Abstract
Dietary supplements (DS) represent a possible approach to improve sperm parameters and male fertility. A wide range of DS containing different nutrients is now available. Although many authors demonstrated benefits from some nutrients in the improvement of sperm parameters, their real effectiveness is still under debate. The aim of this study was to critically review the composition of DS using the Italian market as a sample. Active ingredients and their minimal effective daily dose (mED) on sperm parameters were identified through a literature search. Thereafter, we created a formula to classify the expected efficacy of each DS. Considering active ingredients, their concentration and the recommended daily dose, DS were scored into three classes of expected efficacy: higher, lower and none. Twenty-one DS were identified. Most of them had a large number of ingredients, frequently at doses below mED or with undemonstrated efficacy. Zinc was the most common ingredient of DS (70% of products), followed by selenium, arginine, coenzyme Q and folic acid. By applying our scoring system, 9.5% of DS fell in a higher class, 71.4% in a lower class and 19.1% in the class with no expected efficacy. DS marketed in Italy for male infertility frequently includes effective ingredients but also a large number of substances at insufficient doses or with no reported efficacy. Manufacturers and physicians should better consider the scientific evidence on effective ingredients and their doses before formulating and prescribing these products.
1. Introduction
Infertility is a pathological condition defined as the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting couple to achieve pregnancy in one year [1]. Both male and female factors can lead to infertility. In particular, according to the causes, it has been reported that 29.3% is due to a male factor, 37.1% to a female factor, 17.6% to both male and female factors, with the remaining percentage considered as idiopathic [2].
It is estimated that around 10%–15% of all couples are affected by infertility, thus representing a global concern in most developed countries [3].
Among male infertility causes, many recent studies have emphasized the role of genital tract inflammation, incorrect lifestyles and malnutrition [4]. On this regard, weight excess and other conditions such as metabolic syndrome, alcohol abuse, cigarette smoking, exposure to environmental pollutants etc. have been strongly related to a decrease in sperm quality and fertility. A major driving hypothesis is that these conditions, by inducing an elevation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitrogen species (RONS), are able to alter the balance of the redox status of both the steroidogenic cell population and the germ line cell populations, leading to the impairment of the hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular axis and the reduction of sperm quality [5].
A large number of recent studies have focused on the ability of many substances, generally termed as nutraceuticals, to improve the hormonal status and sperm parameters by different mechanisms [6]. Nutraceuticals are used as ingredients of dietary supplements (DS), widely marketed for the prevention or treatment of the most disparate pathological conditions. From a legislative point of view, the European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) defines that DS are not intended for the treatment or prevention of disease in humans, but only to support specific physiological function [7]. Currently, DS are widely prescribed to improve physiological aspects related to male fertility.
Many DS are available on the market with various formulations, containing both nutrients and botanicals at different doses. Despite many authors demonstrating positive effects of some ingredients on semen parameters and fertility outcomes [8], many others have also shown a lack of efficacy and even potentially harmful side effects [9]. In a recent position statement, the Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS) summarized the state of the art on each single ingredient currently used in the andrological field. In this paper, authors concluded that there was still limited scientific evidence on the possible role of any nutraceutical in andrology and the use of antioxidants could be suggested in patients with idiopathic infertility in the presence of documented abnormal sperm parameters only after a specific diagnostic workup. However, to date, no regulation or guidelines are available for the use of these products, generating confusion for both prescribers and patients [10]. Moreover, several factors make it difficult to empirically address the right ingredient for the right patient. In particular, it is difficult to identify the correct DS since each product contains different ingredients at different doses.
The purpose of this study was to critically evaluate the composition of DS employed in male infertility, using the Italian market as a sample.
2. Materials and Methods
In order to evaluate the potential efficacy of DS, a systematic literature review on substances used to improve sperm parameters was preliminarily performed. The literature search was conducted in MEDLINE, Scopus, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library registers until 31 March 2020. Only randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and systematic reviews or meta-analysis of RCTs were considered eligible. With the aim to rule out possible interactions between ingredients, only studies that used active substances alone or in combination with at most the other three ingredients were considered. The key terms used for the search were: fertility or male reproduction or semen parameters and supplements or ingredients. Figure 1 displays the flow diagram of the selection of eligible papers.
