Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Data
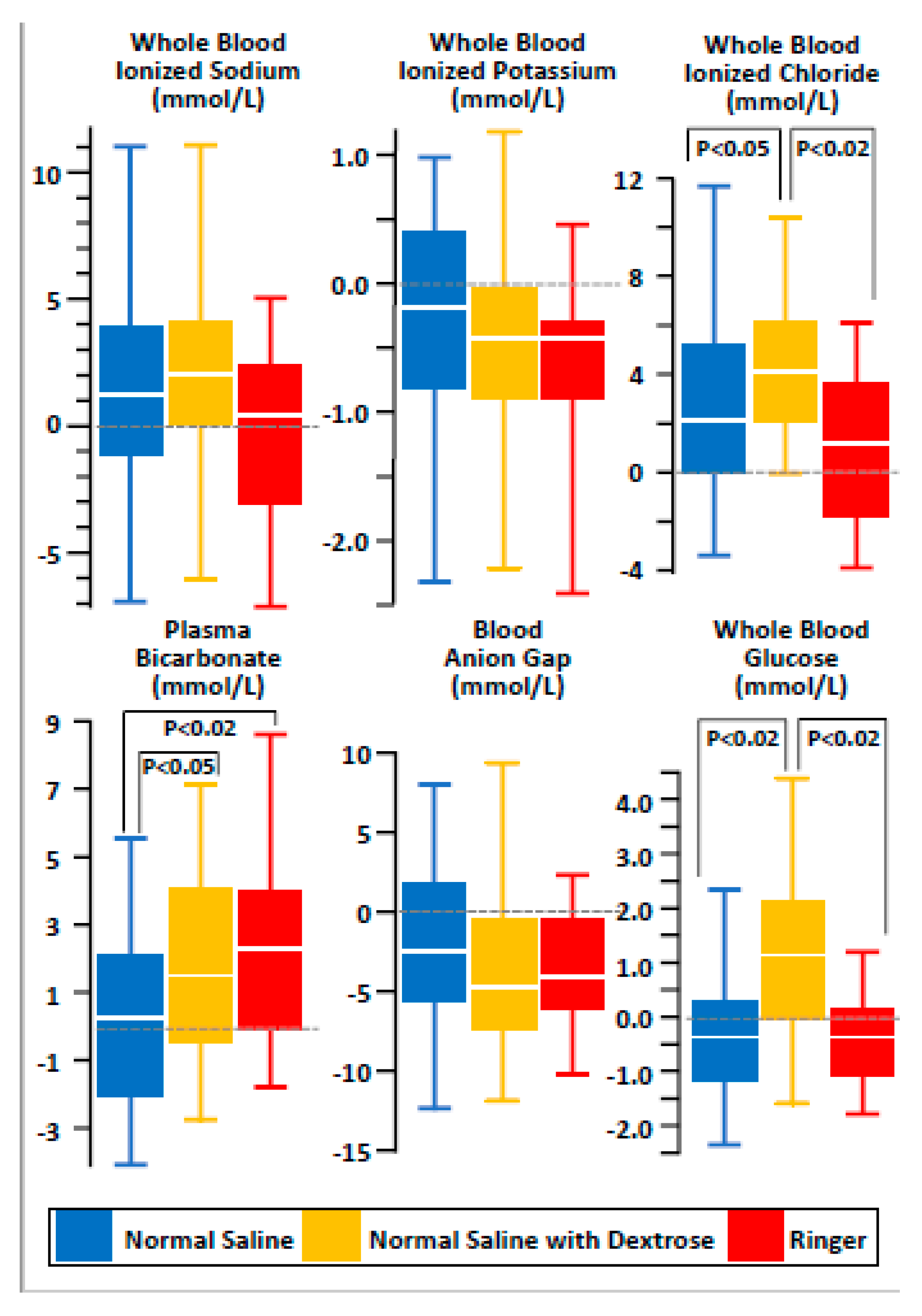
3.2. Effects of Maintenance Fluid Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moritz, M.L.; Ayus, J.C. Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santi, M.; Lava, S.A.G.; Camozzi, P.; Giannini, O.; Milani, G.P.; Simonetti, G.D.; Fossali, E.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Faré, P.B. The great fluid debate: Saline or so-called "balanced" salt solutions? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2015, 41, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semler, M.W.; Kellum, J.A. Balanced Crystalloid Solutions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, L.G.; Neuspiel, D.R.; Foster, B.A.; Leu, M.G.; Garber, M.D.; Austin, K.; Basu, R.K.; Conway, E.E.; Fehr, J.J.; Hawkins, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Children. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20183083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guarino, A.; Ashkenazi, S.; Gendrel, M.; Vecchio, A.L.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children in Europe. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canziani, B.C.; Uestuener, P.; Fossali, E.; Lava, S.A.G.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Clinical Practice: Nausea and vomiting in acute gastroenteritis: Physiopathology and management. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 177, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, M.B.; Milani, G.P.; Bernardi, S.; Odone, L.; Rocchi, A.; D’Angelo, E.A.; Alberzoni, M.; Agostoni, C.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Fossali, E.F. Hyponatremia in infants with community-acquired infections on hospital admission. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.R.; Losek, J.D. Rehydration: Role for early use of intravenous dextrose. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2009, 25, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.A.; Waltzman, M.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Bachur, R. Value of Point-of-care Ketones in Assessing Dehydration and Acidosis in Children with Gastroenteritis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severs, D.; Hoorn, E.J.; Rookmaaker, M.B. A critical appraisal of intravenous fluids: From the physiological basis to clinical evidence. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 30, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moritz, M.L. Why 0.9% saline is isotonic: Understanding the aqueous phase of plasma and the difference between osmolarity and osmolality. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 34, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, R.W.; Covington, A.K.; Fogh-Andersen, N.; Külpmann, W.R.; Lewenstam, A.; Maas, A.H.; Muller-Plathe, O.; Sachs, C.; Siggaard-Andersen, O.; Vankessel, A.L.; et al. Recommendations for Measurement of and Conventions for Reporting Sodium and Potassium by Ion-Selective Electrodes in Undiluted Serum, Plasma or Whole Blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavagno, C.; Milani, G.P.; Uestuener, P.; Simonetti, G.D.; Casaulta, C.