Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
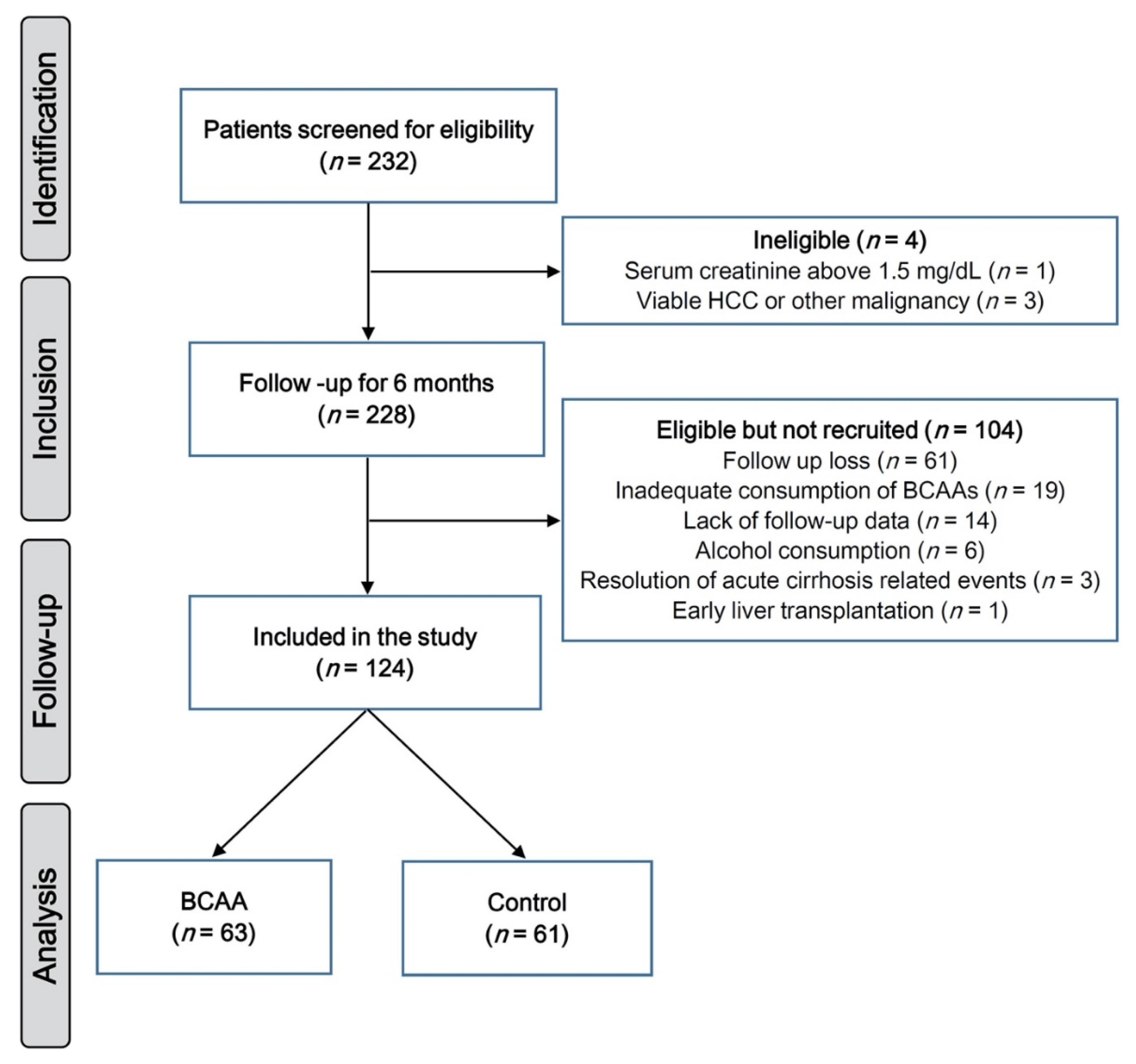
2.1. Study Population
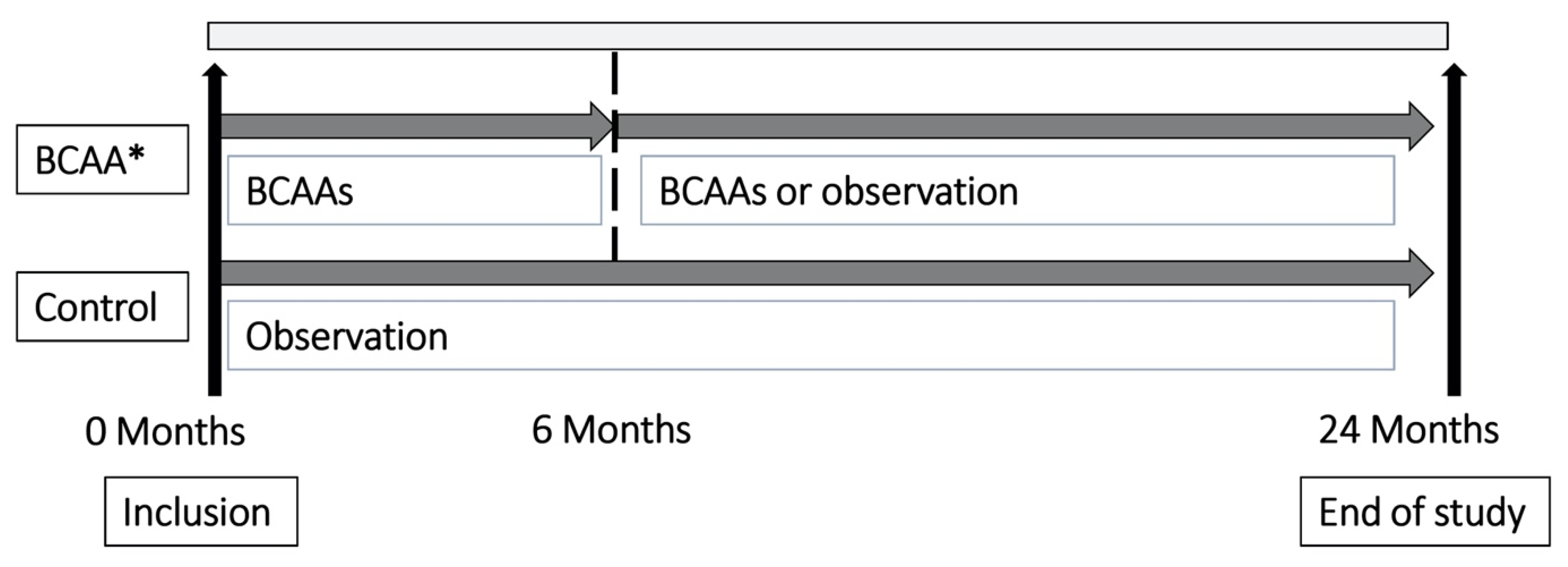
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Baseline Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.4. Follow-up Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Outcomes Related to Liver Function
3.3. Cirrhosis-Related Events and HCC
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Sam, J.; Nguyen, G.C. Protein-calorie malnutrition as a prognostic indicator of mortality among patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2009, 29, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Bianchi, G.; Merli, M.; Amodio, P.; Panella, C.; Loguercio, C.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Abbiati, R.; Italian, B.S.G. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: A double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochs, H.; Plauth, M. Liver cirrhosis: Rationale and modalities for nutritional support—The European Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition consensus and beyond. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 1999, 2, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberino, F.; Gatta, A.; Amodio, P.; Merkel, C.; Di Pascoli, L.; Boffo, G.; Caregaro, L. Nutrition and survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2001, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, J.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease: Clinical and Molecular Advances. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Song, K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Han, K.H. Sarcopenia is associated with significant liver fibrosis independently of obesity and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008-2011). Hepatology 2016, 63, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, D.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Seo, Y.S.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, T.H.; Jung, Y.K.; Kandemir, A.; Kim, J.H.; An, H.; et al. Clinical usefulness of psoas muscle thickness for the diagnosis of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.H. Branched chain amino acids in heptatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Surg. 2002, 183, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Izumi, N.; Charlton, M.R.; Sata, M. Branched-chain amino acids as pharmacological nutrients in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlton, M. Branched-chain amino acid enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 295S–298S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in treatment of liver cirrhosis: Updated views on how to attenuate their harmful effects on cataplerosis and ammonia formation. Nutrition 2017, 41, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluud, L.L.; Dam, G.; Les, I.; Cordoba, J.; Marchesini, G.; Borre, M.; Aagaard, N.K.; Vilstrup, H. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis: Ascites and related complications. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 230–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.G.; Tak, W.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Jang, S.