Kevorkian, S.; Martin, S.; Barbu, C.; Copaescu, C.; Smeu, B.; Fica, S. Adiponectin expression in visceral adiposity is an important determinant of insulin resistance in morbid obesity. Endokrynol. Pol. 2018, 69, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitfeld, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Kovacs, P. Genetics of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, F.; Whitehead, J.P. Adiponectin: it’s all about the modifications. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Andel, M.; Heijboer, A.C.; Drent, M.L. Adiponectin and Its Isoforms in Pathophysiology. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 85, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investing. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 18, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochu-Gaudreau, K.; Rehfeldt, C.; Blouin, R.; Bordignon, V.; Murphy, B.D.; Palin, M.F. Adiponectin action from head to toe. Endocrine 2010, 37, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Schettino, P.; Polito, R.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; De Palma, G.D.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin and colon cancer: Evidence for inhibitory effects on viability and migration of human colorectal cell lines. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 448, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Tschritter, O.; Fritsche, A.; Staiger, H.; Renn, W.; Weisser, M.; Machicao, F.; Häring, H. Association of the T-G polymorphism in adiponectin (exon 2) with obesity and insulin sensitivity: Interaction with family history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Herbert, A.; Gerry, N.P.; McQueen, M.B.; Heid, I.M.; Pfeufer, A.; Illig, T.; Wichmann, H.E.; Meitinger, T.; Hunter, D.; Hu, F.B.; et al. A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science 2006, 14, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzaghi, C.; Trischitta, V.; Doria, A. Genetic influences of adiponectin on insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungtrakoon, P.; Plengvidhya, N.; Tangjittipokin, W.; Chimnaronk, S.; Salaemae, W.; Chongjaroen, N.; Chanprasert, K.; Sujjitjoon, J.; Srisawat, C.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T. Novel adiponectin variants identified in type 2 diabetic patients reveal multimerization and secretion defects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, V.; Thivel, D.; Costes, F.; Touron, J.; Boirie, Y.; Pereira, B.; Perrault, H.; Duclos, M.; Richard, R. Eccentric Training Improves Body Composition by Inducing Mechanical and Metabolic Adaptations: A Promising Approach for Overweight and Obese Individuals. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargeant, J.A.; Gray, L.J.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Willis, S.A.; Stensel, D.J.; Nimmo, M.A.; Aithal, G.P.; King, J.A. The effect of exercise training on intrahepatic triglyceride and hepatic insulin sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.M.M.; Ferreira, R.M.P.; Moreira-Gonçalves, D. Exercise Training as Therapy for Cancer-Induced Cardiac Cachexia. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheggen, R.J.H.M.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Catoire, M.; Terink, R.; Ramakers, R.; Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Mensink, M.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; Thijssen, D.H.J.; Hopman, M.T.E. Cytokine responses to repeated. prolonged walking in lean versus overweight/obese individuals. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.Y. The role of exercise-induced myokines in regulating metabolism. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Sangiorgio, D.