PROFAST: A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic among People with Prediabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Randomization and Blinding
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Data Collection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
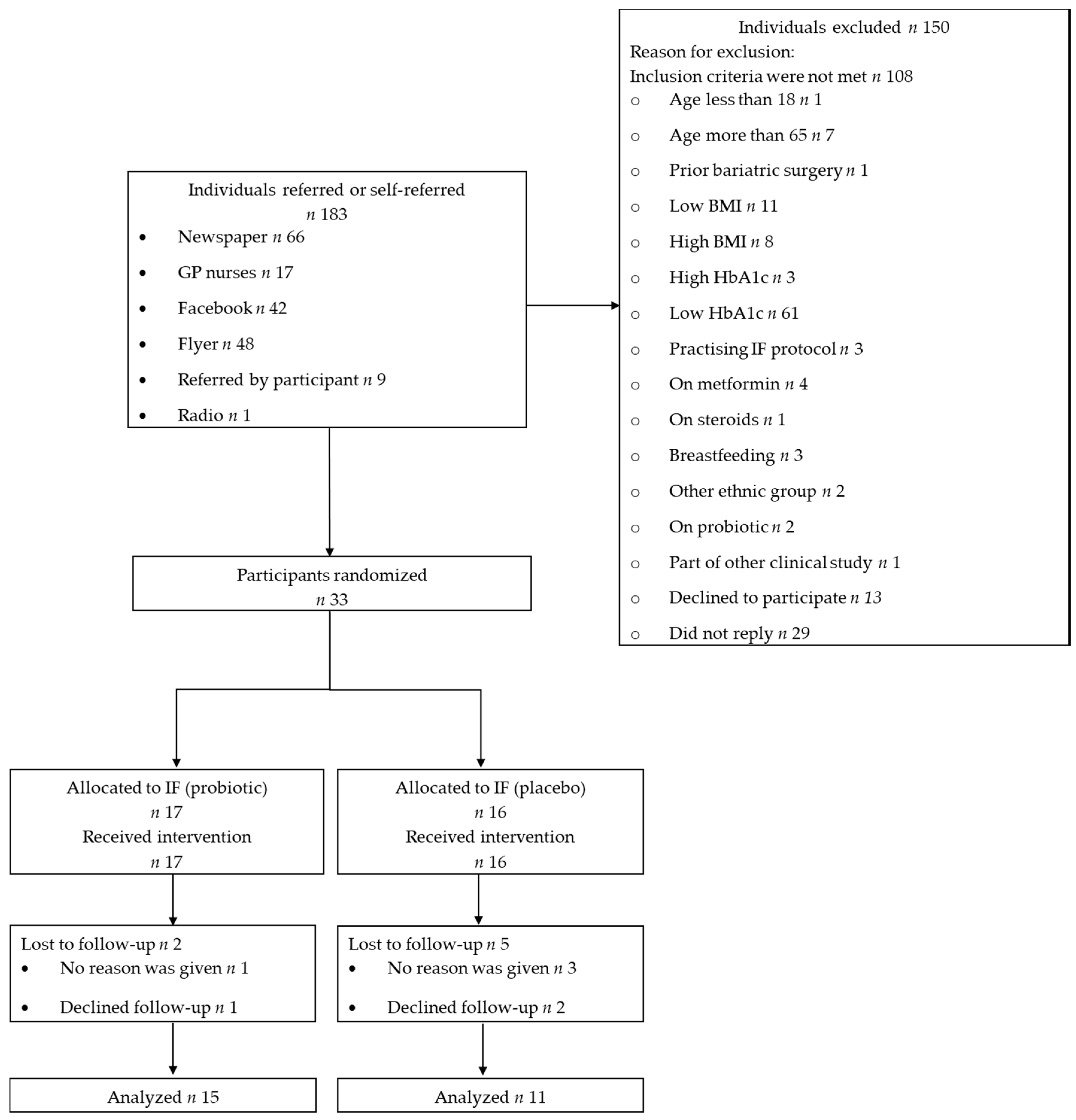
3.1. Recruitment
3.2. Baseline Data
3.3. Outcomes
3.3.1. Glucose and Biochemistry
3.3.2. Weight and Body Composition
3.3.3. Resting Energy Expenditure
3.3.4. Dietary Intake
3.3.5. Psychological Outcomes
3.3.6. Side Effects
3.3.7. Ancillary Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, J.; Sicree, R.; Zimmet, P. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppell, K.; Mann, J.; Williams, S.M.; Jo, E.; Drury, P.L.; Miller, J.C.; Parnell, W.R. Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes and prediabetes in New Zealand: Findings from the 2008/09 Adult Nutrition Survey. N. Z. Med. J. 2013, 126, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Khaw, K.-T.; Wareham, N.; Luben, R.; Bingham, S.; Oakes, S.; Welch, A.; Day, N. Glycated haemoglobin, diabetes, and mortality in men in Norfolk cohort of European Prospective Investigation of Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-Norfolk). BMJ 2001, 322, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabák, Á.G.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M. Prediabetes: A high-risk state for diabetes development. Lancet 2012, 379, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Zaghloul, H.; Chagoury, O.; Elhadad, S.; Ahmed, S.H.; El Khatib, N.; Amona, R.A.; El Nahas, K.; Suleiman, N.; Alnaama, A.; et al. Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on bodyweight and glycaemia in early type 2 diabetes (DIADEM-I): An open-label, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, M.E.J.; Leslie, W.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Brosnahan, N.; Thom, G.; McCombie, L.; Peters, C.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; et al. Durability of a primary care-led weight-management intervention for remission of type 2 diabetes: 2-year results of the DiRECT open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogelholm, M.; Larsen, T.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Macdonald, I.A.; Abete, I.; Boyadjieva, N.I.; Poppitt, S.D.; Schlicht, W.; Stratton, G.; Sundvall, J.; et al. PREVIEW: Prevention of Diabetes through Lifestyle Intervention and Population Studies in Europe and around the World. Design, Methods, and Baseline Participant Description of an Adult Cohort Enrolled into a Three-Year Randomised Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkley, A.J.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Greaves, C.J.; Russell, C.; Yates, T.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Diabetes Prevention in the Real World: Effectiveness of Pragmatic Lifestyle Interventions for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes and of the Impact of Adherence to Guideline Recommendations. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnosky, A.R.; Hoddy, K.K.; Unterman, T.G.; Varady, K.A. Intermittent fasting vs daily calorie restriction for type 2 diabetes prevention: A review of human findings. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, R.E.; Laughlin, G.A.; Lacroix, A.Z.; Hartman, S.J.; Natarajan, L.; Senger, C.M.; Martínez, M.E.; Villaseñor, A.; Sears, D.D.; Marinac, C.R.; et al. Intermittent Fasting and Human Metabolic Health. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, M.; Wright, C.; Pegington, M.; McMullan, D.; Mitchell, E.; Martin, B.; Cutler, R.G.; Evans, G.; Whiteside, S.; Maudsley, S.; et al. The effect of intermittent energy and carbohydrate restriction v. daily energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers in overweight women. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.; Clifton, P.M.; Keogh, J. The effects of intermittent compared to continuous energy restriction on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes; a pragmatic pilot trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2016, 122, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Varady, K.; Bhutani, S.; Klempel, M.C.; Kroeger, C.M.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Haus, J.M.; Hoddy, K.K.; Calvo, Y. Alternate day fasting for weight loss in normal weight and overweight subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Long-Term Persistence of Hormonal Adaptations to Weight Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K.; Moto, M.; Uchida, N.; He, F.; Hashizume, N. Anti-diabetic effects of lactic acid bacteria in normal and type 2 diabetic mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 51, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, F.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Chai, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-T.; Lu, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-S. Oral administration of Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-263 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high fructose-fed rats. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Bueno, A.A.; De Souza, R.G.M.; Mota, J.F. Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, K.; Barthow, C.A.; Murphy, R.; Abels, P.R.; Maude, R.M.; Stone, P.R.; Mitchell, E.A.; Stanley, T.V.; Purdie, G.L.; Kang, J.M.; et al. Early pregnancy probiotic supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 may reduce the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemi, Z.; Zare, Z.; Shakeri, H.; Sabihi, S.-S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effect of Multispecies Probiotic Supplements on Metabolic Profiles, hs-CRP, and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohtadi-Nia, J.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Niafar, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mofid, V. Probiotic yogurt improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutrients 2012, 28, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Darimont, C.; Drapeau, V.; Emady-Azar, S.; Lepage, M.; Rezzonico, E.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Berger, B.; Philippe, L.; Ammon-Zuffrey, C.; et al. Effect ofLactobacillus rhamnosusCGMCC1.3724 supplementation on weight loss and maintenance in obese men and women. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madjd, A.; A Taylor, M.; Mousavi, N.; Delavari, A.; Malekzadeh, R.; A Macdonald, I.; Farshchi, H.R. Comparison of the effect of daily consumption of probiotic compared with low-fat conventional yogurt on weight loss in healthy obese women following an energy-restricted diet: A randomized controlled trial1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 103, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafedtinov, K.K.; Plotnikova, O.A.; Alexeeva, R., I; Sentsova, T.B.; Songisepp, E.; Štšepetova, J.; Smidt, I.; Mikelsaar, M. Hypocaloric diet supplemented with probiotic cheese improves body mass index and blood pressure indices of obese hypertensive patients - a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, A.; Huang, M.; Dawkins, E. Using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) to Measure Perceived Hunger and Satiety at Various Mealtimes and Environments. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, A99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K.; Andrews, G. The SF-12 in the Australian population: Cross-validation of item selection. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2002, 26, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.G.; Zuellig, A.R.; Kachin, K.E.; Constantino, M.J.; Przeworski, A.; Erickson, T.; Cashman-McGrath, L. Preliminary reliability and validity of the generalized anxiety disorder questionnaire-IV: A revised self-report diagnostic measure of generalized anxiety disorder. Behav. Ther. 2002, 33, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.; Hatsukami, D.; Eckert, E.; Pyle, R. Eating disorders questionnaire. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1985, 21, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar]
- The New Zealand Institute for Plant & Food Research Limited and Ministry of Health. New Zealand Food Composition Database: New Zealand FOODfiles 2016 Version 01; The New Zealand Institute for Plant & Food Research Limited and Ministry of Health: Wellington, New Zealand, 2015; Available online: https://www.foodcomposition.co.nz/foodfiles/ (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Slykerman, R.; Hood, F.; Wickens, K.; Thompson, J.; Barthow, C.; Murphy, R.; Kang, J.; Rowden, J.; Stone, P.; Crane, J.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in Pregnancy on Postpartum Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: A Randomised Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. EBioMedicine 2017, 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.M.; Bruffaerts, R.; Simon, G.E.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.; De Girolamo, G.; Demyttenaere, K.; Gasquet, I.; Haro, J.M.; Karam, E.; et al. Obesity and mental disorders in the general population: Results from the world mental health surveys. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummesson, A.; Nyman, E.; Knutsson, M.; Karpefors, M. Effect of weight reduction on glycated haemoglobin in weight loss trials in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, S.; Reeves, M.M.; Yeo, S.; Morrison, G.; Carey, D.; Capra, S.M. Effect of intensive dietetic interventions on weight and glycaemic control in overweight men with Type II diabetes: A randomised trial. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, C.; Marossy, A.; Griffiths, Z.; Adegboye, A. Evaluation of a type 2 diabetes prevention program using a commercial weight management provider for non-diabetic hyperglycemic patients referred by primary care in the UK. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashra, N.B.; Spong, R.; Carter, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Assessing the Effectiveness of Lifestyle Interventions for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Routine Practice; Public Health England: London, UK, 2015. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/733053/PHE_Evidence_Review_of_diabetes_prevention_programmes-_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- American Diabetes Association. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2019, 43, S32–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Luz, F.Q.; Hay, P.; Gibson, A.A.; Touyz, S.W.; Swinbourne, J.M.; Roekenes, J.A.; Sainsbury, A. Does severe dietary energy restriction increase binge eating in overweight or obese individuals? A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Clemow, L.; Pbert, L.; Ockene, I.S.; Ockene, J.K. Social Desirability Bias in Dietary Self-Report May Compromise the Validity of Dietary Intake Measures. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Shi, B. Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: The role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | IF (Placebo) | IF (Probiotic) | All Completers | Non-Completers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants | 11 | 15 | 26 | 7 |
| Age (years) | 54.1 ± 6.4 | 52.9 ± 8.7 | 53.4 ± 7.6 | 48 ± 8.8 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male n (%) | 2 (18) | 6 (40) | 8 (31) | 1 (14) |
| Female n (%) | 9 (82) | 9 (60) | 18 (69) | 6 (86) |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| NZ European n (%) | 6 (55) | 6 (40) | 12 (46) | 2 (29) |
| Māori n (%) | 1 (9) | 3 (20) | 4 (15) | 3 (43) |
| Pacific n (%) | 1 (9) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (14) |
| Indian n (%) | 3 (27) | 6 (40) | 9 (35) | 1 (14) |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 42.9 ± 2.6 | 43.1 ± 2.9 | 43.0 ± 2.7 | 45.4 ± 3.3 |
| Anthropometry | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 91.3 ± 13.9 | 98.6 ± 18.4 | 95.5 ± 16.8 | 100.5 ± 15.3 |
| Height (cm) | 164.7 ± 7.4 | 168.4 ± 11.7 | 166.8 ± 10.1 | 165.1 ± 11.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.6 ± 3.7 | 34.7 ± 4.9 | 34.2 ± 4.4 | 36.7 ± 2.4 |
| Waist (cm) | 111.1 ± 11.0 | 112.7 ± 16.3 | 112.0 ± 14.1 | 112.5 ± 10.0 |
| Hip (cm) | 116.3 ± 9.8 | 122 ± 13.1 | 119.6 ± 12.0 | 122.5 ± 7.5 |
| WHR | 0.96 ± 0.1 | 0.92 ± 0.1 | 0.94 ± 0.1 | 0.90 ± 0.10 |
| Neck (cm) | 39.1 ± 4.2 | 40.9 ± 3.8 | 40.1 ± 4.0 | 41.0 ± 4.0 |
| Variable | IF (Placebo) n = 11 | IF (Probiotic) n = 15 | p-Value 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 12 weeks | Baseline | 12 weeks | Time × group interaction | Time effect | |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 42.9 ± 2.6 | 40.9 ± 2.9 | 43.1 ± 2.9 | 41.1 ± 1.9 | 0.938 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 91.3 ± 13.9 | 86.7 ± 13.7 | 98.6 ± 18.4 | 93.7 ± 18.1 | 0.859 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.6 ± 3.7 | 31.9 ± 4.0 | 34.7 ± 4.9 | 33.0 ± 5.2 | 0.967 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 111.1 ± 11.0 | 107.5 ± 10.9 | 112.7 ± 16.7 | 106.5 ± 16.1 | 0.211 | <0.001 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 116.3 ± 9.8 | 115.5 ± 14.8 | 122.0 ± 13.1 | 117.9 ± 15.3 | 0.258 | 0.105 |
