Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Current Strategies and Interventions
1.3. Importance of This Review
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection and Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Collection and Measurement
2.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Characteristics
3.2. Meta-Analysis
3.2.1. Efficacy of Vitamin A Supplementation
3.2.2. Efficacy of Zinc Supplementation
3.2.3. Efficacy of Iron Supplementation
3.2.4. Efficacy of Iron-Folic Acid Supplementation
3.2.5. Efficacy of MMN Supplementation
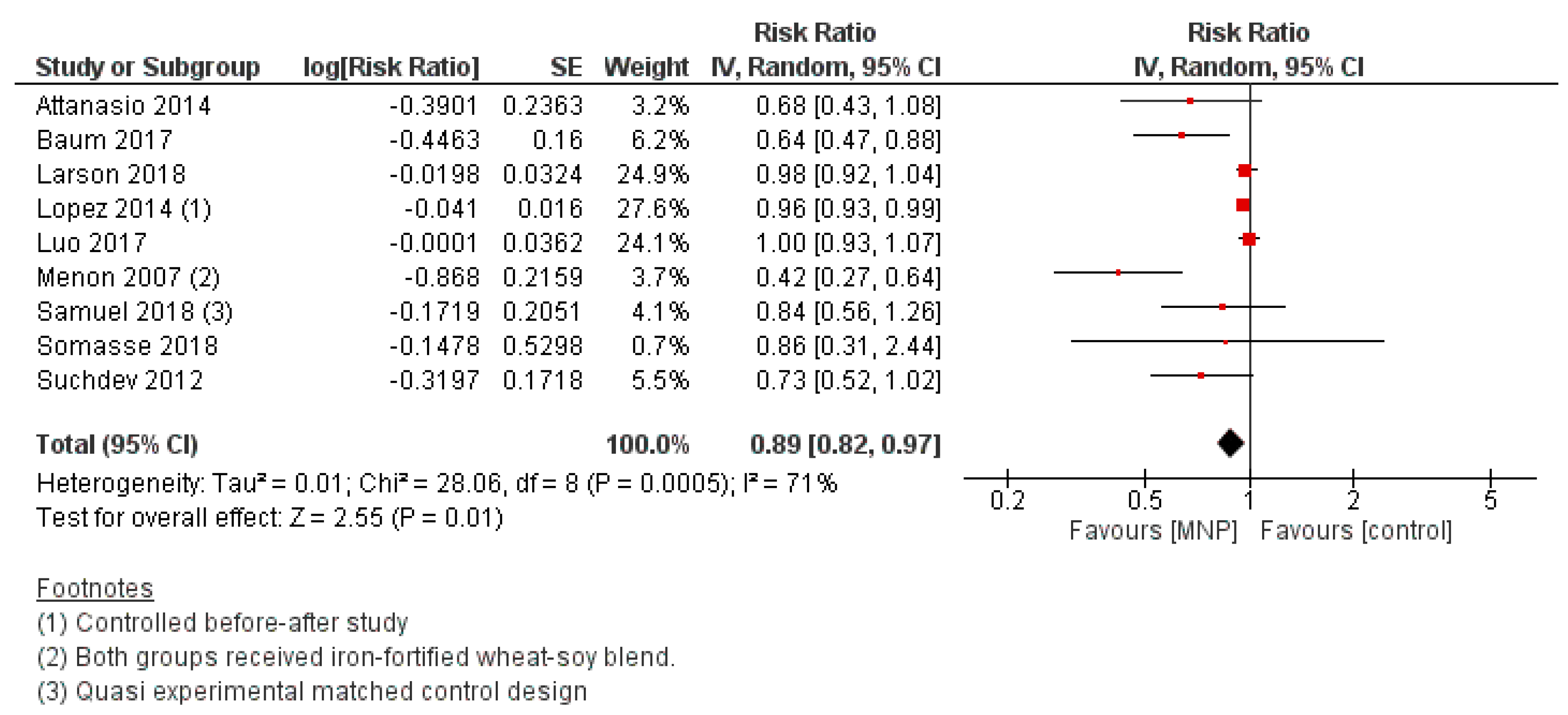
3.2.6. Efficacy of MNP Supplementation
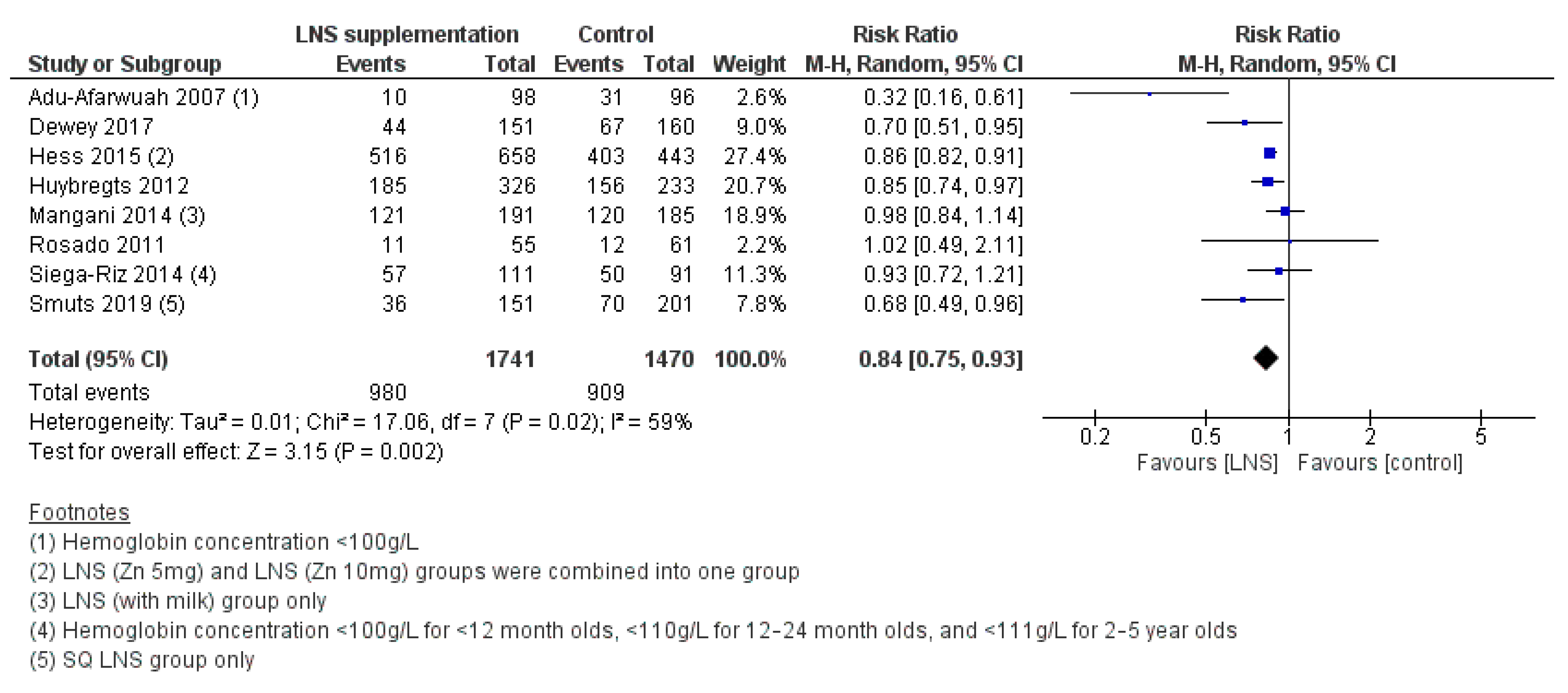
3.2.7. Efficacy of LNS Supplementation
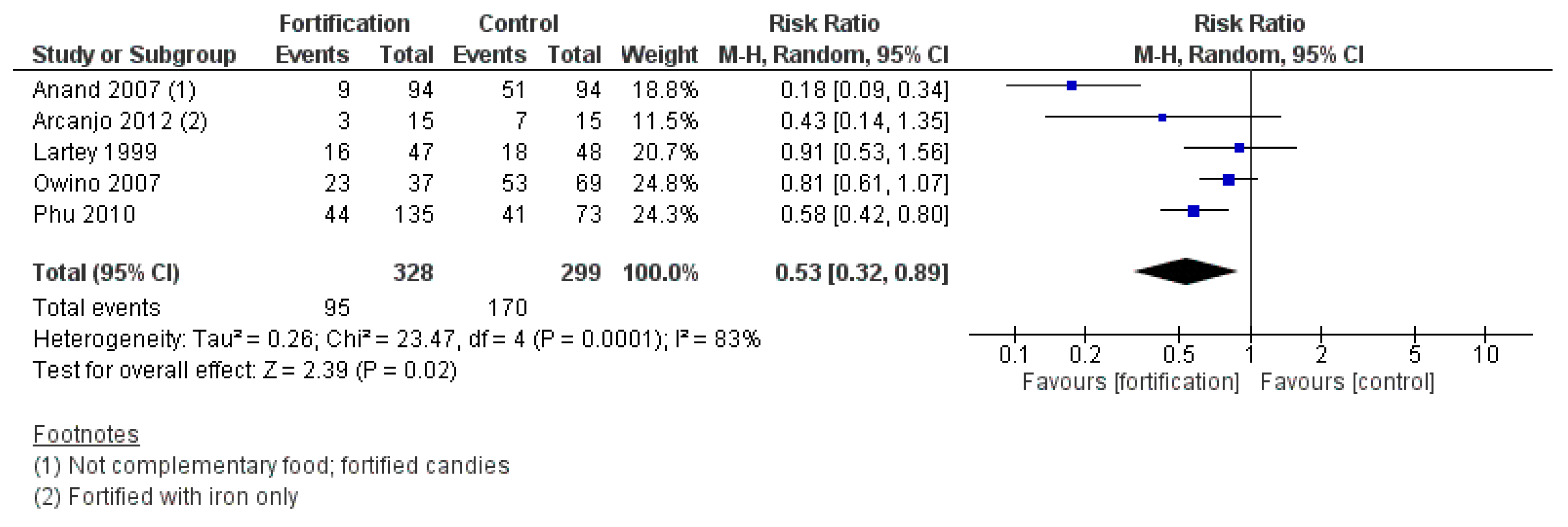
3.2.8. Efficacy of Targeted Fortification
3.2.9. Efficacy of Large-Scale Food Fortification
3.2.10. Effectiveness of MNP Supplementation
3.2.11. Effectiveness of LNS Supplementation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bailey, R.L.; West, K.P., Jr.; Black, R.E. The epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. 2), 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.A.; Finucane, M.M.; De-Regil, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Flaxman, S.R.; Branca, F.; Pena-Rosas, J.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Ezzati, M.; Nutrition Impact Model Study Group. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995–2011: A systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e16–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.A.; Bennett, J.E.; Hennocq, Q.; Lu, Y.; De-Regil, L.M.; Rogers, L.; Danaei, G.; Li, G.; White, R.A.; Flaxman, S.R.; et al. Trends and mortality effects of vitamin A deficiency in children in 138 low-income and middle-income countries between 1991 and 2013: A pooled analysis of population-based surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e528–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Karumbunathan, V.; Zimmermann, M.B. Global iodine status in 2011 and trends over the past decade. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessells, K.R.; Brown, K.H. Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: Results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Nutritional Anaemias: Tools for Effective Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lozoff, B. Iron deficiency and child development. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, S560–S571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghvi, T.; Van Ameringen, M.; Baker, J.; Fiedler, J.; Borwankar, R.; Phillips, M.; Houston, R.; Ross, J.; Heymann, H.; Dary, O. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies technical situation analysis: A report for the Ten Year Strategy for the Reduction of Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, S160–S219. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J. Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, P.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Khatry, S.K.; Katz, J.; Schaefer, B.A.; Cole, P.M.; Leclerq, S.C.; Tielsch, J.M. Prenatal micronutrient supplementation and intellectual and motor function in early school-aged children in Nepal. JAMA 2010, 304, 2716–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.P.; Wachs, T.D.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Black, M.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Huffman, S.L.; Baker-Henningham, H.; Chang, S.M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Lozoff, B.; et al. Inequality in early childhood: Risk and protective factors for early child development. Lancet 2011, 378, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, A.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Herzer, K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, CD008524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo-Wilson, E.; Junior, J.A.; Imdad, A.; Dean, S.; Chan, X.H.; Chan, E.S.; Jaswal, A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Zinc supplementation for preventing mortality, morbidity, and growth failure in children aged 6 months to 12 years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 15, CD009384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.H.; Peerson, J.M.; Baker, S.K.; Hess, S.Y. Preventive zinc supplementation among infants, preschoolers, and older prepubertal children. Food Nutr. Bull. 2009, 30, S12–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Food Fortification with Micronutrients; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, K.; Spiegelman, D.; Shankar, A.H.; Fawzi, W.W. Maternal multiple micronutrient supplementation and pregnancy outcomes in developing countries: Meta-analysis and meta-regression. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 402B–411B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, K.G.; Arimond, M. Lipid-based nutrient supplements: How can they combat child malnutrition? PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home Fortification Technical Advisory Group. Home Fortification with Micronutrient Powders Sight and Life; Home Fortification Technical Advisory Group: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De-Regil, L.M.; Jefferds, M.E.; Sylvetsky, A.C.; Dowswell, T. Intermittent iron supplementation for improving nutrition and development in children under 12 years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 7, CD009085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, H.; Gera, T.; Nestel, P. Effect of iron supplementation on mental and motor development in children: Systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogia, S.; Sachdev, H.S. Zinc supplementation for mental and motor development in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12, CD007991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoob, M.Y.; Salam, R.A.; Khan, F.R.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin D supplementation for preventing infections in children under five years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD008824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.H.; Peerson, J.M.; Olney, D.K. Provision of multiple rather than two or fewer micronutrients more effectively improves growth and other outcomes in micronutrient-deficient children and adults. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, U.; Nguyen, P.; Martorell, R. Effects of micronutrients on growth of children under 5 y of age: Meta-analyses of single and multiple nutrient interventions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Regil, L.M.; Jefferds, M.E.D.; Pena-Rosas, J.P. Point-of-use fortification of foods with micronutrient powders containing iron in children of preschool and school-age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD009666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Regil, L.M.; Suchdev, P.S.; Vist, G.E.; Walleser, S.; Pena-Rosas, J.P. Home fortification of foods with multiple micronutrient powders for health and nutrition in children under two years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 7, CD008959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, R.A.; MacPhail, C.; Das, J.K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Effectiveness of Micronutrient Powders (MNP) in women and children. BMC Public Health 2013, 13 (Suppl. 3), S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Hadi, Y.B.; Sadiq Sheikh, S.; Bhutta, A.Z.; Weise Prinzo, Z.; Bhutta, Z.A. Preventive lipid-based nutrient supplements given with complementary foods to infants and young children 6 to 23 months of age for health, nutrition, and developmental outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 5, CD012611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.P.; Wessells, K.R.; Arnold, C.D.; Huybregts, L.; Ashorn, P.; Becquey, E.; Humphrey, J.H.; Dewey, K.G. Lipid-based nutrient supplements and all-cause mortality in children 6-24 months of age: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 111, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, K.; Wieser, S.; Ruthemann, I.; Brugger, U. Effects of micronutrient fortified milk and cereal food for infants and children: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, U.; Goldenberg, T.; Allen, L.H. Do multiple micronutrient interventions improve child health, growth, and development? J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Kumar, R.; Bhutta, Z.A. Micronutrient fortification of food and its impact on woman and child health: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keats, E.C.; Neufeld, L.M.; Garrett, G.S.; Mbuya, M.N.N.; Bhutta, Z.A. Improved micronutrient status and health outcomes in low- and middle-income countries following large-scale fortification: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, M.; Harb, T.; David, M.; Davies, P.S.; Hill, R.J. Effect of fortified milk on growth and nutritional status in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keats, E.C.; Imdad, A.; Das, J.K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Protocol: Efficacy and effectiveness of micronutrient supplementation and fortification interventions on the health and nutritional status of children under-five in low and middle-income countries. