Nutrition Mediates the Relationship between Osteosarcopenia and Frailty: A Pathway Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Association between Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia and Osteosarcopenia with Frailty
3.3. Association between Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia and Osteosarcopenia with Nutrition
3.4. Mediating Effect of Nutrition on the Relationship between Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia and Osteosarcopenia with Frailty
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sepúlveda-Loyola, W.; Phu, S.; Hassan, E.B.; Brennan-Olsen, S.L.; Zanker, J.; Vogrin, S.; Conzade, R.; Kirk, B.; Al Saedi, A.; Probst, V.; et al. The Joint Occurrence of Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia (Osteosarcopenia): Definitions and Characteristics. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-I.; Kim, H.; Ha, Y.-C.; Kwon, H.-B.; Koo, K.-H. Osteosarcopenia in Patients with Hip Fracture Is Related with High Mortality. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Seibel, M.; Cumming, R.; Naganathan, V.; Blyth, F.; Le Couteur, D.; Handelsman, D.J.; Waite, L.M.; Hirani, V. Does Combined Osteopenia/Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia Confer Greater Risk of Falls and Fracture than Either Condition Alone in Older Men? The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 74, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, S.; Winzenberg, T.M.; Wills, K.E.; Scott, D.; Callisaya, M.L.; Cicuttini, F.; Jones, G.; Aitken, D. Prospective associations of osteosarcopenia and osteodynapenia with incident fracture and mortality over 10 years in community-dwelling older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 82, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, N.; Muraki, S.; Oka, H.; Iidaka, T.; Kodama, R.; Horii, C.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Akune, T.; Tanaka, S. Do sarcopenia and/or osteoporosis increase the risk of frailty? A 4-year observation of the second and third ROAD study surveys. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoli, A., Jr.; Chaves, P.H.; Ingham, S.J.M.; Fried, L.P. Severe osteopenia and osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and frailty status in community-dwelling older women: Results from the Women’s Health and Aging Study (WHAS) II. Bone 2011, 48, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.A.; Pietschmann, P.; Savastano, S. Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia Increase Frailty Syndrome in the Elderly. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; O’Donoghue, M.; Casey, M.C.; Walsh, J. Malnutrition in the elderly and its effects on bone health—A review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 21, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rui, M.; Inelmen, E.M.; Pigozzo, S.; Trevisan, C.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G. Dietary strategies for mitigating osteosarcopenia in older adults: A narrative review. