The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of KYJ
2.3. Cell Culture
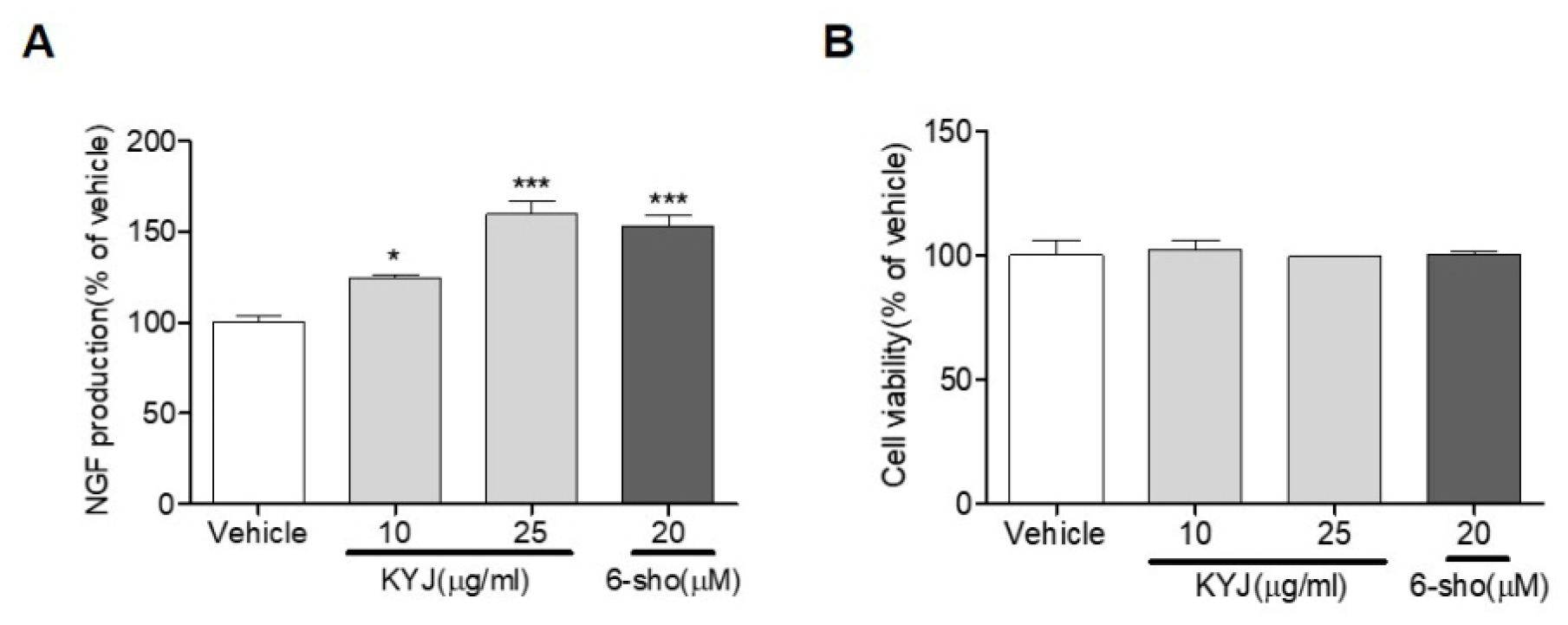
2.4. Measurement of NGF Concentration
2.5. Measurement of Neurite Outgrowth
2.6. Animals and Sample Treatment
2.7. Behavioral Test
2.8. Brain Tissue Preparation
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. KYJ Increased NGF Production in C6 Glioma
3.2. KYJ Induced Neurite Outgrowth in N2a Cells
3.3. KYJ Induced Memory Enhancement in Mice
3.4. KYJ Triggered the Phosphorylation of CREB in the Mouse Hippocampus
3.5. KYJ Promoted Synaptic Formation in the Mouse Hippocampus
3.6. KYJ Stimulated Hippocampal Differentiation of Progenitor Cells and Neurite Extension in Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prince, M.; Ali, G.C.; Guerchet, M.; Prina, A.M.; Albanese, E.; Wu, Y.T. Recent global trends in the prevalence and incidence of dementia, and survival with dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2016 Dementia Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheff, S.W.; Price, D.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; Mufson, E.J. Hippocampal synaptic loss in early Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, J.W.; Gould, T.J. Modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning and synaptic plasticity by nicotine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 38, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conner, J.M.; Franks, K.M.; Titterness, A.K.; Russell, K.; Merrill, D.A.; Christie, B.R.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Tuszynski, M.H. NGF is essential for hippocampal plasticity and learning. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10883–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, N.A.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Adenan, M.I.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T.; Basir, R. Establishing Natural Nootropics: Recent Molecular Enhancement Influenced by Natural Nootropic. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4391375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Khanna, V.K.; Seth, P.K.; Singh, P.N.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Brain neurotransmitter receptor binding and nootropic studies on Indian Hypericum perforatum Linn. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghumatkar, P.J.; Patil, S.P.; Jain, P.D.; Tambe, R.M.; Sathaye, S. Nootropic, neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of phloretin in scopolamine induced amnesia in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovskaya, R.U.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Zaplina, A.P.; Vahitova, J.V.; Salimgareeva, M.H.; Jamidanov, R.S.; Seredenin, S.B. Noopept stimulates the expression of NGF and BDNF in rat hippocampus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 146, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.G.; Caruso, M.; Murchison, C.F.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wright, K.M.; Harris, C.J.; Gray, N.E.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A. Centella Asiatica Improves Memory and Promotes Antioxidative Signaling in 5XFAD Mice. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boondam, Y.; Songvut, P.; Tantisira, M.H.; Tapechum, S.; Tilokskulchai, K.; Pakaprot, N. Inverted U-shaped response of a standardized extract of Centella asiatica (ECa 233) on memory enhancement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, G.; Dan, V.M.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Nair, A.S.; Rajendran Nair, A.P.; Baby, S. Protection of mouse brain from paracetamol-induced stress by Centella asiatica methanol extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Tsai, W.H.; Chen, C.J.; Pan, T.M. Centella asiatica extract protects against amyloid beta1-40-induced neurotoxicity in neuronal cells by activating the antioxidative defence system. J. Tradit. Complement Med. 2016, 6, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giribabu, N.; Srinivasarao, N.; Swapna Rekha, S.; Muniandy, S.; Salleh, N. Centella asiatica Attenuates Diabetes Induced Hippocampal Changes in Experimental Diabetic Rats. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 592062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.R.; Lin, L.W.; Hsieh, C.L.; Wang, W.