Transport of a Peptide from Bovine αs1-Casein across Models of the Intestinal and Blood–Brain Barriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Purification of Milk Peptides
2.3. Synthetic Peptides
2.4. In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.5. Cell Cultures
2.6. Transfer Studies
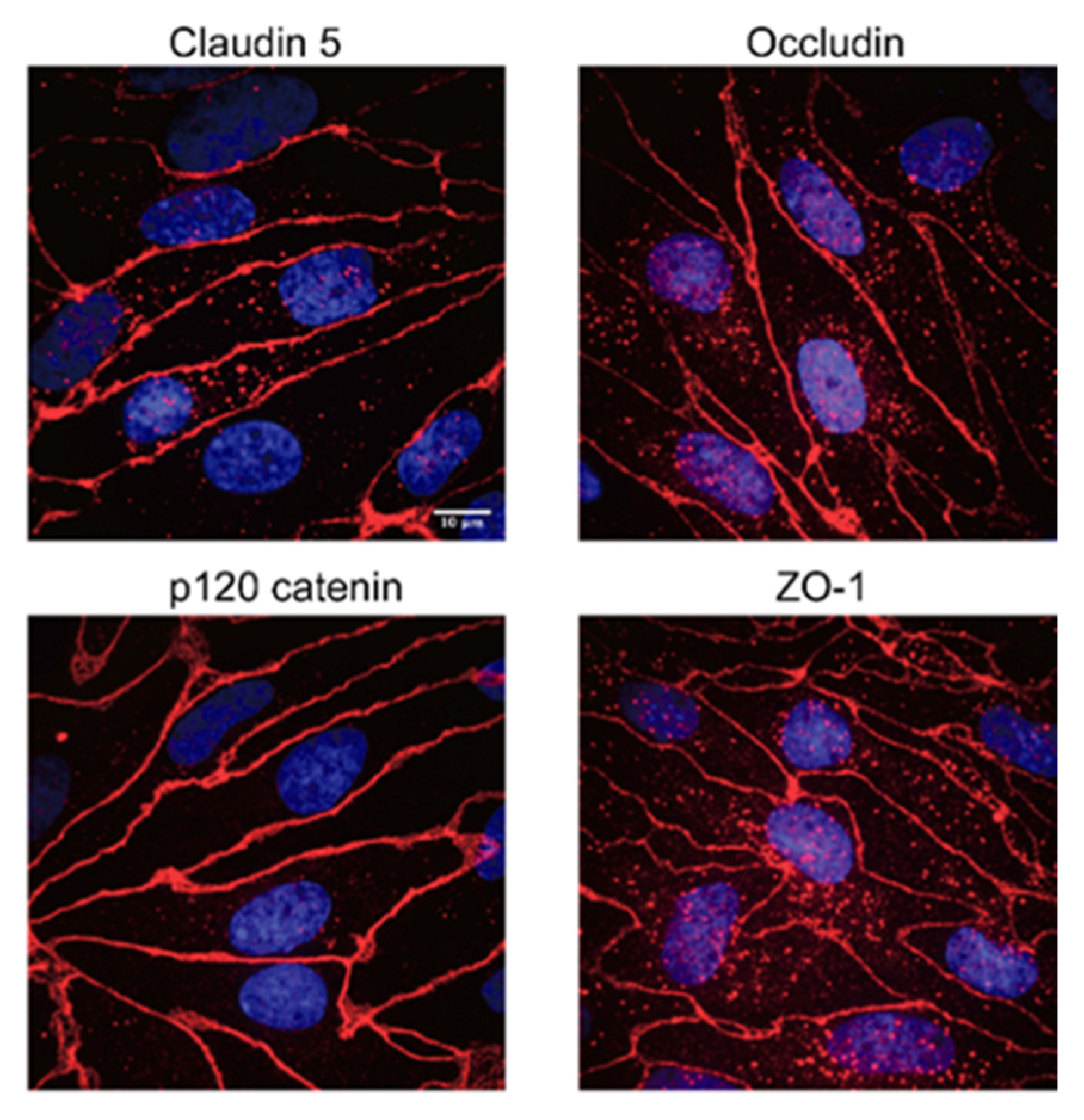
2.7. Western Blotting, Immunocytochemistry and Confocal Microscopy
2.8. Mass Spectrometry
2.9. Statistics
2.10. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
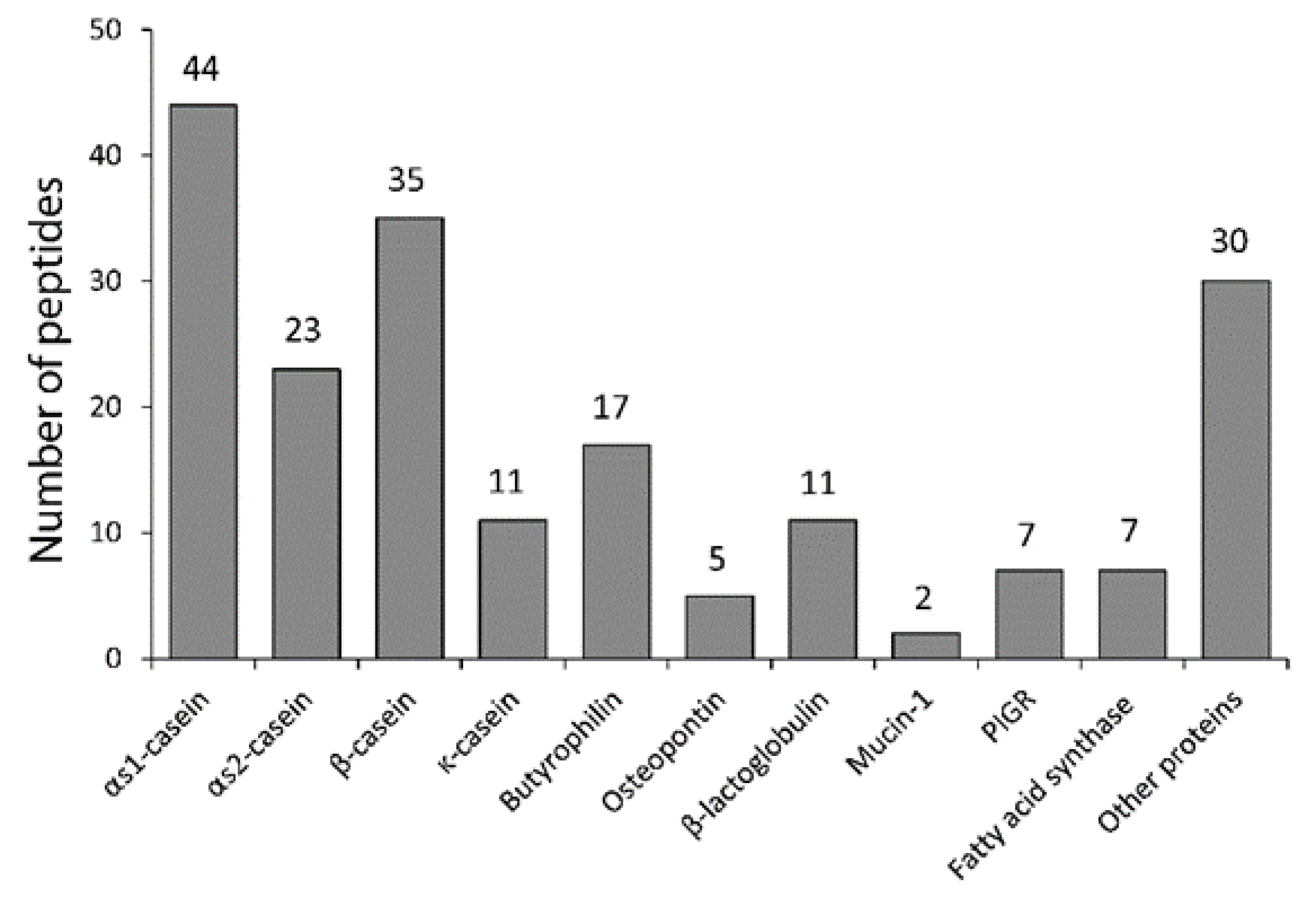
3.1. Purification of Milk Peptides
3.2. Transfer of Milk Peptides Across Caco-2 and PBEC Monolayers
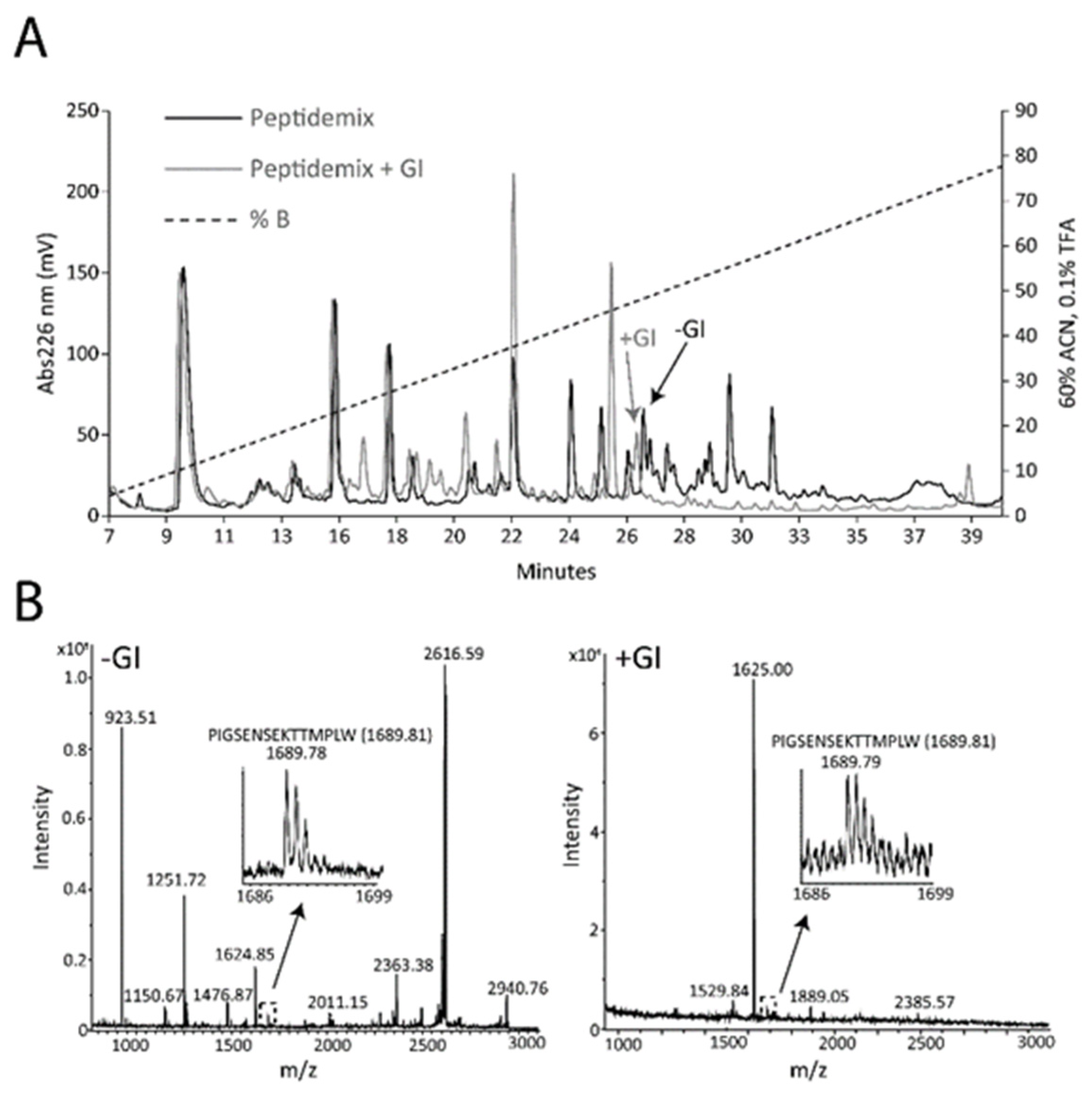
3.3. Digestion of the PIGSENSEKTTMPLW Peptide
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagpal, R.; Behare, P.; Rana, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Arora, S.; Morotta, F.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins and their health beneficial potentials: An update. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins—Mechanisms of action. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, H. Milk-derived bioactive peptides: From science to applications. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, F.; Fedorova, M.; Ebner, J.; Hoffmann, R.; Pischetsrieder, M. Analysis of the endogenous peptide profile of milk: Identification of 248 mainly casein-derived peptides. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5447–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picariello, G.; Ferranti, P.; Fierro, O.; Mamone, G.; Caira, S.; Di Luccia, A.; Monica, S.; Addeo, F. Peptides surviving the simulated gastrointestinal digestion of milk proteins: Biological and toxicological implications. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P.; Palm, K.; Luthman, K. Caco-2 monolayers in experimental and theoretical predictions of drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Pan, D. Production and transepithelial transportation of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from whey protein hydrolyzed by immobilized Lactobacillus helveticus proteinase. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Su, M.; Jiang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pan, D. Transepithelial transport route and liposome encapsulation of milk-derived ACE-inhibitory peptide Arg-Leu-Ser-Phe-Asn-Pro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5544–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, H.E.; Wichers, H.J.; Tomassen, M.M.M.; Boeren, S.; De Jong, N.W.; Hettinga, K.A. Peptide release after simulated infant in vitro digestion of dry heated cow’s milk protein and transport of potentially immunoreactive peptides across the Caco-2 cell monolayer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz-Szłapka, E.; Jarmołowska, B.; Krawczuk, S.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Bielikowicz, K. Transport of bovine milk-derived opioid peptides across a Caco-2 monolayer. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Miclo, L.; Balandras, F.; Dary, A.; Soligot, C.; Roux, Y.L. Transport across Caco-2 cell monolayer and sensitivity to hydrolysis of two anxiolytic peptides from αs1-Casein, α-Casozepine, and αs1-Casein-(f91–97): Effect of bile salts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11956–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regazzo, D.; Mollé, D.; Gabai, G.; Tomé, D.; Dupont, D.; Leonil, J.; Boutrou, R. The (193–209) 17-residues peptide of bovine β-casein is transported through Caco-2 monolayer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabance, B.; Jollès, P.; Izquierdo, C.; Mazoyer, E.; Francoual, C.; Drouet, L.; Fiat, A.-M. Characterization of an antithrombotic peptide from α-casein in newborn plasma after milk ingestion. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 73, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chabance, B.; Marteau, P.; Rambaud, J.C.; Migliore-Samour, D.; Boynard, M.; Perrotin, P.; Guillet, R.; Jollès, P.; Fiat, A.M. Casein peptide release and passage to the blood in humans during digestion of milk or yogurt. Biochimie 1998, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.; Karlsen, N.J.; Jørgensen, S.D.S.; Jacobsen, L.N.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Petersen, S.V.; Müllertz, A.; Sørensen, E.S. Milk osteopontin retains integrin-binding activity after in vitro gastrointestinal transit. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rittling, S.R.; Wejse, P.L.; Yagiz, K.; Warot, G.A.; Hui, T. Suppression of tumour growth by orally administered osteopontin is accompanied by alterations in tumour blood vessels. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, R.; Lönnerdal, B. Osteopontin in human milk and infant formula affects infant plasma osteopontin concentrations. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Ohtsuki, S.; Uchida, Y.; Terasaki, T. Quantitative determination of luminal and abluminal membrane distributions of transporters in Porcine Brain Capillaries by Plasma Membrane Fractionation and Quantitative Targeted Proteomics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.S.E.; Siupka, P.; Georgian, A.; Preston, J.E.; Tóth, A.E.; Yusof, S.R.; Abbott, N.J.; Nielsen, M.S. Improved method for the establishment of an in vitro blood-brain barrier model based on porcine brain endothelial cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, H.-J. Monocultures of primary porcine brain capillary endothelial cells: Still a functional in vitro model for the blood-brain-barrier. J. Control. Release 2018, 285, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenger, D.; Cudennec, B.; Kouach, M.; Touche, V.; Landry, C.; Lesage, J.; Gosselet, F.; Lestavel, S.; Goossens, J.-F.; Dhulster, P.; et al. Food-derived hemorphins cross intestinal and blood-brain barriers in vitro. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.-J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Mogi, M.; Tsukuda, K.; Yamada, A.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F.; Iwanami, J.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Horiuchi, M. Administration of bovine casein-derived peptide prevents cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease model mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, R.; Prell, C.; Lönnerdal, B. Milk osteopontin promotes brain development by up-regulating osteopontin in the brain in early life. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picariello, G.; Iacomino, G.; Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P.; Fierro, O.; Gianfrani, C.; Di Luccia, A.; Addeo, F. Transport across Caco-2 monolayers of peptides arising from in vitro digestion of bovine milk proteins. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Mandalari, G.; Molle, D.; Jardin, J.; Léonil, J.; Faulks, R.M.; Wickham, M.S.J.; Mills, E.N.C.; Mackie, A.R. Comparative resistance of food proteins to adult and infant in vitro digestion models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, E.S.; Højrup, P.; Petersen, T.E. Posttranslational modifications of bovine osteopontin: Identification of twenty-eight phosphorylation and three O-glycosylation sites. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappsilber, J.; Mann, M.; Ishihama, Y. Protocol for micro-purification, enrichment, pre-fractionation and storage of peptides for proteomics using StageTips. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubatsch, I.; Ragnarsson, E.G.E.; Artursson, P. Determination of drug permeability and prediction of drug absorption in Caco-2 monolayers. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, L.B.; Burkhart, A.; Moos, T. A triple culture model of the blood-brain barrier using porcine brain endothelial cells, astrocytes and pericytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, B.; Nielsen, M.S.; Haselmann, K.F.; Petersen, T.E.; Sørensen, E.S. Post-translationally modified residues of native human osteopontin are located in clusters: Identification of 36 phosphorylation and five O-glycosylation sites and their biological implications. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picariello, G.; Miralles, B.; Mamone, G.; Sánchez-Rivera, L.; Recio, I.; Addeo, F.; Ferranti, P. Role of intestinal brush border peptidases in the simulated digestion of milk proteins. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalabasmaz, S.; Dittrich, D.; Kellner, I.; Drewello, T.; Pischetsrieder, M. Identification of peptides reflecting the storage of UHT milk by MALDI-TOF-MS peptide profiling. J. Proteom. 2019, 207, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, G.E.; Chang, O.K.; Jo, S.-M.; Han, G.-S.; Park, B.-Y.; Ham, J.-S.; Jeong, S.-G. Identification of antihypertensive peptides derived from low molecular weight casein hydrolysates generated during fermentation by bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Guo, T.