The Sun’s Vitamin in Adult Patients Affected by Prader–Willi Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Design and Setting
2.2. Population Study
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- chronic diseases that could interfere with fluid homeostasis, such as liver or chronic renal diseases, cancer, and acute or chronic inflammatory diseases;
- altered levels of serum creatinine, serum calcium, or albumin;
- current therapy with calcium, osteoporosis therapies, and medications that may affect vitamin D absorption or metabolism including anti-inflammatory drugs, sex hormone therapy, statins and other hypolipidemic agents, and medications to reduce body weight;
- pacemakers or defibrillators that could potentially interfere with BIA assessment.
2.3. Power Size Justification
2.4. Anthropometric Measurements
2.5. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
2.6. Dietary Records
2.7. Assay Methods
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWS | Prader–Willi syndrome; 25OHD, 25-hydroxy vitamin D |
| BMI | body mass index |
| RDA | recommended dietary allowance |
| DXA | dual energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| rhGH | recombinant human growth hormone |
| SD | standard deviation |
| CVs | coefficients of variation |
| ROC | receiver operator characteristic |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CI | confidence interval |
References
- Savastano, S.; Barrea, L.; Savanelli, M.C.; Nappi, F.; Di Somma, C.; Orio, F.; Colao, A. Low vitamin D status and obesity: Role of nutritionist. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Savastano, S.; Di Somma, C.; Savanelli, M.C.; Nappi, F.; Albanese, L.; Orio, F.; Colao, A. Low serum vitamin D-status, air pollution and obesity: A dangerous liaison. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orces, C. The Association between Body Mass Index and Vitamin D Supplement Use among Adults in the United States. Cureus 2019, 11, e5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, S.B.; Schwartz, S.; Miller, J.L.; Driscoll, D.J. Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, J.; Holland, A.; Webb, T.; Butler, J.; Clarke, D.; Boer, H. Cognitive abilities and genotype in a population-based sample of people with Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2004, 48 Pt 2, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Formoso, G.; Pugliese, G.