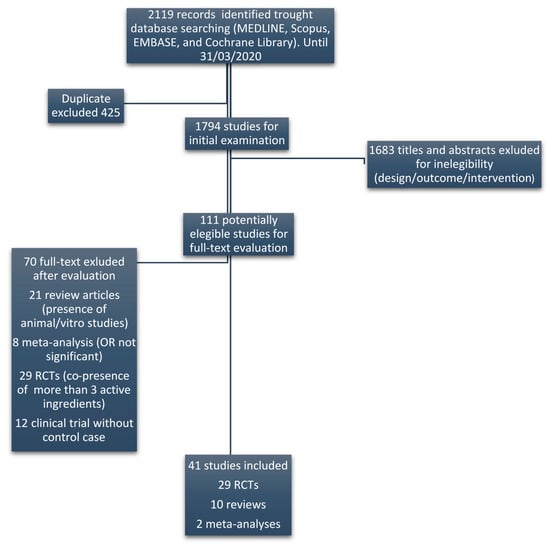
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the selection of eligible papers.
To establish the efficacy of each ingredient we considered only those having at least one RCT or systematic review or meta-analysis of RCTs, demonstrating a significant effect on any sperm parameters involved in male fertility. Significance was set at p-value < 0.05. When evaluating the findings of meta-analyses, we verified whether statistical methods incorporated substantial heterogeneity (Higgins I2 > 30%) into a random-effects model, as appropriate. Regarding the daily dose of each active ingredient with nutrient characteristics, we referred to the tolerable Upper intake Levels (UL) as reported in Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) [11].
Based on the results of available articles, we were able to identify, for each active ingredient, the minimal effective daily dose (mED) able to improve sperm parameters. To define mED we used the lowest effective dose reported in RCTs, systematic review or meta-analysis of RCTs. Therefore, we classified the ingredients contained in each supplement and suggested daily dose into three categories: reported efficacy with a dose achieving the mED (A), reported efficacy but with a dose below mED (B) and unreported data of efficacy (C). To classify DS, we created a formula taking into consideration the three classes of ingredients and their number:
In particular, the above formula was conceived based on the following sequential steps:
- (1)
- Each class of ingredients was given an arbitrary value: A = +2, B = +1 and C = −1;
- (2)
- These values were multiplied for the respective number of ingredients within each supplement (A, B and C respectively), obtaining a total score given by the sum of each category (2A + B − C);
- (3)
- As the number of ingredients highly differed between supplements, we standardized the above total score by dividing it for the maximum possible score for that supplement, by assuming that each ingredient was of class A (=2N, where N is the total number of ingredients in each supplement);
- (4)
- In order to correct this value for the number of ingredients of only categories A and B, the relative score was multiplied for the sum of high efficacy ingredients plus half (as a proxy of their lower efficacy) the number of moderate efficacy ingredients (A + B/2), finally obtaining a corrected score for each supplement.
- (5)
- Given the distribution of the scores resulted in three main clusters, we classified DS into three categories, resembling the efficacy of the ingredients: higher expected efficacy (corrected score ≥ 4), lower expected efficacy (4 < corrected score > 1) and no expected efficacy (corrected score ≤ 1).
We collected the names and formulations of the DS registered in Italy by referring to the register of the Italian Ministry of Health [12].
3. Results
The literature search on active ingredients allowed us to identify 41 studies (RCTs or meta-analyses) reporting their efficacy on sperm parameters (Figure 1). By this analysis we found that 18 of these ingredients had a reported efficacy. The complete list of ingredients with clinical evidence of efficacy, the respective references, evaluated sperm parameters and employed daily doses, are summarized in Table 1. In the right column, the mED of each ingredient is reported. In some studies, marked with an asterisk, the employed dose exceeded the reported UL. In particular, all the studies involving zinc evaluated the effect of this ingredient at a dose exceeding UL. For each active ingredient, the evidence of efficacy was supported by at least two RCTs or meta-analysis, excluding astaxanthin, D-aspartic acid and L-citrulline, which had only one reference.

Table 1.