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; Polito, R.; Villone, G.; Daniele, A. Gene molecular analysis and Adiponectin expression in professional Water Polo players. Cytokine 2016, 81, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.S.; Nicklas, B.J.; Berman, D.M.; Elahi, D. Adiponectin levels do not change with moderate dietary induced weight loss and exercise in obese postmenopausal women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord 2003, 27, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, R.H.; Williams, R.H.; Kortebein, P.M.; Sullivan, D.H.; Evans, W.J. Influence of exercise intensity on abdominal fat and adiponectin in elderly adults. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numao, S.; Katayama, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Tanaka, K. Influence of acute aerobic exercise on adiponectin oligomer concentrations in middle-aged abdominally obese men. Metabolism 2011, 60, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, A.; Nigro, E.; Polito, R.; Monaco, M.L.; Scudiero, O.; Mormile, I.; Cesoni Marcelli, A.; Capasso, M.; Habetswallner, F.; Genovese, A.; et al. Total and High Molecular Weight Adiponectin Expression Is Decreased in Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Correlation with Ig Replacement Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, R.; Labruna, G.; Finelli, C.; Daniele, A.; Sacchetti, L.; Oriani, G.; Contaldo, F.; Pasanisi, F. The absence of polymorphisms in ADRB3, UCP1, PPARγ, and ADIPOQ genes protects morbid obese patients toward insulin resistance. J. Endocrinol. Investing. 2012, 35, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A.; Kuvalekar, A.A. Adiponectin: A potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 39, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg, A.D.V.; Reis, A.F.; Gerchman, F. Relationships between adiponectin levels, the metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: A literature review. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotidis, E.V.; Koliakos, G.G.; Baltzopoulos, V.G.; Ioannidis, K.N.; Yovos, J.G.; Papavramidis, S.T. Serum ghrelin, leptin and adiponectin levels before and after weight loss: Comparison of three methods of treatment—A prospective study. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, E.L.; Rissanen, A.; Bruun, J.M.; Skogstrand, K.; Tonstad, S.; Hougaard, D.M.; Richelsen, B. Weight loss larger than 10% is needed for general improvement of levels of circulating adiponectin and markers of inflammation in obese subjects: A 3-year weight loss study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivert, M.F.; Manning, A.K.; McAteer, J.B.; Florez, J.C.; Dupuis, J.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Meigs, J.B. Common variants in the adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) associated with plasma adiponectin levels, type 2 diabetes, and diabetes-related quantitative traits: The Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Long, J.; Liu, Q.; Deng, H.C. Association of the ADIPOQ rs17360539 and rs266729 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 325, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Boutin, P.; Mori, Y.; Tobe, K.; Dina, C.; Yasuda, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Otabe, S.; Okada, T.; Eto, K.; et al. Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 2002, 51, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, B.S.; Weinert, S.; Langefeld, C.D.; Williams, A.H.; Campbell, J.K.; Saad, M.F.; Haffner, S.M.; Norris, J.M.; Bowden, D.W. Genetic analysis of adiponectin and obesity in Hispanic families: The IRAS Family Study. Hum. Genet. 2005, 117, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Jiao, M.L.; Hao, Y.H.; Liang, L.B.; Gao, L.J.; Legge, D.G.; Quan, H.; Zhao, M.M.; Ning, N.; et al. Associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (+45T>G. +276G>T. -11377C>G. -11391G>A) of adiponectin gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, I.M.; Henneman, P.; Hicks, A.; Coassin, S.; Winkler, T.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Fuchsberger, C.; Song, K.; Hivert, M.