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsieh, M.T. Petroleum ether extract of Cnidium monnieri ameliorated scopolamine-induced amnesia through adrenal gland-mediated mechanism in male rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.Y.; Kang, M.; Hong, S.B.; Bae, H.; Cho, S.H. Standardized Lycium chinense fruit extract enhances attention and cognitive function in healthy young people by a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2019, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Dang, L.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J. The effects of Gouqi extracts on Morris maze learning in the APP/PS1 double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.G.; Khan, Z.; Choi, S.Z.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. DA-9801, a standardized Dioscorea extract, improves memory function via the activation of nerve growth factor-mediated signaling. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, W.S.; Kim, C.S.; Subedi, L.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. Iridoid Glycosides from the Twigs of Sambucus williamsii var. coreana and Their Biological Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2502–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, R.; Shim, W.S.; Yeo, E.J.; Kim, S.Y. Lactucopicrin potentiates neuritogenesis and neurotrophic effects by regulating Ca(2+)/CaMKII/ATF1 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, E.; Kim, H.G.; Park, H.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, B.; Oh, M.S. Houttuynia cordata Improves Cognitive Deficits in Cholinergic Dysfunction Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Models. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2014, 22, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.G.; Moon, M.; Jeong, H.U.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. Cistanches Herba enhances learning and memory by inducing nerve growth factor. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, H.; Huh, E.; Sim, Y.; Oh, M.S. Ukgansan protects dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity via activation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 factor signaling pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 122, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.G.; Yang, W.M.; Kang, T.H.; Oh, M.S. Effects of optimized-SopungSunkiwon on memory impairment and enhancement. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Compact 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, the Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, J. (6)-shogaol attenuates neuronal apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-treated astrocytes through the up-regulation of neurotrophic factors. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Tuchida, H.; Kiyohara, H.; Takeda, T.; Yamada, H. Induction of NGF synthesis in astrocytes by onjisaponins of Polygala tenuifolia, constituents of kampo (Japanese herbal) medicine, Ninjin-yoei-to. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viosca, J.; Malleret, G.; Bourtchouladze, R.; Benito, E.; Vronskava, S.; Kandel, E.R.; Barco, A. Chronic enhancement of CREB activity in the hippocampus interferes with the retrieval of spatial information. Learn. Mem. 2009, 16, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, S.L.; Leube, R.E.; Cousin, M.A. Synaptophysin is required for synaptobrevin retrieval during synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14032–14036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, L.; Zenke, F.; Kastner, D.B.; Gerstner, W. Synaptic consolidation: From synapses to behavioral modeling. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tischler, A.S.; Riseberg, J.C.; Hardenbrook, M.A.; Cherington, V. Nerve growth factor is a potent inducer of proliferation and neuronal differentiation for adult rat chromaffin cells in vitro. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.Q.; Zhou, J.; Dedhar, S.; Wu, Y.H.; Snider, W.D. NGF-induced axon growth is mediated by localized inactivation of GSK-3beta and functions of the microtubule plus end binding protein APC. Neuron 2004, 42, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagase, H.; Yamakuni, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Kasahara, J.; Hinohara, Y.; Kondo, S.