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2018, 14, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Effective Practice Organisation of Care (EPOC). Suggested risk of bias criteria for EPOC reviews. In EPOC Resources for Review Authors; EPOC: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, T.; Steiner-Asiedu, M.; Sakyi-Dawson, E.; Anderson, A.K. Effect of fortification of maize with cowpea and iron on growth and anaemia status of children. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2010, 4, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Afarwuah, S.; Lartey, A.; Brown, K.H.; Zlotkin, S.; Briend, A.; Dewey, K.G. Randomized comparison of 3 types of micronutrient supplements for home fortification of complementary foods in Ghana: Effects on growth and motor development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Afarwuah, S.; Lartey, A.; Okronipa, H.; Ashorn, P.; Peerson, J.M.; Arimond, M.; Ashorn, U.; Zeilani, M.; Vosti, S.; Dewey, K.G. Small-quantity, lipid-based nutrient supplements provided to women during pregnancy and 6 mo postpartum and to their infants from 6 mo of age increase the mean attained length of 18-mo-old children in semi-urban Ghana: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Lakshmy, R.; Janakarajan, V.N.; Ritvik, A.; Misra, P.; Pandey, R.M.; Kapoor, S.K.; Sankar, R.; Bulusu, S. Effect of consumption of micronutrient fortified candies on the iron and vitamin A status of children aged 3-6 years in rural Haryana. Indian Pediatr. 2007, 44, 823–829. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Randomised trial to assess benefits and safety of vitamin A supplementation linked to immunisation in early infancy. WHO/CHD Immunisation-Linked Vitamin A Supplementation Study Group. Lancet 1998, 352, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorn, P.; Alho, L.; Ashorn, U.; Cheung, Y.B.; Dewey, K.G.; Gondwe, A.; Harjunmaa, U.; Lartey, A.; Phiri, N.; Phiri, T.E.; et al. Supplementation of Maternal Diets during Pregnancy and for 6 Months Postpartum and Infant Diets Thereafter with Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements Does Not Promote Child Growth by 18 Months of Age in Rural Malawi: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asibey-Berko, E.; Zlotkin, S.H.; Yeung, G.S.; Nti-Nimako, W.; Ahunu, B.; Kyei-Faried, S.; Johnston, J.L.; Tondeur, M.C.; Mannar, V. Dual fortification of salt with iron and iodine in women and children in rural Ghana. East Afr. Med. J. 2007, 84, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ayah, R.A.; Mwaniki, D.L.; Magnussen, P.; Tedstone, A.E.; Marshall, T.; Alusala, D.; Luoba, A.; Kaestel, P.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Friis, H. The effects of maternal and infant vitamin A supplementation on vitamin A status: A randomised trial in Kenya. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baqui, A.H.; de Francisco, A.; Arifeen, S.E.; Siddique, A.K.; Sack, R.B. Bulging fontanelle after supplementation with 25,000 IU of vitamin A in infancy using immunization contacts. Acta Paediatr. 1995, 84, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqui, A.H.; Zaman, K.; Persson, L.A.; El Arifeen, S.; Yunus, M.; Begum, N.; Black, R.E. Simultaneous weekly supplementation of iron and zinc is associated with lower morbidity due to diarrhea and acute lower respiratory infection in Bangladeshi infants. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4150–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth-Jaeggi, T.; Moretti, D.; Kvalsvig, J.; Holding, P.A.; Njenga, J.; Mwangi, A.; Chhagan, M.K.; Lacroix, C.; Zimmermann, M.B. In-home fortification with 2.5 mg iron as NaFeEDTA does not reduce anaemia but increases weight gain: A randomised controlled trial in Kenyan infants. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 4), 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begin, F.; Santizo, M.C.; Peerson, J.M.; Torun, B.; Brown, K.H. Effects of bovine serum concentrate, with or without supplemental micronutrients, on the growth, morbidity, and micronutrient status of young children in a low-income, peri-urban Guatemalan community. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bentley, M.E.; Caulfield, L.E.; Ram, M.; Santizo, M.C.; Hurtado, E.; Rivera, J.A.; Ruel, M.T.; Brown, K.H. Zinc supplementation affects the activity patterns of rural Guatemalan infants. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berger, J.; Dyck, J.L.; Galan, P.; Aplogan, A.; Schneider, D.; Traissac, P.; Hercberg, S. Effect of daily iron supplementation on iron status, cell-mediated immunity, and incidence of infections in 6-36 month old Togolese children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Ninh, N.X.; Khan, N.C.; Nhien, N.V.; Lien, D.K.; Trung, N.Q.; Khoi, H.H. Efficacy of combined iron and zinc supplementation on micronutrient status and growth in Vietnamese infants. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, N.; Bahl, R.; Taneja, S.; Strand, T.; Molbak, K.; Ulvik, R.J.; Sommerfelt, H.; Bhan, M.K. Substantial reduction in severe diarrheal morbidity by daily zinc supplementation in young north Indian children. Pediatrics 2002, 109, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisimwa, G.; Owino, V.O.; Bahwere, P.; Dramaix, M.; Donnen, P.; Dibari, F.; Collins, S. Randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of a soybean-maize-sorghum-based ready-to-use complementary food paste on infant growth in South Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, W.A.; Santosham, M.; Naheed, A.; Goswami, D.; Wahed, M.A.; Diener-West, M.; Faruque, A.S.; Black, R.E. Effect of weekly zinc supplements on incidence of pneumonia and diarrhoea in children younger than 2 years in an urban, low-income population in Bangladesh: Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, L.E.; Zavaleta, N.; Chen, P.; Colombo, J.; Kannass, K. Mineral status of non-anemic Peruvian infants taking an iron and copper syrup with or without zinc from 6 to 18 months of age: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; El Arifeen, S.; Bari, S.; Wahed, M.A.; Rahman, K.M.; Rahman, M.T.; Mahmud, A.B.; Begum, N.; Zaman, K.; Baqui, A.H.; et al. Supplementing iron and zinc: Double blind, randomized evaluation of separate or combined delivery. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chang, S.Y. Effect of in-home fortification of complementary feeding on intellectual development of Chinese children. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 23, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.R.; Zhang, L.; Luo, H.Y.; Gao, N.; Wang, J.; Fu, G.Y.; Mao, M. Effect of simultaneous supplementation of vitamin A and iron on diarrheal and respiratory tract infection in preschool children in Chengdu City, China. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, T.Y.; Chen, L.; Qu, P.; Liu, Y.X. Effects of vitamin A, vitamin A plus iron and multiple micronutrient-fortified seasoning powder on preschool children in a suburb of Chongqing, China. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 2008, 54, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drammeh, B.S.; Marquis, G.S.; Funkhouser, E.; Bates, C.; Eto, I.; Stephensen, C.B. A randomized, 4-month mango and fat supplementation trial improved vitamin A status among young Gambian children. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3693–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dutra-de-Oliveira, J.E.; de Almeida, C.A. Domestic drinking water—An effective way to prevent anemia among low socioeconomic families in Brazil. Food Nutr. Bull. 2002, 23, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekvall, H.; Premji, Z.; Bjorkman, A. Micronutrient and iron supplementation and effective antimalarial treatment synergistically improve childhood anaemia. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2000, 5, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermis, B.; Demirel, F.; Demircan, N.; Gurel, A. Effects of three different iron supplementations in term healthy infants after 5 months of life. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2002, 48, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esamai, F.; Liechty, E.; Ikemeri, J.; Westcott, J.; Kemp, J.; Culbertson, D.; Miller, L.V.; Hambidge, K.M.; Krebs, N.F. Zinc absorption from micronutrient powder is low but is not affected by iron in Kenyan infants. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5636–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, M.; Kvalsvig, J.D.; Lombard, C.J.; Benade, A.J. Effect of a fortified maize-meal porridge on anemia, micronutrient status, and motor development of infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmida, U.; Rumawas, J.S.; Utomo, B.; Patmonodewo, S.; Schultink, W. Zinc-iron, but not zinc-alone supplementation, increased linear growth of stunted infants with low haemoglobin. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fawzi, W.W.; Herrera, M.G.; Willett, W.C.; Nestel, P.; el Amin, A.; Mohamed, K.A. The effect of vitamin A supplementation on the growth of preschool children in the Sudan. Am. J. Public Health 1997, 87, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisker, A.B.; Bale, C.; Jorgensen, M.J.; Balde, I.; Hornshoj, L.; Bibby, B.M.; Aaby, P.; Benn, C.S. High-dose vitamin A supplementation administered with vaccinations after 6 months of age: Sex-differential adverse reactions and morbidity. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M.; Sala, D.; Usuelli, M.; Livio, L.; Francescato, G.; Braga, M.; Radaelli, G.; Riva, E. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing effects of supplementation with two different combinations of micronutrients delivered as sprinkles on growth, anemia, and iron deficiency in cambodian infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 42, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcay, G.; Ozden, T.; Karakas, Z.; Karabayir, N.; Yildiz, I.; Abali, S.; Sahip, Y. Effect of iron supplementation on development of iron deficiency anemia in breastfed infants. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2012, 58, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.N.; Mondal, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Rajendran, K.; Sur, D.; Manna, B. Impact of zinc supplementation on diarrhoeal morbidity in rural children of West Bengal, India. Acta Paediatr. 2003, 92, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.N.; Rajendran, K.; Mondal, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Operational feasibility of implementing community-based zinc supplementation: Impact on childhood diarrheal morbidity. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadani, J.D.; Fuchs, G.J.; Osendarp, S.J.; Khatun, F.; Huda, S.N.; Grantham-McGregor, S.M. Randomized controlled trial of the effect of zinc supplementation on the mental development of Bangladeshi infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannotti, L.L.; Dulience, S.J.; Green, J.; Joseph, S.; Francois, J.; Antenor, M.L.; Lesorogol, C.; Mounce, J.; Nickerson, N.M. Linear growth increased in young children in an urban slum of Haiti: A randomized controlled trial of a lipid-based nutrient supplement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, J.; Sachdev, H.P.; Singh, T.; Mallika, V. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in breastfed young infants initiated on complementary feeding: Effect on haematological status. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2004, 22, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, D.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, K.N. Effectiveness of nutrition education, iron supplementation or both on iron status in children. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Kartasasmita, C.B.; Rosmayudi, O.; Deville, W.; Demedts, M. Plasma retinol level, vitamin A supplementation and acute respiratory infections in children of 1-5 years old in a developing country. Respiratory Diseases Working Group. Tuber. Lung Dis. 1995, 76, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmer, T.M.; Omer, P.S.; Gidvani-Diaz, V.K.; and Coello, M. Acceptance and Effect of Ferrous Fumarate Containing Micronutrient Sprinkles on Anemia, Iron Deficiency and Anthropometrics in Honduran Children. In Anemia; Donald, S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kikafunda, J.K.; Walker, A.F.; Allan, E.F.; Tumwine, J.K. Effect of zinc supplementation on growth and body composition of Ugandan preschool children: A randomized, controlled, intervention trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kounnavong, S.; Sunahara, T.; Mascie-Taylor, C.G.; Hashizume, M.; Okumura, J.; Moji, K.; Boupha, B.; Yamamoto, T. Effect of daily versus weekly home fortification with multiple micronutrient powder on haemoglobin concentration of young children in a rural area, Lao People’s Democratic Republic: A randomised trial. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujinga, P.; Galetti, V.; Onyango, E.; Jakab, V.; Buerkli, S.; Andang’o, P.; Brouwer, I.D.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Moretti, D. Effectiveness of zinc-fortified water on zinc intake, status and morbidity in Kenyan pre-school children: A randomised controlled trial. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartey, A.; Manu, A.; Brown, K.H.; Peerson, J.M.; Dewey, K.G. A randomized, community-based trial of the effects of improved, centrally processed complementary foods on growth and micronutrient status of Ghanaian infants from 6 to 12 mo of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, L.T.; Berger, J. Multiple micronutrient supplementation improves anemia, micronutrient nutrient status, and growth of Vietnamese infants: Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 660S–665S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, T.; Lonnerdal, B.; Stenlund, H.; Ismail, D.; Seswandhana, R.; Ekstrom, E.C.; Persson, L.A. A community-based randomized controlled trial of iron and zinc supplementation in Indonesian infants: Interactions between iron and zinc. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, N.B.; Aaron, G.J.; Hess, S.Y.; Dossou, N.I.; Guiro, A.T.; Wade, S.; Brown, K.H. Plasma zinc concentration responds to short-term zinc supplementation, but not zinc fortification, in young children in Senegal1,2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.Z.; Montoya, Y.; Hertzmark, E.; Santos, J.I.; Rosado, J.L. A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.Z.; Rosado, J.L.; DuPont, H.L.; Hertzmark, E.; Santos, J.I. Supplementation with vitamin A reduces watery diarrhoea and respiratory infections in Mexican children. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de Romana, G.; Cusirramos, S.; Lopez de Romana, D.; Gross, R. Efficacy of multiple micronutrient supplementation for improving anemia, micronutrient status, growth, and morbidity of Peruvian infants. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 646S–652S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoff, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Richards, B.; Xu, G.; Clark, K.M.; Liang, F.; Kaciroti, N.; Zhao, G.; et al. Low-Dose Iron Supplementation in Infancy Modestly Increases Infant Iron Status at 9 Mo without Decreasing Growth or Increasing Illness in a Randomized Clinical Trial in Rural China. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoff, B.; Wolf, A.W.; Jimenez, E. Iron-deficiency anemia and infant development: Effects of extended oral iron therapy. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luabeya, K.K.; Mpontshane, N.; Mackay, M.; Ward, H.; Elson, I.; Chhagan, M.; Tomkins, A.; Van den Broeck, J.; Bennish, M.L. Zinc or multiple micronutrient supplementation to reduce diarrhea and respiratory disease in South African children: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macharia-Mutie, C.W.; Moretti, D.; Van den Briel, N.; Omusundi, A.M.; Mwangi, A.M.; Kok, F.J.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Brouwer, I.D. Maize porridge enriched with a micronutrient powder containing low-dose iron as NaFeEDTA but not amaranth grain flour reduces anemia and iron deficiency in Kenyan preschool children. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleta, K.M.; Phuka, J.; Alho, L.; Cheung, Y.B.; Dewey, K.G.; Ashorn, U.; Phiri, N.; Phiri, T.E.; Vosti, S.A.; Zeilani, M.; et al. Provision of 10-40 g/d Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements from 6 to 18 Months of Age Does Not Prevent Linear Growth Faltering in Malawi. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Taneja, D.K.; Devasenapathy, N.; Rajeshwari, K. Short-course prophylactic zinc supplementation for diarrhea morbidity in infants of 6 to 11 months. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e46–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaseki-Holland, S.; Maroof, Z.; Bruce, J.; Mughal, M.Z.; Masher, M.I.