Eurycoma longifolia—Infused Coffee—An Oral Toxicity Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test and Reference Item Preparation
2.2. Care and Handling of Experimental Animal
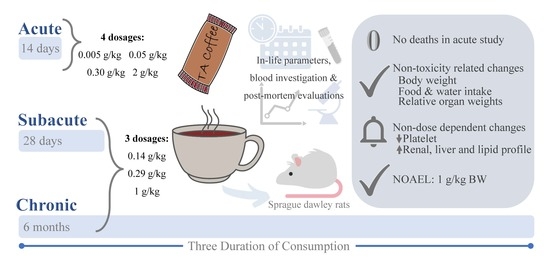
2.3. Single Dose Acute Oral Toxicity Study
2.4. Subacute 28-Day and Chronic 6-Month Oral Toxicity Studies
2.4.1. Subacute 28-Day Experimental Design
2.4.2. Chronic 6-Month Experimental Design
2.4.3. Hematology Analysis
2.4.4. Clinical Biochemistry Analysis
2.4.5. Relative Organ Weight
2.4.6. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Single Dose Acute Oral Toxicity Study
3.2. Subacute 28-Day and Chronic 6-Month Oral Toxicity Studies
3.2.1. Clinical Signs and Mortality
3.2.2. Body Weights, Food and Water Intake
3.2.3. Hematology Analysis
3.2.4. Clinical Biochemistry Analysis
3.2.5. Organ Weights
3.2.6. Gross Necropsy and Histopathology Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Test System | Dosage (g/kg BW) | Mortality | Clinical Signs of Toxicity | Body Weight (g) | Body Weight Gain (%) | Food Intake (g) | Organs Gross Pathology Findings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 1 | Week 2 | ||||||
| 1 | 0.005 | 0/1 | NAD | 219.87 | 234.52 | 246.07 | 10.60 | 86.05 | 69.45 | NAD |
| 2 | 0.050 | 0/1 | NAD | 216.90 | 254.89 | 292.81 | 25.90 | 87.35 | 112.47 | NAD |
| 3 | 0.300 | 0/1 | NAD | 216.94 | 246.34 | 278.95 | 22.20 | 93.79 | 113.47 | NAD |
| 4 | 2.000 | 0/1 | NAD | 234.14 | 260.60 | 274.50 | 14.70 | 106.92 | 82.80 | NAD |
| 5 | 2.000 | 0/1 | NAD | 243.15 | 275.31 | 291.17 | 16.50 | 132.83 | 76.80 | NAD |
| 6 | 2.000 | 0/1 | NAD | 202.05 | 219.19 | 222.79 | 9.31 | 92.12 | 62.31 | NAD |
| 7 | 2.000 | 0/1 | NAD | 211.36 | 244.51 | 250.01 | 15.50 | 113.11 | 76.19 | NAD |
| 8 | 2.000 | 0/1 | NAD | 218.59 | 268.09 | 253.17 | 13.70 | 125.38 | 67.20 | NAD |
| 221.90 ± 16.71 | 253.50 ± 22.34 | 258.30 ± 25.98 | 13.92 ± 2.78 | 114.10 ± 15.92 | 73.06 ± 8.19 | |||||
| Weekly Food Consumption | Male Dosage (g/kg BW) | Female Dosage (g/kg BW) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (n = 5) | 0.14 (n = 5) | 0.29 (n = 5) | 1.00 (n = 5) | 0 (n = 5) | 0.14 (n = 5) | 0.29 (n = 4) | 1.00 (n = 5) | |
| Week 1 | 117.00 ± 11.51 | 123.00 ± 17.89 | 109.00 ± 12.94 | 117.00 ± 16.43 | 85.00 ± 7.91 | 91.00 ± 15.17 | 108.00 ± 28.64 | 84.00 ± 11.94 |
| Week 2 | 134.00 ± 17.10 | 116.40 ± 14.74 | 130.00 ± 9.35 | 135.00 ± 12.75 | 91.00 ± 6.52 | 99.00 ± 8.94 | 109.00 ± 38.63 | 81.00 ± 14.32 |
| Week 3 | 160.00 ± 20.92 | 160.00 ± 12.75 | 145.00 ± 14.14 | 157.00 ± 17.18 | 98.00 ± 13.51 | 116.00 ± 39.91 | 111.25 ± 49.56 | 108.00 ± 33.28 |
| Week 4 | 173.00 ± 8.37 | 136.00 ± 30.50 | 148.00 ± 22.80 | 162.00 ± 13.04 | 128.00 ± 21.68 | 166.00 ± 28.81 | 147.50 ± 22.17 | 126.00 ± 27.02 |
References
- Rehman, S.U.; Choe, K.; Yoo, H.H. Review on a traditional herbal medicine, Eurycoma longifolia Jack (Tongkat Ali): Its traditional uses, chemistry, evidence-based pharmacology and toxicology. Molecules 2016, 21, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotirum, S.; Ismail, S.B.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Efficacy of Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia) on erectile function improvement: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henkel, R.R.; Wang, R.; Bassett, S.H.; Chen, T.; Liu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Tambi, M.I. Tongkat Ali as a potential herbal supplement for physically active male and female seniors—A pilot study. Phytother. Res. PTR 2014, 28, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.C.; Erasmus, N.; Henkel, R.R. In vivo effects of Eurycoma longifolia Jack (Tongkat Ali) extract on reproductive functions in the rat. Andrologia 2014, 46, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Razak, H.S.; Shuid, A.N.; Naina Mohamed, I. Combined effects of Eurycoma longifolia and testosterone on androgen-deficient osteoporosis in a male rat model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 872406. [Google Scholar]
