Probiotic Bacillus Spores Protect Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of MegaSporeBiotic™ and Silymarin on Liver Functions
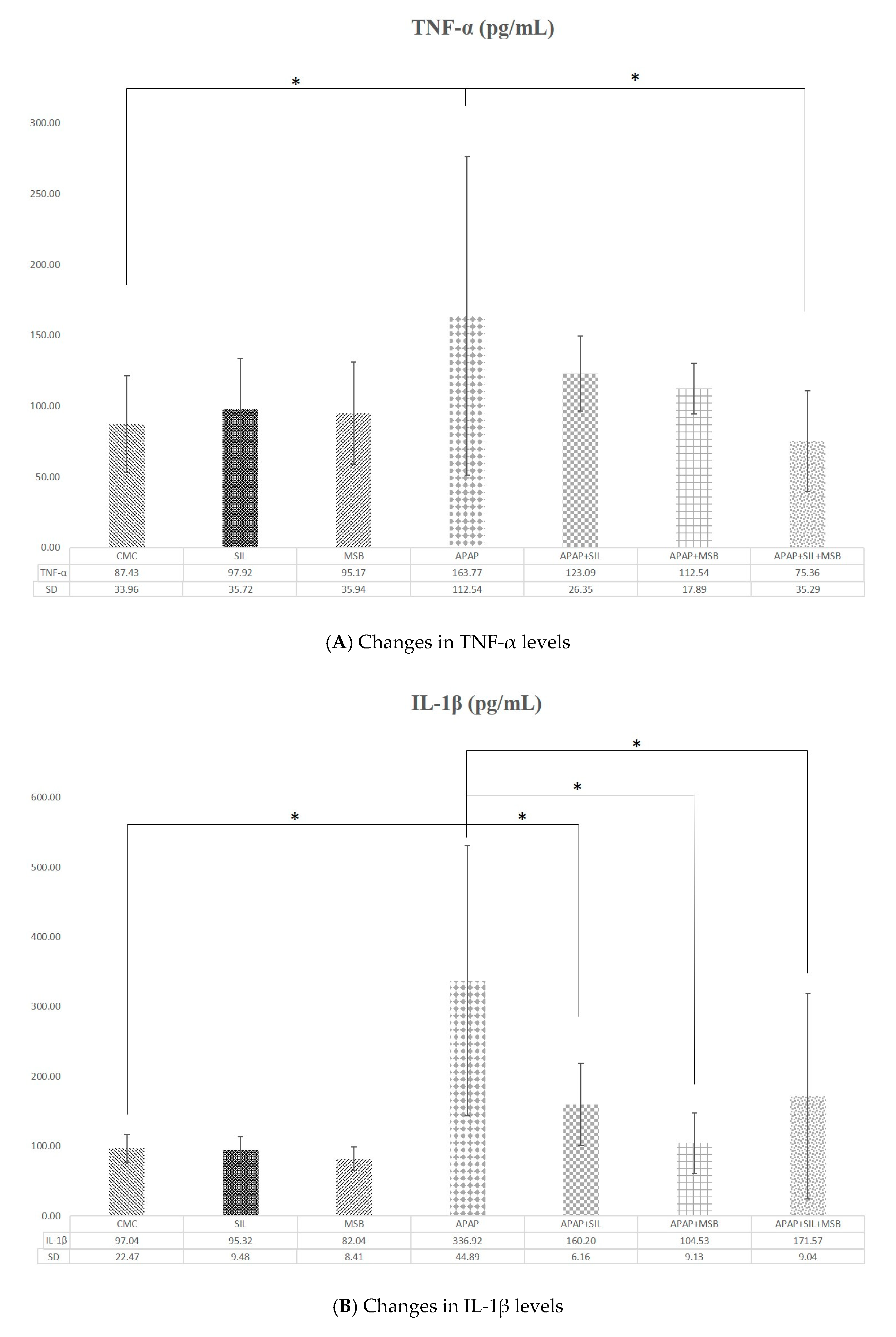
3.2. Effect of MegaSporeBiotic™ and Silymarin on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
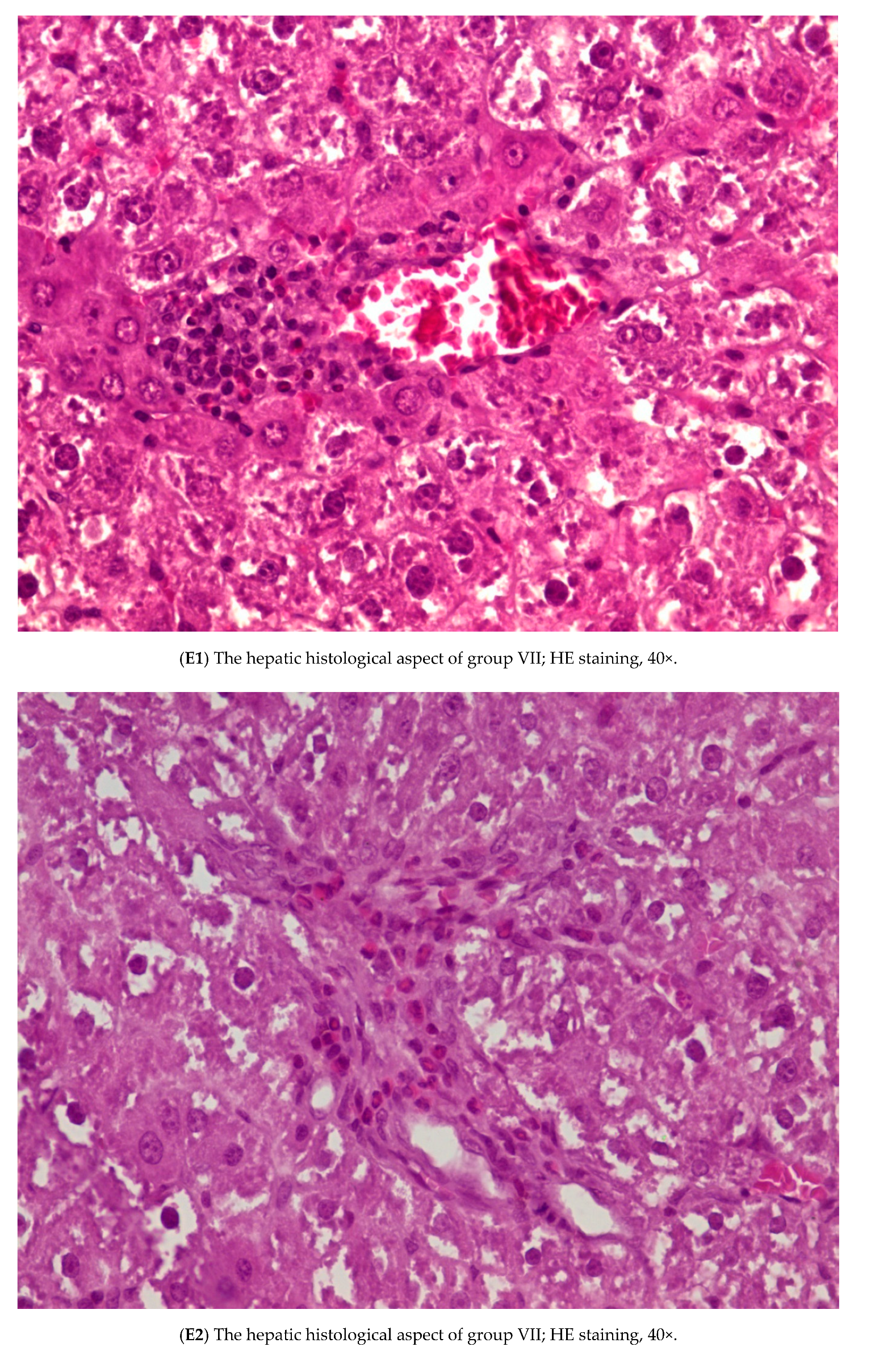
3.3. Histopathology
3.4. Effect of MegaSporeBiotic™ and Silymarin on Tight Junction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandit, A.; Sachdeva, T.; Bafna, P. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity: A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghanem, C.I.; Pérez, M.J.; Manautou, J.E.; Mottino, A.D. Acetaminophen from liver to brain: New insights into drug pharmacological action and toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 109, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Mccullough, S.S.; Hennings, L.; Letzig, L.; Simpson, P.M.; Hinson, J.A.; James, L.P. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and HIF-1 α induction in acetaminophen toxicity in mice occurs without hypoxia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W. Protective effects of p-coumaric acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, C. Inhibition of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by exogenous thymosinβ4 treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.A.; Jresat, I. Hepatoprotective effect of coenzyme Q10 in rats with acetaminophen toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, A.; Abdelkader, A.; Abdo, M.; Wareth, G.; Aboubakr, M.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M. Protective effect of cinnamon against acetaminophen-mediated cellular damage and apoptosis in renal tissue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.; Abushouk, A.I.; Reggi, R.; Yarla, N.S.; Palmery, M.; Peluso, I. Association of antioxidant nutraceuticals and acetaminophen (paracetamol): Friend or foe? J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, S78–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usami, M.; Miyoshi, M.; Yamashita, H. Gut microbiota and host metabolism in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11597–11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamirano-Barrera, A.; Uribe, M.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Nuño-Lámbarri, N. The role of the gut microbiota in the pathology and prevention of liver disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catinean, A.; Neag, M.A.; Mitre, A.O.; Bocsan, C.I.; Buzoianu, A.D. Microbiota and Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases—An Overview. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Van Doan, H. Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khadragy, M.F.