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Walraven, G.; Chandramohan, D. Effect on the incidence of pneumonia of vitamin D supplementation by quarterly bolus dose to infants in Kabul: A randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangani, C.; Ashorn, P.; Maleta, K.; Phuka, J.; Thakwalakwa, C.; Dewey, K.; Manary, M.; Puumalainen, T.; Cheung, Y.B. Lipid-based nutrient supplements do not affect the risk of malaria or respiratory morbidity in 6- to 18-month-old Malawian children in a randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Estevez, N.S.; Alvarez-Guevara, A.N.; Rodriguez-Martinez, C.E. Effects of zinc supplementation in the prevention of respiratory tract infections and diarrheal disease in Colombian children: A 12-month randomised controlled trial. Allergol. Immunopathol. (Madr.) 2016, 44, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaga, J.J.; Kitua, A.Y.; Lemnge, M.M.; Akida, J.A.; Malle, L.N.; Ronn, A.M.; Theander, T.G.; Bygbjerg, I.C. Effect of intermittent treatment with amodiaquine on anaemia and malarial fevers in infants in Tanzania: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, S.L.; Vargas-Vasquez, A.; Bado Perez, R.; Alcazar Valdivia, L.; Aquino Vivanco, O.; Rodriguez Martin, A.; Novalbos Ruiz, J.P. Effects of lipid-based nutrient supplements v. micronutrient powders on nutritional and developmental outcomes among Peruvian infants. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazariegos, M.; Hambidge, K.M.; Westcott, J.E.; Solomons, N.W.; Raboy, V.; Das, A.; Goco, N.; Kindem, M.; Wright, L.L.; Krebs, N.F. Neither a zinc supplement nor phytate-reduced maize nor their combination enhance growth of 6- to 12-month-old Guatemalan infants. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Manji, K.P.; Kisenge, R.; Aboud, S.; Spiegelman, D.; Fawzi, W.W.; Duggan, C.P. Daily Zinc but Not Multivitamin Supplementation Reduces Diarrhea and Upper Respiratory Infections in Tanzanian Infants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, C.; Kahigwa, E.; Hirt, R.; Vounatsou, P.; Aponte, J.J.; Font, F.; Acosta, C.J.; Schellenberg, D.M.; Galindo, C.M.; Kimario, J.; et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation and malaria chemoprophylaxis for prevention of severe anaemia and malaria in Tanzanian infants. Lancet 1997, 350, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, P.; Ruel, M.T.; Loechl, C.U.; Arimond, M.; Habicht, J.P.; Pelto, G.; Michaud, L. Micronutrient Sprinkles reduce anemia among 9- to 24-mo-old children when delivered through an integrated health and nutrition program in rural Haiti. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.K.; Akramuzzaman, S.M.; Fuchs, G.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Mahalanabis, D. Long-term oral supplementation with iron is not harmful for young children in a poor community of Bangladesh. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, O.; Becher, H.; van Zweeden, A.B.; Ye, Y.; Diallo, D.A.; Konate, A.T.; Gbangou, A.; Kouyate, B.; Garenne, M. Effect of zinc supplementation on malaria and other causes of morbidity in west African children: Randomised double blind placebo controlled trial. BMJ 2001, 322, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, S.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Asante, K.P.; Amoaful, E.; Mahama, E.; Tchum, S.K.; Ali, M.; Adjei, K.; Davis, C.R.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Vitamin A status and body pool size of infants before and after consuming fortified home-based complementary foods. Arch. Public Health 2016, 74, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop-Clewes, C.A.; Paracha, P.I.; McLoone, U.J.; Thurnham, D.I. Effect of improved vitamin A status on response to iron supplementation in Pakistani infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oelofse, A.; Van Raaij, J.M.; Benade, A.J.; Dhansay, M.A.; Tolboom, J.J.; Hautvast, J.G. The effect of a micronutrient-fortified complementary food on micronutrient status, growth and development of 6- to 12-month-old disadvantaged urban South African infants. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 54, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, A.O.; Kruger, H.S.; Jerling, J.C.; Smuts, C.M.; Covic, N.; Hanekom, S.M.; Mamabolo, R.L.; Kvalsvig, J. Point-of-use micronutrient fortification: Lessons learned in implementing a preschool-based pilot trial in South Africa. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, H.Z.; Traore, T.; Zeba, A.N.; Dramaix-Wilmet, M.; Hennart, P.; Donnen, P. Effect of an improved local ingredient-based complementary food fortified or not with iron and selected multiple micronutrients on Hb concentration. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owino, V.O.; Kasonka, L.M.; Sinkala, M.M.; Wells, J.K.; Eaton, S.; Darch, T.; Coward, A.; Tomkins, A.M.; Filteau, S.M. Fortified complementary foods with or without alpha-amylase treatment increase hemoglobin but do not reduce breast milk intake of 9-mo-old Zambian infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Agyei, S.; Newton, S.; Mahama, E.; Febir, L.G.; Ali, M.; Adjei, K.; Tchum, K.; Alhassan, L.; Moleah, T.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Impact of vitamin A with zinc supplementation on malaria morbidity in Ghana. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganini, D.; Uyoga, M.A.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Cercamondi, C.I.; Moretti, D.; Barth-Jaeggi, T.; Schwab, C.; Boekhorst, J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Lacroix, C.; et al. Prebiotic galacto-oligosaccharides mitigate the adverse effects of iron fortification on the gut microbiome: A randomised controlled study in Kenyan infants. Gut 2017, 66, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palupi, L.; Schultink, W.; Achadi, E.; Gross, R. Effective community intervention to improve hemoglobin status in preschoolers receiving once-weekly iron supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuka, J.C.; Maleta, K.; Thakwalakwa, C.; Cheung, Y.B.; Briend, A.; Manary, M.J.; Ashorn, P. Complementary feeding with fortified spread and incidence of severe stunting in 6- to 18-month-old rural Malawians. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2008, 162, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishna, K.V.; Hemalatha, R.; Geddam, J.J.; Kumar, P.A.; Balakrishna, N.; Shatrugna, V. Effectiveness of zinc supplementation to full term normal infants: A community based double blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Akramuzzaman, S.M.; Mitra, A.K.; Fuchs, G.J.; Mahalanabis, D. Long-term supplementation with iron does not enhance growth in malnourished Bangladeshi children. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mahalanabis, D.; Alvarez, J.O.; Wahed, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Habte, D.; Khaled, M.A. Acute respiratory infections prevent improvement of vitamin A status in young infants supplemented with vitamin A. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Vermund, S.H.; Wahed, M.A.; Fuchs, G.J.; Baqui, A.H.; Alvarez, J.O. Simultaneous zinc and vitamin A supplementation in Bangladeshi children: Randomised double blind controlled trial. BMJ 2001, 323, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, H.; Kim, S.; Sim, B.; Gang, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, R.; Yang, M.; Kim, S. Effect of iron fortification of nursery complementary food on iron status of infants in the DPRKorea. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.A.; Gonzalez-Cossio, T.; Flores, M.; Romero, M.; Rivera, M.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Rosado, J.L.; Brown, K.H. Multiple micronutrient supplementation increases the growth of Mexican infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.L.; Lopez, P.; Munoz, E.; Martinez, H.; Allen, L.H. Zinc supplementation reduced morbidity, but neither zinc nor iron supplementation affected growth or body composition of Mexican preschoolers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.L.; Lopez, P.; Garcia, O.P.; Alatorre, J.; Alvarado, C. Effectiveness of the nutritional supplement used in the Mexican Oportunidades programme on growth, anaemia, morbidity and cognitive development in children aged 12-24 months. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.A.; Kirkwood, B.R.; Binka, F.N.; Arthur, P.; Dollimore, N.; Morris, S.S.; Shier, R.P.; Gyapong, J.O.; Smith, P.G. Child morbidity and mortality following vitamin A supplementation in Ghana: Time since dosing, number of doses, and time of year. Am. J. Public Health 1995, 85, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, D.L.; Mattos, A.P.; Ribeiro, T.C.; Leite, M.E.; Cole, C.R.; Costa-Ribeiro, H., Jr. Zinc and other micronutrients supplementation through the use of sprinkles: Impact on the occurrence of diarrhea and respiratory infections in institutionalized children. J. Pediatr. (Rio J.) 2013, 89, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazawal, S.; Black, R.E.; Bhan, M.K.; Jalla, S.; Sinha, A.; Bhandari, N. Efficacy of zinc supplementation in reducing the incidence and prevalence of acute diarrhea—A community-based, double-blind, controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazawal, S.; Black, R.E.; Ramsan, M.; Chwaya, H.M.