Protein Intakes during Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition Drive Growth Gain and Body Composition in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Nutritional Practices
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Body Composition Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Goudoever, J.B. Nutrition for Preterm Infants: 75 Years of History. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbury, M.R.; Unger, S.; Kiss, A.; Ng, D.V.Y.; Luk, Y.; Bando, N.; Bishara, R.; Tomlinson, C.; O’Connor, D.L.; GTA-DoMINO Feeding Group. Optimizing the growth of very-low-birth-weight infants requires targeting both nutritional and non-nutritional modifiable factors specific to stage of hospitalization. Am. J. Clin Nutr. 2019, 110, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.E.; Cormack, B.; Alexander, T.; Alsweiler, J.M.; Bloomfield, F.H. Advances in nutrition of the newborn infant. Lancet 2017, 389, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Vaidya, R.; Rastogi, D.; Bhutada, A.; Rastogi, S. From parenteral to enteral nutrition: A nutrition-based approach for evaluating postnatal growth failure in preterm infants. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, A.M.; Fenton, S.; Murphy, B.P.; Kiely, M.E. Transition Phase Nutrition Recommendations: A Missing Link in the Nutrition Management of Preterm Infants. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciglia, G.H.; Murthy, K.; Holl, J.L.; Palac, H.L.; Oumarbaeva, Y.; Woods, D.M.; Robinson, D.T. Energy and Protein Intake During the Transition from Parenteral to Enteral Nutrition in Infants of Very Low Birth Weight. J. Pediatr. 2018, 202, 38–43.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Donda, A.; Bhutada, A.; Rastogi, S. Transitioning Preterm Infants From Parenteral Nutrition: A Comparison of 2 Protocols. JPEN J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.M.; Kiely, M.E.; Fenton, S.; Murphy, B.P. Standardized parenteral nutrition for the transition phase in preterm infants: A bag that fits. Nutrients 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Amato, O.; Orsi, A.; Piemontese, P.; Morlacchi, L.; Mosca, F. Is term newborn body composition being achieved postnatally in preterm infants? Early Hum. Dev. 2009, 85, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner, M.; Khan, Z.; Binder, C.; Morris, N.; Windisch, B.; Holasek, S.; Urlesberger, B. Extremely Preterm Infants Have a Higher Fat Mass Percentage in Comparison to Very Preterm Infants at Term-Equivalent Age. Front Pediatr. 