- Shuid, A.N.; El-arabi, E.; Effendy, N.M.; Abdul Razak, H.M.; Muhammad, N.; Mohamed, N.; Soelaiman, I.M. Eurycoma longifolia upregulates osteoprotegerin gene expression in androgen-deficient osteoporosis rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, B.S.; Teh, C.H.; Yuen, K.H.; Chan, K.L. Physico-chemical effects of the major quassinoids in a standardized Eurycoma longifolia extract (Fr 2) on the bioavailability and pharmacokinetic properties, and their implications for oral antimalarial activity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Abdul Razak, M.R.; Abdullah, N.R.; Ismail, Z.; Ismail, Z. Effect of Eurycoma longifolia extract on the glutathione level in Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes in vitro. Trop. Biomed. 2005, 22, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Satayavivad, J.; Noppamas, S.; Aimon, S.; Yodhathai, T. Toxicological and antimalaria activity of Eurycoma longifolia Jack extracts in mice. Thai. J. Phytopharm. 1998, 5, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, Y.K.; Bommu, P.; Ming, Y.K. Acute, subacute and subchronic 90-days toxicity of Eurycoma longifolia aqueous extract (Physta) in Wistar rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Shuid, A.N.; Siang, L.K.; Chin, T.G.; Muhammad, N.; Mohamed, N.; Soelaiman, I.N. Acute and subacute toxicity studies of Eurycoma longifolia in male rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 7, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.H.; Liao, J.W.; Liao, P.L.; Huang, W.K.; Tse, L.S.; Lin, C.H.; Kang, J.J.; Cheng, Y.W. Evaluation of acute 13-week subchronic toxicity and genotoxicity of the powdered root of Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia jack). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 102987. [Google Scholar]
- Lenssen, K.G.M.; Bast, A.; de Boer, A. International perspectives on substantiating the efficacy of herbal dietary supplements and herbal medicines through evidence on traditional use. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Health. Food Act; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 1983.
- Ministry of Health. Food Regulation; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 1985.
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Safety Monitoring of Herbal Medicines in Pharmacovigilance Systems; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Tawab, M. Do we need plant food supplements? A critical examination of quality, safety, efficacy, and necessity for a new regulatory framework. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khedkar, S.; Carraresi, L.; Bröring, S. Food or pharmaceuticals? Consumers’ perception of health-related borderline products. PharmaNutrition 2017, 5, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, A.; van Hunsel, F.; Bast, A. Adverse food-drug interactions. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2015, 73, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintus, C.; Schweim, H.G. European regulation of herbal medicinal products on the border area to the food sector. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.A.; Cunningham, D.G.; Marles, R.J. Assessment of herbal medicinal products: Challenges, and opportunities to increase the knowledge base for safety assessment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 243, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals No. 420: Acute Oral Toxicity—Fixed Dose Procedure; OECD: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals No. 407: Repeated Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents; OECD: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals No. 452: Chronic Toxcity Studies; OECD: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health. Principles and Guide to Ethical Use of Laboratory Animals; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2002.