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Fare, P.B.; Lava, S.A.G. Hyponatremia in children with acute respiratory infections: A reappraisal. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 92, 430–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmeier, T.G.; Rehberg, S.; Ertmer, C. Evolution of fluid therapy. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterns, R.H.; Silver, S. Salt and water: Read the package insert. QJM Int. J. Med. 2003, 96, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| All Cases | Normal Saline | Dextrose-Supplemented Saline | Lactated Ringer Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 134 | 56 | 48 | 30 |
| Gender (females:males) | 56:78 | 19:37 | 29:19 * | 8:22 |
| Age, years | 2.4 (1.2–5.1) | 3.6 ◆ (1.3–7.7) | 2.2 (1.6–4.6) | 1.8 (1.0–2.7) |
| Whole blood concentration | ||||
| Ionized sodium, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 134 (131–137) | 135 (133–137) | 133 (130–136) | 135 (131–138) |
| 4–6 h later | 135 (133–138) | 136 (133–138) | 135 (133–138) | 135 (133–137) |
| Ionized potassium, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 4.2 (3.8–4.6) | 4.3 (3.8–4.9) | 4.2 (3.9–4.5) | 4.2 (3.5–4.5) |
| 4–6 h later | 3.8 (3.4–4.2) | 4.0 (3.4–4.4) | 3.8 (3.5–4.1) | 3.7 (3.2–4.0) |
| Ionized chloride, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 104 (102–107) | 104 (102–107) | 103 (100–104) | 108 ✙ (104–111) |
| 4–6 h later | 107 (104–110) | 107 (103–109) | 107 (105–109) | 107 (105–113) |
| L-lactate ≥2.5 mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4–6 h later | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 4.4 (3.7–5.6) | 4.9 (4.3–6.4) | 3.6 ▪ (3.2–4.3) | 4.4 (3.9–6.8) |
| 4–6 h later | 4.6 (3.9–5.7) | 4.6 (3.8–5.7) | 5.3 ▪ (4.3–6.6) | 4.3 (3.7–4.8) |
| Plasma bicarbonate, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 17.1 (14.7–20.2) | 19.9 (15.9–22.3) | 16.1 (14.7–18.6) | 15.2 ✙ (13.7–17.7) |
| 4–6 h later | 19.0 (16.0–21.6) | 19.3 (16.0–22.5) | 19.1 (16.2–21.3) | 18.5 (15.6–20.3) |
| Blood, anion gap, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 12 (9–16) | 10 (8–14) | 14 ☩ (11–17) | 12 (9–15) |
| 4–6 h later | 9 (6–12) | 9 (7–12) | 9 (7–11) | 7 (4–12) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricciuti, A.; Milani, G.P.; Tarantino, S.; Ghilardi, R.; Lava, S.A.G.; Alberzoni, M.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Agostoni, C. Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
Ricciuti A, Milani GP, Tarantino S, Ghilardi R, Lava SAG, Alberzoni M, Bianchetti MG, Agostoni C. Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicciuti, Alessandra, Gregorio P. Milani, Silvia Tarantino, Roberta Ghilardi, Sebastiano A.G. Lava, Marco Alberzoni, Mario G. Bianchetti, and Carlo Agostoni. 2020. "Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
APA StyleRicciuti, A., Milani, G. P., Tarantino, S., Ghilardi, R., Lava, S. A. G., Alberzoni, M., Bianchetti, M. G., & Agostoni, C. (2020). Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients, 12(5), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449








