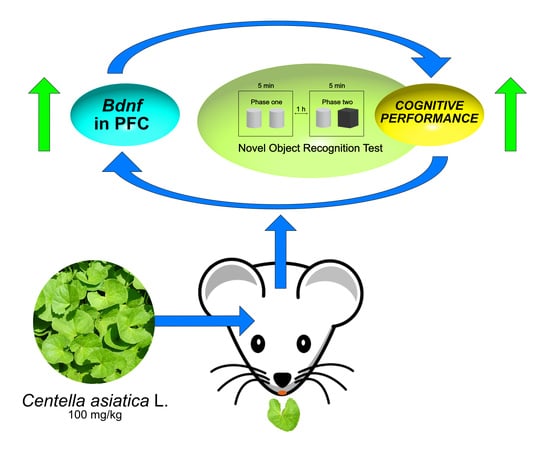
Centella asiatica L. Phytosome Improves Cognitive Performance by Promoting Bdnf Expression in Rat Prefrontal Cortex
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sbrini, G.; Brivio, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Giavarini, F.; Caruso, D.; Racagni, G.; Dell’Agli, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Calabrese, F. Centella asiatica L. Phytosome Improves Cognitive Performance by Promoting Bdnf Expression in Rat Prefrontal Cortex. Nutrients 2020, 12, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020355
Sbrini G, Brivio P, Fumagalli M, Giavarini F, Caruso D, Racagni G, Dell’Agli M, Sangiovanni E, Calabrese F. Centella asiatica L. Phytosome Improves Cognitive Performance by Promoting Bdnf Expression in Rat Prefrontal Cortex. Nutrients. 2020; 12(2):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020355
Chicago/Turabian StyleSbrini, Giulia, Paola Brivio, Marco Fumagalli, Flavio Giavarini, Donatella Caruso, Giorgio Racagni, Mario Dell’Agli, Enrico Sangiovanni, and Francesca Calabrese. 2020. "Centella asiatica L. Phytosome Improves Cognitive Performance by Promoting Bdnf Expression in Rat Prefrontal Cortex" Nutrients 12, no. 2: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020355
APA StyleSbrini, G., Brivio, P., Fumagalli, M., Giavarini, F., Caruso, D., Racagni, G., Dell’Agli, M., Sangiovanni, E., & Calabrese, F. (2020). Centella asiatica L. Phytosome Improves Cognitive Performance by Promoting Bdnf Expression in Rat Prefrontal Cortex. Nutrients, 12(2), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020355