Active ingredients with evidence of efficacy, references, evaluated sperm parameters, employed daily doses and minimal effective dose (mED).
Ingredients without clinical evidence in the improvement of sperm parameters (no RCT or meta-analyses) are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ingredients without clinical evidence of efficacy.
We found 21 DS marketed in Italy for male infertility. Their composition and the daily doses of their active ingredients are summarized in Table 3. Moreover, for each supplement, the scores of expected efficacy and the symbols summarizing the efficacy of their ingredients are reported.

Table 3.
List of dietary supplements (DS) and relative composition.
A detailed analysis of this table raised the following considerations: (i) all supplements were mixtures of active ingredients; (ii) in each supplement the number of ingredients ranged from 2 up to 17, with a mean number higher than 7; (iii) 13 of 21 supplements contained at least one ingredient without reported efficacy; (iv) 19 supplements had ingredients below mED; (v) indeed, 1 supplement contained seven ingredients dosed below mED; (vi) 1 supplement contained only active ingredients satisfying mED; (vii) the product number 9 had a nutrient reaching UL (zinc 40 mg/day); (viii) zinc was the most used ingredient, followed by selenium, arginine, coenzyme Q, folic acid and carnitine. These substances were present in more than 50% of DS, whereas all the remaining ingredients were represented in 10% or less of products.
The distribution of DS into the three classes of efficacy is reported in Figure 2. Two DS out of 21 (9.5%) were included in the higher expected efficacy group. The majority of remaining products (71.4%) fell in the lower expected efficacy group, and four (19.1%) in the group with no efficacy.

Figure 2.
Distribution of supplements in classes of expected efficacy. * This supplement has a content of Zinc reaching the UL. Numbers refer to a specific supplement.
4. Discussion
This critical review aimed to evaluate the formulation of supplements for male infertility using the Italian market as a sample. In general, there is still poor evidence in terms of large well-designed randomized and placebo-controlled trials availability, supporting the efficacy of nutraceutical products in the field of male reproductive health [54,55]. Nevertheless, these products are commonly administered to infertile patients [8,56]. Since a medical prescription is not necessary to purchase dietary supplements, subjects seeking fertility may have easy access to these products [10,57]. As a proof of concept, the Italian market of supplements generated 3.3 billion euros in 2019, with an increase of 4.3% compared to 2018 [58].
Whilst a rational use of supplements may be potentially beneficial for the improvement of sperm parameters, we need to stress that their uncontrolled use is potentially harmful for patients’ health due to direct toxic effects and interaction with drugs or nutrients [59]. In this respect, we were surprised to point out that all RCTs and meta-analyses on zinc for male infertility relied on doses always exceeding the UL. Over this background, in the near future it would be desirable to better define thoughtful criteria for each supplement in use.
Our analysis found that beside the gap of literature, the market of food supplements is still supported by poor scientific evidence. The majority of DS contained a huge number of ingredients, up to 17. The mixture of such a high number of ingredients may generate different issues, including a low concentration of each substance (i.e., necessitating of two or more administrations to reach the daily effective dose), a large volume of pills and a high risk of interactions. What is more, we found that some ingredients included in many DS had no scientific evidence of efficacy (i.e., astragalus, vitamin D3, taurine and riboflavin). The formulation of pills with a large number of ingredients, some of which cause uncertain benefits, denotes a gap of knowledge of potential biologic targets by manufacturers. Moreover, it has been reported that some plant extracts, present in many of these supplements, are likely to interact with drug metabolism [60,61]. This aspect raises further concerns on the safety of these products.
Very frequently, nutrients were present in DS at a dosage below mED. This situation was more common among products with a high number of ingredients. The administration of any active substance with a dose below mED appears as scientifically unjustified due to uncertainties in the therapeutic results. Differently, when the number of ingredients was small, the dose often satisfied mED. Another major aspect in the evaluation of supplements concerns safety. Some ingredients, particularly when administrated in high doses, are not free from risks when used as dietary supplements. For example, folates can mask the B12 deficiency favoring the progression of neurological damage [62]. The combination of these two vitamins could have a synergic effect in improving homocysteine metabolism hence the sperm quality. It should be noted that vitamin B12, when present, was rarely associated to folic acid [63,64]. Furthermore, zinc reduces the copper intestinal absorption interfering with its carrier [65]. With respect to this, we want to stress that one supplement on the market contained a dose of zinc reaching the UL.
