Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Gene Selection and Primer Design
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Sequencing
2.6. End-Point PCR
2.7. Protein Extraction
2.8. One-Dimensional Electrophoresis (1-DE)
2.9. Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis (2-DE)
2.10. Allergic Patients and Immunoblot
2.11. Mass Spectrometry and Protein Identification
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
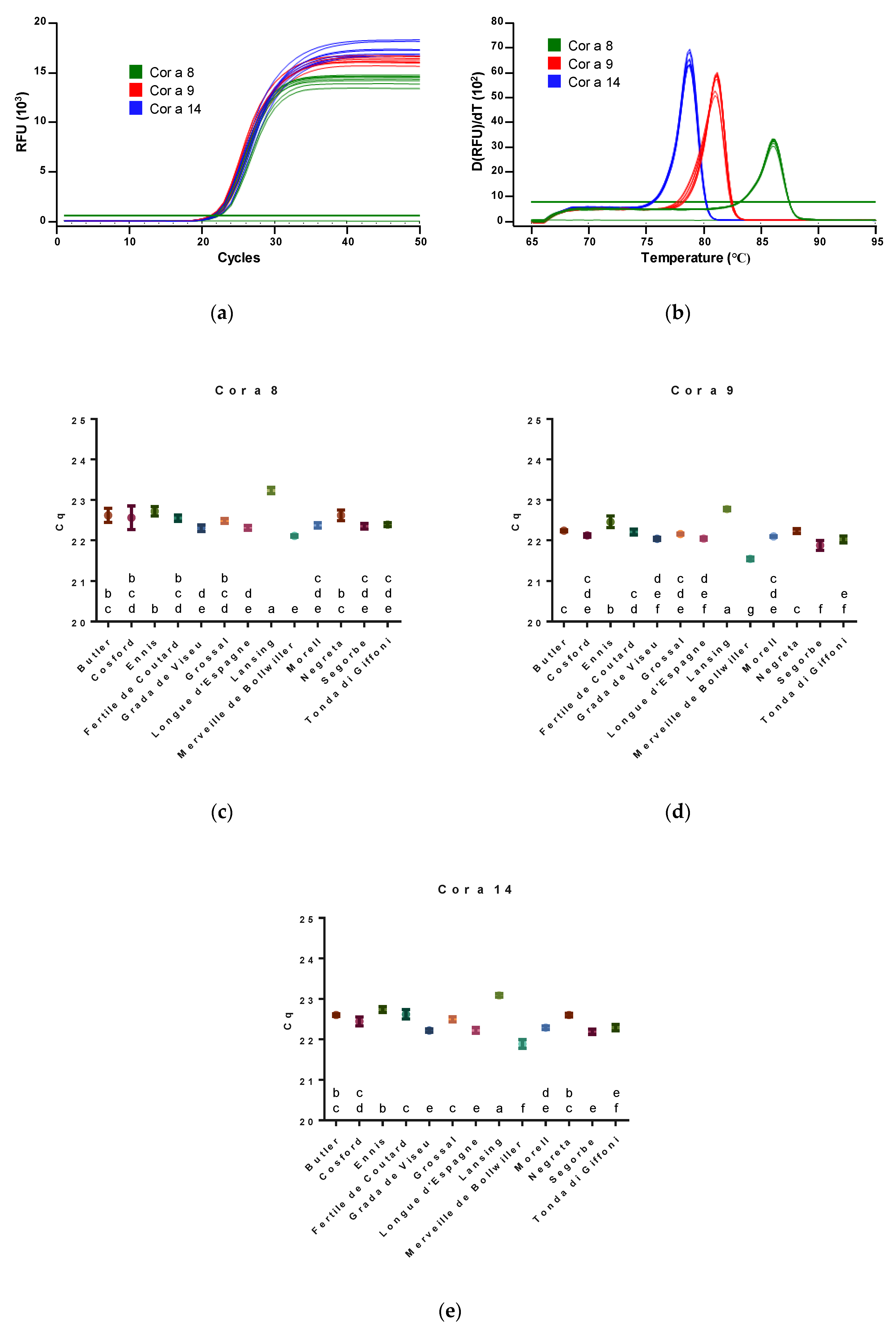
3.1. Cor a 8, Cor a 9 and Cor a 14 Gene Quantification
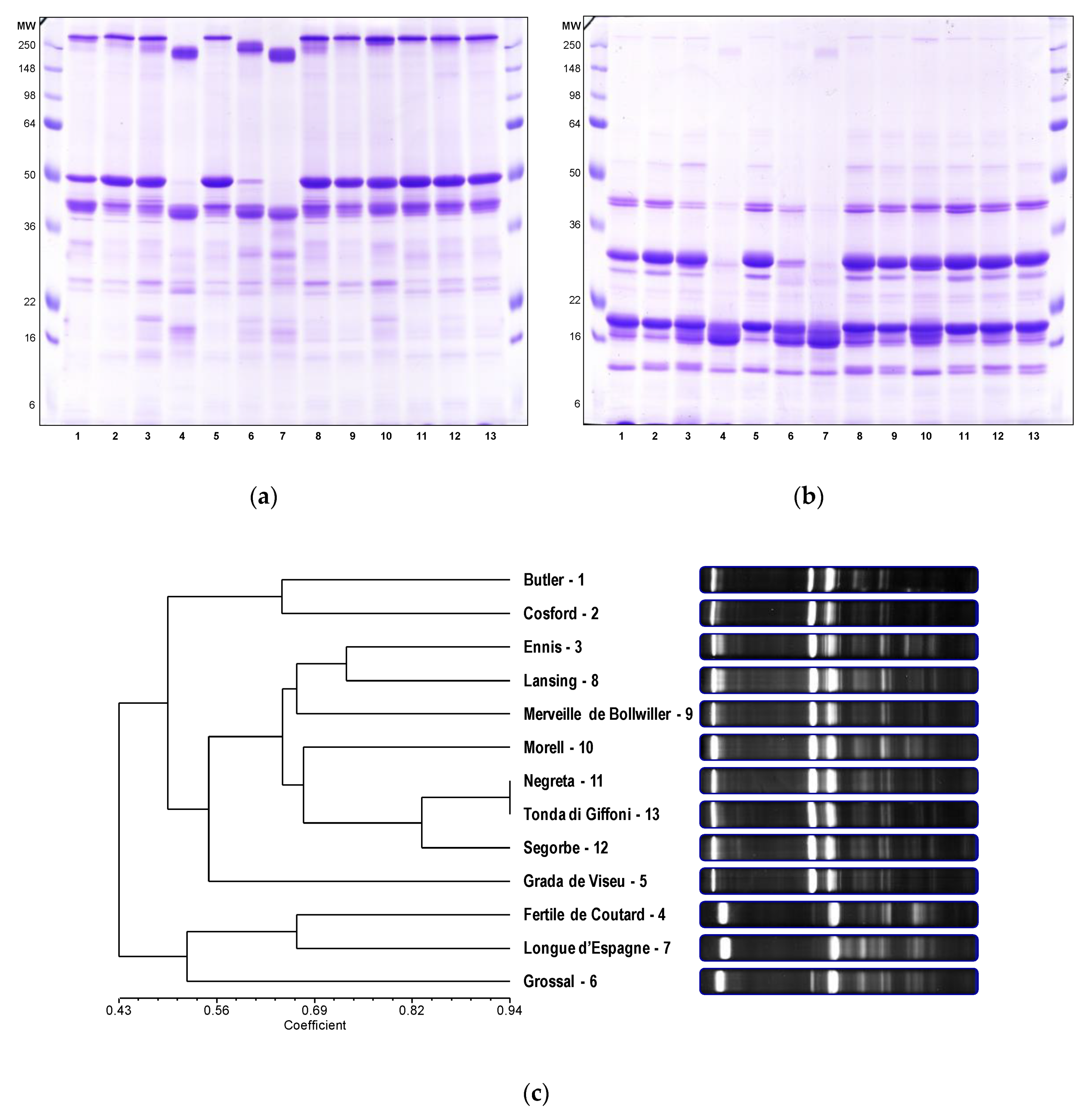
3.2. Protein Polymorphism
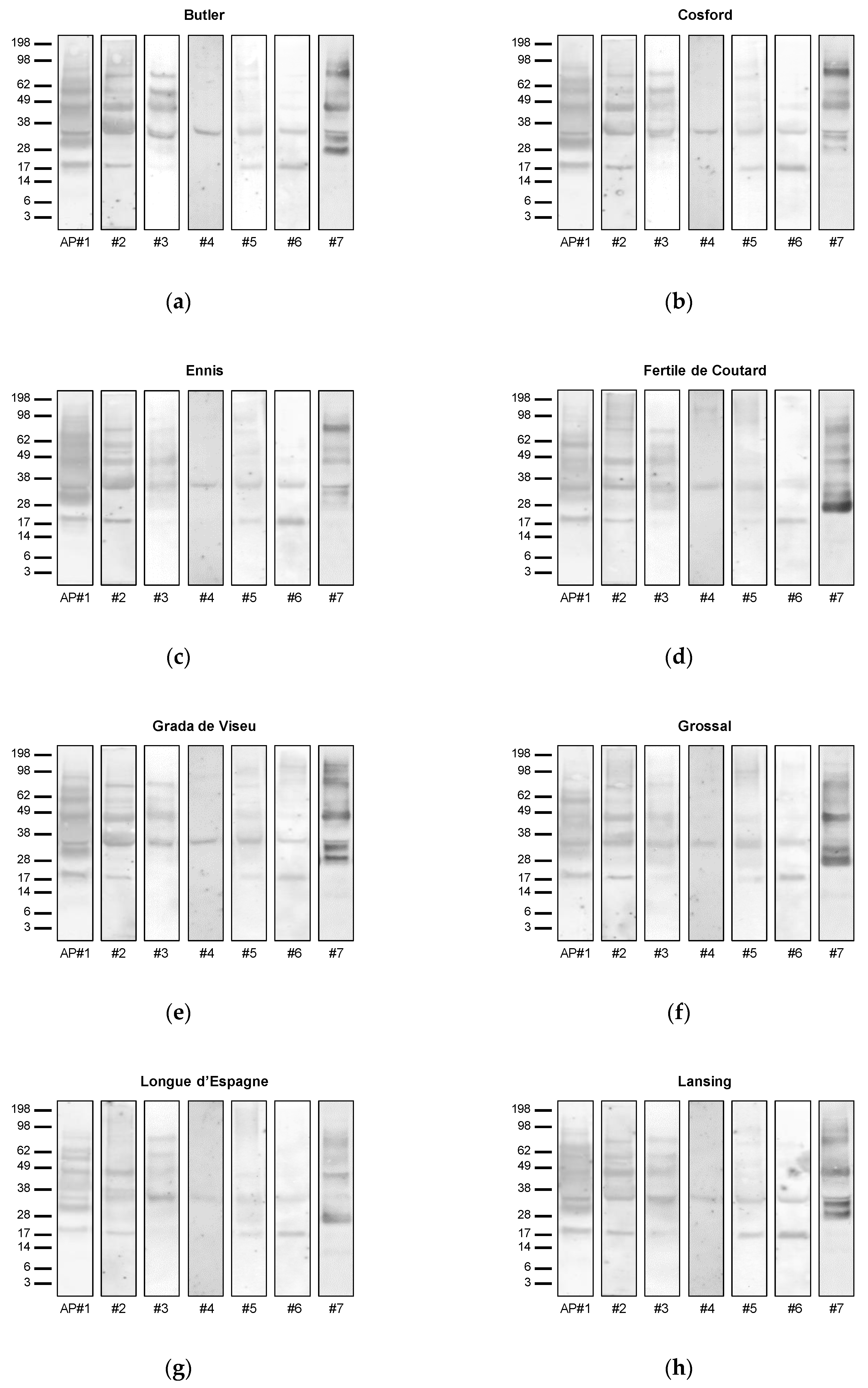
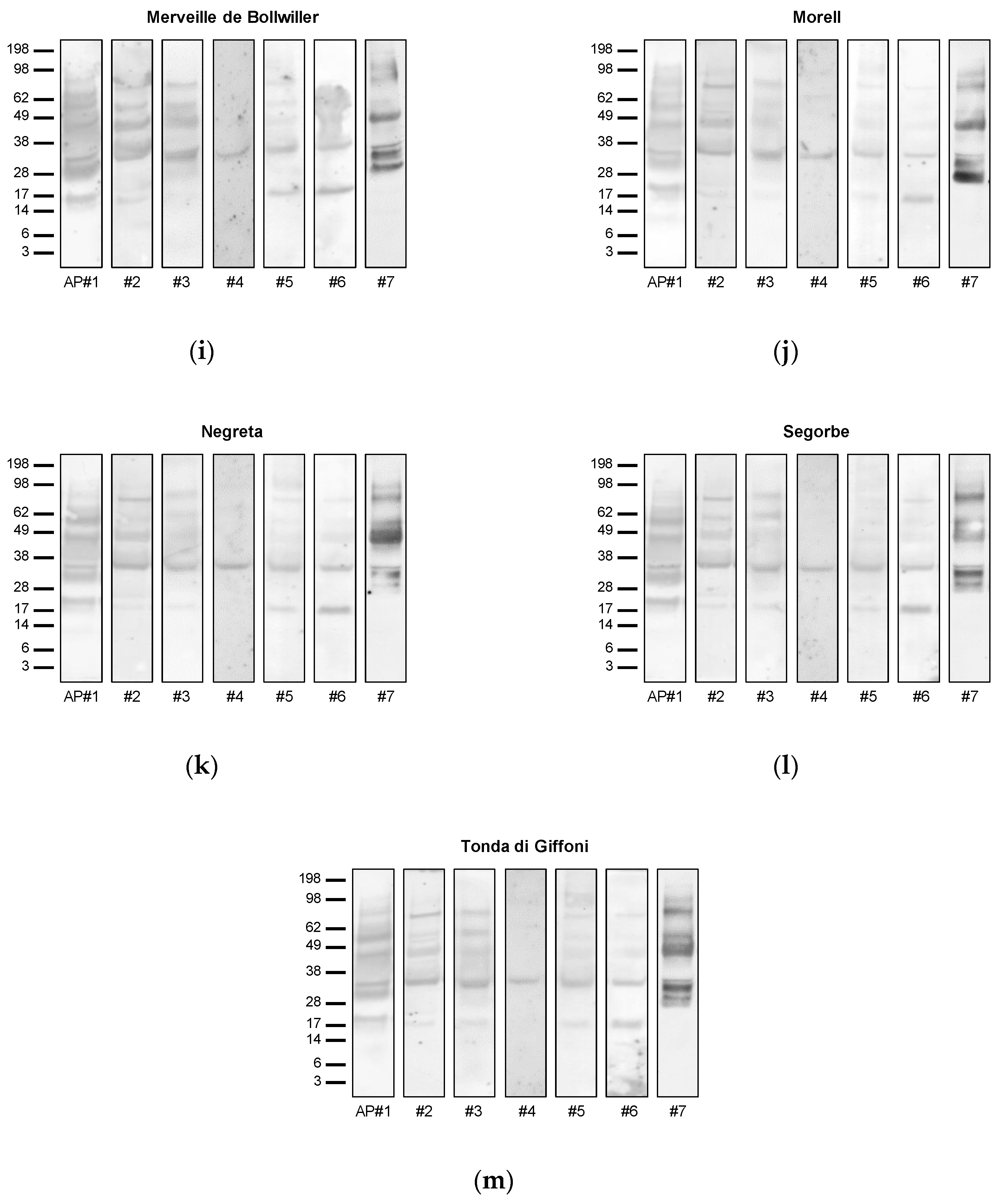
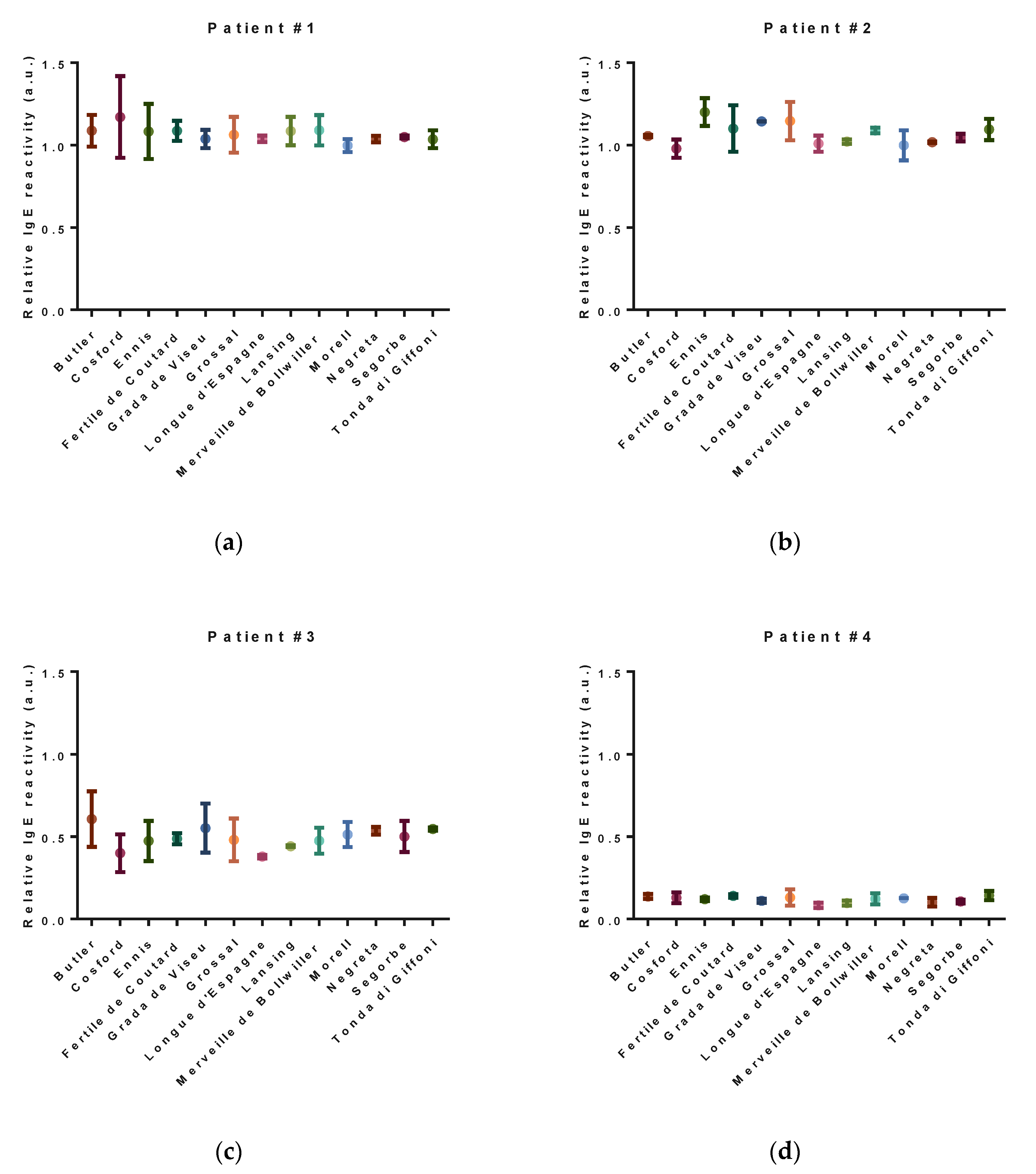
3.3. Allergenic Potential
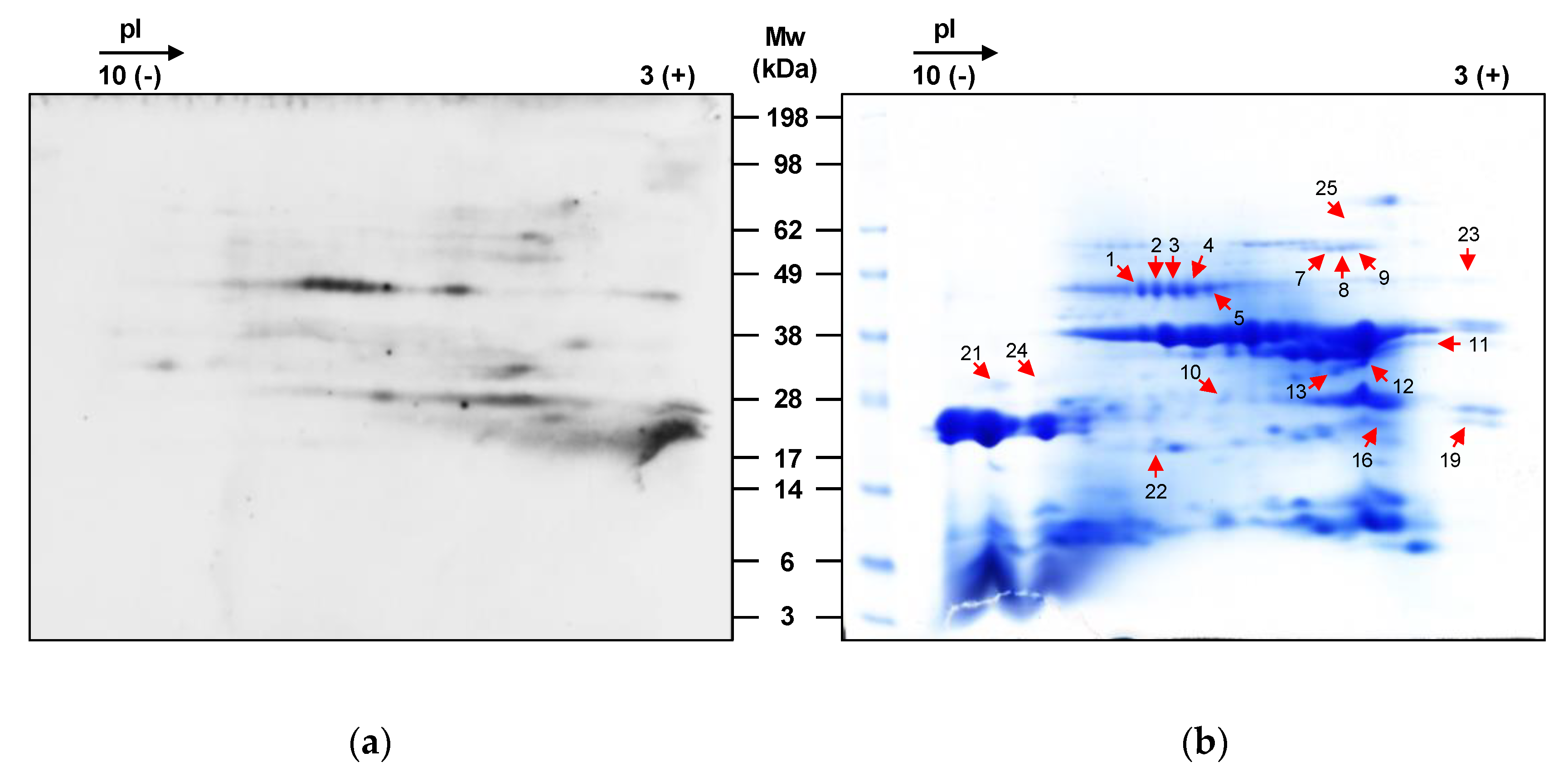
3.4. Allergen Identification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, W.; Freeland, D.M.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedé, S.; Blazquez, A.B.; Chiang, D.; Tordesillas, L.; Berin, M.C. The rise of food allergy: Environmental factors and emerging treatments. EBioMedicine 2016, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhondalay, G.K.; Rael, E.; Acharya, S.; Zhang, W.; Sampath, V.; Galli, S.J.; Tibshirani, R.; Boyd, S.D.; Maecker, H.; Nadeau, K.C.; et al. Food allergy and omics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Carrapatoso, I.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Hazelnut allergens: Molecular characterisation, detection and clinical relevance. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 56, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nitride, C.; Mamone, G.; Picariello, G.; Mills, C.; Nocerino, R.; Canani, R.B.; Ferranti, P. Proteomic and immunological characterization of a new food allergen from hazelnut (Corylus avellana). J. Proteom. 