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmon, L.R.; Batton, D.G.; Bell, E.F.; Denson, S.E.; Engle, W.A.; Kanto, W.P.; Martin, G.I.; Stark, A. Age terminology during the perinatal period. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Morlacchi, L.; Mallardi, D.; Giannì, M.L.; Roggero, P.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Consonni, D.; Mosca, F. Is targeted fortification of human breast milk an optimal nutrition strategy for preterm infants? An interventional study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemontese, P.; Liotto, N.; Menis, C.; Mallardi, D.; Tabasso, C.; Perrone, M.; Bezze, E.; Plevani, L.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. Effect of Target Fortification on Osmolality and Microbiological Safety of Human Milk Over Time. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the european society of paediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition committee on nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21 st Century Anthropometry Handbook. 2012, pp. 1–59. Available online: https://www.medscinet.net/Interbio/Uploads/ProtocolDocs/Draft%20Anthropometry%20Handbook.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Fenton, T.R.; Ohuma, E.O.; Ismail, L.C.; Kennedy, S.H. INTERGROWTH-21st very preterm size at birth reference charts. Lancet 2016, 387, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Victora, C.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; et al. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bertino, E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Ismail, L.C.; Barros, F.C.; Altman, D.G.; Victora, C.; Noble, J.A.; et al. Postnatal growth standards for preterm infants: The Preterm Postnatal Follow-up Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet Glob. Heath 2015, 3, e681–e691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.L.; Engstrom, J.L.; Meier, P.P.; Kimura, R.E.; States, U.; States, U. Calculating Postnatal Growth Velocity in Very Low Birth Weight (VLBW) Premature Infants. J. Perinatol. 