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Scarano, E.; Colao, A.; RESTARE. Prader-Willi syndrome: An uptodate on endocrine and metabolic complications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintini, D.; Pedicelli, S.; Bocchini, S.; Bizzarri, C.; Grugni, G.; Cappa, M.; Crinò, A. 25OH vitamin D levels in pediatric patients affected by Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, M.L.; Triador, L.; Gill, J.K.; Pakseresht, M.; Mager, D.; Field, C.J.; Haqq, A.M. Dietary intake in youth with prader-willi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.G.; Knehans, A.; Arnold, S.; Dionne, C.; Hoffman, L.; Turner, P.; Baldwin, J. The associations between diet and physical activity with body composition and walking a timed distance in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Scannapieco, M.; Di Somma, C.; Scacchi, M.; Aimaretti, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Marzullo, P. The lullaby of the sun: The role of vitamin D in sleep disturbance. Sleep Med. 2019, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, C.; Scarano, E.; Barrea, L.; Zhukouskaya, V.V.; Savastano, S.; Mele, C.; Scacchi, M.; Aimaretti, G.; Colao, A.; Marzullo, P. Vitamin D and Neurological Diseases: An Endocrine View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2482. [Google Scholar]
- Barrea, L.; Di Somma, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Tarantino, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Orio, F.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Nutrition, inflammation and liver-spleen axis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 3141–3158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Savanelli, M.C.; Di Somma, C.; Napolitano, M.; Megna, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Vitamin D and its role in psoriasis: An overview of the dermatologist and nutritionist. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altieri, B.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Mathieu, C.; Vallone, C.V.; Mascitelli, L.; Bizzaro, G.; Altieri, V.M.; Tirabassi, G.; Balercia, G.; et al. Does vitamin D play a role in autoimmune endocrine disorders? A proof of concept. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manousopoulou, A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Garbis, S.D.; Chrousos, G.P. Vitamin D and cardiovascular risk among adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Altieri, B.; Di Somma, C.; Bhattoa, H.P.; Laudisio, D.; Duval, G.T.; Pugliese, G.; Annweiler, C.; Orio, F.; et al. Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation. Myths and Realities with Regard to Cardiovascular Risk. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Braun, W.; Geisler, C.; Norman, K.; Müller, M.J. Body composition and cardiometabolic health: The need for novel concepts. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 638–644. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, G.; Grugni, G.; Nobili, V.; Agosti, F.; Saezza, A.; Sartorio, A. Is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease less frequent among women with Prader-Willi syndrome? Obes. Facts 2014, 7, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, G.; Grugni, G.; Tringali, G.; Marazzi, N.; Sartorio, A. Does segmental body composition differ in women with Prader-Willi syndrome compared to women with essential obesity? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chen, M.R.; Chuang, C.K.; Huang, C.Y.; Niu, D.M.; Lin, S.P. Assessment of body composition using bioelectrical impedance analysis in Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 719–723. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, G.; Grugni, G.; Tringali, G.; Agosti, F.; Sartorio, A. Assessment of fat-free mass from bioelectrical impedance analysis in obese women with Prader-Willi syndrome. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2015, 42, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bridges, N. What is the value of growth hormone therapy in Prader Willi syndrome? Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Grugni, G.; Tringali, G.; Tamini, S.; Marzullo, P.; Sartorio, A. Assessment of fat-free mass from bioelectrical impedance analysis in men and women with Prader-Willi syndrome: Cross-sectional study. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forbes, G.B. A distinctive obesity: Body composition provides the clue. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1540–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoro, M.F.; Talebizadeh, Z.; Butler, M.G. Body composition and fatness patterns in Prader-Willi syndrome: Comparison with simple obesity. Obesity 2006, 14, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orsso, C.E.; Mackenzie, M.; Alberga, A.S.; Sharma, A.M.; Richer, L.; Rubin, D.A.; Prado, C.M.; Haqq, A.M. The use of magnetic resonance imaging to characterize abnormal body composition phenotypes in youth with Prader-Willi syndrome. Metabolism 2017, 69, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Reus, L.; Zwarts, M.; van Vlimmeren, L.A.; Willemsen, M.A.; Otten, B.J.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W. Motor problems in Prader-Willi syndrome: A systematic review on body composition and neuromuscular functioning. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 956–969. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, D.A.; Cano-Sokoloff, N.; Castner, D.L.; Judelson, D.A.; Wright, P.; Duran, A.; Haqq, A.M. Update on body composition and bone density in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2013, 79, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla, P.; Bosio, L.; Manzoni, P.; Pietrobelli, A.; Beccaria, L.; Chiumello, G. Peculiar body composition in patients with Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Höybye, C.; Hilding, A.; Jacobsson, H.; Thorén, M. Metabolic profile and body composition in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome and severe obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3590–3597. [Google Scholar]