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.X.; Zhang, S. Isolation and identification of novel casein-derived bioactive peptides and potential functions in fermented casein with Lactobacillus helveticus. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlanto-Leppälä, A.; Rokka, T.; Korhonen, H. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from bovine milk proteins. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Stanton, C.; Slattery, H.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P. Casein fermentate of lactobacillus animalis DPC6134 contains a range of novel propeptide angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. AEM 2007, 73, 4658–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farag, E.; Sessler, D.I.; Ebrahim, Z.; Kurz, A.; Morgan, J.; Ahuja, S.; Maheshwari, K.; John Doyle, D. The renin angiotensin system and the brain: New developments. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Hilaire, Z.D.; Messaoudi, M.; Desor, D.; Kobayashi, T. Effects of a bovine alpha S1-Casein Tryptic Hydrolysate (CTH) on sleep disorder in Japanese general population. Open Sleep J. 2009, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Peña, I.J.I.; Kim, H.J.; de la Peña, J.B.; Kim, M.; Botanas, C.J.; You, K.Y.; Woo, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, J.-C.; Kim, K.-M.; et al. A tryptic hydrolysate from bovine milk αs1-casein enhances pentobarbital-induced sleep in mice via the GABAA receptor. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 313, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Protein | Peptide | Calculated | Measured | Expect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| αS1-casein | PIGSENSEKTTMPLW (Mox) | 1704.7971 | 1704.7971 | 6.00 × 107 |
| PIGSENSEKTTMP (Mox) | 1405.6395 | 1405.6429 | 1.60 × 104 | |
| κ-casein | EVIESPPEINTVQVTSTAV | 2012.0314 | 2012.0378 | 1.90 × 104 |
| αS2-casein | KNTMEHVSSSEESIISQETY | 2314.0271 | 2314.0082 | 8.60 × 104 |
| KNTMEHVSSSEESIISQETY | 2298.0321 | 2298.0254 | 2.30 × 104 |
| Protein | Peptide | Calculated | Measured | Expect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| αS1-casein | PIGSENSEKTTMPLW (Mox) | 1704.8029 | 1704.7983 | 9.50 × 108 |