-F.; Waterworth, D.M.; et al. Clear detection of ADIPOQ locus as the major gene for plasma adiponectin: Results of genome-wide association analyses including 4659 European individuals. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lange, E.M.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Kuzawa, C.W.; McDade, T.W.; Qin, L.; Curocichin, G.; Borja, J.B.; Lange, L.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study for adiponectin levels in Filipino women identifies CDH13 and a novel uncommon haplotype at KNG1-ADIPOQ. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4955–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.E.; Beilby, J.; Cadby, G.; Warrington, N.M.; Bruce, D.G.; Davis, W.A.; Davis, T.M.; Wiltshire, S.; Knuiman, M.; McQuillan, B.M.; et al. A comprehensive investigation of variants in genes encoding adiponectin (ADIPOQ) and its receptors (ADIPOR1/R2), and their association with serum adiponectin. type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobbert, T.; Rochlitz, H.; Wegewitz, U.; Akpulat, S.; Mai, K.; Weickert, M.O.; Möhlig, M.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Spranger, J. Changes of adiponectin oligomer composition by moderate weight reduction. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engl, J.; Bobbert, T.; Ciardi, C.; Laimer, M.; Tatarczyk, T.; Kaser, S.; Weiss, H.; Molnar, C.; Tilg, H.; Patsch, J.R.; et al. Effects of pronounced weight loss on adiponectin oligomer composition and metabolic parameters. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007, 15, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, M.; Havel, P.J.; Phélis, S.; Blank, D.; Sniderman, A.D.; Cianflone, K. Plasma acylation-stimulating protein, adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin before and after weight loss induced by gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.J.; Jang, Y.; Koh, S.J.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, O.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Ordovas, J.M.; Lee, J.H. The association of SNP276G>T at adiponectin gene with circulating adiponectin and insulin resistance in response to mild weight loss. Int, J. Obes. (Lond.) 2006, 30, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nascimento, H.; Vieira, E.; Coimbra, S.; Catarino, C.; Costa, E.; Bronze-da-Rocha, E.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Carvalho, M.; Ferreira Mansilha, H.; Rêgo, C.; et al. Adipokine Gene Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Portuguese Obese Adolescents: Associations with Plasma Concentrations of Adiponectin, Resistin, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Child. Obes. 2016, 12, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
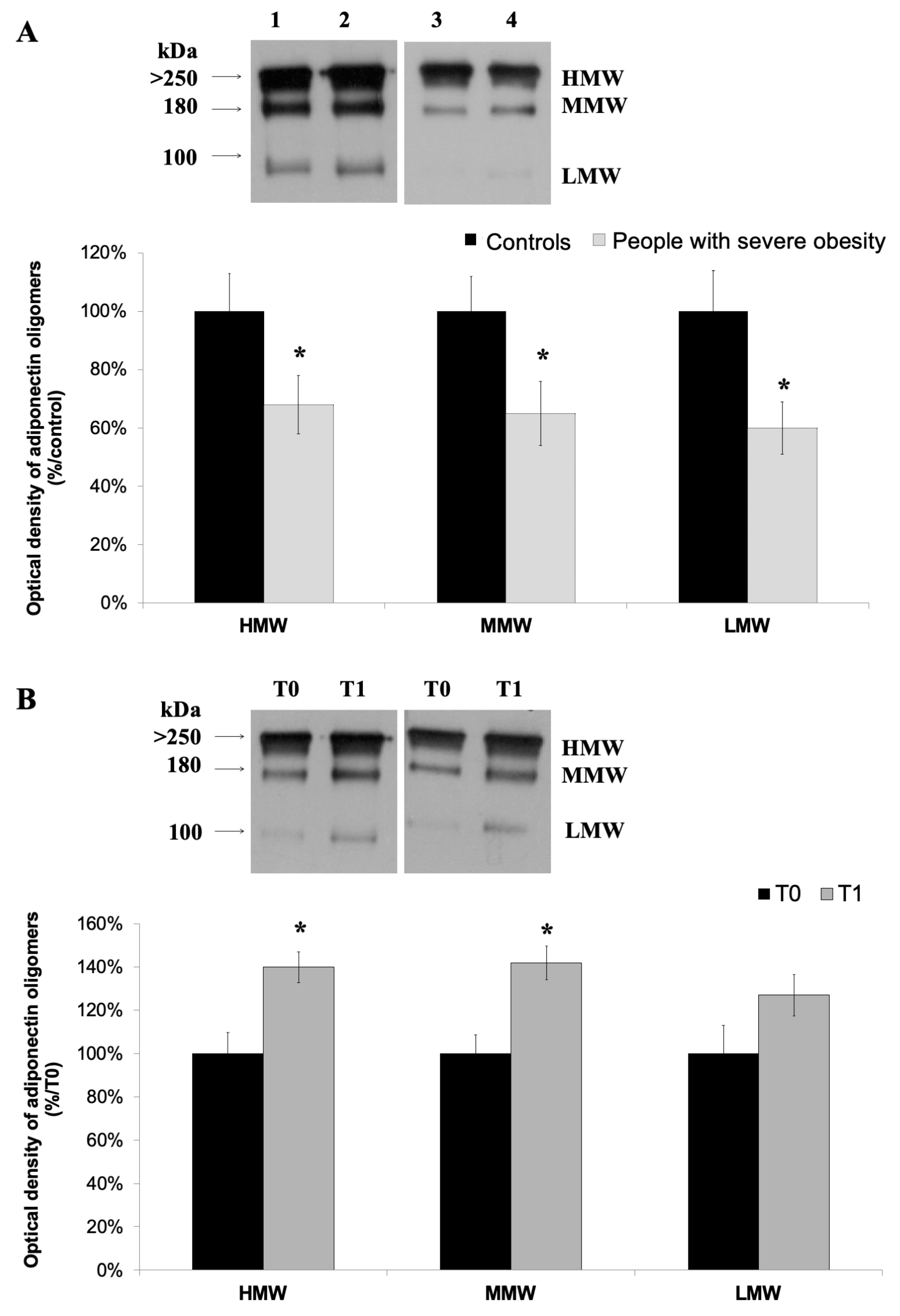
| Controls mean ± SD | People with Severe Obesity mean ± SD | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 40.84 ± 9.40 | 42.28 ± 13.81 | 0.390 |
| Gender (F/M) | 101/49 | 181/87 | 0.966 |
| Weight (Kg) | 67.08 ± 11.81 | 128.83 ± 23.31 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 23.46± 2.89 | 48.55 ± 7.60 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 81.38 ± 12.14 | 96.57 ± 34.80 | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 150.03 ± 41.83 | 183.44 ± 36.87 | <0.0001 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.46 ± 16.37 | 41.15 ± 10.32 | <0.0001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 104.23 ± 31.97 | 119.28± 30.15 | 0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 98.71 ± 38.88 | 146.28 ± 50.73 | <0.0001 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 274.67 ± 44.57 | 422.57 ± 104.85 | <0.0001 |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 29.89 ± 9.86 | 24.07 ± 6.67 | <0 0001 |
| People with Severe Obesity | T0 mean ± SD | T1 mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (Kg) | 128.83 ± 23.31 | 120.49 ± 22.31 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 48.55 ± 7.60 | 45.46 ± 7.11 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.57 ± 34.80 | 86.62 ± 23.22 | <0.0001 |
