Immunomodulatory Effect of a Salvia plebeia R. Aqueous Extract in Forced Swimming Exercise-induced Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Animals
2.4. Forced Swimming Test
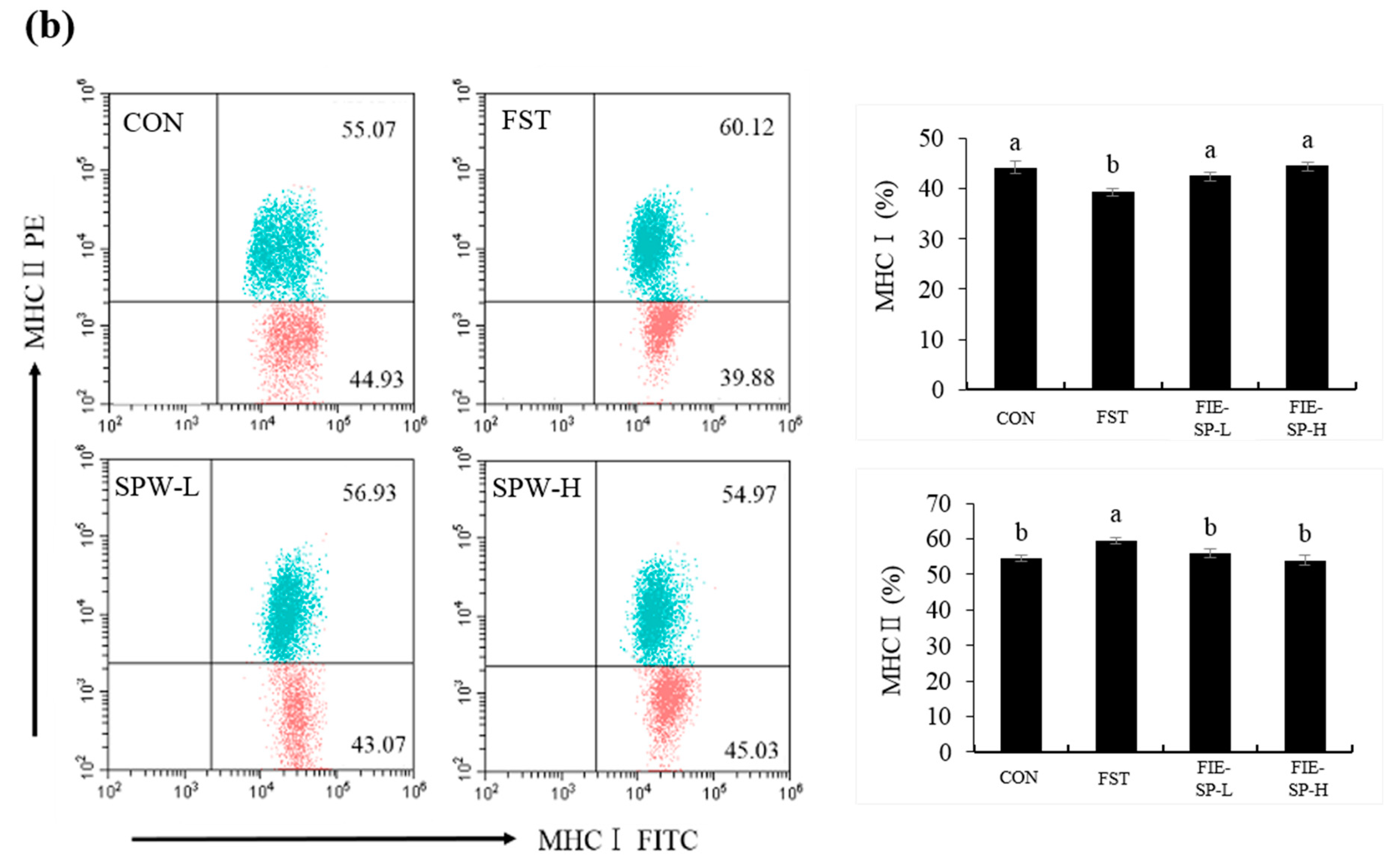
2.5. Flow Cytometry
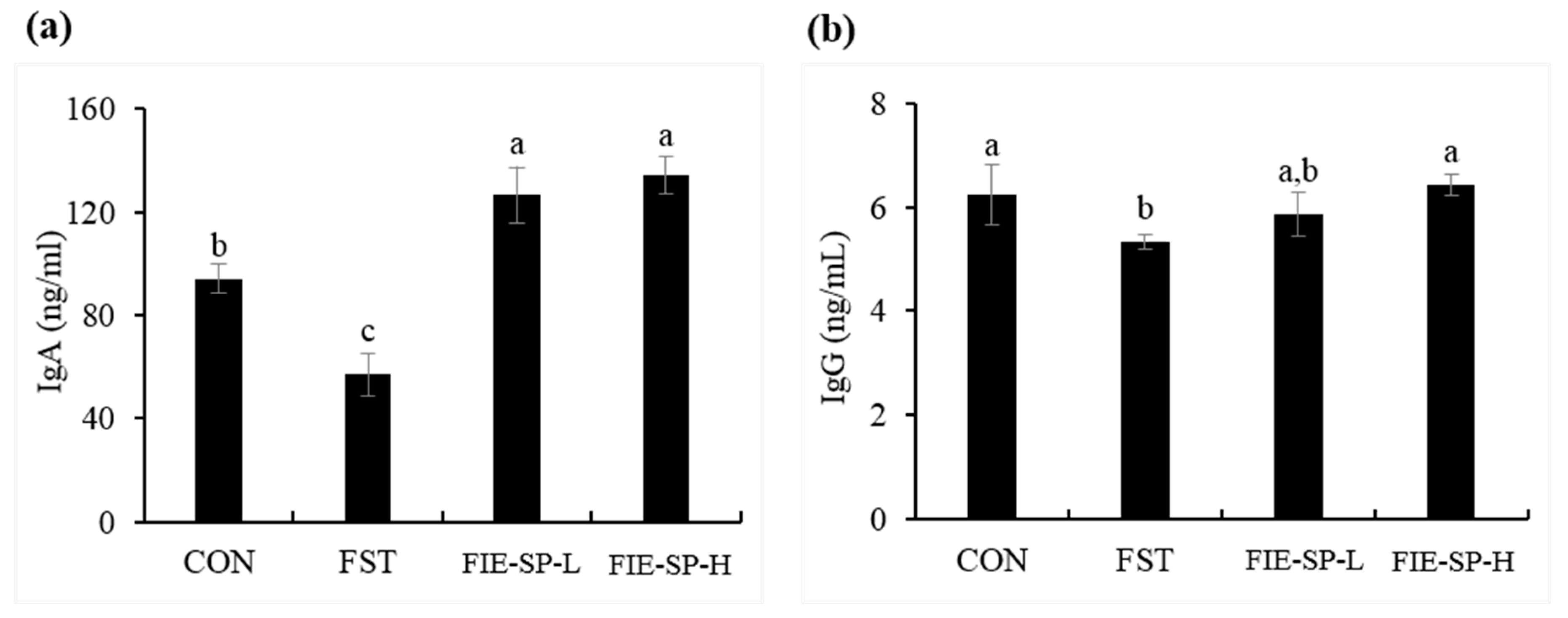
2.6. Measurement of Immunoglobulin in the Serum
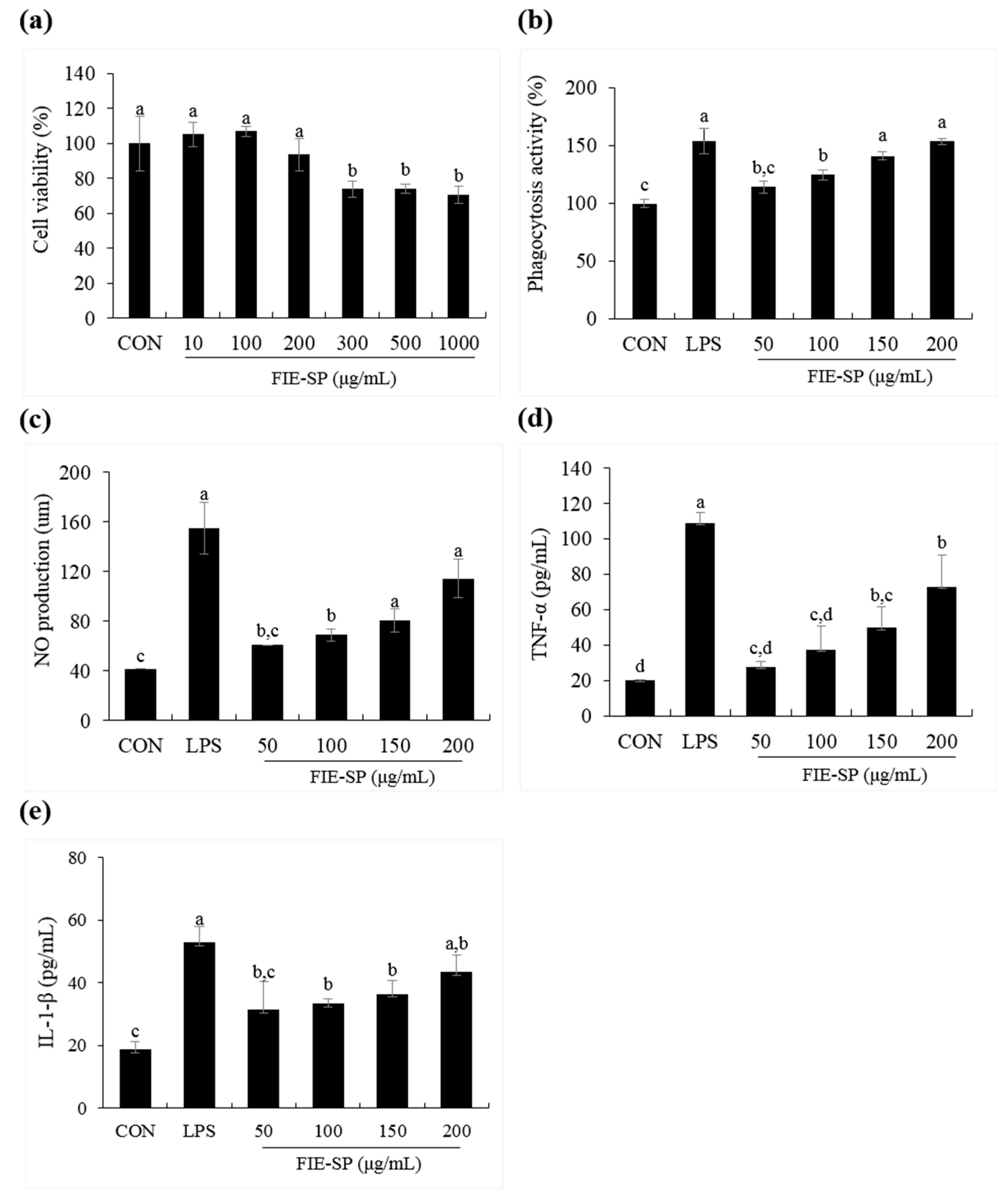
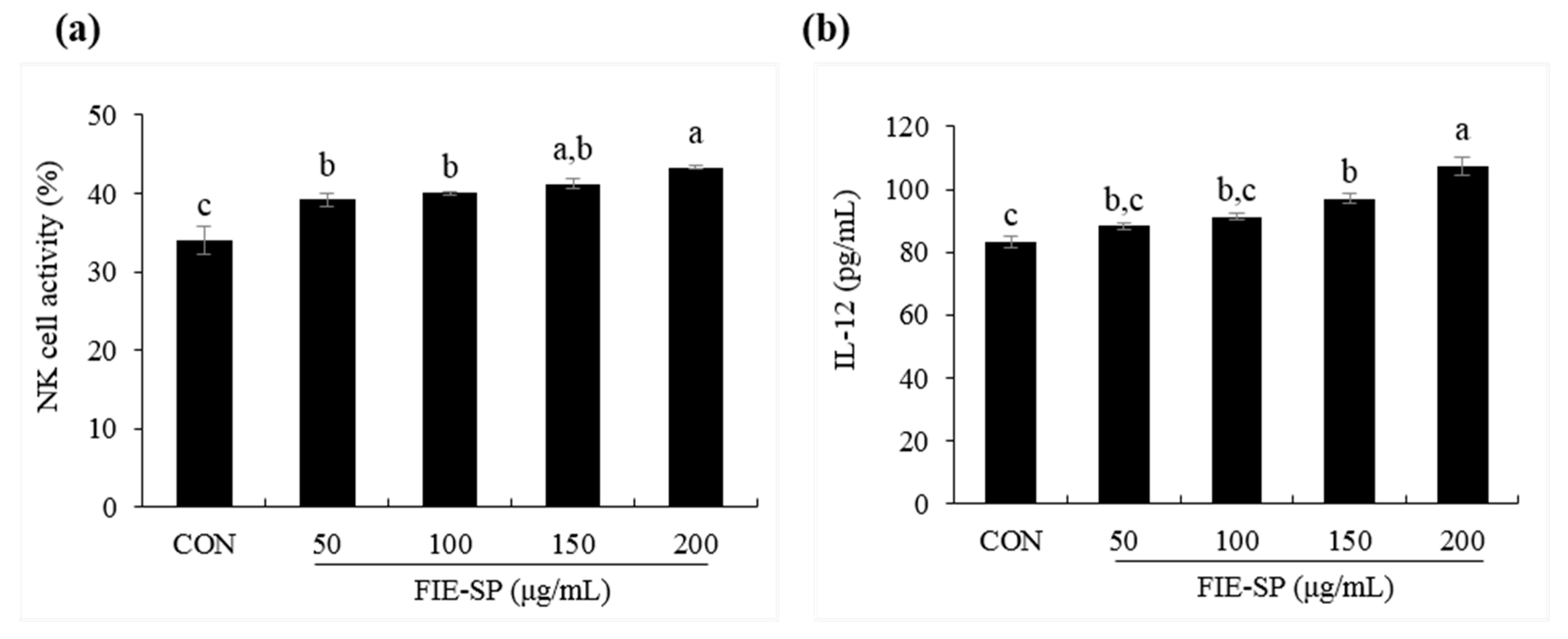
2.7. Measurement of Cytokine Production
2.8. Cytotoxicity in Raw264.7 Cells
2.9. Phagocytosis Activity in RAW264.7 Cells
2.10. Measurement of NK Cell Activity
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of FIE-SP on CD4/CD8 and MHCI/MHCII Ratio in Forced Exercise-Induced Mice
3.2. Effect of FIE-SP on Serum Immunoglobulin in Forced Exercise-Induced Mice
3.3. Effect of FIE-SP on Th1/Th2 Cytokine Production in Forced Exercise-Induced Mice
3.4. Effect of FIE-SP on Macrophage Activities in Raw264.7 Cells
3.5. Effect of FIE-SP on NK Cell Activities in Splenocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, C.; Lunney, J.K. Immune system. Dis. Swine 2019, 264–291. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, L.B. The immune system. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, J.S.; Warrington, R.; Watson, W.; Kim, H.L. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yatim, K.M.; Lakkis, F.G. A brief journey through the immune system. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travis, J. On the origin of the immune system. Science 2009, 324, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booth, F.W.; Roberts, C.K.; Laye, M.J. Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 2, 1143–1211. [Google Scholar]
- König, D.; Weinstock, C.; Keul, J.; Northoff, H.; Berg, A. Zinc, iron, and magnesium status in athletes--influence on the regulation of exercise-induced stress and immune function. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 4, 2–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, M.; Lancaster, G.I.; Bishop, N.C. Nutritional strategies to minimise exercise-induced immunosuppression in athletes. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 26, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, C.E.; Ockene, I.S.; Freedson, P.S.; Rosal, M.C.; Merriam, P.A.; Hebert, J.R. Moderate to vigorous physical activity and risk of upper-respiratory tract infection. Med. Sci. Sports. Exerc. 2002, 34, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M. Exercise, Nutrition and Immunity; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 652–685. [Google Scholar]
- Tvede, N.; Kappel, M.; Halkjœr-Kristensen, J.; Galbo, H.; Pedersen, B. The effect of light, moderate and severe bicycle exercise on lymphocyte subsets, natural and lymphokine activated killer cells, lymphocyte proliferative response and interleukin 2 production. Int. J. Sports Med. 1993, 14, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieger, W.P.; Weiss, M.; Michel, G.; Weicker, H. Exercise-induced monocytosis and modulation of monocyte function. Int. J. Sports Med. 1980, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M. Effects of exercise on immune function. Sport Sci. Exch. 2015, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, M.J.; Ye, E.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Yee, S.T.; Park, E.M. The effects of plebeiae herba (Salvia plebeia R. Br.) on the anticancer (in vitro) and activation of immune cells. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 36, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, S.Y.; Lee, U.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Her, J.W.; Yoon, T.J. A study on the anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect of Salvia plebeia R. extracts. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2010, 41, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.A.; Yun, B.W.; Baek, S.H. Antioxidative activity and nitrite scavenging ability of methanol extract from Salvia plebeia R. Br. Korean J. Med. Crop. Sci. 2007, 15, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.R.; Xu, H.; Duan, C.H.; Chou, G.X. Two new flavones from Salvia plebeia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Weng, X. Antioxidant activity and components of Salvia plebeia R.Br.