| WHR | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 0.94 ± 0.09 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | 0.90 ± 0.09 | 0.934 | 0.025 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | 39.1 ± 4.2 | 38.1 ± 3.4 | 40.9 ± 3.8 | 39.8 ± 3.8 | 0.971 | 0.048 |
| Total body fat (kg) (DXA) | 41.3 ± 9.1 | 37.9 ± 9.3 | 43.9 ± 12.3 | 40.3 ± 13.6 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
| Abdominal fat (kg) (DXA) | 4.2 ± 1.1 | 3.7 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 1.7 | 4.0 ± 1.8 | 0.692 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat (kg) (DXA) | 2.0 ± 0.81 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 1.18 | 1.8 ± 1.06 | 0.771 | <0.001 |
| Fat-free mass (kg) (DXA) | 50.8 ± 9.3 | 49.8 ± 9.6 | 55.1 ± 12.4 | 54.1 ± 12.4 | 0.992 | 0.005 |
| REE (kcal/day) | 1561.3 ± 162.9 | 1495.9 ± 193.8 | 1760.2 ± 422.3 | 1640.5 ± 317.0 | 0.393 | 0.007 |
| RQ | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 0.77 ± 0.06 | 0.79 ± 0.05 | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 0.368 | 0.057 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 5.99 ± 0.35 | 5.76 ± 0.43 | 6.19 ± 0.55 | 6.00 ± 0.82 | 0.862 | 0.087 |
| Fasting insulin (mU/L) | 17.4 ± 8.0 | 13.6 ± 7.4 | 17.0 ± 10.8 | 16.8 ± 10.5 | 0.309 | 0.247 |
| Fasting C-peptide (ng/mL) | 3.74 ± 0.61 | 3.36 ± 0.86 | 3.61 ± 1.28 | 3.65 ± 1.61 | 0.149 | 0.234 |
| AUC0-120 min glucose (mmol/L × h) | 20.9 ± 3.6 | 18.5 ± 3.7 | 19.8± 3.8 | 19.6 ± 3.7 | 0.056 | 0.020 |
| AUC0-120 min insulin (mU/L × h) | 255 ± 81 | 194 ± 71 | 258 ± 223 | 248 ± 207 | 0.225 | 0.097 |
| AUC0-120 min C-peptide (pmol/L × h) | 23.2 ± 3.6 | 22.2 ± 4.4 | 22.6 ± 10.5 | 21.6 ± 10.8 | 0.984 | 0.210 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | 0.374 | 0.222 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 0.984 | 0.167 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.332 | 0.312 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.7 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 3.6 ± 1.0 | 3.7 ± 1.3 | 0.218 | 0.394 |
| AST (U/L) | 30.4 ± 6.4 | 29.4 ± 9.4 | 27.7 ± 11.4 | 26.3 ± 7.7 | 0.953 | 0.632 |
| ALT (U/L) | 35.7 ± 17.9 | 24.7 ± 6.0 | 27.3 ± 12.6 | 30.0 ± 12.4 | 0.073 | 0.258 |
| Leptin (μg/mL) | 16.2 ± 11.9 | 12.5 ± 10.7 | 18.9 ± 10.8 | 15.8 ± 9.8 | 0.844 | 0.045 |
| TNF-α (ng/mL) | 3.6 ± 1.0 | 4.3 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 1.7 | 0.607 | 0.062 |
| IL-6 (ng/mL) | 2.4 ± 0.92 | 2.9 ± 0.94 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 0.131 | 0.264 |
| Measurement | IF (Placebo) n = 8 | IF (Probiotic) n = 11 | p Value 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 12 Weeks | Baseline | 12 Weeks | Time x Group Interaction | Time Effect | |
| Energy (kcal/d) including fasting days | 2222 ± 394 | 1693 ± 316 | 2374 ± 731 | 1778 ± 624 | 0.832 | 0.002 |
| Energy (kcal/kg/d) including fasting days | 25.0 ± 4.7 | 20.5 ± 4.4 | 24.9 ± 8.6 | 19.1 ± 4.4 | 0.713 | 0.008 |
| Energy (kcal/d) excluding fasting days | 2222 ± 394 | 1863 ± 383 | 2374 ± 731 | 2061 ± 866 | 0.891 | 0.058 |
| Energy (kcal/d) on fasting days | N/A | 755.4 ± 207.8 | N/A | 651.6 ± 147.7 | 0.206 | N/A |
| Protein (g/d) | 92.9 ± 24.1 | 77.0 ± 14.6 | 108.7 ± 43.1 | 87.8 ± 34.1 | 0.767 | 0.039 |