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.S.; Lim, J.P.; Chew, J.; Tan, A.W.K. Influence of Obesity on Diagnostic Accuracy and Optimal Cutoffs for Sarcopenia Screening in Non-Frail Older Adults: A Comparison of SARC-F versus SARC-CalF. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K. A simple frailty questionnaire (FRAIL) predicts outcomes in middle aged African Americans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahadevan, S.; Lim, P.P.J.; Tan, N.J.L.; Chan, S.P. Diagnostic performance of two mental status tests in the older Chinese: Influence of education and age on cut-off values. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. MD State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, J.A. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: Synopsis of a WHO report. Osteoporos. Int. 1994, 4, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, T.-W.; Arai, H.; Chen, L.K.; Woo, J. Letter to the editor: Normative data of handgrip strength in 26344 older adults—A pooled dataset from eight cohorts in Asia. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, J.; Tay, L.; Lim, J.P.; Leung, B.P.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Ding, Y.Y.; Lim, W.S. Serum Myostatin and IGF-1 as Gender-Specific Biomarkers of Frailty and Low Muscle Mass in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuling, J.; De Haan, R.; Limburg, M.; Groenier, K.H. The Frenchay Activities Index. Assessment of functional status in stroke patients. Stroke 1993, 24, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellas, B.; Guigoz, Y.; Garry, P.J.; Nourhashemi, F.; Bennahum, D.; Lauque, S.; Albarede, J.-L. The mini nutritional assessment (MNA) and its use in grading the nutritional state of elderly patients. Nutrition 1999, 15, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Preacher, K.J. Statistical mediation analysis with a multicategorical independent variable. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2014, 67, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, N.; Muraki, S.; Oka, H.; Iidaka, T.; Kodama, R.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, S.; Akune, T. Is osteoporosis a predictor for future sarcopenia or vice versa? Four-year observations between the second and third ROAD study surveys. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kudo, Y.; Matsuoka, A.; Maruyama, H.; Emori, H.; Yamamura, R.; Hayakawa, C.; Tani, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; et al. Risk factors predicting osteosarcopenia in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: A retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.R.; Abdulla, J.; Andersen, H.E.; Schwarz, P.; Suetta, C. Sarcopenia and osteoporosis in older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, L.; Pluijm, S.M.F.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Colbert, L.H.; Pahor, M.; Rubin, S.