- Sode-Carlsen, R.; Farholt, S.; Rabben, K.F.; Bollerslev, J.; Schreiner, T.; Jurik, A.G.; Christiansen, J.S.; Höybye, C. Body composition, endocrine and metabolic profiles in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2010, 20, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Di Somma, C.; Maisto, M.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Trimethylamine N-oxide, Mediterranean diet, and nutrition in healthy, normal-weight adults: Also a matter of sex? Nutrition 2019, 62, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Di Somma, C.; Annunziata, G.; Megna, M.; Falco, A.; Balato, A.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Coffee consumption, metabolic syndrome and clinical severity of psoriasis: Good or bad stuff? Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1831–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Di Somma, C.; Macchia, P.E.; Falco, A.; Savanelli, M.C.; Orio, F.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Influence of nutrition on somatotropic axis: Milk consumption in adult individuals with moderate-severe obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savastano, S.; Di Somma, C.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Orio, F.; Finelli, C.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F.; Tarantino, G. Preliminary data on the relationship between circulating levels of Sirtuin 4, anthropometric and metabolic parameters in obese subjects according to growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 status. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2015, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body Mass Index. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Nishida, C.; Ko, G.T.; Kumanyika, S. Body fat distribution and noncommunicable diseases in populations: Overview of the 2008 WHO Expert Consultation on Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Arnone, A.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Salzano, C.; Pugliese, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Dietary Patterns and Body Composition in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Macchia, P.E.; Di Somma, C.; Falco, A.; Savanelli, M.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Mediterranean Diet and Phase Angle in a Sample of Adult Population: Results of a Pilot Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Macchia, P.E.; Di Somma, C.; Napolitano, M.; Balato, A.; Falco, A.; Savanelli, M.C.; Balato, N.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Bioelectrical phase angle and psoriasis: A novel association with psoriasis severity, quality of life and metabolic syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Fabbrocini, G.