- Damsch, S.; Eichenbaum, G.; Tonelli, A.; Lammens, L.; Van den Bulck, K.; Feyen, B.; Vandenberghe, J.; Megens, A.; Knight, E.; Kelley, M. Gavage-related reflux in rats: Identification, pathogenesis, and toxicological implications. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clifton, P.G. Eating. In The Behaviour of the Laboratory Rat. A Handbook with Tests; Whishaw, I.Q., Kolb, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, N.E. Drinking. In The Behaviour of the Laboratory Rat. A Handbook with Tests; Whishaw, I.Q., Kolb, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Nolen, G.A. The effect of brewed and instant coffee on reproduction and teratogenesis in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1981, 58, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob Filho, W.; Lima, C.C.; Paunksnis, M.R.R.; Silva, A.A.; Perilhão, M.S.; Caldeira, M.; Bocalini, D.; de Souza, R.R. Reference database of hematological parameters for growing and aging rats. Aging Male 2018, 21, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Su, G.; Liu, K.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, M.; Xie, H. Sex-specific reference intervals of hematologic and biochemical analytes in Sprague-Dawley rats using the nonparametric rank percentile method. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lillie, L.E.; Temple, N.J.; Florence, L.Z. Reference values for young normal Sprague-Dawley rats: Weight gain, hematology and clinical chemistry. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1996, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petterino, C.; Argentino-Storino, A. Clinical chemistry and haematology historical data in control Sprague-Dawley rats from pre-clinical toxicity studies. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 57, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, O. Characteristics of rat platelets and relative contributions of platelets and blood coagulation to haemostasis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B.; Bryś, M. Effects of coffee, energy drinks and their components on hemostasis: The hypothetical mechanisms of their action. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 127, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwatta, S.L.; Gunatilake, M.; Baumans, V.; Seneviratne, M.D.; Dissanayaka, M.; Batagoda, S.S.; Udagedara, A.H.; Walpola, P.B. Reference values for selected hematological, biochemical and physiological parameters of Sprague-Dawley rats at the animal house, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2018, 1, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riza, M.; Andina Putri, A. The comparison effect of energy drinks and coffee on creatinin level in rats. Int. J. Hum. Health Sci. 2019, 3, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curti, V.; Verri, M.; Baldi, A.; Dacrema, M.; Masiello, I.; Dossena, M.; Daglia, M. In vivo modulatory effect of coffee (Coffea canephora var. Robusta) on the expression levels of murine microRNA-124-3p associated with antioxidant defenses. eFood 2020, 1, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolb, H.; Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Health effects of coffee: Mechanism unraveled? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Lu, F.B.; Hu, Y.B.; Xu, L.M.; Zheng, M.H.; Hu, E.D. A systematic review and a dose-response meta-analysis of coffee dose and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2552–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, T.O.; Melka, D.S.; Menon, M.; Labisso, W.L.; Habte, M.L. Investigation of the effect of coffee on body weight, serum glucose, uric acid and lipid profile levels in male albino Wistar rats feeding on high-fructose diet. Lab. Anim. Res. 2019, 35, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, G.; Mirshekar, M.A.; Amirpour, M.; Montazerifar, F.; Miri, S.; Shourestani, S. Sub-chronic administration of brewed coffee on rat behavior and cognition and oxidative stress Alzheimer’s disease model. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2019, 28, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, R.; Ogiso, T.; Imaida, K.; Shirai, T.; Ito, N. Analysis of the potential carcinogenicity of coffee and its related compounds in a medium-term liver bioassay of rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; George, O.; Kimbrough, A. Chronic voluntary caffeine intake in male Wistar rats reveals individual differences in addiction-like behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 191, 172880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, D.; Welsh, B.T.; Henderson, R.; Brorby, G.P.; Britt, J.; Myers, E.; Goldberger, J.; Lieberman, H.R.; O’Brien, C.; Peck, J.; et al. Systematic review of the potential adverse effects of caffeine consumption in healthy adults, pregnant women, adolescents, and children. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 585–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, R.H. The acute lethal dose 50 (LD50) of caffeine in albino rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2016, 80, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, N.; Samiulla, D.S.; Teh, B.P.; Zainol, M.; Zolkifli, N.A.; Muhammad, A.; Matom, E.; Zulkapli, A.; Abdullah, N.R.; Ismail, Z.; et al. Bioavailability of eurycomanone in its pure form and in a standardised Eurycoma longifolia water extract. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, B.S.; Ng, B.H.; Choy, W.P.; Yuen, K.H.; Chan, K.L. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetic studies of eurycomanone from Eurycoma longifolia. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, M.; Das, S.; Deborah, S.; Latt, S.; Soe, T. Coffee modify pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen. EC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 7, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A.W.; Wang, T.; Dixon, D. Chapter 13—Toxicologic testing methods. In Loomis’s Essentials of Toxicology, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 189–222. [Google Scholar]



| Sex | Dosage (g/kg BW) | WBC (10 3/µL) | RBC (10 6/µL) | HGB (g/dL) | HCT (%) | MCHC (g/dL) | PLT (10 5/µL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 0.00 | 5.18 ± 2.01 | 8.05 ± 0.48 | 16.40 ± 0.82 | 49.10 ± 2.53 | 33.40 ± 0.39 | 11.17 ± 1.97 |
| 0.14 | 4.06 ± 2.52 | 8.44 ± 0.31 | 16.70 ± 0.74 | 50.74 ± 2.40 | 32.92 ± 0.40 | 10.64 ± 0.90 | |
| 0.29 | 5.40 ± 1.66 | 8.09 ± 0.55 | 16.34 ± 0.84 | 48.62 ± 2.92 | 33.64 ± 0.53 | 11.77 ± 1.57 | |
| 1.00 | 4.22 ± 1.43 | 8.03 ± 0.63 | 16.36 ± 0.82 | 48.22 ± 2.91 | 33.94 ± 0.48 | 11.48 ± 1.04 | |
| Female | 0.00 | 6.52 ± 3.29 | 6.92 ± 0.19 | 14.42 ± 0.54 | 40.46 ± 1.42 | 35.64 ± 0.46 | 10.82 ± 0.91 |
| 0.14 | 4.66 ± 2.84 | 6.63 ± 0.79 | 13.50 ± 1.90 | 38.56 ± 5.04 | 34.98 ± 0.87 | 10.21 ± 3.30 | |
| 0.29 | 5.30 ± 1.48 | 6.76 ± 0.36 | 14.13 ± 0.34 | 39.38 ± 1.79 | 35.90 ± 1.23 | 9.16 ± 4.68 | |
| 1.00 | 3.00 ± 1.78 | 6.88 ± 0.57 | 14.34 ± 0.72 | 40.38 ± 2.17 | 35.50 ± 0.32 | 12.51 ± 1.44 |
| Sex | Dosage (g/kg BW) | RBC (10 6/µL) | HGB (g/dL) | HCT (%) | PLT (10 5/µL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 0.00 (n = 19) | 8.41 ± 0.57 | 72.99 ±3.76 | 44.92 ± 2.96 | 6.87 ± 1.42 |
| 0.14 (n = 20) | 8.03 ± 0.92 | 71.99 ± 8.0 | 43.39 ± 5.27 | 5.51 ± 1.12 * | |
| 0.29 (n = 20) | 8.10 ± 0.39 | 73.25 ± 3.03 | 44.78 ± 2.07 | 5.57 ± 0.95 * | |
| 1.00 (n = 19) | 8.06 ± 0.52 | 72.99 ± 3.49 | 44.66 ± 3.26 | 5.35 ± 0.74 * | |
| Female | 0.00 (n = 19) | 7.11 ± 0.77 | 65.02 ± 6.58 | 39.38 ± 4.25 | 7.81 ± 1.39 |