2013, 86, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, P.; Summers, C.; Chinn, S.; Hooper, R.L.; Van Ree, R.; Lidholm, J. Prevalence and distribution of sensitization to foods in the European community respiratory health survey: A europrevall analysis. Allergy 2010, 65, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, S.; Bublin, M.; Dubiela, P.; Hummel, K.; Wortmann, J.; Hofer, G.; Keller, W.; Radauer, C.; Sommergruber, K.H. Cor a 14, the allergenic 2S albumin from hazelnut, is highly thermostable and resistant to gastrointestinal digestion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, E.N.C.; Jenkins, J.; Marigheto, N.; Belton, P.S.; Gunning, A.P.; Morris, V.J. Allergens of the cupin superfamily. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öztürk, S.C.; Balık, S.K.; Kızılcı, G.; Duyar, Ö.; Doğanlar, S.; Frary, A.; Balık, H.I. Molecular genetic diversity of the Turkish national hazelnut collection and selection of a core set. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garino, C.; Locatelli, M.; Coisson, J.D.; D’Andrea, M.; Cereti, E.; Travaglia, F.; Arlorio, M. Gene transcription analysis of hazelnut (Corylus avellanaL.) allergens Cor a 1, Cor a 8 and Cor a 11: A comparative study. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, R.; Happe, J.; Brümmer, I.; Brockmeyer, J. Structural Characterization of the Allergenic 2S Albumin Cor a 14: Comparing Proteoform Patterns across Hazelnut Cultivars. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, E.A.; Vieths, S.; Pravettoni, V.; Farioli, L.; Trambaioli, C.; Fortunato, D.; Lüttkopf, D.; Calamari, M.; Ansaloni, R.; Scibilia, J.; et al. Identification of hazelnut major allergens in sensitive patients with positive double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge results. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Nunes, F.M.; Guedes, S.D.M.; Domingues, P.; Silva, A.