A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
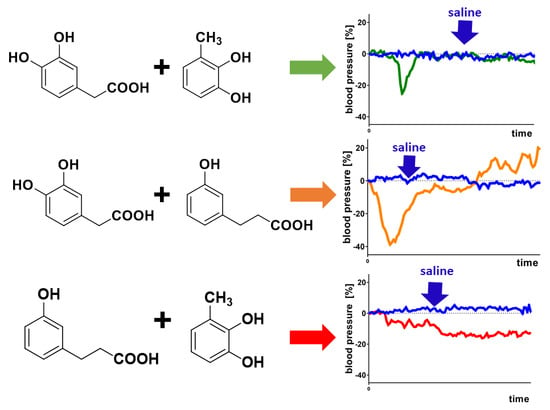
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perez, A.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Jimenez, R.; Perez-Abud, R.; Haro, J.M.; Osuna, A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Duarte, J.; Perez-Vizcaino, F. The flavonoid quercetin induces acute vasodilator effects in healthy volunteers: Correlation with beta-glucuronidase activity. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 89, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.L.; Lyon, T.; Litwin, S.E.; Rabovsky, A.; Symons, J.D.; Jalili, T. Quercetin reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rechner, A.R.; Smith, M.A.; Kuhnle, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Debnam, E.S.; Srai, S.K.; Moore, K.P.; Rice-Evans, C.A. Colonic metabolism of dietary polyphenols: Influence of structure on microbial fermentation products. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyne, T.; Steenput, B.; Roth, L.; De Meyer, G.R.Y.; Santos, C.N.D.; Valentova, K.; Dambrova, M.; Hermans, N. Dietary Polyphenols Targeting Arterial Stiffness: Interplay of Contributing Mechanisms and Gut Microbiome-Related Metabolism. Nutrients 2019, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galindo, P.; Rodriguez-Gomez, I.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Duenas, M.; Jimenez, R.; Menendez, C.; Vargas, F.; Tamargo, J.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; et al. Glucuronidated quercetin lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats via deconjugation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najmanova, I.; Pourova, J.; Voprsalova, M.; Pilarova, V.; Semecky, V.; Novakova, L.; Mladenka, P. Flavonoid metabolite 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid formed by human microflora decreases arterial blood pressure in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourova, J.; Najmanova, I.; Voprsalova, M.; Migkos, T.; Pilarova, V.; Applova, L.; Novakova, L.; Mladenka, P. Two flavonoid metabolites, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-methylcatechol, relax arteries ex vivo and decrease blood pressure in vivo. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 111, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciano, R.P.; Boeres, A.; Massacessi, L.; Istas, G.; Ventura, M.R.; Nunes Dos Santos, C.; Heiss, C.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A. Identification and quantification of novel cranberry-derived plasma and urinary (poly) phenols. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 599, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, M.; Iglesias-Carres, L.; Pons, Z.; Bravo, F.I.; Muguerza, B.; Arola-Arnal, A. Age related differences in the plasma kinetics of flavanols in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 29, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, M.; Pons, Z.; Iglesias-Carres, L.; Bravo, F.I.; Muguerza, B.; Arola-Arnal, A. Flavanol plasma bioavailability is affected by metabolic syndrome in rats. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conterno, L.; Martinelli, F.; Tamburini, M.; Fava, F.; Mancini, A.; Sordo, M.; Pindo, M.; Martens, S.; Masuero, D.; Vrhovsek, U.; et al. Measuring the impact of olive pomace enriched biscuits on the gut microbiota and its metabolic activity in mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Applova, L.; Karlickova, J.; Warncke, P.; Macakova, K.; Hrubsa, M.; Machacek, M.; Tvrdy, V.; Fischer, D.; Mladenka, P. 4-Methylcatechol, a Flavonoid Metabolite with Potent Antiplatelet Effects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudot, C.; Gomes, A.; Nicolas, V.; Le Gall, M.; Chaffey, P.; Broussard, C.; Calamita, G.; Mastrodonato, M.; Gena, P.; Perfettini, J.L.; et al. CSRP3 mediates polyphenols-induced cardioprotection in hypertension. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 66, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najmanová, I.; Pourová, J.; Mladěnka, P. A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses. Nutrients 2020, 12, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010213
Najmanová I, Pourová J, Mladěnka P. A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses. Nutrients. 2020; 12(1):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010213
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajmanová, Iveta, Jana Pourová, and Přemysl Mladěnka. 2020. "A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses" Nutrients 12, no. 1: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010213
APA StyleNajmanová, I., Pourová, J., & Mladěnka, P. (2020). A Mixture of Phenolic Metabolites of Quercetin Can Decrease Elevated Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Even in Low Doses. Nutrients, 12(1), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010213