Interplay of an Obesity-Based Genetic Risk Score with Dietary and Endocrine Factors on Insulin Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. GRS Calculation
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Functional Network Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population by Insulin Resistance Status
3.2. Nutritional Profile Categorized by Insulin Resistance Status
3.3. Association of Genetic Variants with Insulin Resistance
3.4. Multiprotein Network and Functional Enrichment Analyses
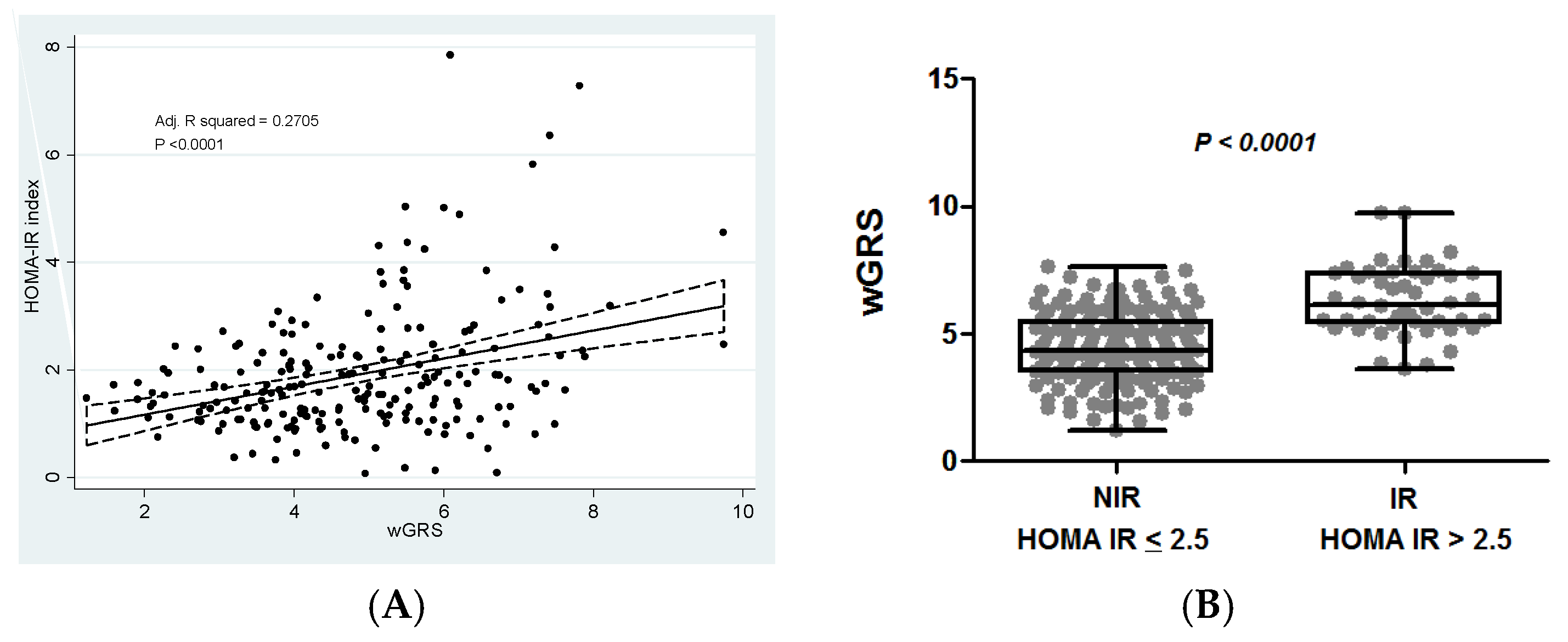
3.5. Association of the Weighted Genetic Risk Score with Insulin Resistance
3.6. Interactions between wGRS, Diet, and Metabolic Factors on Insulin Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, P.; Bardoloi, A.; Parkash, A.A. Metabolic effects of obesity: A review. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: Integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schinner, S.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Bornstein, S.R.; Barthel, A. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Storm, P.; Käräjämäki, A.; Martinell, M.; Dorkhan, M.; Carlsson, A.; Vikman, P.; Prasad, R.B.; Aly, D.M.; Almgren, P.; et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: A data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sari, C.I.; Eikelis, N.; Head, G.A.; Schlaich, M.; Meikle, P.; Lambert, G.; Lambert, E. Android Fat Deposition and Its Association with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Overweight Young Males. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Cuervo, M.; Goni, L.; Martinez, J.A. Genetic and nongenetic factors explaining metabolically healthy and unhealthy phenotypes in participants with excessive adiposity: Relevance for personalized nutrition. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Højlund, K. Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, B4890. [Google Scholar]
- Murea, M.; Ma, L.; Freedman, B.I. Genetic and environmental factors associated with type 2 diabetes and diabetic vascular complications. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2012, 9, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolb, H.; Martin, S. Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Arnett, D.K.; Corella, D.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lai, C.Q.; Parnell, L.D.; Lee, Y.C.; Ordovás, J.M. Perilipin polymorphism interacts with saturated fat and carbohydrates to modulate insulin resistance. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Rojo, R.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Lai, C.Q.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.; Smith, C.E.; Hidalgo, B.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; et al. Interaction of an S100A9 gene variant with saturated fat and carbohydrates to modulate insulin resistance in 3 populations of different ancestries. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Huang, J.; Qi, Q.; Li, Y.; Bray, G.A.; Rood, J.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. PCSK7 genotype modifies effect of a weight-loss diet on 2-year changes of insulin resistance: The POUNDS LOST trial. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goni, L.; Qi, L.; Cuervo, M.; Milagro, F.I.; Saris, W.H.; MacDonald, I.A.; Langin, D.; Astrup, A.; Arner, P.; Oppert, J.M.; et al. Effect of the interaction between diet composition and the PPM1K genetic variant on insulin resistance and β cell function markers during weight loss: Results from the Nutrient Gene Interactions in Human Obesity: Implications for dietary guidelines (NUGENOB) randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goni, L.