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rodríguez-Quijano, M.; Branlard, G.; Igrejas, G. Efficient chemo-enzymatic gluten detoxification: Reducing toxic epitopes for celiac patients improving functional properties. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portugal, C.; Pinto, L.; Ribeiro, M.; Tenorio, C.; Igrejas, G.; Ruiz-Larrea, M.F. Potential spoilage yeasts in winery environments: Characterization and proteomic analysis of Trigonopsis cantarellii. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 210, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Seabra, L.; Ramos, A.; Santos, S.; Pinto-Carnide, O.; Carvalho, C.; Igrejas, G. Polymorphism of the storage proteins in Portuguese rye (Secale cereale L.) populations. Hereditas 2012, 149, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Bancel, E.; Faye, A.; Dardevet, M.; Ravel, C.; Branlard, G.; Igrejas, G. Proteogenomic characterization of novel x-type high molecular weight glutenin subunit 1Ax1.1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5650–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero-Calvo, I.; Ocón, B.; Martínez-Moya, P.; Suárez, M.D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; De Medina, F.S. Reversible Ponceau staining as a loading control alternative to actin in Western blots. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 401, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research--an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolph, F.J. NTSYS, numerical taxonomy and multivarietal analysis system (2.1): User guide. Biostatistics 2000, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Marzano, V.; Tilocca, B.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Vernocchi, P.; Mortera, S.L.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P.; Putignani, L. Perusal of food allergens analysis by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzo, D.; Bernal, J.