| Protein (g/kg/d) | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.672 | 0.079 |
| Protein (% TE) | 16.8 ± 2.2 | 18.9 ± 4.8 | 18.7 ± 4.1 | 20.4 ± 5.3 | 0.885 | 0.193 |
| Carbohydrate (g/d) | 219.5 ± 17.1 | 169.6 ± 62.8 | 226.1 ± 86.8 | 160.4 ± 81.6 | 0.696 | 0.010 |
| Carbohydrate (% TE) | 40.5 ± 9.6 | 38.0 ± 11 | 37.5 ± 5.7 | 35.8 ± 10.7 | 0.870 | 0.349 |
| Total fat (g/d) | 98.9 ± 34.6 | 70.7 ± 13.3 | 101.4 ± 35.5 | 77.5 ± 32.6 | 0.799 | 0.005 |
| Total fat (% TE) | 38.1 ± 9.4 | 37.5 ± 7.8 | 37.6 ± 4.8 | 38.2 ± 6.9 | 0.701 | 0.990 |
| Saturated fat (% TE) | 16.1 ± 4.3 | 14.1 ± 2.5 | 16.3 ± 2.4 | 14.5 ± 2.9 | 0.884 | 0.039 |
| Saturated fat (% total fat) | 47.5 ± 6.0 | 42.1 ± 6.3 | 49.4 ± 6.7 | 43.1 ± 4.9 | 0.766 | 0.002 |
| Monounsaturated fat (% total fat) | 37.0 ± 4.5 | 41.4 ± 5.0 | 36.1 ± 3.7 | 38.6 ± 4.5 | 0.474 | 0.016 |
| Polyunsaturated fat (% total fat) | 15.5 ± 7.1 | 16.5 ± 4.0 | 14.5 ± 5.4 | 18.3 ± 6.3 | 0.301 | 0.094 |
| Total sugars (g/d) | 101 ± 33.7 | 84.6 ± 37.1 | 86.2 ± 35.4 | 72.1 ± 31.6 | 0.919 | 0.172 |
| Fiber (g/d) | 27.5 ± 4.2 | 22.2 ± 7.8 | 26.5 ± 11.4 | 23.4 ± 6.3 | 0.645 | 0.095 |
| Alcohol (g/d) | 3.8 ± 9.4 | 3.6 ± 8.2 | 9.5 ± 12.1 | 5.8 ± 10.9 | 0.203 | 0.172 |
| IF (Placebo) n = 10 | IF (Probiotic) n = 15 | p-Value 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 12 Weeks | Baseline | 12 Weeks | Time x Group Interaction | Time Effect | |
| PHQ9 2 | 4.5 (0–12) | 1.5 (0–10) | 3 (0–15) | 4 (0–6) | 0.845 | 0.003 |
| GAD 2 | 3.5 (0–16) | 3.5 (0–17) | 2 (0–12) | 1 (0–10) | 0.137 | 0.132 |
| SF-12 domains: | ||||||
| Physical Functioning | 67.5 ± 26.5 | 77.5 ± 24.9 | 78.3 ± 22.9 | 75.0 ± 28.4 | 0.233 | 0.546 |
| Role Physical | 73.8 ± 17.1 | 85.0 ± 21.1 | 82.5 ± 22.6 | 80.8 ± 17.6 | 0.179 | 0.314 |
| Bodily Pain | 82.5 ± 26.5 | 80.0 ± 30.7 | 68.3 ± 29.1 | 80.0 ± 21.6 | 0.201 | 0.413 |
| General Health | 63.0 ± 23.2 | 75.5 ± 21.5 | 59.0 ± 28.0 | 69.7 ± 19.9 | 0.834 | 0.013 |
| Vitality | 60.0 ± 17.5 | 57.5 ± 23.7 | 51.7 ± 25.8 | 60.0 ± 18.4 | 0.269 | 0.548 |
| Social Functioning | 85.0 ± 21.1 | 85.0 ± 17.5 | 76.7 ± 22.1 | 91.7 ± 20.4 | 0.050 | 0.050 |
| Role Emotional | 81.3 ± 14.7 | 80.0 ± 16.9 | 83.0 ± 20.6 | 88.4 ± 21.6 | 0.256 | 0.476 |
| Mental Health | 73.8 ± 13.8 | 72.5 ± 12.9 | 69.2 ± 14.8 | 80.0 ± 10.4 | 0.007 | 0.028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tay, A.; Pringle, H.; Penning, E.; Plank, L.D.; Murphy, R. PROFAST: A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic among People with Prediabetes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113530
Tay A, Pringle H, Penning E, Plank LD, Murphy R. PROFAST: A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic among People with Prediabetes. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113530
Chicago/Turabian StyleTay, Audrey, Hannah Pringle, Elise Penning, Lindsay D. Plank, and Rinki Murphy. 2020. "PROFAST: A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic among People with Prediabetes" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113530
APA StyleTay, A., Pringle, H., Penning, E., Plank, L. D., & Murphy, R. (2020). PROFAST: A Randomized Trial Assessing the Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic among People with Prediabetes. Nutrients, 12(11), 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113530