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Corrales, F.J.; Ortiz, L.; Cuervo, M.; Martínez, J.A. Interaction between an ADCY3 Genetic Variant and Two Weight-Lowering Diets Affecting Body Fatness and Body Composition Outcomes Depending on Macronutrient Distribution: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Goni, L.; Cuervo, M.; Martinez, J.A. Differential lipid metabolism outcomes associated with ADRB2 gene polymorphisms in response to two dietary interventions in overweight/obese subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Cuervo, M.; Goni, L.; Martinez, J.A. Prediction of Blood Lipid Phenotypes Using Obesity-Related Genetic Polymorphisms and Lifestyle Data in Subjects with Excessive Body Weight. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 4283078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Song, P.; Xu, L. Optimal cut-off values for the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and pre-diabetes screening: Developments in research and prospects for the future. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro-González, D.; Sánchez-Íñigo, L.; Pastrana-Delgado, J.; Fernández-Montero, A.; Martinez, J.A. Triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) in comparison with fasting plasma glucose improved diabetes prediction in patients with normal fasting glucose: The Vascular-Metabolic CUN cohort. Prev. Med. 2016, 86, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Cuervo, M.; Goni, L.; Martinez, J.A. Models Integrating Genetic and Lifestyle Interactions on Two Adiposity Phenotypes for Personalized Prescription of Energy-Restricted Diets With Different Macronutrient Distribution. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequin (version 3.0): An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2007, 1, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Aa, M.P.; Fazeli Farsani, S.; Knibbe, C.A.; de Boer, A.; van der Vorst, M.M. Population-Based Studies on the Epidemiology of Insulin Resistance in Children. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 362375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziaee, A.; Esmailzadehha, N.; Oveisi, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Ghanei, L. The threshold value of homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance in Qazvin Metabolic Diseases Study (QMDS): Assessment of metabolic syndrome. J. Res. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Timóteo, A.T.; Miranda, F.; Carmo, M.M.; Ferreira, R.C. Optimal cut-off value for homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) index of insulin-resistance in a population of patients admitted electively in a Portuguese cardiology ward. Acta Medica Port. 2014, 27, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahalle, N.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Naik, S.S.; Garg, M.K. Association of dietary factors with insulin resistance and inflammatory markers in subjects with diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease in Indian population. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Jago, R.; Thompson, J.L. Dietary risk factors for the development of insulin resistance in adolescent girls: A 3-year prospective study. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macdonald, I.A. A review of recent evidence relating to sugars, insulin resistance and diabetes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, C.; Faerch, K.; Glümer, C.; Tetens, I.; Pedersen, O.; Carstensen, B.; Jørgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, fiber, simple sugars, and insulin resistance: The Inter99 study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basciano, H.; Miller, A.E.; Naples, M.; Baker, C.; Kohen, R.; Xu, E.; Su, Q.; Allister, E.M.; Wheeler, M.B.; Adeli, K. Metabolic effects of dietary cholesterol in an animal model of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E462–E473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, L.M.; Andersen, C.J. Effects of dietary cholesterol in diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 9, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickert, M.O.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Impact of Dietary Fiber Consumption on Insulin Resistance and the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.E.; Walker, M. Genetics of Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2016, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karaderi, T.; Drong, A.W.; Lindgren, C.M. Insights into the Genetic Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes from Genome-Wide Association Studies of Obesity-Related Traits. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2015, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingelsson, E.; McCarthy, M.I. Human Genetics of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Past, Present, and Future. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, B.; Zhao, X.; Shen, Y.; Wu, L.; Hou, D.; Cheng, H.; Mi, J. An obesity genetic risk score predicts risk of insulin resistance among Chinese children. Endocrine 2014, 47, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graae, A.S.; Hollensted, M.; Kloppenborg, J.T.; Mahendran, Y.; Schnurr, T.M.; Appel, E.V.R.; Rask, J.; Nielsen, T.R.H.; Johansen, M.Ø.; Linneberg, A.; et al. An adult-based insulin resistance genetic risk score associates with insulin resistance, metabolic traits and altered fat distribution in Danish children and adolescents who are overweight or obese. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Shen, J. Gene-environment interactions and susceptibility to metabolic syndrome and other chronic diseases. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, F. Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 508409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihn, A.S.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Adiponectin: Action, regulation and association to insulin sensitivity. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Park, S. Interactions among the variants of insulin-related genes and nutrients increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Res. 2018, 51, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, B.C.; Daily, J.W.; Park, S. High genetic risk scores for impaired insulin secretory capacity doubles the risk for type 2 diabetes in Asians and is exacerbated by Western-type diets. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, J.W.; Liu, M.; Park, S. High genetic risk scores of SLIT3, PLEKHA5 and PPP2R2C variants increased insulin resistance and interacted with coffee and caffeine consumption in middle-aged adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Cuervo, M.; Goni, L.; Milagro, F.I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Martinez, J.A. Modeling of an integrative prototype based on genetic, phenotypic and environmental information for personalized prescription of energy-restricted diets in overweight/obese subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | NIR HOMA-IR ≤ 2.5 | IR HOMA-IR > 2.5 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 45.3 ± 0.7 | 48.6 ± 0.2 | 0.038 |
| Sex (F/M) | 129/50 | 32/21 | 0.105 |
| Anthropometrics and clinical data | |||
| Weight (kg) | 84.9 ± 0.1 | 96.5 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.9 ± 0.3 | 34.0 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 101.2 ± 0.4 | 104.4 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| TFAT (kg) | 36.4 ± 0.03 | 37.8 ± 0.05 | 0.025 |
| VFAT (kg) | 1.35 ± 0.03 | 1.73 ± 0.06 | 0.052 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 128 ± 1 | 129 ± 2 | 0.537 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79 ± 1 | 81 ± 1 | 0.131 |
| Biochemical profile | |||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 93.8 ± 0.7 | 101.9 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 14.4 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR index | 1.40 ± 0.06 | 3.69 ± 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 217.4 ± 2.8 | 214.5 ± 5.4 | 0.649 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 141.9 ± 2.5 | 137.9 ± 4.8 | 0.466 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 57.1 ± 0.9 | 50.8 ± 1.7 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 91.9 ± 3.6 | 129.3 ± 6.9 | <0.001 |
| TyG index (ratio) | 8.29 ± 0.03 | 8.65 ± 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.13 ± 0.08 | 5.31 ± 0.16 | 0.336 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 22.3 ± 1.1 | 30.3 ± 2.0 | <0.001 |