| Fasting Insulin | 12.43 ± 6.03 | 13.06 ± 7.50 | 0.085 |
| HOMA-IR- | 3.03 ± 2.04 | 2.95 ± 2.28 | 0.455 |
| 2-h glucose | 107.78 ± 38.17 | 103.67 ± 22.33 | 0.030 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 183.46 ± 36.93 | 164.10 ± 34.15 | <0.0001 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 45.36 ± 13.44 | 40.82 ± 10.92 | <0.0001 |
| LDL cholesterol(mg/dL) | 118.35 ± 31.89 | 96.99 ± 29.67 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides(mg/dL) | 146.28 ± 50.73 | 128.76 ± 41.47 | <0.0001 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL). | 418.32 ± 107.05 | 403.26 ± 101.71 | 0.007 |
| VES | 33.01 ± 25.05 | 26.67 ± 22.00 | <0.0001 |
| CRP | 10.00 ± 10.72 | 7.76 ± 11.67 | 0.002 |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 24.03 ± 6.63 | 24.81 ± 6.95 | <0.0001 |
| Controls n (%) | People with Severe Obesity n (%) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs 266729 c.-11377 C > G | Wt | 111 (74) | 183 (68.3) | 0.217 |
| Hetero | 31 (20.7) | 75 (28.0) | ||
| Homo | 8 (5.3) | 10 (3.7) | ||
| rs 16861194 c.-11426 A > G | Wt | 141 (94) | 240 (89.6) | 0.053 |
| Hetero | 9 (6.0) | 18 (6.7) | ||
| Homo | 0 (0.0) | 10 (3.7) | ||
| rs 17300539 c.-11391 G > A | Wt | 115 (76.7) | 230 (86.0) | 0.012 |
| Hetero | 35 (23.3) | 36 (13.4) | ||
| Homo | 0 (0.0) 1 | 2 (0.6) | ||
| rs60806105 c.-11156 insCA | Wt | 141 (94) | 241 (89.9) | 0.018 |
| Hetero | 9 (6) | 27 (10.1) | ||
| Homo | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| rs 2241766 c.45 T > G | Wt | 104 (69.3) | 178 (66.4) | 0.820 |
| Hetero | 41 (27.3) | 81 (30.2) | ||
| Homo | 5 (3.3) | 9 (3.4) | ||
| rs1501299 c.214+62 G > T | Wt | 103 (68.7) | 138 (51.6) | <0 0001 |
| Hetero | 42 (28.0) | 107 (39.8) | ||
| Homo | 5 (3.3) | 23 (8.6) | ||
| rs62625753 c.268G > A | Wt | 148 (98.7) | 264 (98.5) | 0.896 |
| Hetero | 2 (1.3) | 4 (1.5) | ||
| Homo | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| rs 17366743 c.331T > C | Wt | 144 (96.0) | 252 (94.0) | 0.266 |
| Hetero | 6 (4) | 16 (6.0) | ||
| Homo | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Variables | WT n (%) | Hetero n (%) | Homo n (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs266729 c.-11377C>G | 183 (68.3) | 75 (28.0) | 10 (3.7) | |
| ΔGlucose | 8.36 ± 13.24 * | 9.31 ± 11.94 * | 42.70 ± 23.65 | <0.0001 |
| ΔTriglycerides | 14.63 ± 19.16 | 24.77 ± 19.80 # | 23.90 ± 7.98 | <0.0001 |
| rs17300539c.11391G>A | 230 (86.0) | 36 (13.4) | 2 (0.6) | |
| ΔWeight | 7.78 ± 3.49 | 9.16 ± 3.52 $ | 12.9 ± 4.4 | 0.005 |
| rs62625753 c.268G>A | 264 (98.5) | 4 (1.5) | 0 (0) | |
| Δtotal cholesterol | 20.25 ± 15.41 | −3.0 ± 1.73 @ | - | 0.010 |
| ΔLDL-cholesterol | 24.46 ± 12.37 | 9.33 ± 4.04 ! | - | 0.036 |
| ΔAdiponectin | −1.06 ± 2.06 | −4.48 ± 1.78 ^ | - | 0.005 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corbi, G.; Polito, R.; Monaco, M.L.; Cacciatore, F.; Scioli, M.; Ferrara, N.; Daniele, A.; Nigro, E. Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092195
Corbi G, Polito R, Monaco ML, Cacciatore F, Scioli M, Ferrara N, Daniele A, Nigro E. Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program. Nutrients. 2019; 11(9):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092195
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorbi, Graziamaria, Rita Polito, Maria Ludovica Monaco, Francesco Cacciatore, Michelina Scioli, Nicola Ferrara, Aurora Daniele, and Ersilia Nigro. 2019. "Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program" Nutrients 11, no. 9: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092195
APA StyleCorbi, G., Polito, R., Monaco, M. L., Cacciatore, F., Scioli, M., Ferrara, N., Daniele, A., & Nigro, E. (2019). Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program. Nutrients, 11(9), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092195





