Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nutritional Treatment
2.2. Geriatric Assessment and Body Composition
2.3. REE Measured and Predicted
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frisard, M.I.; Broussard, A.; Davies, S.S.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd; Rood, J.; de Jonge, L.; Fang, X.; Jazwinski, S.M.; Deutsch, W.A.; Ravussin, E. Aging, resting metabolic rate, and oxidative damage: Results from the Louisiana Healthy Aging Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Gallagher, D. Body composition changes with aging: The cause or the result of alterations in metabolic rate and macronutrient oxidation? Nutrition 2010, 26, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cereda, E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; de Groot, L.; Grosshauser, F.; Kiesswetter, E.; Norman, K.; et al. Management of Malnutrition in Older Patients-Current Approaches, Evidence and Open Questions. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boullata, J.; Williams, J.; Cottrell, F.; Hudson, L.; Compher, C. Accurate determination of energy needs in hospitalized patients. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.A.; Feinberg, T.M.; Wappel, S.; Verceles, A.C. Considerations When Using Predictive Equations to Estimate Energy Needs Among Older, Hospitalized Patients: A Narrative Review. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2017, 6, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segadilha, N.; Rocha, E.E.M.; Tanaka, L.M.S.; Gomes, K.L.P.; Espinoza, R.E.A.; Peres, W.A.F. Energy Expenditure in Critically Ill Elderly Patients: Indirect Calorimetry vs Predictive Equations. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siervo, M.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A.; Wells, J.C.; Lara, J.; Ferraris, C.; Tagliabue, A. Accuracy of predictive equations for the measurement of resting energy expenditure in older subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A Biometric Study of Human Basal Metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1918, 4, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B. The Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) for grading the nutritional state of elderly patients: Presentation of the MNA, history and validation. Nestle Nutr. Workshop Series. Clin. Perform. Programme 1999, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelemaat, F.; van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A.; Thijs, A.; Seidell, J.C.; Weijs, P.J. Resting energy expenditure in malnourished older patients at hospital admission and three months after discharge: Predictive equations versus measurements. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K. A simple frailty questionnaire (FRAIL) predicts outcomes in middle aged African Americans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bedirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenblut, S.; Zank, S. Entwicklung eines neuen Depressionsscreenings für den Einsatz in der Geriatrie. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2010, 43, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.J.; Palmer, C.R. A new mobility score for predicting mortality after hip fracture. J. Bone Jt. Surgery 1993, 75, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.B. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J. Physiol. 1949, 109, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, C.; Alix, E.; Salle, A.; Berrut, G.; Ritz, P. A practical approach to estimate resting energy expenditure in frail elderly people. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, K.; Laurie Karsegard, V.; Genton, L.; Kossovsky, M.P.; Kayser, B.; Pichard, C. Comparison of equations for estimating resting metabolic rate in healthy subjects over 70 years of age. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Badilla, O.; Kammar-García, A.; Vera-López, O.; Aguilar-Alonso, P.; Lazcano-Hernández, M.; Avila-Sosa, R.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R. Simplified equation for resting energy expenditure in a population of elderly chileans compared to indirect calorimetry. NFS J. 2018, 13, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Duerksen, D.R.; Munroe, S.; Bistrian, B.R. An evaluation of resting energy expenditure in hospitalized, severely underweight patients. Nutrition 1999, 15, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roza, A.M.; Shizgal, H.M. The Harris Benedict equation reevaluated: Resting energy requirements and the body cell mass. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compher, C.; Cato, R.; Bader, J.; Kinosian, B. Harris-Benedict equations do not adequately predict energy requirements in elderly hospitalized African Americans. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2004, 96, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenfield, D.C.; Muth, E.R.; Rowe, W.A. The Harris-Benedict studies of human basal metabolism: History and limitations. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1998, 98, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, C.; Braun, W.; Pourhassan, M.; Schweitzer, L.; Gluer, C.C.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Muller, M.J. Age-Dependent Changes in Resting Energy Expenditure (REE): Insights from Detailed Body Composition Analysis in Normal and Overweight Healthy Caucasians. Nutrients 2016, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Eichhorn, C.; Kutzner, D.; Illner, K.; Heller, M.; Muller, M.J. The age-related decline in resting energy expenditure in humans is due to the loss of fat-free mass and to alterations in its metabolically active components. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ancum, J.M.; Scheerman, K.; Pierik, V.D.; Numans, S.T.; Verlaan, S.; Smeenk, H.E.; Slee-Valentijn, M.; Kruizinga, R.C.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Muscle Strength and Muscle Mass in Older Patients during Hospitalization: The EMPOWER Study. Gerontology 2017, 63, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All (n = 23) | |
|---|---|
| Gender (number, %) | |
| Females | 15 (65) |
| Males | 8 (35) |
| Age (y) | 81.8 ± 8.1 |
| Height (m) | 1.63 ± 0.1 |
| Bodyweight (kg) | 62.4 ± 11.4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.4 ± 4.0 |
| Geriatric assessments, Median (IQR) | |
| MNA-LF | 14 (12–15) |
| Barthel-Index | 45 (40–55) |
| Parker mobility score | 2 (2–4) |
| Frail Simple score | 5 (4–5) |
| SARC-F scores | 8 (6–9) |
| Depression score (DIA-S) | 3 (2–6) |
| Cognitive function (MoCA) | 17 (15–21) |
| Bioelectrical impedance analysis (kg) | |
| FM | 18.8 ± 9.6 |
| FFM | 46.1 ± 7.7 |
| SMM | 17.9 ± 4.9 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 3.2 ± 2.9 |
| TSH (mU/mL) | 2.1 ± 1.9 |
| All (n = 23) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On admission | At discharge | Changes | |
| REEmeasured (kcal/d) | 967.5 ± 260.0 | 1180.1 ± 397.9 | 212.6 ± 363.0 aa |
| REEpredicted (kcal/d) | 1190.4 ± 152.3 b | 1209.9 ± 150.0 | 19.5 ± 45.7 a,b |
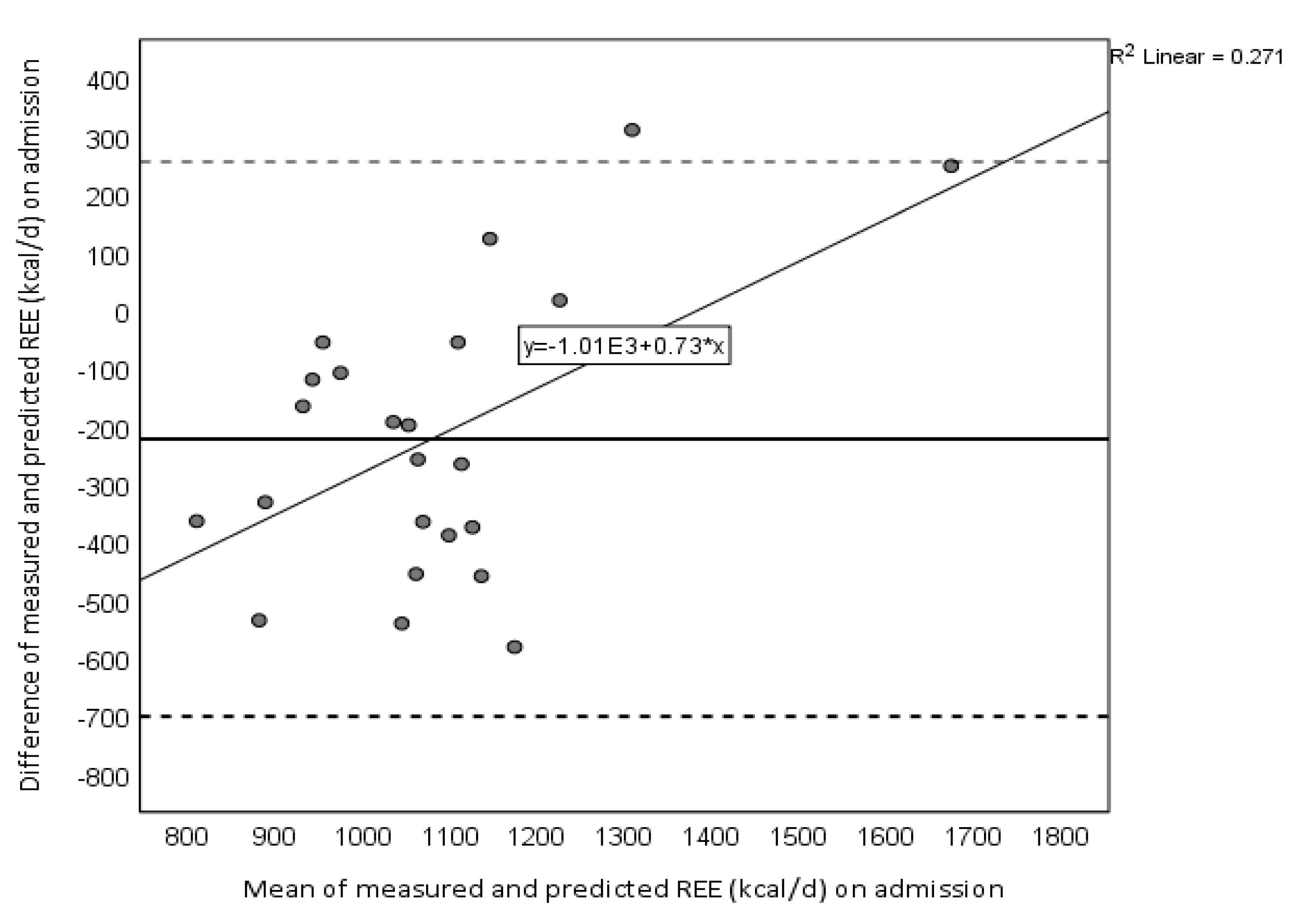
| REEmeasured−REEpredicted (kcal/d) | −223.0 ± 244.2 | −29.8 ± 383.3 | 193.1 ± 360.7 aa |
| (REEpredicted/REEmeasured) × 100 (%) | 129% | 111% | 18% |
| Beta Coefficient | SE | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difference between REEmeasured and REEpredicted | |||
| Parker mobility score on admission | 26.44 | 46.46 | 0.647 |
| FFM | 6.09 | 9.18 | 0.231 |
| TSH | −25.03 | 53.33 | 0.826 |
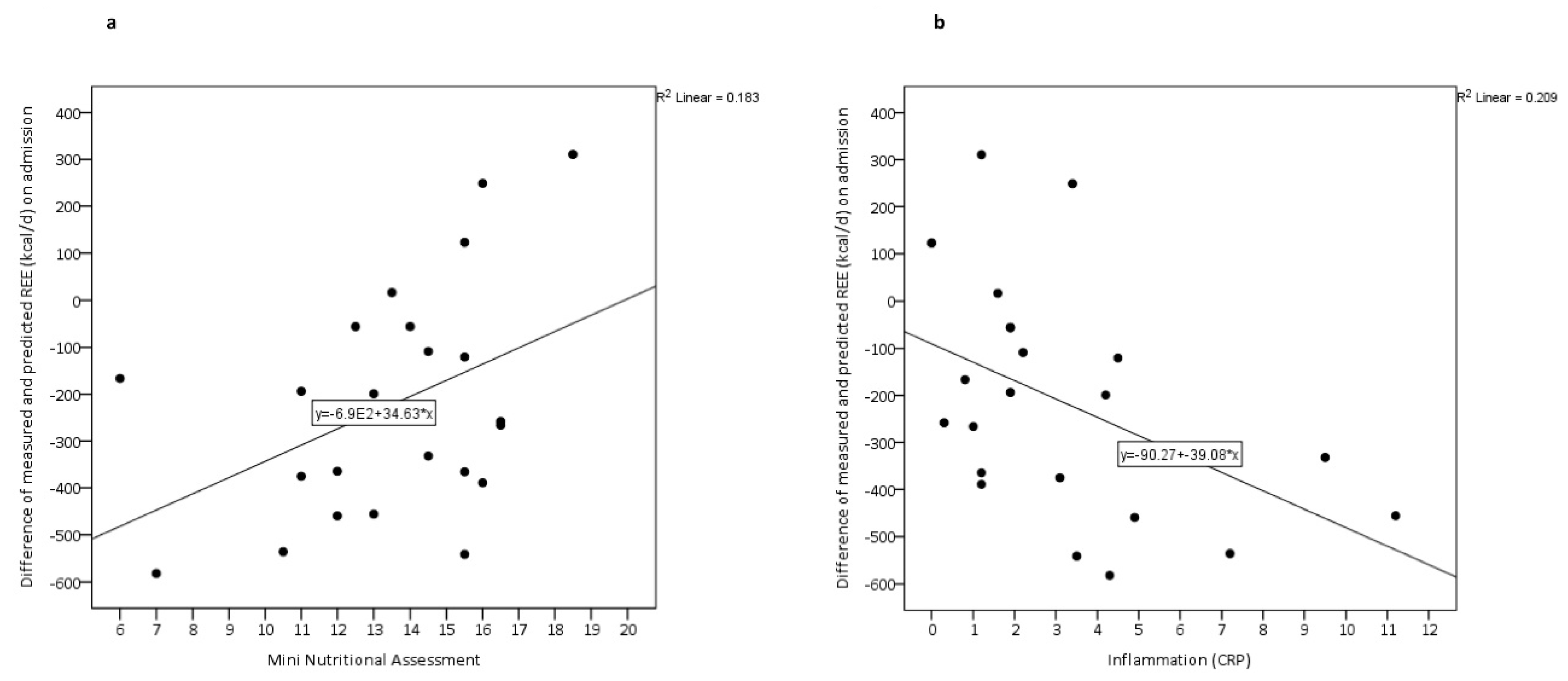
| Inflammation (CRP) | −33.88 | 15.88 | 0.046 |
| Total MNA-LF | 31.96 | 15.09 | 0.048 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pourhassan, M.; Daubert, D.; Wirth, R. Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082240
Pourhassan M, Daubert D, Wirth R. Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082240
Chicago/Turabian StylePourhassan, Maryam, Diana Daubert, and Rainer Wirth. 2020. "Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082240
APA StylePourhassan, M., Daubert, D., & Wirth, R. (2020). Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Malnourished Older Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Comparison. Nutrients, 12(8), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082240