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Franco, D.; Zapata, C. Advances in the Biology of Seed and Vegetative Storage Proteins Based on Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis Coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 23, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Ma, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Békés, F.; Appels, R.; Yan, Y. Characterization and comparative analysis of wheat high molecular weight glutenin subunits by SDS-PAGE, RP-HPLC, HPCE, and MALDI-TOF-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2777–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Grishina, G.; Bardina, L.; Grishin, A.; Sampson, H.A. Identification of an 11S globulin as a major hazelnut food allergen in hazelnut-induced systemic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Kothary, M.H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Howard, A.J.; Fu, T.J.; Zhang, Y. Purification and crystallization of Cor a 9, a major hazelnut allergen. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Boil. Cryst. Commun. 2008, 65, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rougé, P.; Brunet, E.; Borges, J.-P.; Jauneau, A.; Saggio, B.; Bourrier, T.; Rancé, F.; Didier, A.; Barre, A. Les protéines à motif cupine: Allergènes majeurs des graines. Revue Française d’Allergologie 2011, 51, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Matta, N.K. Phylogenetic relationship and germplasm evaluation of different taxa of the genusCucurbitausing seed storage protein profiling. Plant. Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. all Asp. Plant. Biol. 2015, 150, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccacci, P.; Akkak, A.; Botta, R. DNA typing and genetic relations among European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using microsatellite markers. Genome 2006, 49, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Freitas, M.; Domínguez-Perles, R.