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Dutta, A.; Dhingra, U.; Kabole, I.; Deb, S.; Othman, M.K.; et al. Effects of routine prophylactic supplementation with iron and folic acid on admission to hospital and mortality in preschool children in a high malaria transmission setting: Community-based, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 367, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazawal, S.; Dhingra, U.; Dhingra, P.; Hiremath, G.; Kumar, J.; Sarkar, A.; Menon, V.P.; Black, R.E. Effects of fortified milk on morbidity in young children in north India: Community based, randomised, double masked placebo controlled trial. BMJ 2007, 334, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempertegui, F.; Estrella, B.; Camaniero, V.; Betancourt, V.; Izurieta, R.; Ortiz, W.; Fiallo, E.; Troya, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths, J.K. The beneficial effects of weekly low-dose vitamin A supplementation on acute lower respiratory infections and diarrhea in Ecuadorian children. Pediatrics 1999, 104, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Villalpando, S.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.A.; Mundo-Rosas, V.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Jimenez-Aguilar, A. Ferrous gluconate and ferrous sulfate added to a complementary food distributed by the Mexican nutrition program Oportunidades have a comparable efficacy to reduce iron deficiency in toddlers. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 47, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.H.; Genton, B.; Semba, R.D.; Baisor, M.; Paino, J.; Tamja, S.; Adiguma, T.; Wu, L.; Rare, L.; Tielsch, J.M.; et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on morbidity due to Plasmodium falciparum in young children in Papua New Guinea: A randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 354, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.P.; Vitolo, M.R.; Zara, L.F.; Castro, C.F. Effects of zinc supplementation on 1- to 5-year old children. J. Pediatr. (Rio J.) 2006, 82, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuts, C.M.; Dhansay, M.A.; Faber, M.; van Stuijvenberg, M.E.; Swanevelder, S.; Gross, R.; Benade, A.J. Efficacy of multiple micronutrient supplementation for improving anemia, micronutrient status, and growth in South African infants. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 653S–659S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltzfus, R.J.; Kvalsvig, J.D.; Chwaya, H.M.; Montresor, A.; Albonico, M.; Tielsch, J.M.; Savioli, L.; Pollitt, E. Effects of iron supplementation and anthelmintic treatment on motor and language development of preschool children in Zanzibar: Double blind, placebo controlled study. BMJ 2001, 323, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Martono, P.D.; Kameo, S.; Suradji, E.W.; Koyama, H. Effect of probiotic L. plantarum IS-10506 and zinc supplementation on humoral immune response and zinc status of Indonesian pre-school children. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, S.; Strand, T.A.; Kumar, T.; Mahesh, M.; Mohan, S.; Manger, M.S.; Refsum, H.; Yajnik, C.S.; Bhandari, N. Folic acid and vitamin B-12 supplementation and common infections in 6-30-mo-old children in India: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshome, E.M.; Andang’o, P.E.A.; Osoti, V.; Terwel, S.R.; Otieno, W.; Demir, A.Y.; Prentice, A.M.; Verhoef, H. Daily home fortification with iron as ferrous fumarate versus NaFeEDTA: A randomised, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority trial in Kenyan children. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, B.D.; Schultink, W.; Dillon, D.; Gross, R.; Leswara, N.D.; Khoi, H.H. Effect of daily and weekly micronutrient supplementation on micronutrient deficiencies and growth in young Vietnamese children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeta, M.; West, C.E.; Haidar, J.; Deurenberg, P.; Hautvast, J.G. Zinc supplementation and stunted infants in Ethiopia: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2000, 355, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untoro, J.; Karyadi, E.; Wibowo, L.; Erhardt, M.W.; Gross, R. Multiple micronutrient supplements improve micronutrient status and anemia but not growth and morbidity of Indonesian infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 639S–645S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatarao, T.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Nair, N.G.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Sundaramoorthy, L.; Koya, P.K.; Kumar, S.K. Effect of vitamin A supplementation to mother and infant on morbidity in infancy. Indian Pediatr. 1996, 33, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Warthon-Medina, M.; Qualter, P.; Zavaleta, N.; Dillon, S.; Lazarte, F.; Lowe, N.M. The Long Term Impact of Micronutrient Supplementation during Infancy on Cognition and Executive Function Performance in Pre-School Children. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6606–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasantwisut, E.; Winichagoon, P.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Yamborisut, U.; Boonpraderm, A.; Pongcharoen, T.; Sranacharoenpong, K.; Russameesopaphorn, W. Iron and zinc supplementation improved iron and zinc status, but not physical growth, of apparently healthy, breast-fed infants in rural communities of northeast Thailand. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessells, K.R.; Ouedraogo, Z.P.; Rouamba, N.; Hess, S.Y.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Brown, K.H. Short-term zinc supplementation with dispersible tablets or zinc sulfate solution yields similar positive effects on plasma zinc concentration of young children in Burkina Faso: A randomized controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 129–135 e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieringa, F.T.; Dijkhuizen, M.A.; West, C.E.; Thurnham, D.I.; Van der Meer, J.W. Redistribution of vitamin A after iron supplementation in Indonesian infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdakok, K.; Temiz, F.; Yalcin, S.S.; Gumruk, F. Efficacy of daily and weekly iron supplementation on iron status in exclusively breast-fed infants. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2004, 26, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotkin, S.; Antwi, K.Y.; Schauer, C.; Yeung, G. Use of microencapsulated iron(II) fumarate sprinkles to prevent recurrence of anaemia in infants and young children at high risk. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cobra, C.; Rusmil, K.; Rustama, D.; Suwardi, S.S.; Permaesih, D.; Martuti, S.; Semba, R.D. Infant survival is improved by oral iodine supplementation. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibley, M.J.; Sadjimin, T.; Kjolhede, C.L.; Moulton, L.H. Vitamin A supplementation fails to reduce incidence of acute respiratory illness and diarrhea in preschool-age Indonesian children. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhuizen, M.A.; Wieringa, F.T.; West, C.E.; Martuti, S. Effects of iron and zinc supplementation in Indonesian infants on micronutrient status and growth. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2860–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domellof, M.; Cohen, R.J.; Dewey, K.G.; Hernell, O.; Rivera, L.L.; Lonnerdal, B. Iron supplementation of breast-fed Honduran and Swedish infants from 4 to 9 months of age. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossa, R.A.; Ategbo, E.A.; de Koning, F.L.; van Raaij, J.M.; Hautvast, J.G. Impact of iron supplementation and deworming on growth performance in preschool Beninese children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 55, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barffour, M.A.; Hinnouho, G.M.; Kounnavong, S.; Wessells, K.R.; Ratsavong, K.; Bounheuang, B.; Chanhthavong, B.; Sitthideth, D.; Sengnam, K.; Arnold, C.D.; et al. Effects of Daily Zinc, Daily Multiple Micronutrient Powder, or Therapeutic Zinc Supplementation for Diarrhea Prevention on Physical Growth, Anemia, and Micronutrient Status in Rural Laotian Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. 