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; et al. Higher Inflammatory Marker Levels in Older Persons: Associations with 5-Year Change in Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginaldi, L.; Di Benedetto, M.C.; De Martinis, M. Osteoporosis, inflammation and ageing. Immun. Ageing 2005, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.P.; Chong, M.S.; Tay, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Leung, B.P.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Tan, C.H.; Lim, W.S. Inter-muscular adipose tissue is associated with adipose tissue inflammation and poorer functional performance in central adiposity. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, K.E.; Lui, L.-Y.; Ensrud, K.E.; Hillier, T.A.; Leblanc, E.S.; Ing, S.W.; Hochberg, M.C.; Cauley, J.A.; Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Research Group. Inflammatory markers and risk of hip fracture in older white women: The study of osteoporotic fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Carreira, M.C.; Cignarelli, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Giorgino, F. The GH/IGF1 axis and signaling pathways in the muscle and bone: Mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 205, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Makizako, H.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Hotta, R.; Nakakubo, S.; Makino, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shimada, H. Association between Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Frailty among Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, J.; Iglseder, B.; Alzner, R.; Mayr-Pirker, B.; Pirich, C.; Kässmann, H.; Kreutzer, M.; Dovjak, P.; Reiter, R. Sarcopenia and osteoporosis are interrelated in geriatric inpatients. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 52, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.R.; Suriyaarachchi, P.; Gomez, F.; Curcio, C.-L.; Boersma, D.; Gunawardene, P.; Demontiero, O.; Duque, G. Comprehensive nutritional status in sarco-osteoporotic older fallers. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 19, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.L.; Coppinger, T.; McCarthy, A.L. The role of nutrition and physical activity in frailty: A review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pek, K.; Chew, J.; Lim, J.P.; Yew, S.; Tan, C.N.; Yeo, A.; Ding, Y.Y.; Lim, W.S. Social Frailty Is Independently Associated with Mood, Nutrition, Physical Performance, and Physical Activity: Insights from a Theory-Guided Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.; Pek, K.; Chew, J.; Lim, J.P.; Ismail, N.H.; Ding, Y.Y.; Cesari, M.; Lim, W.S. The Simplified Nutritional Appetite Questionnaire (SNAQ) as a Screening Tool for Risk of Malnutrition: Optimal Cutoff, Factor Structure, and Validation in Healthy Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Liang, C.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Kang, L.; Lee, W.-J.; Lim, J.; Sugimoto, K.; Akishita, M.; Chia, S.; et al. COVID-19 and older people in Asia: Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia calls to actions. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Normal (N = 132) | O (N = 36) | S (N = 35) | OS (N = 27) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years, mean (SD) | 65.7 (7.3) | 67.6 (7.0) | 69.3 (7.1) * | 71.4 (6.9) * | 0.0005 |