| PIGSENSEKTT | 1161.5513 | 1161.5549 | 3.70 × 103 | |
| PIGSENSEKTTMP (Mox) | 1405.6395 | 1405.6472 | 1.90 × 107 | |
| IGSENSEKTTMP (Mox) | 1308.5867 | 1308.5918 | 6.50 × 105 | |
| β-casein | EPVLGPVRGPFPIIV | 1588.9341 | 1588.9289 | 2.10 × 104 |
| PVLGPVRGPFPIIV | 1459.8915 | 1459.8866 | 5.20 × 106 | |
| PIGR | AAPAGAAIQS | 855.445 | 855.4435 | 1.90 × 103 |
| AAPAGAAIQSR | 1011.5461 | 1011.5526 | 4.40 × 104 |
| Monolayer | Peptide (Basolateral) | Calculated | Measured | Expect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco-2 | PIGSENSEKTTMP (Mox) | 1405.6395 | 1405.6444 | 7.60 × 107 |
| PIGSENSEKTT | 1161.5513 | 1161.555 | 6.80 × 107 | |
| PBEC | PIGSENSEKTTMP (Mox) | 1405.6395 | 1405.6397 | 6.70 × 106 |
| PIGSENSEKTT | 1161.5513 | 1161.5586 | 2.30 × 106 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christensen, B.; Toth, A.E.; Nielsen, S.S.E.; Scavenius, C.; Petersen, S.V.; Enghild, J.J.; Rasmussen, J.T.; Nielsen, M.S.; Sørensen, E.S. Transport of a Peptide from Bovine αs1-Casein across Models of the Intestinal and Blood–Brain Barriers. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103157
Christensen B, Toth AE, Nielsen SSE, Scavenius C, Petersen SV, Enghild JJ, Rasmussen JT, Nielsen MS, Sørensen ES. Transport of a Peptide from Bovine αs1-Casein across Models of the Intestinal and Blood–Brain Barriers. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103157
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristensen, Brian, Andrea E. Toth, Simone S. E. Nielsen, Carsten Scavenius, Steen V. Petersen, Jan J. Enghild, Jan T. Rasmussen, Morten S. Nielsen, and Esben S. Sørensen. 2020. "Transport of a Peptide from Bovine αs1-Casein across Models of the Intestinal and Blood–Brain Barriers" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103157
APA StyleChristensen, B., Toth, A. E., Nielsen, S. S. E., Scavenius, C., Petersen, S. V., Enghild, J. J., Rasmussen, J. T., Nielsen, M. S., & Sørensen, E. S. (2020). Transport of a Peptide from Bovine αs1-Casein across Models of the Intestinal and Blood–Brain Barriers. Nutrients, 12(10), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103157