-A Chinese herb. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, Y.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of Salvia plebeia R. Br extract in vitro and in ovalbumin-induced mouse model. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.I.; Cho, I.H.; Han, S.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Choi, J.G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.H. Antiobesity effects of Salvia plebeia R. Br. extract in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.K.; Oh, H.M.; Park, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Sa, K.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Kim, S.H. Salvia plebeia extract inhibits the inflammatory response in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and a murine model of arthritis. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, A.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, J.; Baek, N.I.; Park, H.J. In vivo sedative and gastroprotective activities of Salvia plebeia extract and its composition of polyphenols. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shek, P.N.; Shephard, R.J. Physical exercise as a human model of limited inflammatory response. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, S.; Shore, S.; Shek, P.N.; Shephard, R.J. Acute exercise and immune function. Int. J. Sports Med. 1992, 13, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, N.C. Exercise and infection risk. Immune Funct. Sport Exerc. 2006, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C. Modification of immune responses to exercise by carbohydrate, glutamine and anti-oxidant supplements. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, D.P.; Hussey, S.; Sebring, R.; Rushlow, K.E.; Radecki, S.V.; Whitaker-Dowling, P.; Horohov, D.W. Safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity of a modified-live equine influenza virus vaccine in ponies after induction of exercise-induced immunosuppression. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benquet, C.; Krzystyniak, K.; Savard, R.; Guertin, F.; Oth, D.; Fournier, M. Modulation of exercise-induced immunosuppression by dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids in mice. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1994, 43, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Toft, A.D. Effects of exercise on lymphocytes and cytokines. Br. J. Sports Med. 2000, 34, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krüger, K.; Mooren, F.C. Exercise-induced leukocyte apoptosis. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 20, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goon, J.A.; Noor Aini, A.H.; Musalmah, M.; Yasmin Anum, M.Y.; Wan Ngah, W.Z. Long term tai chi exercise reduced dna damage and increased lymphocyte apoptosis and proliferation in older adults. Med. J. Malays. 2008, 63, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Raberg, L.; Grahn, M.; Hasselquist, D.; Svensson, E. On the adaptive significance of stress-induced immunosuppression. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hedfors, E.; Holm, G.; Ivansen, M.; Wahren, J. Physiological variation of blood lymphocyte reactivity: T-cell subsets, immunoglobulin production, and mixed-lymphocyte reactivity. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1983, 27, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Nehlsen-Cannarella, S.L.; Donohue, K.M.; Chritton, D.B.; Haddock, B.L.; Stout, R.W.; Lee, J.W. The effects of acute moderate exercise on leukocyte and lymphocyte subpopulations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1991, 23, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshida, Y.; Yamanouchi, K.; Hayamizu, S.; Sato, Y. Effect of acute physical exercise on lymphocyte subpopulations in trained and untrained subjects. Int. J. Sports Med. 1988, 9, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricken, K.H.; Rieder, T.; Hauck, G.; Kindermann, W. Changes in lymphocyte