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Tank, A.W.; et al. Mechanism of neurotrophic action of nobiletin in PC12D cells. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13683–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Giuditta, A. Role of a transcription factor (CREB) in memory processes. Riv. Biol. 1997, 90, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sekeres, M.J.; Neve, R.L.; Frankland, P.W.; Josselyn, S.A. Dorsal hippocampal CREB is both necessary and sufficient for spatial memory. Learn. Mem. 2010, 17, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, T.J.; Alkon, D.L. Molecular regulation of synaptogenesis during associative learning and memory. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.; Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counts, S.E.; Nadeem, M.; Lad, S.P.; Wuu, J.; Mufson, E.J. Differential expression of synaptic proteins in the frontal and temporal cortex of elderly subjects with mild cognitive impairment. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wei, L.; Zhuo, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, A.; Huang, Q. Beneficial effects of asiaticoside on cognitive deficits in senescence-accelerated mice. Fitoterapia 2013, 87, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yin, Z.J.; Jiang, C.; Ma, Z.Q.; Fu, Q.; Qu, R.; Ma, S.P. Asiaticoside attenuates memory impairment induced by transient cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice through anti-inflammatory mechanism. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 122, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Meng, X. Osthole improves synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and cognitive function of Alzheimer’s disease rats via regulating glutamate. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Hu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, J. The Coumarin Derivative Osthole Stimulates Adult Neural Stem Cells, Promotes Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus, and Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xue, X.; Shi, H.; Qi, L.; Gong, D. Osthole Upregulates BDNF to Enhance Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J. Osthole decreases tau protein phosphorylation via PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pi, R.; Zou, Y.; Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, X.; Hu, X. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57 BL/6 mice by osthole, a natural coumarin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 629, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.S.; Jiang, X.; Ni, Z.F.; Ma, Z.W.; Xie, A.J.; Cheng, X.S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, G.P. Betaine attenuates Alzheimer-like pathological changes and memory deficits induced by homocysteine. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunisawa, K.; Kido, K.; Nakashima, N.; Matsukura, T.; Nabeshima, T.; Hiramatsu, M. Betaine attenuates memory impairment after water-immersion restraint stress and is regulated by the GABAergic neuronal system in the hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibi, D.; Tsuchihashi, A.; Nomura, T.; Hiramatsu, M. Involvement of GAT2/BGT-1 in the preventive effects of betaine on cognitive impairment and brain oxidative stress in amyloid beta peptide-injected mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.G.; Khan, Z.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051372
Choi JG, Khan Z, Hong SM, Kim YC, Oh MS, Kim SY. The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051372
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jin Gyu, Zahra Khan, Seong Min Hong, Young Choong Kim, Myung Sook Oh, and Sun Yeou Kim. 2020. "The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051372
APA StyleChoi, J. G., Khan, Z., Hong, S. M., Kim, Y. C., Oh, M. S., & Kim, S. Y. (2020). The Mixture of Gotu Kola, Cnidium Fruit, and Goji Berry Enhances Memory Functions by Inducing Nerve-Growth-Factor-Mediated Actions Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients, 12(5), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051372





