Protective Effects of Myo-Inositol and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Thyroid Toxicity in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Protocol
2.2. Histological Evaluation
2.3. Immunohistochemistry for Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) and C-X-C Motif Chemokine 10 (CXCL10)
2.4. Morphometric and Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.5. Drugs and Chemicals
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
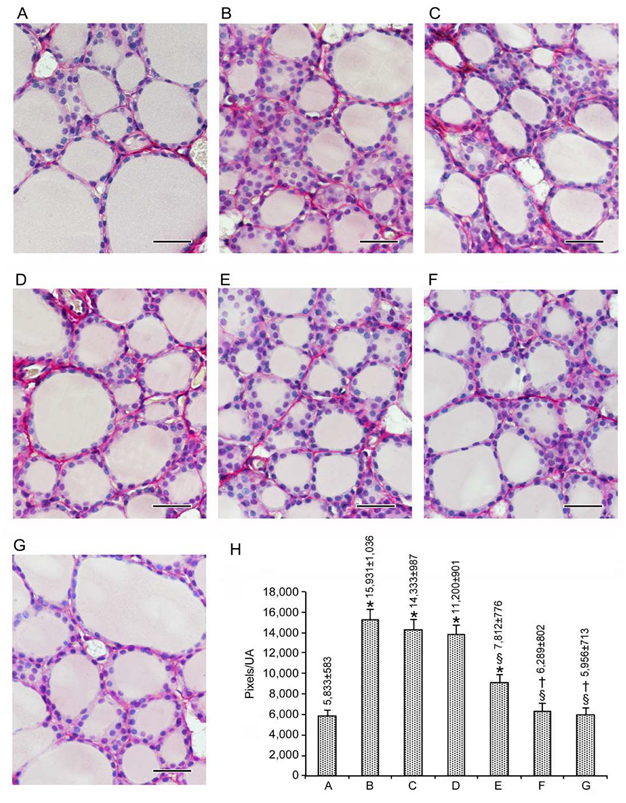
3.1. Histopathological Data
3.1.1. Follicular Epithelium
3.1.2. Stroma
3.2. Immunohistochemical Expression of MCP-1/CCL2
3.3. Immunohistochemical Expression of CXCL10
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiersinga, W.M. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. In Thyroid Diseases. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment; Vitti, P., Hegedus, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, L.; Morris, L.G.; Haymart, M.; Chen, A.Y.; Goldenberg, D.; Morris, J.; Ogilvie, J.B.; Terris, D.J.; Netterville, J.; Wong, R.J.; et al. AACE Endocrine Surgery Scientific Committee. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology disease state clinical review: The increasing incidence of thyroid cancer. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhrle, J. Environment and endocrinology: The case of thyroidology. Ann. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.K.; Salwan, P.; Salwan, S. Various possible toxicants involved in thyroid dysfunction: A review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, FE01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoeller, T.R. Environmental chemicals targeting thyroid. Hormones 2010, 9, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, F.; Mostafalou, S.; Bahadar, H.; Abdollahi, M. Review of endocrine disorders associated with environmental toxicants and possible involved mechanisms. Life Sci. 2016, 145, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, A.; Matovic, V.; Antonijevic, B.; Bulat, Z.; Curcic, M.; Renieri, E.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Schweitzer, A.; Wallace, D. Overview of Cadmium Thyroid Disrupting Effects and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A.; Vita, R. Thyroid nodules and thyroid autoimmunity in the context of environmental pollution. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenod, F.; Lee, W.K. Toxicology of cadmium and its damage in mammalian organs. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 11, 415–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoshes, M.; Vallee, B.L. A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Diwan, B. Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, V.; Buha, A.; Bulat, Z.; Đukić-Ćosić, D. Cadmium Toxicity Revisited: Focus on Oxidative Stress Induction and Interactions with Zinc and Magnesium. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2011, 62, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, V.; Buha, A.; Dukić-Ćosić, D.; Bulat, Z. Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, M.; Micali, A.; Marini, H.; Adamo, E.B.; Puzzolo, D.; Pisani, A.; Trichilo, V.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F.; Minutoli, L. Cadmium, organ toxicity and therapeutic approaches: A review on brain, kidney and testis damage. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3879–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezynska, M.; Brzóska, M.M. Environmental exposure to cadmium—A risk for health of the general population in industrialized countries and preventive strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3211–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetani, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Honda, R.; Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kido, T.; Nogawa, K. Tissue cadmium (Cd) concentrations of people living in a Cd polluted area, Japan. BioMetals 2006, 19, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Personal Habits and Indoor Combustions. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, S.C.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Urinary cadmium concentration and risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 182, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, A.; Wallace, D.; Matovic, V.; Schweitzer, A.; Oluic, B.; Micic, D.; Djordjevic, V. Cadmium Exposure as a Putative Risk Factor for the Development of Pancreatic Cancer: Three Different Lines of Evidence. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki-Tounsi, M.; Hamza-Chaffai, A. Cadmium as a possible cause of bladder cancer: A review of accumulated evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10561–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojsavljević, A.; Rovčanin, B.; Krstić, Đ.; Jagodić, J.; Borković-Mitić, S.; Paunović, I.; Živaljević, V.; Mitić, B.; Gavrović-Jankulović, M.; Manojlović, D. Cadmium as main endocrine disruptor in papillary thyroid carcinoma and the significance of Cd/Se ratio for thyroid tissue pathophysiology. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 55, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, F.; Messaoudi, I.; El Hani, J.; Baati, T.; Saïd, K.; Kerkeni, A. Reversal of cadmium-induced thyroid dysfunction by selenium, zinc, or their combination in rat. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 126, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, A.; Antonijević, B.; Bulat, Z.; Jaćević, V.; Milovanović, V.; Matović, V. The impact of prolonged cadmium exposure and co-exposure with polychlorinated biphenyls on thyroid function in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 221, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancic, S.A.; Stosic, B.Z. Cadmium effects on the thyroid gland. Vitam. Horm. 2014, 94, 391–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piłat-Marcinkiewicz, B.; Brzóska, M.M.; Sawicki, B.; Moniuszko-Jakoniuk, J. Structure and function of thyroid follicular cells in female rats chronically exposed to cadmium. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2003, 47, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Aaseth, J.; Frey, H.; Glattre, E.; Norheim, G.; Ringstad, J.; Thomassen, Y. Selenium concentrations in the human thyroid gland. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1990, 24, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrle, J.; Jakob, F.; Contempré, B.; Dumont, J.E. Selenium, the thyroid, and the endocrine system. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 944–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrle, J. Selenium and the thyroid. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duntas, L.H.; Benvenga, S. Selenium: An element for life. Endocrine 2015, 48, 756–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, N.V.; Raymond, L.J. Dietary selenium’s protective effects against methylmercury toxicity. Toxicology 2010, 278, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Han, B.; Li, Q.; Zhu, C.; Xia, F.; Zhai, H.; Wang, N.; et al. Lead and cadmium exposure, higher thyroid antibodies and thyroid dysfunction in Chinese women. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.M.; Moon, J.S.; Yoon, J.S.; Won, K.C.; Lee, H.W. Sex-specific effects of blood cadmium on thyroid hormones and thyroid function status: Korean nationwide cross-sectional study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 53, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Itoh, M.; Hirai, S.; Suna, S.; Naito, M.; Qu, N.; Terayama, H.; Ikeda, A.; Miyaso, H.; Matsuno, Y.; et al. Cadmium exposure increases susceptibility to testicular autoimmunity in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastero, R.N.; Vacchi-Suzzi, C.; Marsit, C.; Demple, B.; Meliker, J.R. Expression of Genes Involved in Stress, Toxicity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity in Relation to Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead in Human Blood: A Pilot Study. Toxics 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; Pant, M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2014, 24, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekheet, S.H. Comparative effects of repeated administration of cadmium chloride during pregnancy and lactation and selenium protection against cadmium toxicity on some organs in immature rats’ offsprings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, G.M.; Elsawy, H.; Sedky, A.; Eid, R.; Ali, A.; Abdallah, B.M.; Alzahrani, A.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.M. Protective effects of quercetin supplementation against short-term toxicity of cadmium-induced hematological impairment, hypothyroidism, and testicular disturbances in albino rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 8202–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenga, S.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Bonofiglio, D.; Asamoah, E. Nutraceutical Supplements in the Thyroid Setting: Health Benefits beyond Basic Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Micali, A.; Pallio, G.; Vita, R.; Malta, C.; Puzzolo, D.; Irrera, N.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Minutoli, L. Effects of Myo-inositol Alone and in Combination with Seleno-L-methionine on Cadmium-Induced Testicular Damage in Mice. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallio, G.; Micali, A.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A.; Marini, H.R.; Puzzolo, D.; Macaione, V.; Trichilo, V.; Santoro, G.; Irrera, N.; et al. Myo-inositol in the protection from cadmium-induced toxicity in mice kidney: An emerging nutraceutical challenge. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, R.A.; La Vignera, S.; Di Bari, F.; Unfer, V.; Calogero, A.E. Effects of myoinositol on sperm mitochondrial function in-vitro. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Condorelli, R.A.; La Vignera, S.; Bellanca, S.; Vicari, E.; Calogero, A.E. Myoinositol: Does it improve sperm mitochondrial function and sperm motility? Urology 2012, 79, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprio, F.; D’Eufemia, M.D.; Trotta, C.; Campitiello, M.R.; Ianniello, R.; Mele, D.; Colacurci, N. Myo-inositol therapy for poor-responders during IVF: A prospective controlled observational trial. J. Ovarian Res. 2015, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Kuang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Hu, K.; Li, S.H.; Tang, L.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Myo-inositol prevents copper-induced oxidative damage and changes in antioxidant capacity in various organs and the enterocytes of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, K.; Banba, N.; Motohashi, S.; Hattori, Y.; Manaka, K.; Shimoda, S.I. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 mRNA and protein in cultured human thyrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1996, 394, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Elia, G.; Ragusa, F.; Paparo, S.R.; Caruso, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Antonelli, A. Myo-inositol in autoimmune thyroiditis, and hypothyroidism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Di Bari, F.; Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. Myo-inositol and selenium reduce the risk of developing overt hypothyroidism in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benvenga, S.; Vicchio, T.; Di Bari, F.; Vita, R.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Catania, S.; Costa, C.; Antonelli, A. Favorable effects of myo-inositol, selenomethionine or their combination on the hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress of peripheral mononuclear cells from patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Preliminary in vitro studies. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nordio, M.; Basciani, S. Treatment with Myo-Inositol and Selenium Ensures Euthyroidism in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 2549491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Kar, A. Role of ascorbic acid in cadmium-induced thyroid dysfunction and lipid peroxidation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1998, 18, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleawa, S.M.; Alkhateeb, M.A.; Alhashem, F.H.; Bin-Jaliah, I.; Sakr, H.F.; Elrefaey, H.M.; Elkarib, A.O.; Alessa, R.M.; Haidara, M.A.; Shatoor, A.S.; et al. Resveratrol reverses cadmium chloride-induced testicular damage and subfertility by downregulating p53 and Bax and upregulating gonadotropins and Bcl-2 gene expression. J. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 60, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, A.; Hoseini, L.; Babai, A.; Noorafshan, A.; Haghbin, H.; Karbalay-Doust, S. Mitigating Effect of Resveratrol on the Structural Changes of Mice Liver and Kidney Induced by Cadmium; A Stereological Study. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 20, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giammanco, M.; Leto, G. Selenium and autoimmune thyroiditis. EC Nutr. 2019, 14, 449–450. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Sikder, M.T.; Akter, M.; Bondad, S.E.C.; Rahaman, M.S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. Selenium and zinc protections against metal-(loids)-induced toxicity and disease manifestations: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwolak, I. The Role of Selenium in Arsenic and Cadmium Toxicity: An Updated Review of Scientific Literature. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, N.; Xu, Z.; Liu, T.; Min, Y.; Li, S. Ameliorative Effects of Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Injury in the Chicken Ovary: Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cadmium-Induced Apoptosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Chen, J.X.; Wu, L.K.; Li, B.Y.; Tian, Y.F.; Xian, M.; Huang, Z.P.; Yu, R.A. Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Cadmium and Its Regulation on Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Kidneys of Rats. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. Inositol(s) in thyroid function, growth and autoimmunity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenta, G.; Caballero, A.S.; Nunes, M.T. Case finding for hypothyroidism should include type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome patients: A Latin American Thyroid Society (LATS) position statement. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hua, S.C.; Chang, C.H.; Kao, W.Y.; Lee, H.L.; Chuang, L.M.; Huang, Y.T.; Lai, M.S. High TSH Level within Normal Range Is Associated with Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Hypertension, Inflammation, Hypercoagulability, and the Metabolic Syndrome: A Novel Cardiometabolic Marker. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Tortora, A.; Ambrosino, P.; Lupoli, G.A.; Di Minno, M.N. Effects of treatment with metformin on TSH levels: A meta-analysis of literature studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E143–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimic, D.; Golubovic, M.V.; Radenkovic, S.; Radojkovic, D.; Pesic, M. The effect of metformin on TSH levels in euthyroid and hypothyroid newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus type 2 patients. Bratisl. Med. J. 2016, 117, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Fan, Q.; Li, H.; Di, Y. The Effect of Metformin on Thyroid-Associated Serum Hormone Levels and Physiological Indexes: A Meta-Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3257–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anna, R.; Di Benedetto, A.; Scilipoti, A.; Santamaria, A.; Interdonato, M.L.; Petrella, E.; Neri, I.; Pintaudi, B.; Corrado, F.; Facchinetti, F. Myo-inositol Supplementation for Prevention of Gestational Diabetes in Obese Pregnant Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 126, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anna, R.; Santamaria, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Corrado, F.; Di Benedetto, A.; Facchinetti, F. Myo-Inositol for the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. A Brief Review. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S59–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Melo, M.; Carrilho, F. Selenium and Thyroid Disease: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 1297658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benvenga, S.; Marini, H.R.; Micali, A.; Freni, J.; Pallio, G.; Irrera, N.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; et al. Protective Effects of Myo-Inositol and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Thyroid Toxicity in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051222
Benvenga S, Marini HR, Micali A, Freni J, Pallio G, Irrera N, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, et al. Protective Effects of Myo-Inositol and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Thyroid Toxicity in Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051222
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenvenga, Salvatore, Herbert R. Marini, Antonio Micali, Jose Freni, Giovanni Pallio, Natasha Irrera, Francesco Squadrito, Domenica Altavilla, Alessandro Antonelli, Silvia Martina Ferrari, and et al. 2020. "Protective Effects of Myo-Inositol and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Thyroid Toxicity in Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051222
APA StyleBenvenga, S., Marini, H. R., Micali, A., Freni, J., Pallio, G., Irrera, N., Squadrito, F., Altavilla, D., Antonelli, A., Ferrari, S. M., Fallahi, P., Puzzolo, D., & Minutoli, L. (2020). Protective Effects of Myo-Inositol and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Thyroid Toxicity in Mice. Nutrients, 12(5), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051222