| AST (IU/L) | 21.6 ± 0.7 | 24.5 ± 1.4 | 0.064 |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 11.9 ± 0.3 | 9.4 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 35.4 ± 1.6 | 41.1 ± 3.1 | 0.107 |
| CRP (µg/mL) | 2.50 ± 0.19 | 3.32 ± 0.38 | 0.065 |
| TNFα (pg/mL) | 0.98 ± 0.03 | 1.10 ± 0.06 | 0.082 |
| Variable | NIR HOMA-IR ≤ 2.5 | IR HOMA-IR > 2.5 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kilocalories/day) | 1948 ± 38 | 2042 ± 72 | 0.265 |
| Nutrient intake | |||
| Complex carbohydrates (%E/day) | 22.9 ± 0.5 | 24.2 ± 0.9 | 0.211 |
| Simple carbohydrates (%E/day) | 17.4 ± 0.8 | 19.9 ± 0.4 | 0.011 |
| Total protein (%E/day) | 19.5 ± 0.3 | 20.0 ± 0.6 | 0.496 |
| Animal protein (%E/day) | 13.4 ± 0.3 | 14.1 ± 0.6 | 0.305 |
| Vegetal protein (%E/day) | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 0.490 |
| Total fat (%E/day) | 37.2 ± 0.5 | 37.6 ± 1.0 | 0.732 |
| SFA (%E/day) | 10.3 ± 0.2 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 0.840 |
| MUFA (%E/day) | 15.7 ± 0.3 | 15.9 ± 0.5 | 0.791 |
| PUFA (%E/day) | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 0.766 |
| Dietary cholesterol (mg/day) | 380 ± 14 | 457 ± 28 | 0.017 |
| Fiber (g/day) | 22.4 ± 0.6 | 19.6 ± 1.1 | 0.031 |
| Water (mL/day) | 1132 ± 24 | 1158 ± 47 | 0.633 |
| Lifestyle factor | |||
| Physical activity (METs/day) | 24.2 ± 1.4 | 22.3 ± 2.7 | 0.555 |
| No. | SNP ID | Gene | Alleles | Risk Genotype | Risk Genotype in NIR, n (%) | Risk Genotype in IR, n (%) | p-Value | HWE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs1800544 | ADRA2A | G/C | GG + CC | 102 (57.0) | 41 (77.4) | 0.007 | 0.626 |
| 2 | rs7903146 | TCF7L2 | C/T | CC | 64 (35.8) | 29 (54.7) | 0.013 | 0.998 |
| 3 | rs2289487 | PLIN1 | C/T | CC + CT | 93 (52.0) | 37 (71.2) | 0.014 | 0.762 |
| 4 | rs12255372 | TCF7L2 | G/T | GG | 63 (35.2) | 28 (52.8) | 0.021 | 0.681 |
| 5 | rs894160 | PLIN1 | C/T | CT + TT | 80 (44.7) | 33 (62.3) | 0.025 | 0.996 |
| 6 | rs206936 | NUDT3 | A/G | AA | 98 (54.7) | 38 (71.7) | 0.028 | 0.450 |
| 7 | rs1799883 | FABP2 | T/C | TT + TC | 78 (43.6) | 32 (60.4) | 0.031 | 0.340 |
| 8 | rs2734827 | UCP3 | G/A | GA + AA | 92 (51.4) | 36 (67.9) | 0.034 | 0.935 |
| 9 | rs10838738 | MTCH2 | A/G | AA | 66 (36.9) | 28 (52.8) | 0.038 | 0.185 |
| 10 | rs519887 | ABCB11 | T/C | TC + CC | 115 (64.2) | 42 (79.2) | 0.040 | 0.288 |
| 11 | rs7799039 | LEP | G/A | GG | 35 (19.7) | 17 (33.3) | 0.040 | 0.850 |
| 12 | rs1055144 | NFE2L3 | C/T | CC + TT | 121 (67.6) | 43 (81.1) | 0.057 | 0.344 |
| 13 | rs1805081 | NPC1 | T/C | CC | 22 (12.3) | 12 (22.6) | 0.061 | 0.311 |
| 14 | rs11091046 | AGTR2 | A/C | CC | 56 (32.9) | 24 (47.1) | 0.066 | 0.189 |
| 15 | rs1801133 | MTHFR | G/A | AA | 20 (11.2) | 11 (20.8) | 0.072 | 0.397 |
| 16 | rs1801131 | MTHFR | T/G | TT | 90 (50.3) | 34 (64.2) | 0.075 | 0.921 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Cuervo, M.; Goni, L.; Martinez, J.A. Interplay of an Obesity-Based Genetic Risk Score with Dietary and Endocrine Factors on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010033
Ramos-Lopez O, Riezu-Boj JI, Milagro FI, Cuervo M, Goni L, Martinez JA. Interplay of an Obesity-Based Genetic Risk Score with Dietary and Endocrine Factors on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients. 2020; 12(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos-Lopez, Omar, José Ignacio Riezu-Boj, Fermin I. Milagro, Marta Cuervo, Leticia Goni, and J. Alfredo Martinez. 2020. "Interplay of an Obesity-Based Genetic Risk Score with Dietary and Endocrine Factors on Insulin Resistance" Nutrients 12, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010033
APA StyleRamos-Lopez, O., Riezu-Boj, J. I., Milagro, F. I., Cuervo, M., Goni, L., & Martinez, J. A. (2020). Interplay of an Obesity-Based Genetic Risk Score with Dietary and Endocrine Factors on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients, 12(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010033