2010, 29, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Anderson, D.; Groh-Wargo, S.; Hoyos, A.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Senterre, T. An Attempt to Standardize the Calculation of Growth Velocity of Preterm Infants—Evaluation of Practical Bedside Methods. J. Pediatr. 2018, 196, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Yao, M.; Lin, Y.; Lin, A.; Zou, H.; Urlando, A.; Wong, W.W.; Nommsen-Rivers, L.; Dewey, K.G. Validation of a new pediatric air-displacement plethysmograph for assessing body composition in infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.J.; Yao, M.; Shypailo, R.J.; Urlando, A.; Wong, W.W.; Heird, W.C. Body-composition assessment in infancy: Air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomon, S.J.; Haschke, F.; Ziegler, E.E.; Nelson, S.E. Body composition of reference children from birth to age 10 years. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 35, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Morniroli, D.; Wong, W.W.; Mosca, F. Evaluation of air-displacement plethysmography for body composition assessment in preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 2012, 72, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Orsi, A.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Liotto, N.; Morlacchi, L.; Taroni, F.; Garavaglia, E.; Bracco, B.; et al. Implementation of Nutritional Strategies Decreases Postnatal Growth Restriction in Preterm Infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, T.; Ramel, S.E.; Catalano, P.; Caoimh, C.; Roggero, P.; Murray, D.; Fields, D.A.; Demerath, E.W.; Johnson, W. New charts for the assessment of body composition, according to air-displacement plethysmography, at birth and across the first 6 mo of life. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamatschek, C.; Yousuf, E.I.; Möllers, L.S.; So, H.Y.; Morrison, K.M.; Fusch, C.; Rochow, N. Fat and fat-free mass of preterm and term infants from birth to six months: A review of current evidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramel, S.E.; Haapala, J.; Super, J.; Boys, C.; Demerath, E.W. Nutrition, illness and body composition in very low birth weight preterm infants: Implications for nutritional management and neurocognitive outcomes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paviotti, G.; De Cunto, A.; Zennaro, F.; Boz, G.; Travan, L.; Cont, G.; Bua, J.D.S. Higher growth, fat and fat-free masses correlate with larger cerebellar volumes in preterm infants at term. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.K.; Chomtho, S.; Fewtrell, M.S. Programming of body composition by early growth and nutrition. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
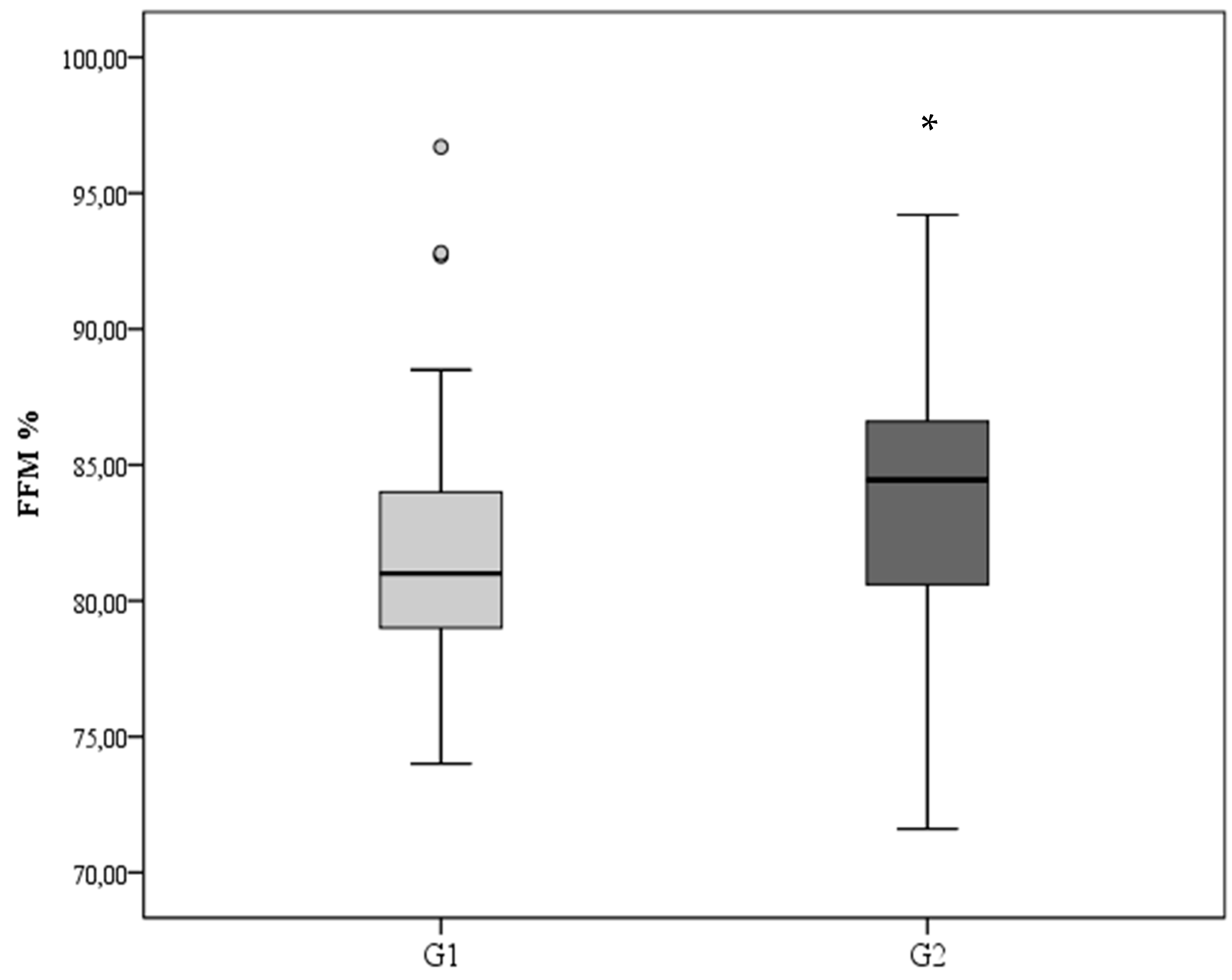
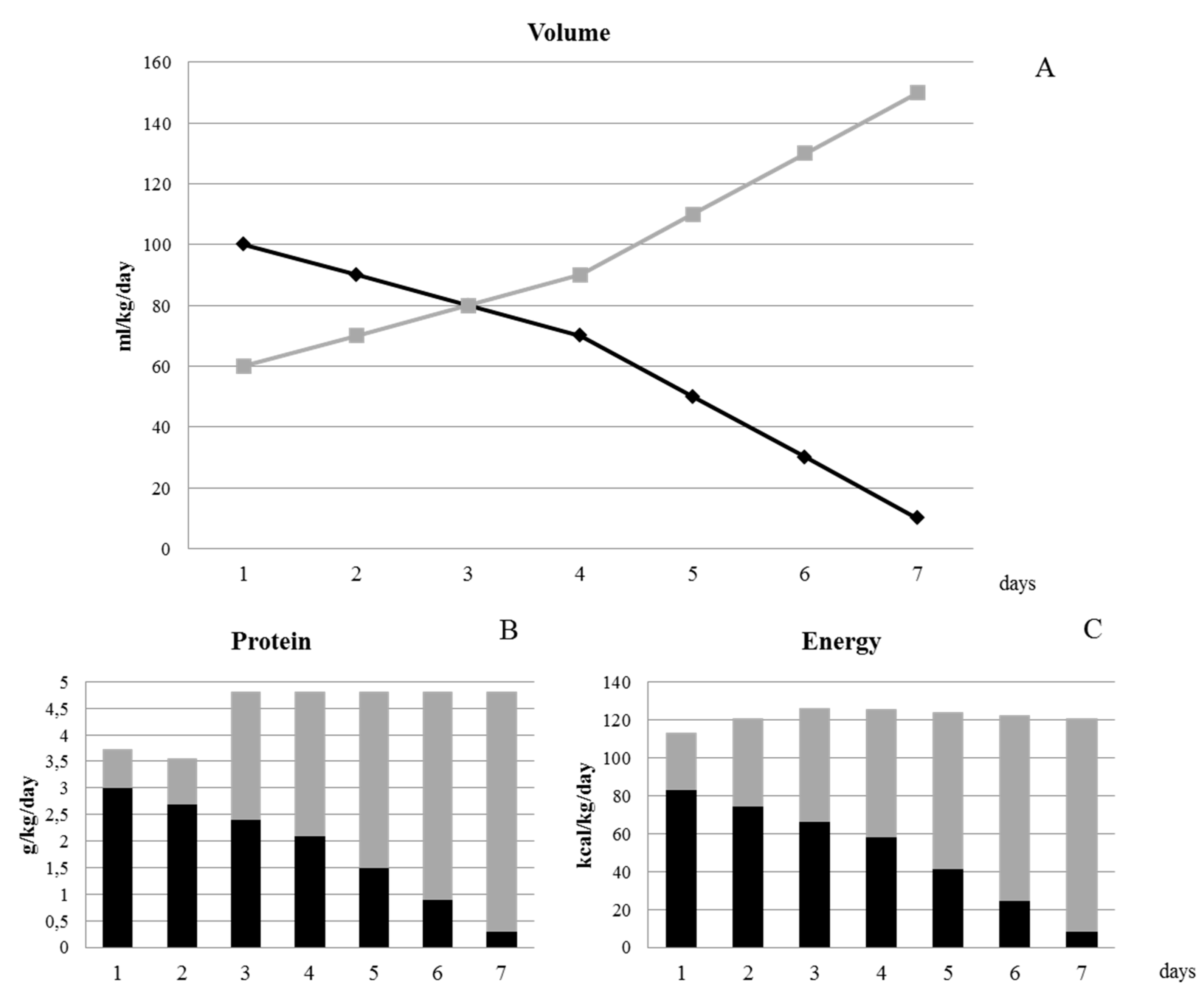
| G1 (GV < 15 g/kg/day) | G2 (GV ≥ 15 g/kg/day) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gestational age (weeks) | 30.1 ± 1.8 | 30.4 ± 1.9 |
| Weight (g) | 1222 ± 199 | 1274 ± 213 |
| Length (cm) | 37.7 ± 2.9 | 37.8 ± 2.1 |
| Head circumference (cm) | 26.5 ± 2.2 | 26.9 ± 2.0 |
| Weight Z-score | −0.59 ± 1.1 | −0.76 ± 0.9 |
| Length Z-score | −0.86 ± 1.1 | −1.07 ± 1.3 |
| Head circumference Z-score | −0.55 ± 1.2 | −0.51 ± 0.9 |
| G1 (GV < 15 g/kg/day) | G2 (GV ≥ 15 g/kg/day) | |
|---|---|---|
| Necrotizing enterocolitis | 2 (3.6) | 1 (2) |
| Cholestasis | 6 (10.7) | 3 (6) |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia | 1 (1.8) | 2 (4) |
| Abdominal surgery | 3 (5.3) | 1 (2) |
| Patent ductus arteriosus | 2 (3.6) | 3 (6) |
| Retinopathy of prematurity | 3 (5.3) | 0 (0) |
| Osteopenia | 4 (7.1) | 5 (10) |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage | 2 (3.6) | 1 (2) |
| Sepsis | 7 (12.5) | 8 (16) |
| G1 (GV < 15 g/kg/day) | G2 (GV ≥ 15 g/kg/day) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-PNI | Parenteral protein intake (g/kg/day) | 2.36 ± 0.7 | 2.45 ± 0.8 | 0.53 |
| Parenteral energy intake (Kcal/kg/day) | 59.4 ± 18.6 | 61.9 ± 24.1 | 0.54 | |
| Enteral protein intake (g/kg/day) | 1.09 ± 0.5 | 1.33 ± 0.7 | 0.05 | |
| Enteral energy intake (Kcal/kg/day) | 45.5 ± 16.4 | 51.5 ± 21.3 | 0.10 | |
| M-ENI | Parenteral protein intake (g/kg/day) | 1.28 ± 0.7 | 1.74 ± 0.9 | 0.01 |
| Parenteral energy intake (Kcal/kg/day) | 30.0 ± 17.0 | 43.6 ± 22.6 | <0.001 | |
| Enteral protein intake (g/kg/day) | 1.82 ± 0.8 | 1.73 ± 0.8 | 0.58 | |
| Enteral energy intake (Kcal/kg/day) | 72.4 ± 20.0 | 64.2 ± 26.5 | 0.07 | |
| G1 (GV < 15 g/kg/day) | G2 (GV ≥ 15 g/kg/day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | Weight (g) | 2438 ± 441 | 2505 ± 453 |