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Donnarumma, M.; Marasca, C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Role of Nutrition and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the Multidisciplinary Approach of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Evaluation of Nutritional Status and Its Association with Severity of Disease. Nutrients 2018, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, S.Z.; Hubbard, V.S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lukaski, H.C. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement: National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference Statement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64 (Suppl. 3), 524S–532S. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Manuel Gómez, J.; Lilienthal Heitmann, B.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. ESPEN. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, R.F. Bioelectrical impedance analysis: A review of principles and applications. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.S.; Bray, G.A.; Gemayel, N.; Kaplan, K. Effect of obesity on bioelectrical impedance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzer, S.; Grugni, G.; Tringali, G.; Sartorio, A. Prediction of basal metabolic rate in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Di Somma, C.; Laudisio, D.; Maisto, M.; de Alteriis, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) as Novel Potential Biomarker of Early Predictors of Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Altieri, B.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Annunziata, G.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A.; Savastano, S. Impact of Nutritional Status on Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (GEP-NET) Aggressiveness. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Di Somma, C.; Tramontano, G.; De Luca, V.; Illario, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Association between Mediterranean diet and hand grip strength in older adult women. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Tarantino, G.; Somma, C.D.; Muscogiuri, G.; Macchia, P.E.; Falco, A.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Circulating Levels of Sirtuin 4 in Obese Patients: A Novel Association. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 6101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turconi, G.; Guarcello, M.; Berzolari, F.G.; Carolei, A.; Bazzano, R.; Roggi, C. An evaluation of a colour food photography atlas as a tool for quantifying food portion size in epidemiological dietary surveys. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VITAMINE—Assunzione Raccomandata per la Popolazione (PRI) e Assunzione Adeguata (AI). Available online: https://sinu.it/2019/07/09/assunzione-raccomandata-per-la-popolazione-pri-e-assunzione-adeguata-ai/ (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Somma, C.D.; Laudisio, D.; Salzano, C.; Pugliese, G.; de Alteriis, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Sex Differences of Vitamin D Status across BMI Classes: An Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Di Somma, C.; Salzano, C.; Pugliese, G.; de Alteriis, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Phase Angle: A Possible Biomarker to Quantify Inflammation in Subjects with Obesity and 25(OH)D Deficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Annunziata, G.; Laudisio, D.; de Alteriis, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. A New Light on Vitamin D in Obesity: A Novel Association with Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savanelli, M.C.; Scarano, E.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Vuolo, L.; Rubino, M.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Di Somma, C. Cardiovascular risk in adult hypopituitaric patients with growth hormone deficiency: Is there a role for vitamin D? Endocrine 2016, 52, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M.; Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlister, K.L.; Fisher, K.L.; Dumont-Driscoll, M.C.; Rubin, D.A. The relationship between metabolic syndrome, cytokines and physical activity in obese youth with and without Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 31, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viardot, A.; Purtell, L.; Nguyen, T.V.; Campbell, L.V. Relative Contributions of Lean and Fat Mass to Bone Mineral Density: Insight from Prader-Willi Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Grugni, G.; Piacente, L.; Delvecchio, M.; Ventura, A.; Giordano, P.; Grano, M.; D’Amato, G.; Laforgia, D.; Crinò, A.; et al. Analysis of Circulating Mediators of Bone Remodeling in Prader-Willi Syndrome. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrein, K.; Scherkl, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Neuwersch-Sommeregger, S.; Köstenberger, M.; Tmava Berisha, A.; Martucci, G.; Pilz, S.; Malle, O. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Gallo, M.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Giacinto, P.D.; Sesti, F.; Prinzi, N.; Adinolfi, V.; Barucca, V.; Renzelli, V.; Muscogiuri, G.; et al. Nutritional status and follicular-derived thyroid cancer: An update. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 30, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, S.; Belfiore, A.; Di Somma, C.; Mauriello, C.; Rossi, A.; Pizza, G.; De Rosa, A.; Prestieri, G.; Angrisani, L.; Colao, A. Validity of bioelectrical impedance analysis to estimate body composition changes after bariatric surgery in premenopausal morbidly women. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