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Elmallah, M.I.Y.; Alharbi, A.M.; Yehia, H.M.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. Probiotics and yogurt modulate oxidative stress and fibrosis in livers of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Hou, F.; Muhammad, A.I.; Ruiling, L.V.; Watharkar, R.B.; Guo, M.; Ding, T.; Liu, D. Synergistic inactivation and mechanism of thermal and ultrasound treatments against Bacillus subtilis spores. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, T.; Vemuri, R.; Shastri, M.D.; Perera, A.P.; Tristram, S.; Stanley, R.; Eri, R. Probiotic Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 spores exhibit excellent in-vitro functional efficacy in simulated gastric survival, mucosal adhesion and immunomodulation. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catinean, A.; Neag, A.M.; Nita, A.; Buzea, M.; Buzoianu, A.D. Bacillus spp. spores-a promising treatment option for patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafari, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Hosseini, H.; Safaei, F.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Probiotic Bacillus: Fate during sausage processing and storage and influence of different culturing conditions on recovery of their spores. Food Res. Int. 2017, 95, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foligné, B.; Peys, E.; Vandenkerckhove, J.; Van hemel, J.; Dewulf, J.; Breton, J.; Pot, B. Spores from two distinct colony types of the strain Bacillus subtilis PB6 substantiate anti-inflammatory probiotic effects in mice. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Erel, O. A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cation. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, B.G.; Misiakos, E.P.; Fotiadis, C.; Stoidis, C.N. Antioxidant properties of probiotics and their protective effects in the pathogenesis of radiation-induced enteritis and colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, J.B.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Nie, H.; Qin, X.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Gong, Q. Curcumin protects against acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in hepatic injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7440–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, F.F.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Hepatoprotective and Antioxidant Activity of Dunaliella salina in Paracetamol-induced Acute Toxicity in Rats. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.P.; Zou, T.