| 0.14 (n = 19) | 6.92 ± 1.43 | 63.49 ± 14.44 | 37.81 ± 7.81 | 8.70 ± 2.44 | |
| 0.29 (n = 18) | 7.21 ± 0.35 | 66.68 ± 2.45 | 39.76 ± 1.65 | 7.88 ± 1.06 | |
| 1.00 (n = 19) | 7.67 ± 0.61 | 71.41 ± 5.46* | 42.79 ± 4.06 | 7.38 ± 0.93 |
| Parameters | Male Dosage (g/kg BW) | Female Dosage (g/kg BW) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (n = 19) | 0.14 (n = 20) | 0.29 (n = 20) | 1.00 (n = 19) | 0 (n = 19) | 0.14 (n = 19) | 0.29 (n = 18) | 1.00 (n = 19) | |
| Liver Function Profile | ||||||||
| Total protein (g/L) | 49.66 ± 12.42 | 43.80 ± 17.07 | 60.49 ± 10.67 * | 56.97 ± 7.49 | 63.42 ± 16.47 | 58.49 ± 5.64 | 66.94 ± 8.18 | 72.30 ± 6.11 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 34.19 ± 10.72 | 24.97 ± 9.61 * | 37.25 ± 7.25 | 32.45 ±5.08 | 39.72 ± 10.60 | 43.39 ± 5.17 | 53.53 ± 5.94 * | 40.46 ± 2.57 |
| Enzymes | ||||||||
| ALP (U/L) | 123.32 ± 115.61 | 46.18 ± 26.25 * | 118.39 ± 42.71 | 88.95 ± 38.77 | 25.79 ± 32.79 | 24.34 ± 43.78 | 33.07 ± 22.50 | 18.44 ± 42.67 |
| ALT (U/L) | 63.69 ± 31.90 | 34.03 ± 21.37 * | 65.75 ± 25.36 | 50.49 ± 14.19 | 54.29 ± 15.50 | 50.29 ± 10.10 | 68.96 ± 17.57 * | 57.94 ± 12.06 |
| AST (U/L) | 155.73 ± 54.04 | 137.55 ± 68.31 | 194.22 ± 54.69 | 171.56 ± 36.13 | 195.82 ± 75.82 | 205.78 ± 59.05 | 270.29 ± 50.25* | 229.72 ± 47.78 |
| LDH (U/L) | 1993.46 ± 904.07 | 1671.46 ± 772.76 | 1430 ± 726.58 | 1690 ± 819.68 | 2053.36 ± 793.69 | 2363.14 ± 721.41 | 2367.04 ± 763.32 | 2615.74 ± 491.17 * |
| CK (U/L) | 408.07 ± 253.91 | 392.64 ± 174.86 | 562.87 ± 342.05 | 701.64 ± 292.43 * | 653.74 ± 422.37 | 537.59 ± 372.26 | 682.9 ± 277.82 | 756.82 ± 443.50 |
| Renal Profile | ||||||||
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 47.08 ± 13.48 | 44.27 ± 22.79 | 61.77 ± 11.69 * | 54.83 ± 6.76 | 55.31 ± 12.92 | 56.18 ± 6.51 | 66.91 ± 8.90 * | 59.86 ± 6.85 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.88 ± 1.33 | 5.02 ± 2.18 | 7.11 ± 1.12 * | 7.00 ± 1.15 | 7.02 ± 1.61 | 7.10 ± 0.81 | 8.65 ± 1.91 * | 8.17 ± 0.87 |
| Uric Acid (µmol/L) | 283.07 ± 140.43 | 247.44 ± 137.08 | 286.70 ± 129.19 | 334.95 ± 131.69 | 379.23 ± 125.43 | 328.01 ± 142.28 | 449.77 ± 161.52 | 382.73 ± 142.01 |
| Lipid Profile | ||||||||
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.59 ± 0.52 | 3.73 ± 11.12 | 1.52 ± 0.36 | 1.2 ± 0.40 | 1.72 ± 0.50 | 1.94 ± 0.46 | 2.28 ± 0.44 * | 2.21 ± 0.31 * |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.29 ± 0.64 | 0.58 ± 0.37* | 1.06 ± 0.59 | 0.92 ± 0.36 | 0.89 ± 0.55 | 0.69 ± 0.45 | 0.92 ± 0.55 | 0.46 ± 0.32 * |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.33 ± 4.38 | 3.83 ± 2.88 | 6.12 ± 4.22 | 6.81 ± 5.45 | 5.27 ± 4.59 | 3.34 ± 3.43 | 5.29 ± 5.98 | 5.60 ± 4.24 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 1.91 ± 0.62 | 1.60 ± 0.60 | 2.12 ± 0.39 | 1.64 ± 0.25 | 1.93 ± 0.57 | 2.22 ± 0.24 | 2.62 ± 0.32 * | 2.36 ± 0.29 * |
| Parameters | Male Dosage (g/kg BW) | Female Dosage (g/kg BW) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (n = 5) | 0.14 (n = 5) | 0.29 (n = 5) | 1.00 (n = 5) | 0 (n = 5) | 0.14 (n = 5) | 0.29 (n = 4) | 1.00 (n = 5) | |
| BW a | 295.00 ± 11.73 | 285.00 ± 17.68 | 292.00 ± 27.06 | 314.00 ± 24.08 | 200.00 ± 16.20 | 215.00 ± 21.21 | 203.75 ± 24.62 | 199.00 ± 24.08 |
| Lung b | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.43 ± 0.06 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 0.57 ± 0.11 | 0.51 ± 0.08 | 0.57 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.12 |
| Heart b | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.05 |
| Spleen b | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.02 * | 0.19 ± 0.01 * | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| Stomach b | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 0.46 ± 0.04 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 0.64 ± 0.03 | 0.56 ± 0.05 * | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.65 ± 0.05 |