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Bae, S.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) on the progression of advanced liver disease: A Korean nationwide, multicenter, retrospective, observational, cohort study. Medicine 2017, 96, e6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, P.S.; Wiesner, R.H.; Malinchoc, M.; Kremers, W.; Therneau, T.M.; Kosberg, C.L.; D’Amico, G.; Dickson, E.R.; Kim, W.R. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 2001, 33, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Cordoba, J.; Mullen, K.D.; Amodio, P.; Shawcross, D.L.; Butterworth, R.F.; Morgan, M.Y. Review article: The design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy—An International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S. Nutrition and Alcoholic Liver Disease: Effects of Alcoholism on Nutrition, Effects of Nutrition on Alcoholic Liver Disease, and Nutritional Therapies for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2005, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Nishimura, K.; Ohnishi, S.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Sarcopenia impairs prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2015, 31, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, K.; Shimizu, Y. Branched-chain amino acids in liver diseases. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wubetu, G.Y.; Utsunomiya, T.; Ishikawa, D.; Ikemoto, T.; Yamada, S.; Morine, Y.; Iwahashi, S.; Saito, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Imura, S.; et al. Branched chain amino acid suppressed insulin-initiated proliferation of human cancer cells through induction of autophagy. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miuma, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Arima, K.; Takeshita, S.; Muraoka, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Ootani, M.; Shibata, H.; Akiyama, M.; Ozawa, E.; et al. Branched-chain amino acid deficiency stabilizes insulin-induced vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayaishi, S.; Chung, H.; Kudo, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Takita, M.; Ueda, T.; Kitai, S.; Inoue, T.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; et al. Oral branched-chain amino acid granules reduce the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and improve event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hiroshima, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Kawaguchi, D.; Murakami, T.; Yabushita, Y.; Endo, I.; Taguri, M.; Koda, K.; Tanaka, K. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Preoperative Administration of Branched-Chain Amino Acids to Prevent Postoperative Ascites in Patients with Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3727–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | BCAA | Control | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 63 | 61 | - |
| Sex, male | 45 (71) | 37 (61) | 0.281 |
| Age, years | 60 ± 10 | 58 ± 11 | 0.742 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.0 [21.3-25.1] | 22.2 [20.2-24.2] | 0.136 |
| Etiology HBV/HCV/alcohol/other | 17/6/31/9 (27/10/49/14) | 15/3/38/5 (25/5/62/8) | 0.400 |