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, Y.Q. Antioxidant and DNA damage protecting activity of exopolysaccharides from the endophytic bacterium Bacillus Cereus SZ1. Molecules 2016, 21, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodali, V.P.; Sen, R. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of an exopolysaccharide from a probiotic bacterium. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duc, L.H.; Fraser, P.D.; Tam, N.K.M.; Cutting, S.M. Carotenoids present in halotolerant Bacillus spore formers. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 255, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulczyński, B.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Kmiecik, D. The role of carotenoids in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease—Current state of knowledge. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.V.; Pal, R.; Vaiphei, K.; Ola, R.P.; Singh, K. Hepatoprotection by carotenoids in isonia-Rifampicin induced hepatic injury in rats. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzo, R.; Mazzoli, A.; Cancelliere, R.; Bucci, A.; Naclerio, G.; Baccigalupi, L.; Cutting, S.M.; Ricca, E.; Iossa, S. Beneficial effects of carotenoid-producing cells of Bacillus indicus HU16 in a rat model of diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tetz, G.; Tetz, V. Bacteriophage infections of microbiota can lead to leaky gut in an experimental rodent model. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duysburgh, C.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Krishnan, K.; Bayne, T.F.; Marzorati, M. A synbiotic concept containing spore-forming Bacillus strains and a prebiotic fiber blend consistently enhanced metabolic activity by modulation of the gut microbiome in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhenyu, M.; Qiao, Y. Butyrate protects rat liver against total hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury with bowel congestion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Mohan, P.; Chinnakali, P.; Vairappan, B. Elevated systemic zonula occludens 1 is positively correlated with inflammation in cirrhosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.J.; Li, D.; Zhao, Q.; Lian, J.; Hu, T.T.; Hong, G.L.; Yao, Y.M.; Lu, Z.Q. Prognostic value of plasma tight-junction proteins for sepsis in emergency department: An observational study. Shock 2016, 45, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamal, W.; Treskes, P.; Samuel, K.; Sullivan, G.J.; Siller, R.; Srsen, V.; Morgan, K.; Bryans, A.; Kozlowska, A.; Koulovasilopoulos, A.; et al. Low-dose acetaminophen induces early disruption of cell-cell tight junctions in human hepatic cells and mouse liver. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlin, B.K.; Henning, A.L.; Bowman, E.M.; Gary, M.A.; Carbajal, K.M. Oral spore-based probiotic supplementation was associated with reduced incidence of post-prandial dietary endotoxin, triglycerides, and disease risk biomarkers. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2017, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lu, D.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, H.; Tu, C.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S. Curcumin Protects Against Intestinal Origin Endotoxemia in Rat Liver Cirrhosis by Targeting PCSK9. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, D.; Geven, C.; Leijte, G.P.; Pickkers, P. Experimental human endotoxemia as a model of systemic inflammation. Biochimie 2019, 159, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazka, M.E.; Elwell, M.R.; Holladay, S.D.; Wilson, R.E.; Luster, M.I. Histopathology of Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Changes: RolE of Interleukin 1α and Tumor Necrosis Factor α. Toxicol. Pathol. 1996, 24, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, K.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Nazifi, S.; Sajedianfard, J.; Eskandari, M.H. The effects of orally administered Bacillus coagulans and inulin on prevention and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 30876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dar, H.Y.; Pal, S.; Shukla, P.; Mishra, P.K.; Tomar, G.B.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Srivastava, R.K. Bacillus clausii inhibits bone loss by skewing Treg-Th17 cell equilibrium in postmenopausal osteoporotic mice model. Nutrition 2018, 54, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neag, M.A.; Catinean, A.; Muntean, D.M.; Pop, M.R.; Bocsan, C.I.; Botan, E.C.; Buzoianu, A.D. Probiotic Bacillus Spores Protect Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030632
Neag MA, Catinean A, Muntean DM, Pop MR, Bocsan CI, Botan EC, Buzoianu AD. Probiotic Bacillus Spores Protect Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats. Nutrients. 2020; 12(3):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030632
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeag, Maria Adriana, Adrian Catinean, Dana Maria Muntean, Maria Raluca Pop, Corina Ioana Bocsan, Emil Claudiu Botan, and Anca Dana Buzoianu. 2020. "Probiotic Bacillus Spores Protect Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats" Nutrients 12, no. 3: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030632
APA StyleNeag, M. A., Catinean, A., Muntean, D. M., Pop, M. R., Bocsan, C. I., Botan, E. C., & Buzoianu, A. D. (2020). Probiotic Bacillus Spores Protect Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats. Nutrients, 12(3), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030632