On a positive note, our analysis revealed that some active ingredients with reported efficacy are frequently present in analyzed supplements. Previous studies demonstrated that some ingredients are particularly effective in specific patients’ conditions. Substances with antioxidant properties are indicated in inflammation of the male accessory glands, both related to microbial and non-microbial origin. Several studies performed in asthenozoospermic infertile patients, showed that the positive effect of selenium supplementation is dependent on the correct structure of the mitochondrial capsule [66,67]. Carnitine supplementation induced a significant increase in sperm motility in cases of asthenozoospermia with preserved mitochondrial function [68,69]. Due to the key role of zinc in the processes of DNA compaction, administration of this micronutrient was successful in improving sperm morphology and DNA integrity in patients with prostate abnormalities [70,71].
Based on active ingredients reaching mED we created a grading scale of supplements distinguishing three classes of expected efficacy. Three products were present in the higher class, some of which contained ineffective or underdosed ingredients. Most of the supplements fell in the lower group of expected efficacy. In this class, a large number of ineffective or underdosed products were also present. For an adequate evaluation of these classes, we considered the number of the effective ingredients as the most important criterion of efficacy. A relevant aspect was the use of ineffective or underdosed ingredients that should be absent or less than possible. Another parameter to evaluate a product was the presence of a lower number of ingredients.
We acknowledge the application of a non-validated statistical method to calculate scores for each DS may represent a point of weakness in this study. Very recently, a validated formula to score supplements was suggested by Kuchakulla et al. [72], based on the Budoff’s score, previously conceived by cardiologists to evaluate their procedures [73]. However, this scoring system when applied to DS, does not take into account the effective dose of ingredients, a crucial point in the evaluation of their efficacy. For example, using this approach, a DS containing ingredients at ineffective or toxic doses would be considered useful. As a point of strength, our scoring system relied on high quality evidence coming from RCTs or a systematic review and meta-analyses of RCTs, which represents a reliable approach to critically weighing the expected efficacy of dietary supplements. The same approach could be applied to evaluate products used in other clinical conditions.
In conclusion, this study showed that most DS marketed in Italy for male infertility contain ingredients with reported efficacy in the improvement of sperm parameters. Nevertheless, a non-negligible number of DS are mixtures of substances with uncertain or unreported benefits, whose administration may be unhelpful or even harmful for infertile patients. On that basis, we believe manufacturers should carefully scrutinize scientific evidence before delivering each supplements’ formulation. Accordingly, physicians should evaluate the composition of DS and the dose of each single constituent before considering their clinical use. Finally, the choice for DS should be tailored to the specific patient’s fertility problem.
Author Contributions
A.G. and G.C.P. contributed to the conception/design of the research and acquisition/analysis of the literature data; A.G., G.C.P. and F.F.-P. equally contributed and drafted the manuscript; A.D.N. concepted and performed data analyses; L.D.T., A.V. and C.F. critically revised the paper for important intellectual content. All authors revised and approved the final manuscript, and agreed to be fully accountable for ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the work. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and are able to take responsibility for the integrity of them and the accuracy of the analysis.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marco Ghezzi for helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Task Force on Methods for the Regulation of Male Fertility. Contraceptive efficacy of testosterone-induced azoospermia in normal men. Lancet 1990, 336, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Available online: http://old.iss.it/binary/rpma/cont/7_2017_Report.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Winters, B.R.; Walsh, T.J. The Epidemiology of Male Infertility. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 41, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, F.; Maggi, M. Ultrasound of the male genital tract in relation to male reproductive health. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2014, 21, 56–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlin, A.; Foresta, C. New genetic markers for male infertility. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 26, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsig, A.L.; Gleerup, C.S.; Knudsen, U.B. The influence of omega-3 fatty acids on semen quality markers: A systematic PRISMA review. Andrology 2019, 7, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUR-Lex. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1924/2012-11-29 (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Cui, T.; Kovell, R.C.; Brooks, D.C.; Terlecki, R.P. A Urologist’s Guide to Ingredients Found in Top-Selling Nutraceuticals for Men’s Sexual Health. J. Sex. Med. 2015, 12, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, R.; Sandhu, I.S.; Agarwal, A. The excessive use of antioxidant therapy: A possible cause of male inferility? Andrologia 2019, 51, 303–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, A.E.; Aversa, A.; La Vignera, S.; Corona, G.; Ferlin, A. The use of nutraceuticals in male sexual and reproductive disturbances: Position statement from the Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, J.J.; Hellwig, J.P.; Meyers, D.L. Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 529–542. [Google Scholar]
- Bardelli, P.; Bardelli, M. Commento alle linee guida emanate dal Ministero della Salute sulle disfunzioni posturali. Med. Chir. Caviglia Piede 2019, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Majzoub, A. Antioxidant therapy in idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia. Indian J. Urol. 2017, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisch, I.M.W.; Pierik, F.H.; De Jong, F.H.; Thomas, C.M.G.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Does folic acid and zinc sulphate intervention affect endocrine parameters and sperm characteristics in men? Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizollahi, G.; Azizollahi, S.; Babaei, H.; Kianinejad, M.; Baneshi, M.M.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N. Effects of supplement therapy on sperm parameters, protamine content and acrosomal integrity of varicocelectomized subjects. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2013, 30, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, R.M.; Mackenzie-Proctor, R.; Yazdani, A.; Stankiewicz, M.T.; Jordan, V.; Showell, M.G. Antioxidants for male subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD007411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarinejad, M.R.; Safarinejad, S. Efficacy of Selenium and/or N-Acetyl-Cysteine for Improving Semen Parameters in Infertile Men: A Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled, Randomized Study. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banihani, S.A. Vitamin B12 and Semen Quality. Biomology 2017, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumamoto, Y.; Maruta, H.; Ishigami, J.; Kamidono, S.; Orikasa, S.; Kimura, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Kurihara, H.; Koiso, K.; Okada, K. Clinical efficacy of mecobalamin in the treatment of oligozoospermia—Results of double-blind comparative clinical study. Hinyokika kiyo. Acta Urol. Jpn. 1988, 34, 1109–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama, H.; Nakamura, K.; Sanda, N.; Fujiwara, E.; Seko, S.; Yamazaki, A.; Mizutani, M.; Sagami, K.; Kitano, T. Studies on the usefulness of a long-term, high-dose treatment of methylcobalamin in patients with oligozoospermia. Hinyokika kiyo. Acta Urol. Jpn. 1987, 33, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Calogero, A.E.; Gullo, G.; La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Vaiarelli, A. Myoinositol improves sperm parameters and serum reproductive hormones in patients with idiopathic infertility: A prospective double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study. Andrology 2015, 3, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.Y.; Merkus, H.M.W.M.; Thomas, C.M.G.; Menkveld, R.; Zielhuis, G.A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P. Effects of folic acid and zinc sulfate on male factor subfertility: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 77, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showell, M.G.; Brown, J.; Yazdani, A.; Stankiewicz, M.T.; Hart, R.J. Antioxidants for male subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislavov, R.; Nikolova, V.; Rohdewald, P. Improvement of seminal parameters with Prelox®: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.; Stanislavov, R.; Vatev, I.; Nalbanski, B.; Pŭnevska, M. Sperm parameters in male idiopathic infertility after treatment with prelox. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia) 2007, 46, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanislavov, R.; Rohdewald, P. Sperm quality in men is improved by supplementation with a combination of L-arginine, L-citrullin, roburins and Pycnogenol®. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2014, 66, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighian, H.K.; Haidari, F.; Mohammadi-Asl, J.; Dadfar, M. Randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial examining the effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplement on the spermatogram and seminal oxidative stress in infertile men. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y. Effect of oral alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) on the treatment of male infertility. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehni, N.M.; Ketabchi, A.A.; Hosseini, E. Combination effect of Pentoxifylline and L-carnitine on idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 12, 817–824. [Google Scholar]