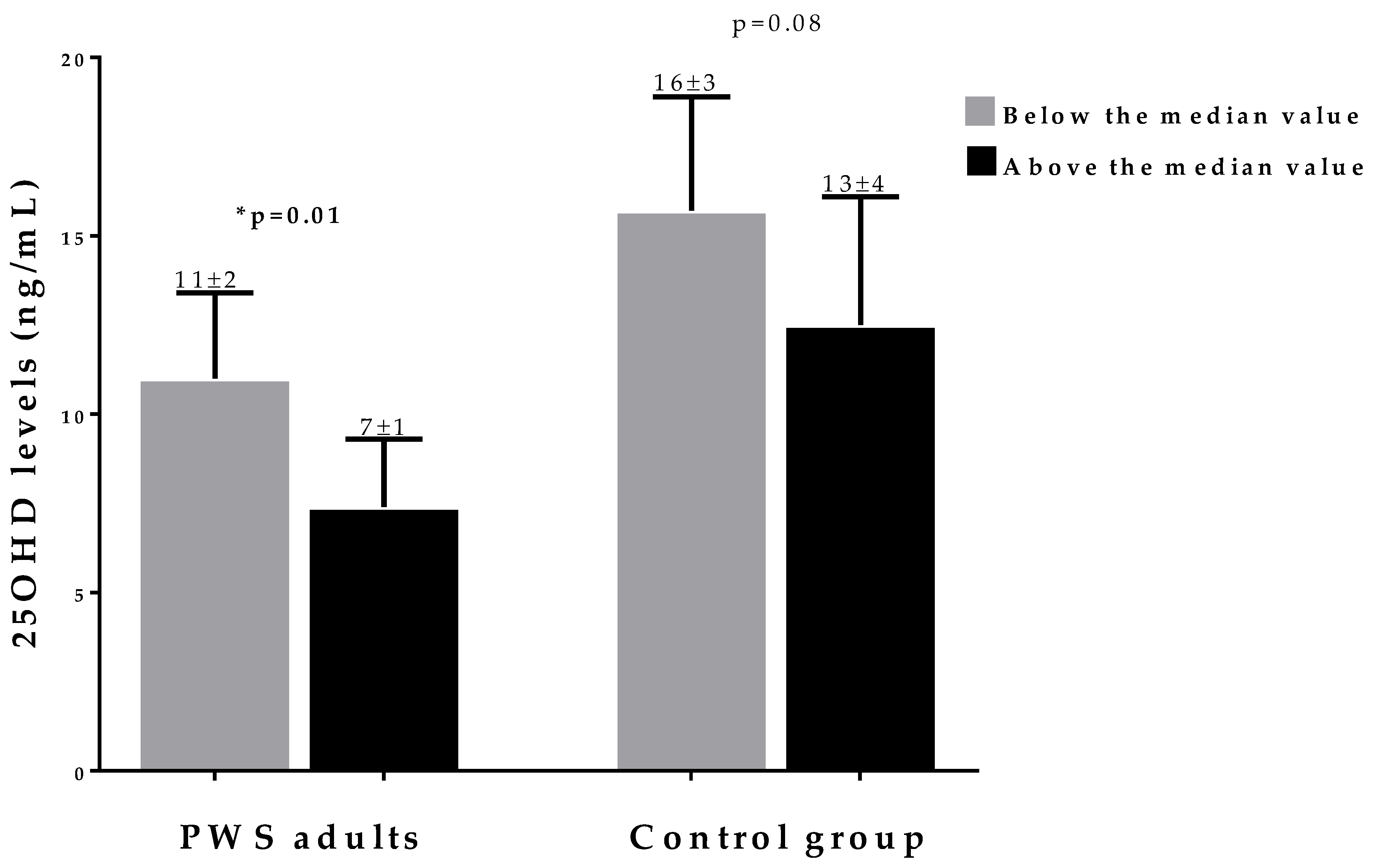


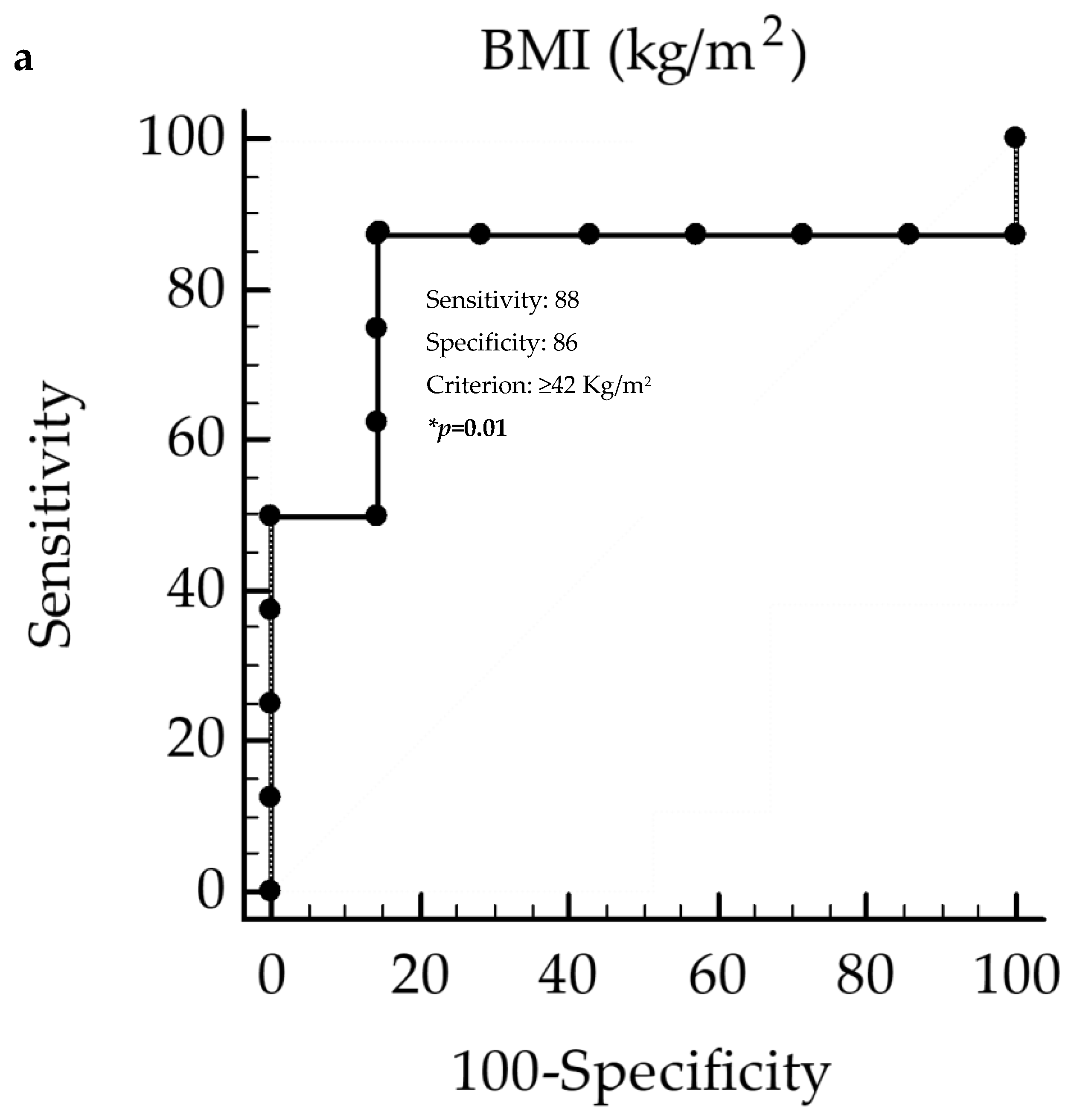
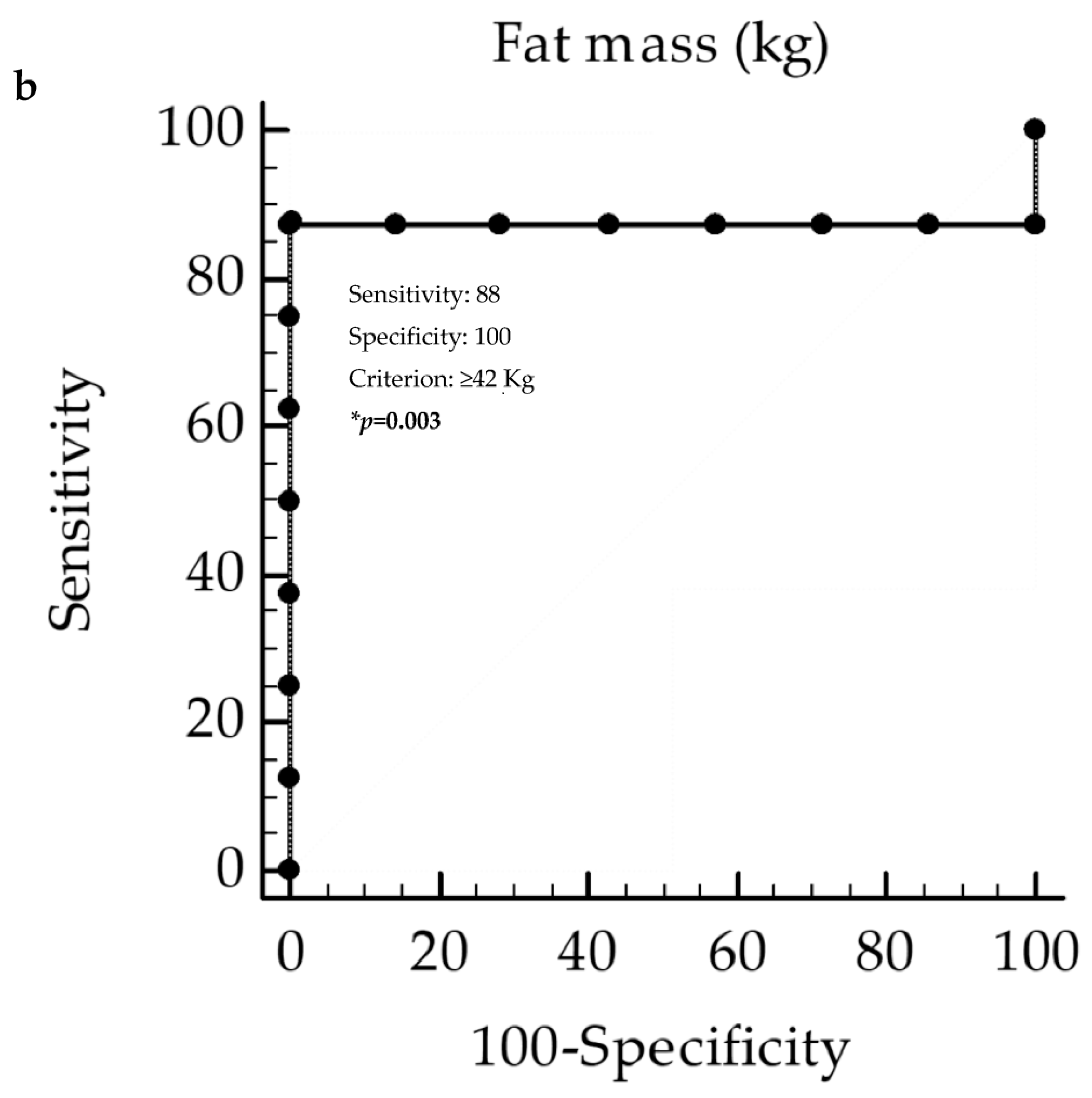
| Parameters | PWS Adults Mean ± SD or Number (%) n = 15 | Controls Mean ± SD or Number (%) n = 15 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M/F) | 6/9 (40/60%) | 6/9 (40/60%) | χ2 = 0.14, p = 0.71 |
| Age (years) | 28 ± 7 | 30 ± 7 | 0.66 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 44 ± 11 | 44 ± 9 | 0.21 |
| Grade I obesity | 3, 20% | 2, 13% | χ2 = 0.34, p = 0.84 |
| Grade II obesity | 3, 20% | 4, 27% | |
| Grade III obesity | 9, 60% | 9, 60% | |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 123 ± 28 | 113 ± 19 | 0.25 |
| Males | 136 ± 33 | 124 ± 16 | 0.49 |
| Females | 115 ± 21 | 105 ± 17 | 0.37 |
| Fat Mass (kg) | 50 ± 24 | 62 ± 23 | 0.26 |
| Males | 54 ± 34 | 73 ± 24 | 0.36 |
| Females | 47 ± 18 | 54 ± 19 | 0.51 |
| Dietary vitamin D intake (μg/1.000 kcal) | 4 ± 1 | 5 ± 1 | 0.01 |
| Parameters. | n = 15 | |
|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 0.12 | 0.68 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.52 | 0.04 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | −0.56 | 0.03 |
| Fat mass (kg) | −0.52 | 0.04 |
| Dietary vitamin D intake (μg/1.000 kcal) | 0.91 | <0.001 |
| Parameters. | Multiple Regression Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | β | t | p-Value | |
| Dietary Vitamin D Intake (μg/1.000 kcal) | 0.84 | 0.92 | 8.2 | <0.001 |
| Excluded variables: BMI, waist circumference, and fat mass | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pugliese, G.; Aprano, S.; de Alteriis, G.; Di Somma, C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. The Sun’s Vitamin in Adult Patients Affected by Prader–Willi Syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041132
Barrea L, Muscogiuri G, Pugliese G, Aprano S, de Alteriis G, Di Somma C, Colao A, Savastano S. The Sun’s Vitamin in Adult Patients Affected by Prader–Willi Syndrome. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041132
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrea, Luigi, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Gabriella Pugliese, Sara Aprano, Giulia de Alteriis, Carolina Di Somma, Annamaria Colao, and Silvia Savastano. 2020. "The Sun’s Vitamin in Adult Patients Affected by Prader–Willi Syndrome" Nutrients 12, no. 4: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041132
APA StyleBarrea, L., Muscogiuri, G., Pugliese, G., Aprano, S., de Alteriis, G., Di Somma, C., Colao, A., & Savastano, S. (2020). The Sun’s Vitamin in Adult Patients Affected by Prader–Willi Syndrome. Nutrients, 12(4), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041132