| Child–Pugh score 8/9/10 | 27/15/21 (43/24/33) | 23/16/22 (38/26/36) | 0.842 |
| MELD score | 14.5 [12.1-16.8] | 14.2 [11.9-16.1] | 0.914 |
| AST, IU/L | 62.0 [36.0-106.0] | 59.0 [37.0-134.0] | 0.772 |
| ALT, IU/L | 31.0 [20.0-41.0] | 31.0 [18.0-57-5] | 0.447 |
| γ-glutamyl transferase, IU/L | 73.0 [32.0-175.0] | 106 [25.0-315.0] | 0.604 |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 2.7 [2.5-3.1] | 2.8 [2.5-3.1] | 0.692 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 2.5 [1.9-4.1] | 2.7 [2.0-3.8] | 0.974 |
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 11.8 [9.0-16.9] | 11.9 [9.2-17.0] | 0.675 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.8±0.2 | 0.8±0.2 | 0.711 |
| INR | 1.4 [1.3-1.5] | 1.4 [1.2-1.5] | 0.649 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 100.0 [64.0-134.5] | 81.0 [57.0-103.0] | 0.079 |
| History of variceal bleeding | 47 (74.6) | 39 (63.9) | 0.274 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy none/grade 1 or 2/grade 3 or 4 | 57/6/0 (90/10/0) | 53/7/1 (87/11/2) | 0.551 |
| Ascites none/mild/moderate to severe | 11/38/14 (18/60/22) | 8/39/14 (13/64/23) | 0.797 |
| History of HCC | 11 (18) | 8 (13) | 0.673 |
| Event | BCAA | Control | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 63 | 61 | - |
| Total events except HCC | 14 (29) | 37 (61) | 0.001 |
| Rupture of varices | 2 (3) | 6 (10) | 0.253 |
| Development or aggravation of ascites | 6 (10) | 17 (28) | 0.017 |
| Hepatorenal syndrome | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1.000 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | 6 (10) | 15 (25) | 0.046 |
| Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis | 2 (3) | 1 (2) | 1.000 |
| Other * | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 0.987 |
| Development of HCC | 14 (22) | 10 (16) | 0.553 |
| Recurrence of HCC | 7 (11) | 4 (7) | 0.565 |
| Death | 6 (10) | 9 (15) | 0.537 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.G.; Tak, W.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Chung, W.J.; Jang, B.K.; Bae, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Suk, K.T.; et al. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051429
Park JG, Tak WY, Park SY, Kweon YO, Chung WJ, Jang BK, Bae SH, Lee HJ, Jang JY, Suk KT, et al. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051429
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jung Gil, Won Young Tak, Soo Young Park, Young Oh Kweon, Woo Jin Chung, Byoung Kuk Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Heon Ju Lee, Jae Young Jang, Ki Tae Suk, and et al. 2020. "Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051429
APA StylePark, J. G., Tak, W. Y., Park, S. Y., Kweon, Y. O., Chung, W. J., Jang, B. K., Bae, S. H., Lee, H. J., Jang, J. Y., Suk, K. T., Oh, M. J., Heo, J., Woo, H. Y., Jang, S. Y., Lee, Y. R., Lee, J. S., Kim, D. Y., Kim, S. H., Suh, J. I., ... Lee, W. K. (2020). Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation on the Progression of Advanced Liver Disease: A Korean Nationwide, Multicenter, Prospective, Observational, Cohort Study. Nutrients, 12(5), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051429