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A.; Ferreira-Cardoso, J.; Igrejas, G. Nutriproteomics survey of sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Miller) genetic resources in Portugal. Food Bioscience 2020, 36, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.H.; Teuber, S.S.; Sathe, S.K. Tree nut allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 131, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooper, M.; Plassen, C.; Holden, L.; Moen, L.H.; Namork, E.; Egaas, E. Antibody binding to hazelnut (Corylus avellana) proteins: The effects of extraction procedure and hazelnut source. Food Agric. Immunol. 2008, 19, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platteau, C.M.F.; Bridts, C.H.; Daeseleire, E.A.; De Loose, M.R.; Ebo, D.; Taverniers, I. Comparison and Functional Evaluation of the Allergenicity of Different Hazelnut (Corylus avellana) Protein Extracts. Food Anal. Methods 2010, 3, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemeseder, T.; Klinglmayr, E.; Moser, S.; Lang, R.; Himly, M.; Oostingh, G.J.; Zumbach, J.; Bathke, A.C.; Hawranek, T.; Gadermaier, G. Influence of intrinsic and lifestyle factors on the development of IgE sensitization. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 173, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barre, A.; Sordet, C.; Culerrier, R.; Rancé, F.; Didier, A.; Rougé, P. Vicilin allergens of peanut and tree nuts (walnut, hazelnut and cashew nut) share structurally related IgE-binding epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotham, J.M.; Hoffman, G.G.; Teuber, S.S.; Beyer, K.; Sampson, H.A.; Sathe, S.K.; Roux, K.H. Linear IgE-epitope mapping and comparative structural homology modeling of hazelnut and English walnut 11S globulins. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmings, O.; Kwok, M.; McKendry, R.; Santos, A.F. Basophil activation test: Old and new applications in allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpicella, M.; Leoni, C.; Dileo, M.C.; Ceci, L.R. Progress in the analysis of food allergens through molecular biology approaches. Cells 2019, 8, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieths, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Holzhauser, T.; Müller, U.; Reindl, J.; Haustein, D. Factors influencing the quality of food extracts forin vitroandin viiodiagnosis. Allergy 1998, 53, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigotzki, M.; Steinhart, H.; Paschke, A. Influence of varieties, storage and heat treatment on ige-binding proteins in hazelnuts (Corylus avellana). Food Agric. Immunol. 2000, 12, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitride, C.; Picariello, G.; Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P. Proteomics of Hazelnut (Corylus avellana). In Proteomics in Food Science; Colgrave, M.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Breiteneder, H.; Radauer, C. A classification of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, S.; Sancho, A.; Vieths, S.; Mills, C.E.N.; Wal, J.-M.; Shewry, P.R.; Rigby, N.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K. High-throughput NMR assessment of the tertiary structure of food allergens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, D.R.M.; Mitsak, M.J.; Elliott, S.T.; Chen, D.; Whelan, S.A.; Hart, G.W.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Whelan, S.A. Two-dimensional gel-based approaches for the assessment of N-Linked and O-GlcNAc glycosylation in human and simian immunodeficiency viruses. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4919–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, M.D.; Pomés, A.; Breiteneder, H.; Ferreira, F. Nomenclature and structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asero, R.; Piantanida, M.; Pinter, E.; Pravettoni, V. The clinical relevance of lipid transfer protein. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 48, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Patient | Sex | Age | Hazelnut Allergy | Concomitant Other Food Allergies | Concomitant Allergy to Aeroallergens | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | CAP specific IgE (f17; kUA/L) | |||||
| 1 | M | 4 | Urticaria | 75.9 | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | F | 18 | Urticaria, anaphylaxis | 35.3 | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | M | 71 | Eczema, rhinitis, asthma | 40.9 | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | M | 19 | Angioedema | 55.1 | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | F | 28 | Angioedema, anaphylaxis | 21.6 | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | F | 45 | Rhinitis, angioedema | 65.4 | Yes | Yes |
| 7 | M | 29 | Rhinitis | 21.3 | Yes | No |
| Spot * | Protein | Function | UniProt † | Mw (Da) | Score | Significant Unique Sequences | MS Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 1362 | 17 | 39 |
| 2 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 1351 | 18 | 45 |
| 3 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 1377 | 19 | 48 |
| 4 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 1104 | 19 | 47 |
| 5 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 1353 | 19 | 47 |
| 7 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 789 | 11 | 26 |
| 8 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 463 | 10 | 25 |
| 9 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 389 | 7 | 30 |
| 10 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 708 | 14 | 35 |