- Peivandi, S.; Abasali, K.; Narges, M. Effects of L-carnitine on infertile men’s spermogram; a randomised clinical trial. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2010, 10, 331. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi, A.; Lombardo, F.; Sgrò, P.; Salacone, P.; Caponecchia, L.; Dondero, F.; Gandini, L. Use of carnitine therapy in selected cases of male factor infertility: A double-blind crossover trial. Fertil. Steril. 2003, 79, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Bashiri, R.; Ghadiri-Anari, A.; Nadjarzadeh, A. Antioxidant supplements and semen parameters: An evidence based review. Int. J. Reprod. BioMed. 2016, 14, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak-Jedrzejowska, R.; Wolski, J.K.; Slowikowska-Hilczer, J. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in male fertility. Central Eur. J. Urol. 2013, 66, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçi, H.; Verit, A.; Savas, M.; Yeni, E.; Erel, O. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Semen Parameters and Oxidative/Antioxidant Status. Urology 2009, 74, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadjarzadeh, A.; Sadeghi, M.R.; Amirjannati, N.; Vafa, M.; Motevalian, S.A.; Gohari, M.R.; Akhondi, M.A.; Yavari, P.; Shidfar, F. Coenzyme Q10 improves seminal oxidative defense but does not affect on semen parameters in idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia: A randomized double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2011, 34, 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- Safarinejad, M.R.; Safarinejad, S.; Shafiei, N.; Safarinejad, S. Effects of the Reduced Form of Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinol) on Semen Parameters in Men with Idiopathic Infertility: A Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled, Randomized Study. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarinejad, M.R. Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 on Semen Parameters, Sperm Function and Reproductive Hormones in Infertile Men. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comhaire, F.H.; El Garem, Y.; Mahmoud, A.; Eertmans, F.; Schoonjans, F. Combined conventional/antioxidant “Astaxanthin” treatment for male infertility: A double blind, randomized trial. Asian J. Androl. 2005, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aniello, A.; Ronsini, S.; Notari, T.; Grieco, N.; Infante, V.; D’Angel, N.; Mascia, F.; Fiore, M.; Fisher, G. D-Aspartate, a Key Element for the Improvement of Sperm Quality. Adv. Sex. Med. 2012, 2, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.B.; Bakar, M.B.; Nik Hussain, N.H.; Norhayati, M.N.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Jaafar, H.; Draman, S.; Ramli, R.; Wan Yusoff, W.Z. Comparison on the effects and safety of tualang honey and tribestaan in sperm parameters, erectile function and hormonal profile among oligospermia males. Evid.-Based Compliment. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 126138. [Google Scholar]
- Setiawan, L. Tribulus terrestris L. extract improves spermatozoa motility and increases the efficiency of acrosome reaction in subjects diagnosed with oligoastheno-teratozoospermia. Adv. Male. Reprod. Physiol. 1996, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sanagoo, S.; Oskouei, B.S.; Abdollahi, N.G.; Salehi-Pourmehr, H.; Hazhir, N.; Farshbaf-Khalili, A. Effect of Tribulus terrestris L. on sperm parameters in men with idiopathic infertility: A systematic review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 42, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Levin, M.H.; Verón, G.L. Myo-inositol in health and disease: Its impact on semen parameters and male fertility. Andrology 2019, 8, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, R.A.; La Vignera, S.; Mongioì, L.M.; Vitale, S.G.; Laganà, A.S.; Cimino, L.; Calogero, A.E. Myo-inositol as a male fertility molecule: Speed them up! Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omu, A.E.; Al-Azemi, M.; Kehinde, E.; Anim, J.; Oriowo, M.; Mathew, T. Indications of the Mechanisms Involved in Improved Sperm Parameters by Zinc Therapy. Med Princ. Pr. 2008, 17, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, S.A.; Ali, M.E.; Zaki, Z.M.; El-Malik, E.M.; Nasr, M.A. Lipid peroxidation and human sperm motility: Protective role of vitamin E. J. Androl. 1996, 17, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greco, E.; Iacobelli, M.; Ferrero, S.; Tesarik, J.; Rienzi, L.; Ubaldi, F. Reduction of the Incidence of Sperm DNA Fragmentation by Oral Antioxidant Treatment. J. Androl. 2005, 26, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyrus, A.; Kabir, A.; Goodarzi, D.; Moghimi, M. The effect of adjuvant vitamin C after varicocele surgery on sperm quality and quantity in infertile men: A double blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2015, 41, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, E.B.; Harris, W.A.; Powell, L.C. Relationship between ascorbic acid and male fertility. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1990, 62, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Safarinejad, M.R. MP-11.10: Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Semen Profile and Enzymatic Anti-Oxidant Capacity of Seminal Plasma in Infertile Men with Idiopathic Oligoasthenoteratospermia: A Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Study. Urology 2009, 74, S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Soto, J.; Domingo, J.; Cordobilla, B.; Palbero, L.; Pellicer, A.; Landeras, J. Effect of dietary DHA supplementation on sperm DNA integrity. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, S235–S236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.P.; Kumar, R. Lycopene therapy in idiopathic male infertility–A preliminary report. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2002, 34, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Durairajanayagam, D.; Ong, C.; Prashast, P. Lycopene and male infertility. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassan, F.L.; Chavarro, J.E.; Tanrikut, C. Diet and men’s fertility: Does diet affect sperm quality? Fertil. Steril. 2018, 110, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terai, K.; Horie, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyagawa, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsujimura, A. Combination therapy with antioxidants improves total motile sperm counts: A Preliminary Study. Reprod. Med. Boil. 2019, 19, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumalic, S.I.; Pinter, B. Review of Clinical Trials on Effects of Oral Antioxidants on Basic Semen and Other Parameters in Idiopathic Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keszthelyi, M.; Sofikitis, N. Administration of Antioxidants in the Infertile Male: When it may have a Beneficial Effect? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federsalus. Available online: https://www.federsalus.it/il-mercato-degli-integratori-dinamiche-aggiornate-a-marzo-2019/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Ronis, M.J.; Pedersen, K.B.; Watt, J. Adverse Effects of Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, K.; Zidorn, C. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and bioactivity of the genus Turnera (Passifloraceae) with a focus on damiana—Turnera diffusa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Roy, A.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, J.S. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of eckol and dieckol isolated from edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis on human monoamine oxidases A and B. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2017, 40, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; House, J.D. Recent Developments in Folate Nutrition. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafipour, R.; Moghbelinejad, S.; Aleyasin, A.; Jalilvand, A. Effect of B9 and B12 vitamin intake on semen parameters and fertility of men with MTHFR polymorphisms. Andrology 2017, 5, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-N.; Ma, J.; Han, R.-Y.; Liu, W.-J.; Wang, S.-S. Correlation of the levels of seminal plasma homocysteine, folate and cobalamin with semen parameters in obese men. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2018, 24, 883–886. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, A.; Yacoubian, C.; Watson, N.; Morrison, I. The risk of copper deficiency in patients prescribed zinc supplements. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresta, C.; Flohé, L.; Garolla, A.; Roveri, A.; Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Male fertility is linked to the selenoprotein phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. Boil. Reprod. 2002, 67, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.M. Do micronutrient deficiencies contribute to mitochondrial failure in critical illness? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garolla, A.; Maiorino, M.; Roverato, A.; Roveri, A.; Ursini, F.; Foresta, C. Oral carnitine supplementation increases sperm motility in asthenozoospermic men with normal sperm phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase levels. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 83, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Dong, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y. The efficacy of combined l-carnitine and l-acetyl carnitine in men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology 2019, 52, e13470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresta, C.; Garolla, A.; Cosci, I.; Menegazzo, M.; Ferigo, M.; Gandin, V.; De Toni, L. Role of zinc trafficking in male fertility: From germ to sperm. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, A.; Mohammad-Hasani, A.; Colagar, A.H. Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2018, 19, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Manish, K.; Yash, S.; Premal, P.; Neel, P.; Ranjith, R. A Systematic Review and Evidence-based Analysis of Ingredients in Popular Male Fertility Supplements. Urology 2020, 136, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Budoff, M.J.; Achenbach, S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Carr, J.J.; Goldin, J.; Greenland, P.; Guerci, A.D.; Lima, J.A.; Rader, D.J.; Rubin, G.D.; et al. Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease by Cardiac Computed Tomography. Circulation 2006, 114, 1761–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).