| Female gender, N (%) | 99 (75) | 30 (83.3) | 23 (65.7) | 15 (55.6) | 0.064 |
| Chinese ethnicity, N (%) | 116 (87.9) | 36 (100) | 35 (100) | 25 (92.6) | 0.024 |
| Comorbidities, N (%) | |||||
| Hypertension | 44 (33.3) | 13 (36.1) | 15 (42.9) | 10 (37.0) | 0.77 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 69 (52.3) | 23 (63.9) | 19 (54.3) | 19 (70.4) | 0.27 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 13 (9.9) | 7 (19.4) | 8 (22.9) | 5 (15.8) | 0.15 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 3 (2.3) | 1 (2.8) | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 0.86 |
| Stroke or transient ischemic attack | 3 (2.3) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 0.66 |
| Kidney disease | 7 (5.3) | 0 | 2 (5.7) | 0 | 0.31 |
| Asthma | 10 (7.6) | 1 (2.8) | 3 (8.6) | 1 (3.7) | 0.65 |
| Arthritis | 16 (12.1) | 1 (2.8) | 5 (14.3) | 3 (11.1) | 0.38 |
| Physical function, mean (SD) | |||||
| ADL | 98.0 (3.3) | 98.9 (3.0) | 98.3 (3.0) | 97.4 (4.2) | 0.31 |
| Cognitive function, mean (SD) | |||||
| CMMSE | 26.3 (1.7) | 25.9 (1.8) | 25.7 (1.8) | 26.2 (1.8) | 0.30 |
| Depressive symptoms, mean (SD) | |||||
| GDS | 1.1 (1.8) | 1.1 (2.0) | 1.2 (1.1) | 1.2 (0.9) | 0.99 |
| Nutrition and anthropometry, mean (SD) | |||||
| MNA total score | 27.6 (1.7) | 26.8 (1.9) | 26.7 (2.0) | 26.5 (1.9) * | 0.0035 |
| MNA categories, N (%) | 0.22 | ||||
| At risk | 4 (3.0) | 4 (11.1) | 3 (8.6) | 2 (7.4) | |
| Normal | 128 (97.0) | 32 (88.9) | 32 (91.4) | 25 (92.6) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.8 (3.4) | 22.9 (2.8) * | 22.5 (2.2) * | 22.3 (2.5) * | <0.001 |
| Calf circumference (cm) | 35.8 (3.0) | 34.5 (2.7) | 33.3 (2.5) * | 32.3 (3.6) */** | <0.001 |
| Mid-arm circumference (cm) | 28.4 (2.8) | 26.9 (2.9) | 27.0 (3.0) * | 25.6 (2.6) */** | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 86.9 (10.0) | 83.2 (8.9) | 84.2 (7.0) | 81.7 (7.7) * | 0.015 |
| DEXA fat% | 38.8 (6.2) | 38.2 (6.0) | 37.5 (7.2) | 36.1 (7.6) | 0.22 |
| Serum Vitamin D levels (μg/L) | 29.9 (8.5) | 30.4 (80) | 31.9 (10.2) | 32.7 (9.3) | 0.38 |
| Fried Frailty total score, mean (SD) | 0.38 (0.64) | 0.33 (0.68) | 1.6 (0.81) */** | 1.7 (0.72) */** | <0.001 |
| Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Frailty Score | β | SE | 95% CI | p | β | SE | 95% CI | p |
| Osteoporosis | −0.045 | 0.13 | −0.30–0.21 | 0.72 | −0.077 | 0.12 | −0.32–0.17 | 0.54 |
| Sarcopenia | 1.25 | 0.13 | 0.99–1.50 | <0.001 | 1.15 | 0.13 | 0.90–1.40 | <0.001 |
| Osteosarcopenia | 1.32 | 0.14 | 1.04–1.61 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 0.14 | 0.86-1.42 | <0.001 |
| R2 = 0.057 | R2 = 0.50 | |||||||
| Unadjusted Models | MNA (Total Score) | BMI, kg/m2 | Calf Circumference, cm | Waist Circumference, cm | Mid-Arm Circumference, cm | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | |
| Osteoporosis | −0.73 | 0.34 | 0.035 | −1.95 | 0.57 | 0.001 | −1.25 | 0.56 | 0.026 | −3.71 | 1.72 | 0.032 | −1.52 | 0.54 | 0.005 |
| Sarcopenia | −0.89 | 0.35 | 0.011 | −2.3 | 0.58 | <0.001 | −2.43 | 0.56 | <0.001 | −2.75 | 1.74 | 0.116 | −1.4 | 0.54 | 0.011 |
| Osteosarcopenia | −1.1 | 0.39 | 0.005 | −2.57 | 0.64 | <0.001 | 3.49 | 0.62 | <0.001 | −5.22 | 1.94 | 0.008 | −2.84 | 0.6 | <0.001 |
| R2 = 0.058 | R2 = 0.12 | R2 = 0.16 | R2 = 0.045 | R2 = 0.11 | |||||||||||
| Adjusted Models * | MNA (Total Score) | BMI, kg/m2 | Calf Circumference, cm | Waist Circumference, cm | Mid-Arm Circumference, cm | ||||||||||
| β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | |
| Osteoporosis | −0.73 | 0.35 | 0.037 | −1.94 | 0.57 | 0.001 | −1.07 | 0.56 | 0.057 | −3.05 | 1.64 | 0.063 | −1.44 | 0.54 | 0.008 |
| Sarcopenia | −1.02 | 0.36 | 0.005 | −2.39 | 0.59 | <0.001 | −2.44 | 0.57 | <0.001 | −3.36 | 1.67 | 0.046 | −1.52 | 0.56 | 0.007 |
| Osteosarcopenia | −1.31 | 0.4 | 0.001 | −2.91 | 0.66 | <0.001 | −3.65 | 0.64 | <0.001 | −7.24 | 1.87 | <0.001 | −3.12 | 0.62 | <0.001 |
| R2 = 0.082 | R2 = 0.16 | R2 = 0.19 | R2 = 0.18 | R2 = 0.13 | |||||||||||
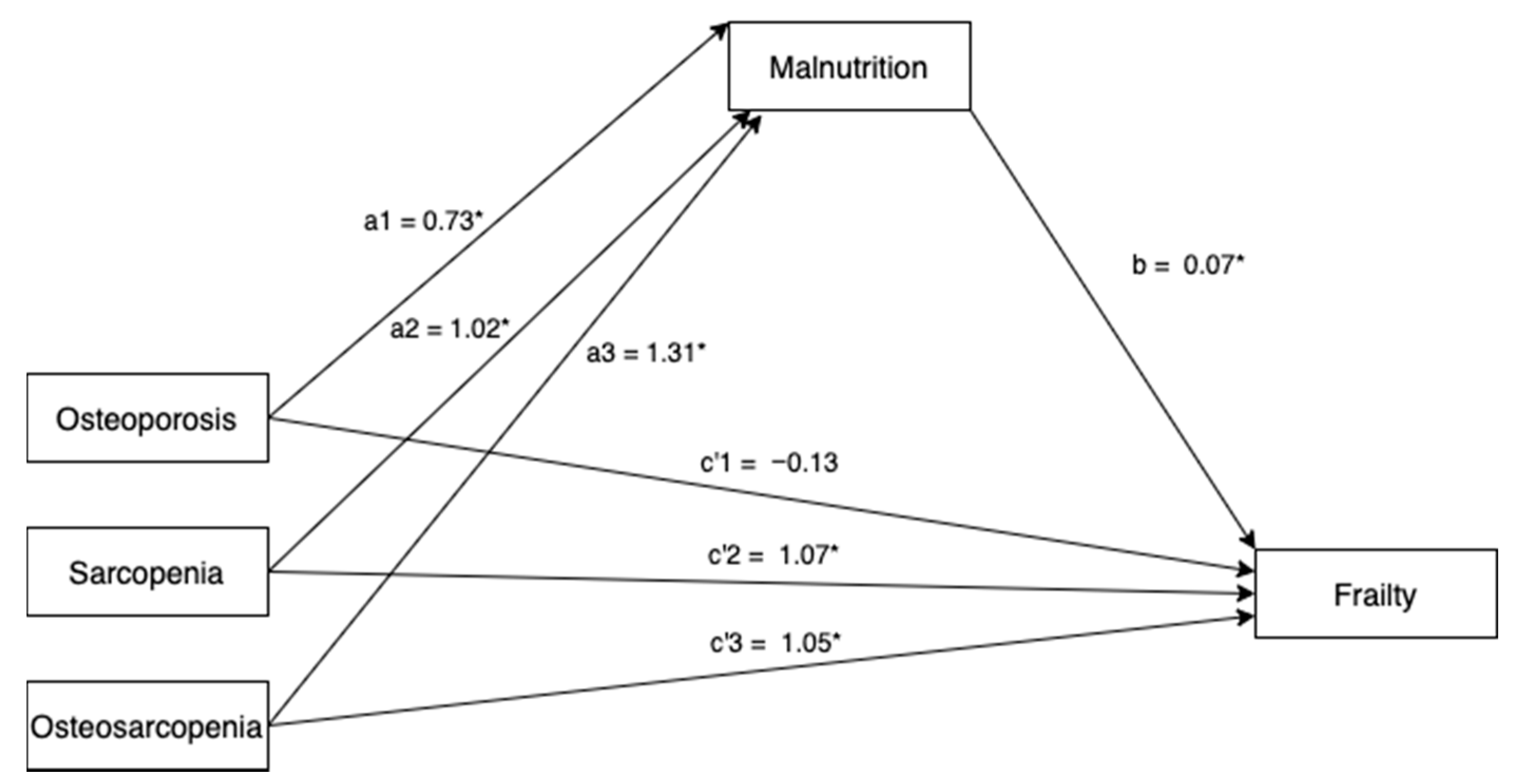
| Coefficient (SE) | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | ||||||||
| a1 | −0.73 (0.34) | 0.033 | ||||||
| Sarcopenia | ||||||||
| a2 | −1.02 (0.35) | 0.004 | ||||||
| Osteosarcopenia | ||||||||
| a3 | −1.31 (0.39) | 0.001 | ||||||
| Relative Total Effects | Relative Direct Effects | Relative Indirect Effects | ||||||
| Coefficient (SE) | p | Coefficient (SE) | p | Coefficient (SE) | 95% CI | |||
| c1 | −0.08 (0.12) | 0.54 | c’1 | −0.13 (0.12) | 0.28 | a1b | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.007–0.14 |
| c2 | 1.15 (0.13) | <0.001 | c’2 | 1.07 (0.12) | <0.001 | a2b | 0.07 (0.04) | 0.02–0.17 |
| c3 | 1.14 (0.14) | <0.001 | c’3 | 1.05 (0.14) | <0.001 | a2c | 0.09 (0.05) | 0.01–0.22 |
| b | −0.07 (0.02) | 0.002 | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chew, J.; Yeo, A.; Yew, S.; Tan, C.N.; Lim, J.P.; Hafizah Ismail, N.; Lim, W.S. Nutrition Mediates the Relationship between Osteosarcopenia and Frailty: A Pathway Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12102957
Chew J, Yeo A, Yew S, Tan CN, Lim JP, Hafizah Ismail N, Lim WS. Nutrition Mediates the Relationship between Osteosarcopenia and Frailty: A Pathway Analysis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12102957
Chicago/Turabian StyleChew, Justin, Audrey Yeo, Suzanne Yew, Cai Ning Tan, Jun Pei Lim, Noor Hafizah Ismail, and Wee Shiong Lim. 2020. "Nutrition Mediates the Relationship between Osteosarcopenia and Frailty: A Pathway Analysis" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12102957
APA StyleChew, J., Yeo, A., Yew, S., Tan, C. N., Lim, J. P., Hafizah Ismail, N., & Lim, W. S. (2020). Nutrition Mediates the Relationship between Osteosarcopenia and Frailty: A Pathway Analysis. Nutrients, 12(10), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12102957