subpopulations after prolonged exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 1990, 11, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Bloming, D.; Lechtermann, A.; Lerch, M.M.; Volker, K. Lymphocyte apoptosis after exhaustive and moderate exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mooren, F.C.; Lechtermann, A.; Lker, K.V. Exercise-induced apoptosis of lymphocytes depends on training status. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Cytokine response to exercise and its modulation. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, G.I.; Halson, S.L.; Khan, Q.; Drysdale, P.; Wallace, F.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Gleeson, M. Effects of acute exhaustive exercise and chronic exercise training on type 1 and type 2 T lymphocytes. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 10, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C. Is infection risk linked to exercise workload. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Kim, O.-k.; Kim, S.; Bae, D.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Jun, W. Immunomodulatory Effect of a Salvia plebeia R. Aqueous Extract in Forced Swimming Exercise-induced Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082260
Shin J, Kim O-k, Kim S, Bae D, Lee J, Park J, Jun W. Immunomodulatory Effect of a Salvia plebeia R. Aqueous Extract in Forced Swimming Exercise-induced Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082260
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jinseop, Ok-kyung Kim, Shintae Kim, Donghyuck Bae, Jeongmin Lee, Jeongjin Park, and Woojin Jun. 2020. "Immunomodulatory Effect of a Salvia plebeia R. Aqueous Extract in Forced Swimming Exercise-induced Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082260
APA StyleShin, J., Kim, O. -k., Kim, S., Bae, D., Lee, J., Park, J., & Jun, W. (2020). Immunomodulatory Effect of a Salvia plebeia R. Aqueous Extract in Forced Swimming Exercise-induced Mice. Nutrients, 12(8), 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082260