| Intestinal tract b | 0.49 ± 0.08 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 0.48 ± 0.20 | 0.65 ± 0.21 | 0.57 ± 0.10 | 0.69 ± 0.10 |
| Liver b | 3.09 ± 0.24 | 3.21 ± 0.41 | 2.91 ± 0.21 | 2.89 ± 0.15 | 3.23 ± 0.14 | 3.29 ± 0.36 | 3.25 ± 0.30 | 3.21 ± 0.46 |
| Kidney R b | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.02 |
| Kidney L b | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.02 |
| Adrenal R b | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Adrenal L b | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| Testes R b | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | ||||
| Testes L b | 0.50 ± 0.09 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.04 | 0.48 ± 0.04 | ||||
| Ovary R b | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | ||||
| Ovary L b | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | ||||
| Parameters | Male Dose (g/kg BW) | Female Dosage (g/kg BW) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (n = 19) | 0.14 (n = 20) | 0.29 (n = 20) | 1.00 (n = 19) | 0 (n = 19) | 0.14 (n = 19) | 0.29 (n = 18) | 1.00 (n = 19) | |
| BW a | 578.95 ± 57.82 | 568.00 ± 50.22 | 557.75 ± 51.75 | 543.42 ± 100.90 | 286.32 ± 41.36 | 291.84 ± 30.70 | 281.94 ± 19.56 | 314.17 ± 26.91 |
| Lung b | 0.36 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.11 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 0.39 ± 0.15 | 0.53 ± 0.12 | 0.51 ± 0.12 | 0.57 ± 0.08 | 0.48 ± 0.14 |
| Heart b | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.03 |
| Spleen b | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.17 ± 0.02 |
| Stomach b | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.04 | 0.44 + 0.05 | 0.49 ± 0.17 | 0.70 ± 0.09 | 0.71 ± 0.11 | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.09 |
| Intestinal tract b | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 0.36 + 0.08 | 0.41 ± 0.10 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 0.49 ± 0.15 | 0.51 ± 0.10 | 0.50 ± 0.12 |
| Liver b | 2.77 ± 0.39 | 2.63 ± 0.29 | 2.80 ± 0.28 | 2.70 ± 0.29 | 3.01 ± 0.26 | 2.94 ± 0.25 | 3.01 ± 0.28 | 2.85 ± 0.24 |
| Kidney R b | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.02 |
| Kidney L b | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.03 |
| Adrenal R b | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.009 ± 0.005 | 0.014 ± 0.015 | 0.011 ± 0.007 | 0.015 ± 0.022 |
| Adrenal L b | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.010 ± 0.005 | 0.011 ± 0.006 | 0.011 ± 0.005 | 0.011 ± 0.004 |
| Testes R b | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.07 | ||||
| Testes L b | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | ||||
| Ovary R b | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | ||||
| Ovary L b | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, N.; Teh, B.P.; Halim, S.Z.; Zolkifli, N.A.; Ramli, N.; Muhammad, H. Eurycoma longifolia—Infused Coffee—An Oral Toxicity Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103125
Ahmad N, Teh BP, Halim SZ, Zolkifli NA, Ramli N, Muhammad H. Eurycoma longifolia—Infused Coffee—An Oral Toxicity Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103125
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Norzahirah, Bee Ping Teh, Siti Zaleha Halim, Nor Azlina Zolkifli, Nurulfariza Ramli, and Hussin Muhammad. 2020. "Eurycoma longifolia—Infused Coffee—An Oral Toxicity Study" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103125
APA StyleAhmad, N., Teh, B. P., Halim, S. Z., Zolkifli, N. A., Ramli, N., & Muhammad, H. (2020). Eurycoma longifolia—Infused Coffee—An Oral Toxicity Study. Nutrients, 12(10), 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103125