| 11 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 186 | 4 | 18 |
| 12 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 616 | 9 | 29 |
| 13 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 377 | 7 | 19 |
| 16 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 676 | 9 | 27 |
| 19 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 669 | 10 | 30 |
| 21 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 299 | 7 | 16 |
| 22 | Variant Cor a 1.0403 | Defense response | Q9FPK3 | 17,527 | 406 | 11 | 76 |
| 23 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 735 | 13 | 31 |
| 24 | 48-kDa glycoprotein | Nutrient reservoir | Q8S4P9 | 50,856 | 140 | 5 | 16 |
| 25 | Cor a 9 allergen | Nutrient reservoir | A0A0A0P7E3 | 58,837 | 375 | 4 | 21 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, M.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Cabo, S.; Silva, A.P.; Gonçalves, B.; Hillion, M.; Hébraud, M.; Igrejas, G. Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072100
Ribeiro M, Costa J, Mafra I, Cabo S, Silva AP, Gonçalves B, Hillion M, Hébraud M, Igrejas G. Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties? Nutrients. 2020; 12(7):2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072100
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Miguel, Joana Costa, Isabel Mafra, Sandra Cabo, Ana Paula Silva, Berta Gonçalves, Mélanie Hillion, Michel Hébraud, and Gilberto Igrejas. 2020. "Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties?" Nutrients 12, no. 7: 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072100
APA StyleRibeiro, M., Costa, J., Mafra, I., Cabo, S., Silva, A. P., Gonçalves, B., Hillion, M., Hébraud, M., & Igrejas, G. (2020). Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties? Nutrients, 12(7), 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072100