2019, 207, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, S.; Ashraf, S.; Siddiqua, S.; Mushtaq, S.; Saleem, M. To compare prophylactic zinc supplementation versus placebo in terms of frequency of diarrhea in infants of 6–11 months. Med. Forum Mon. 2018, 29, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Smuts, C.M.; Matsungo, T.M.; Malan, L.; Kruger, H.S.; Rothman, M.; Kvalsvig, J.D.; Covic, N.; Joosten, K.; Osendarp, S.J.M.; Bruins, M.J.; et al. Effect of small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements on growth, psychomotor development, iron status, and morbidity among 6- to 12-mo-old infants in South Africa: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, R.D.; West, K.P., Jr.; Natadisastra, G.; Eisinger, W.; Lan, Y.; Sommer, A. Hyporetinolemia and acute phase proteins in children with and without xerophthalmia. Am. J. Nutr. 2000, 72, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalpando, S.; Shamah, T.; Rivera, J.A.; Lara, Y.; Monterrubio, E. Fortifying milk with ferrous gluconate and zinc oxide in a public nutrition program reduced the prevalence of anemia in toddlers. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2633–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahi, Z.; Fozouni, F.; Bondarianzadeh, D. Oral Zinc Supplementation Positively Affects Linear Growth, But not Weight, in Children 6–24 Months of Age. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aboud, F.E.; Akhter, S. A cluster-randomized evaluation of a responsive stimulation and feeding intervention in bangladesh. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e1191–e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ramirez-Zea, M.; Neufeld, L.M.; Flores-Ayala, R. The effect of nutritional supplementation on physical activity and exploratory behavior of Mexican infants aged 8–12 months. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agarwal, D.K.; Pandey, C.M.; Agarwal, K.N. Vitamin a administration and preschool child mortality. Nutr. Res. 1995, 15, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, H.; Ndiaye, B.; Linnemayr, S.; Ka, A.; Rokx, C.; Dieng, K.; Mulder-Sibanda, M. Effectiveness of a community-based intervention to improve nutrition in young children in Senegal: A difference in difference analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, C.A.; De Mello, E.D.; Ramos, A.P.; Joao, C.A.; Joao, C.R.; Dutra-de-Oliveira, J.E. Assessment of drinking water fortification with iron plus ascorbic Acid or ascorbic Acid alone in daycare centers as a strategy to control iron-deficiency anemia and iron deficiency: A randomized blind clinical study. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2014, 60, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcanjo, F.P.; Arcanjo, C.C.; Arcanjo, F.C.; Campos Lde, A.; Amancio, O.M.; Braga, J.A. Milk-based cornstarch porridge fortified with iron is effective in reducing anemia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2012, 58, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanasio, O.P.; Fernandez, C.; Fitzsimons, E.O.; Grantham-McGregor, S.M.; Meghir, C.; Rubio-Codina, M. Using the infrastructure of a conditional cash transfer program to deliver a scalable integrated early child development program in Colombia: Cluster randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2014, 349, g5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, S.; Peto, R.; Read, S.; Clark, S.; Pande, V.; Bundy, D.; Team, D. Vitamin A supplementation every 6 months with retinol in 1 million pre-school children in north India: DEVTA, a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagni, U.V.; Baiao, M.R.; Santos, M.M.; Luiz, R.R.; Veiga, G.V. [Effect of weekly rice fortification with iron on anemia prevalence and hemoglobin concentration among children attending public daycare centers in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil]. Cad. Saude Publica 2009, 25, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.N.; Taddei, J.A.; Palma, D.; Ancona-Lopez, F.; Braga, J.A. Double-blind randomized controlled trial of rolls fortified with microencapsulated iron. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 2012, 58, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Schlossman, N.; Balan, I.; Pruzensky, W.; Balan, A.; Brown, C.; Gamache, M.G.; Schleicher, M.M.; de Sa, A.B.; Saltzman, E.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Offering Higher- Compared with Lower-Dairy Second Meals Daily in Preschools in Guinea-Bissau Demonstrates an Attendance-Dependent Increase in Weight Gain for Both Meal Types and an Increase in Mid-Upper Arm Circumference for the Higher-Dairy Meal. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, A.; Elize, W.; Jean-Louis, F. Microfinance Institutions’ Successful Delivery Of Micronutrient Powders: A Randomized Trial In Rural Haiti. Health Aff. (Millwood) 2017, 36, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquey, E.; Ouedraogo, C.T.; Hess, S.Y.; Rouamba, N.; Prince, L.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Vosti, S.A.; Brown, K.H. Comparison of Preventive and Therapeutic Zinc Supplementation in Young Children in Burkina Faso: A Cluster-Randomized, Community-Based Trial. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougma, K.; Aboud, F.E.; Lemma, T.M.; Frongillo, E.A.; Marquis, G.S. Introduction of iodised salt benefits infants’ mental development in a community-based cluster-randomised effectiveness trial in Ethiopia. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S.; Piao, J.; Huo, J.; Yu, B.; Qu, N.; Lu, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Studies on the effectiveness of NaFeEDTA-fortified soy sauce in controlling iron deficiency: A population-based intervention trial. Food Nutr. Bull. 2005, 26, 177–186, discussion 187–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Gong, M.; Jiang, W.; Fan, Z.; Qu, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, T.Y. Effects of vitamin A, vitamin A plus zinc, and multiple micronutrients on anemia in preschool children in Chongqing, China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 21, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christian, P.; Shaikh, S.; Shamim, A.A.; Mehra, S.; Wu, L.; Mitra, M.; Ali, H.; Merrill, R.D.; Choudhury, N.; Parveen, M.; et al. Effect of fortified complementary food supplementation on child growth in rural Bangladesh: A cluster-randomized trial. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, C.A.; Dutra-De-Oliveira, J.E.; Crott, G.C.; Cantolini, A.; Ricco, R.G.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Baptista, M.E. Effect of fortification of drinking water with iron plus ascorbic acid or with ascorbic acid alone on hemoglobin values and anthropometric indicators in preschool children in day-care centers in Southeast Brazil. Food Nutr. Bull. 2005, 26, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, K.G.; Mridha, M.K.; Matias, S.L.; Arnold, C.D.; Cummins, J.R.; Khan, M.S.; Maalouf-Manasseh, Z.; Siddiqui, Z.; Ullah, M.B.; Vosti, S.A. Lipid-based nutrient supplementation in the first 1000 d improves child growth in Bangladesh: A cluster-randomized effectiveness trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinz, D.; Hurrell, R.F.; Ouattara, M.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Brittenham, G.M.; Adiossan, L.G.; Righetti, A.A.; Seifert, B.; Diakite, V.G.; Utzinger, J.; et al. The effect of iron-fortified complementary food and intermittent preventive treatment of malaria on anaemia in 12- to 36-month-old children: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadler, M.C.; Sigulem, D.M.; Alves Mde, F.; Torres, V.M. Treatment and prevention of anemia with ferrous sulfate plus folic acid in children attending daycare centers in Goiania, Goias State, Brazil: A randomized controlled trial. Cad. Saude Publica 2008, 24 (Suppl. 2), S259–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, S.Y.; Abbeddou, S.; Jimenez, E.Y.; Some, J.W.; Vosti, S.A.; Ouedraogo, Z.P.; Guissou, R.M.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Brown, K.H. Small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements, regardless of their zinc content, increase growth and reduce the prevalence of stunting and wasting in young burkinabe children: A cluster-randomized trial. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, M.; Lekamwasam, S.; Liyanage, C. Long-term cereal-based nutritional supplementation improved the total spine bone mineral density amongst Sri Lankan preschool children: A randomized controlled study. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 23, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybregts, L.; Houngbe, F.; Salpeteur, C.; Brown, R.; Roberfroid, D.; Ait-Aissa, M.; Kolsteren, P. The effect of adding ready-to-use supplementary food to a general food distribution on child nutritional status and morbidity: A cluster-randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isanaka, S.; Barnhart, D.A.; McDonald, C.M.; Ackatia-Armah, R.S.; Kupka, R.; Doumbia, S.; Brown, K.H.; Menzies, N.A. Cost-effectiveness of community-based screening and treatment of moderate acute malnutrition in Mali. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, S.J.; Ou, K.; Chea, M.; Chhin, L.; Devenish, R.; Dunbar, M.; Eang, C.; Hou, K.; Ly, S.; Khin, M.; et al. Effect of micronutrient sprinkles on reducing anemia: A cluster-randomized effectiveness trial. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Port, A.; Bernard, T.; Hidrobo, M.; Birba, O.; Rawat, R.; Ruel, M.T. Delivery of iron-fortified yoghurt, through a dairy value chain program, increases hemoglobin concentration among children 24 to 59 months old in Northern Senegal: A cluster-randomized control trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Lucia, C.M.; Santos, L.L.M.; Silva, B.P.d.; Anunciação, P.C.; Alfenas, R.d.C.G.; Franceschini, S.d.C.C.; Martino, H.S.D.; Sant’Ana, H.M.P. Impact of rice fortified with iron, zinc, thiamine and folic acid on laboratory measurements of nutritional status of preschool children. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2017, 22, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeen, E.; Schueth, T.; Toktobaev, N.; Zlotkin, S.; Hyder, S.M.; Houser, R. Daily use of Sprinkles micronutrient powder for 2 months reduces anemia among children 6 to 36 months of age in the Kyrgyz Republic: A cluster-randomized trial. Food Nutr. Bull. 2010, 31, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Yue, A.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Martorell, R.; Medina, A.; Rozelle, S.; Sylvia, S. The effect of a micronutrient powder home fortification program on anemia and cognitive outcomes among young children in rural China: A cluster randomized trial. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, X.; Hambidge, K.M. The Effect of Iron Fortification on Iron (Fe) Status and Inflammation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestel, P.; Nalubola, R.; Sivakaneshan, R.; Wickramasinghe, A.R.; Atukorala, S.; Wickramanayake, T. The use of iron-fortified wheat flour to reduce anemia among the estate population in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2004, 74, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.N.; Berger, J.; Dao, T.Q.; Nguyen, C.K.; Traissac, P.; Ha, H.K. [Efficacy of daily and weekly iron supplementation for the control of iron deficiency anaemia in infants in rural Vietnam]. Sante 2002, 12, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira Arcanjo, F.P.; Santos, P.R.; Arcanjo, C.P.; Amancio, O.M.; Braga, J.A. Use of iron-fortified rice reduces anemia in infants. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2012, 58, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, A.K.; Pandey, P.; Spiro, D.; Adhikari, D.; Haselow, N.; De Morais, C.; Davis, D. Adding multiple micronutrient powders to a homestead food production programme yields marginally significant benefit on anaemia reduction among young children in Nepal. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 4), 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phu, P.V.; Hoan, N.V.; Salvignol, B.; Treche, S.; Wieringa, F.T.; Khan, N.C.; Tuong, P.D.; Berger, J. Complementary foods fortified with micronutrients prevent iron deficiency and anemia in Vietnamese infants. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.A.; Shamah, T.; Villalpando, S.; Monterrubio, E. Effectiveness of a large-scale iron-fortified milk distribution program on anemia and iron deficiency in low-income young children in Mexico. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazawal, S.; Dhingra, P.; Dhingra, U.; Gupta, S.; Iyengar, V.; Menon, V.P.; Sarkar, A.; Black, R.E. Compliance with home-based fortification strategies for delivery of iron and zinc: Its effect on haematological and growth markers among 6-24 months old children in north India. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2014, 32, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharieff, W.; Yin, S.A.; Wu, M.; Yang, Q.; Schauer, C.; Tomlinson, G.; Zlotkin, S. Short-term daily or weekly administration of micronutrient Sprinkles has high compliance and does not cause iron overload in Chinese schoolchildren: A cluster-randomised trial. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Parikh, P.; Desai, F. Effect of daily versus weekly iron folic acid supplementation on the haemoglobin levels of children 6 to 36 months of urban slums of Vadodara. Indian J. Community Med. 2011, 2, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Siega-Riz, A.M.; Estrada Del Campo, Y.; Kinlaw, A.; Reinhart, G.A.; Allen, L.H.; Shahab-Ferdows, S.; Heck, J.; Suchindran, C.M.; Bentley, M.E. Effect of supplementation with a lipid-based nutrient supplement on the micronutrient status of children aged 6–18 months living in the rural region of Intibuca, Honduras. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2014, 28, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasse, Y.E.; Dramaix, M.; Traore, B.; Ngabonziza, I.; Toure, O.; Konate, M.; Diallo, M.; Donnen, P. The WHO recommendation of home fortification of foods with multiple-micronutrient powders in children under 2 years of age and its effectiveness on anaemia and weight: A pragmatic cluster-randomized controlled trial. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soofi, S.; Cousens, S.; Iqbal, S.P.; Akhund, T.; Khan, J.; Ahmed, I.; Zaidi, A.K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Effect of provision of daily zinc and iron with several micronutrients on growth and morbidity among young children in Pakistan: A cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielsch, J.M.; Khatry, S.K.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Katz, J.; LeClerq, S.C.; Adhikari, R.; Mullany, L.C.; Shresta, S.; Black, R.E. Effect of routine prophylactic supplementation with iron and folic acid on preschool child mortality in southern Nepal: Community-based, cluster-randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 367, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, J.L.; Das, S.; Sankar, R.; Mannar, M.G.; Levinson, F.J.; Hamer, D.H. Community-level micronutrient fortification of a food supplement in India: A controlled trial in preschool children aged 36–66 months. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, J.; Sharma, S. Impact of micronutrients sprinkle on weight and height of children aged 6–36 months in Tonk district of Rajasthan state. Indian J Community Health 2014, 26, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- West, K.P., Jr.; Katz, J.; Shrestha, S.R.; LeClerq, S.C.; Khatry, S.K.; Pradhan, E.K.; Adhikari, R.; Wu, L.S.; Pokhrel, R.P.; Sommer, A. Mortality of infants < 6 mo of age supplemented with vitamin A: A randomized, double-masked trial in Nepal. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotkin, S.; Newton, S.; Aimone, A.M.; Azindow, I.; Amenga-Etego, S.; Tchum, K.; Mahama, E.; Thorpe, K.E.; Owusu-Agyei, S. Effect of iron fortification on malaria incidence in infants and young children in Ghana: A randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcanjo, F.P.N.; da Costa Rocha, T.C.; Arcanjo, C.P.C.; Santos, P.R. Micronutrient Fortification at Child-Care Centers Reduces Anemia in Young Children. J. Diet. Suppl. 2019, 16, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galasso, E.; Weber, A.M.; Stewart, C.P.; Ratsifandrihamanana, L.; Fernald, L.C.H. Effects of nutritional supplementation and home visiting on growth and development in young children in Madagascar: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1257–e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.A.; Strutt, N.R.; Otoo, G.E.; Suri, D.J.; Ankrah, J.; Johnson, T.; Nsiah, P.; Furuta, C.; Murakami, H.; Perera, G.; et al. A macro- and micronutrient-fortified complementary food supplement reduced acute infection, improved haemoglobin and showed a dose-response effect in improving linear growth: A 12-month cluster randomised trial. J. Nutr. Sci. 2019, 8, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, L.M.; Young, M.F.; Bauer, P.J.; Mehta, R.; Girard, A.W.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Verma, P.; Chaudhuri, I.; Srikantiah, S.; Martorell, R. Effectiveness of a home fortification programme with multiple micronutrients on infant and young child development: A cluster-randomised trial in rural Bihar, India. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchdev, P.S.; Ruth, L.J.; Woodruff, B.A.; Mbakaya, C.; Mandava, U.; Flores-Ayala, R.; Jefferds, M.E.; Quick, R. Selling Sprinkles micronutrient powder reduces anemia, iron deficiency, and vitamin A deficiency in young children in Western Kenya: A cluster-randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, S.P.; Rahman, M.; Arnold, B.F.; Unicomb, L.; Ashraf, S.; Winch, P.J.; Stewart, C.P.; Begum, F.; Hussain, F.; Benjamin-Chung, J.; et al. Effects of water quality, sanitation, handwashing, and nutritional interventions on diarrhoea and child growth in rural Bangladesh: A cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e302–e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Null, C.; Stewart, C.P.; Pickering, A.J.; Dentz, H.N.; Arnold, B.F.; Arnold, C.D.; Benjamin-Chung, J.; Clasen, T.; Dewey, K.G.; Fernald, L.C.H.; et al. Effects of water quality, sanitation, handwashing, and nutritional interventions on diarrhoea and child growth in rural Kenya: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e316–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, D.K.; Leroy, J.; Bliznashka, L.; Ruel, M.T. PROCOMIDA, a Food-Assisted Maternal and Child Health and Nutrition Program, Reduces Child Stunting in Guatemala: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Intervention Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrazik, N.; Al-Haggar, M.; Al-Marsafawy, H.; Abdel-Hadi, H.; Al-Baz, R.; Mostafa, A.H. Impact of long-term oral iron supplementation in breast-fed infants. Indian J. Pediatr. 2007, 74, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, A.M.O.; Santos, L.M.P.; Prado, M.d.S.; Martins, M.C.; Barreto, M.L. Tolerance of vitamin A application associated with mass immunization of children in Northeast Brazil. Cad. Saude Publica 2000, 16, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cardoso, M.A.; Augusto, R.A.; Bortolini, G.A.; Oliveira, C.S.; Tietzman, D.C.; Sequeira, L.A.; Hadler, M.C.; Peixoto Mdo, R.; Muniz, P.T.; Vitolo, M.R.; et al. Effect of Providing Multiple Micronutrients in Powder through Primary Healthcare on Anemia in Young Brazilian Children: A Multicentre Pragmatic Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutter, C.K.; Rodriguez, A.; Fuenmayor, G.; Avila, L.; Sempertegui, F.; Escobar, J. Growth and micronutrient status in children receiving a fortified complementary food. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Szarfarc, S.C.; Brunken, G.S.; Gross, R.; Conde, W.L. Long-term preventive mass prescription of weekly doses of iron sulfate may be highly effective to reduce endemic child anemia. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2001, 22, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslihah, N.; Khomsan, A.; Briawan, D.; Riyadi, H. Complementary food supplementation with a small-quantity of lipid-based nutrient supplements prevents stunting in 6–12-month-old infants in rural West Madura Island, Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 25, S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.K.M.; Balamurugan, A.S. Effect of iron prophylaxis in preventing iron deficiency anaemia in term infants. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2017, 6, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.S.; Sampaio, P.; Muniz, P.T.; Cardoso, M.A.; Group, E.W. Multiple micronutrients in powder delivered through primary health care reduce iron and vitamin A deficiencies in young Amazonian children. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrour-Aissou, C.; Dupre, T.; Grangaud, J.P.; Assami, M.K. Impact of vitamin D supplementation model on the circulating levels of 25 (OH) D in Algerian children aged 1-23 months. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 196, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez de Romana, D.; Verona, S.; Vivanco, O.A.; Gross, R. Protective effect of multimicronutrient supplementation against anemia among children, women, and adolescent girls in lower-income areas of Chiclayo, Peru. Food Nutr. Bull. 2006, 27, S143–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooze, S.; Mathieu, F.; Claus, W.; Yangzom, T.; Yangzom, D.; Goyens, P.; de Maertelaer, V. Effect of calcium and vitamin D on growth, rickets and Kashin-Beck disease in 0- to 5-year-old children in a rural area of central Tibet. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2016, 21, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, Y. The impact of vitamin A supplementation in childhood on adult outcomes: An exploration of mechanisms, timing of exposure, and heterogeneous effects. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 201, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, H.M.; Thakur, J.S.; Bhatia, S.P. Impact of mass supplementation of vitamin A. Indian J. Pediatr. 2007, 74, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.J.; Pandey, A.; Singh, P. An evaluation of the ICDS food fortification in Uttarakhand. Indian J. Community Health 2012, 24, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Boo, F.; Palloni, G.; Urzua, S. Cost-benefit analysis of a micronutrient supplementation and early childhood stimulation program in Nicaragua. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1308, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.; Brouwer, I.D.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Adish, A.; Kebede, A.; De-Regil, L.M.; Osendarp, S.J.M. Effectiveness of a Program Intervention with Reduced-Iron Multiple Micronutrient Powders on Iron Status, Morbidity and Growth in Young Children in Ethiopia. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, G.R.; Leslie, P.W.; Wang, S.H.; Jiang, X.M.; Zhang, M.L.; Rakeman, M.; Jiang, J.Y.; Ma, T.; Cao, X.Y. Effect on infant mortality of iodination of irrigation water in a severely iodine-deficient area of China. Lancet 1997, 350, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, M.W.; Hye, A.; Wijnroks, M.; Ralte, A.; West, K.P., Jr.; Sommer, A. The role of universal distribution of vitamin A capsules in combatting vitamin A deficiency in Bangladesh. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 142, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, S. Effect of a single high dose vitamin A supplementation on the hemoglobin status of children aged 6-59 months: Propensity score matched retrospective cohort study based on the data of Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey 2011. BMC Pediatr 2014, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisker, A.B.; Aaby, P.; Rodrigues, A.; Frydenberg, M.; Bibby, B.M.; Benn, C.S. Vitamin A supplementation at birth might prime the response to subsequent vitamin A supplements in girls. Three year follow-up of a randomized trial. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogia, S.; Sachdev, H.S. Neonatal vitamin A supplementation for prevention of mortality and morbidity in infancy: Systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2009, 338, b919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.M.; Baqui, A.H.; Zaman, K.; Ake Persson, L.; El Arifeen, S.; Le, K.; McNary, S.W.; Parveen, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Black, R.E. Iron and zinc supplementation promote motor development and exploratory behavior among Bangladeshi infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, T.; Lonnerdal, B.; Stenlund, H.; Gamayanti, I.L.; Ismail, D.; Seswandhana, R.; Persson, L.A. A community-based randomized controlled trial of iron and zinc supplementation in Indonesian infants: Effects on growth and development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongcharoen, T.; DiGirolamo, A.M.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Winichagoon, P.; Flores, R.; Martorell, R. Long-term effects of iron and zinc supplementation during infancy on cognitive function at 9 y of age in northeast Thai children: A follow-up study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.R.; Hayes, E.; Kalumba, K.; Biggs, B.A. Effect of daily iron supplementation on health in children aged 4-23 months: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e77–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, M.; Farrell, A.; Biggs, B.A.; Pasricha, S.R. Effects of daily iron supplementation in primary-school-aged children: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. CMAJ 2013, 185, E791–E802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Biggs, B.A.; Pasricha, S.R. Effects of daily iron supplementation in 2- to 5-year-old children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guideline: Daily Iron Supplementation in Infants and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Swiztherland, 2016. [Google Scholar]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tam, E.; Keats, E.C.; Rind, F.; Das, J.K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020289
Tam E, Keats EC, Rind F, Das JK, Bhutta ZA. Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(2):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020289
Chicago/Turabian StyleTam, Emily, Emily C. Keats, Fahad Rind, Jai K. Das, and Zulfiqar A. Bhutta. 2020. "Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 12, no. 2: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020289
APA StyleTam, E., Keats, E. C., Rind, F., Das, J. K., & Bhutta, Z. A. (2020). Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12(2), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020289