| Length (cm) | 45.2 ± 2.5 | 45.5 ± 2.5 | |
| Head circumference (cm) | 32.3 ± 1.5 | 32.3 ± 1.4 | |
| Weight Z-score | −1.02 ± 1.1 | −0.82 ± 1.1 | |
| Length Z-score | −1.72 ± 1.6 | −1.26 ± 1.2 | |
| Head circumference Z-score | −1.45 ± 1.3 | −0.95 ± 1.3 | |
| TCA | Weight (g) | 3207 ± 464 | 3220 ± 533 |
| Length (cm) | 48.5 ± 2.0 | 48.7 ± 2.5 | |
| Head circumference (cm) | 34.9 ± 1.3 | 34.9 ± 1.4 | |
| Parenteral Nutrition Mixtures Bag “All-in-One” Quantity /100 mL | |
|---|---|
| Amino-acids 10% (g) | 3 |
| Glucose (g) | 14 |
| Lipids (20%) (g) | 3 |
| Sodium (mmol) | 3 |
| Potassium (mmol) | 3 |
| Calcium (mmol) | 1.6 |
| Phosphate (mmol) | 1.6 |
| Oligoelements (mL) | 1 |
| Hydrosoluble vitamins (mL) | 1 |
| Liposoluble vitamins (mL) | 4 |
| Osmolarity (mOsm/L) | 1141 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liotto, N.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Menis, C.; Orsi, A.; Corti, M.G.; Colnaghi, M.; Cecchetti, V.; Pugni, L.; Mosca, F.; et al. Protein Intakes during Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition Drive Growth Gain and Body Composition in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051298
Liotto N, Amato O, Piemontese P, Menis C, Orsi A, Corti MG, Colnaghi M, Cecchetti V, Pugni L, Mosca F, et al. Protein Intakes during Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition Drive Growth Gain and Body Composition in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051298
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiotto, Nadia, Orsola Amato, Pasqua Piemontese, Camilla Menis, Anna Orsi, Maria Grazia Corti, Mariarosa Colnaghi, Valeria Cecchetti, Lorenza Pugni, Fabio Mosca, and et al. 2020. "Protein Intakes during Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition Drive Growth Gain and Body Composition in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051298
APA StyleLiotto, N., Amato, O., Piemontese, P., Menis, C., Orsi, A., Corti, M. G., Colnaghi, M., Cecchetti, V., Pugni, L., Mosca, F., & Roggero, P. (2020). Protein Intakes during Weaning from Parenteral Nutrition Drive Growth Gain and Body Composition in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 12(5), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051298






