Anthocyanin-Enriched Riceberry Rice Extract Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Downregulating Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Their Targeting Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of Riceberry Rice and Phytochemical Analysis
2.3. HPLC
2.4. UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS
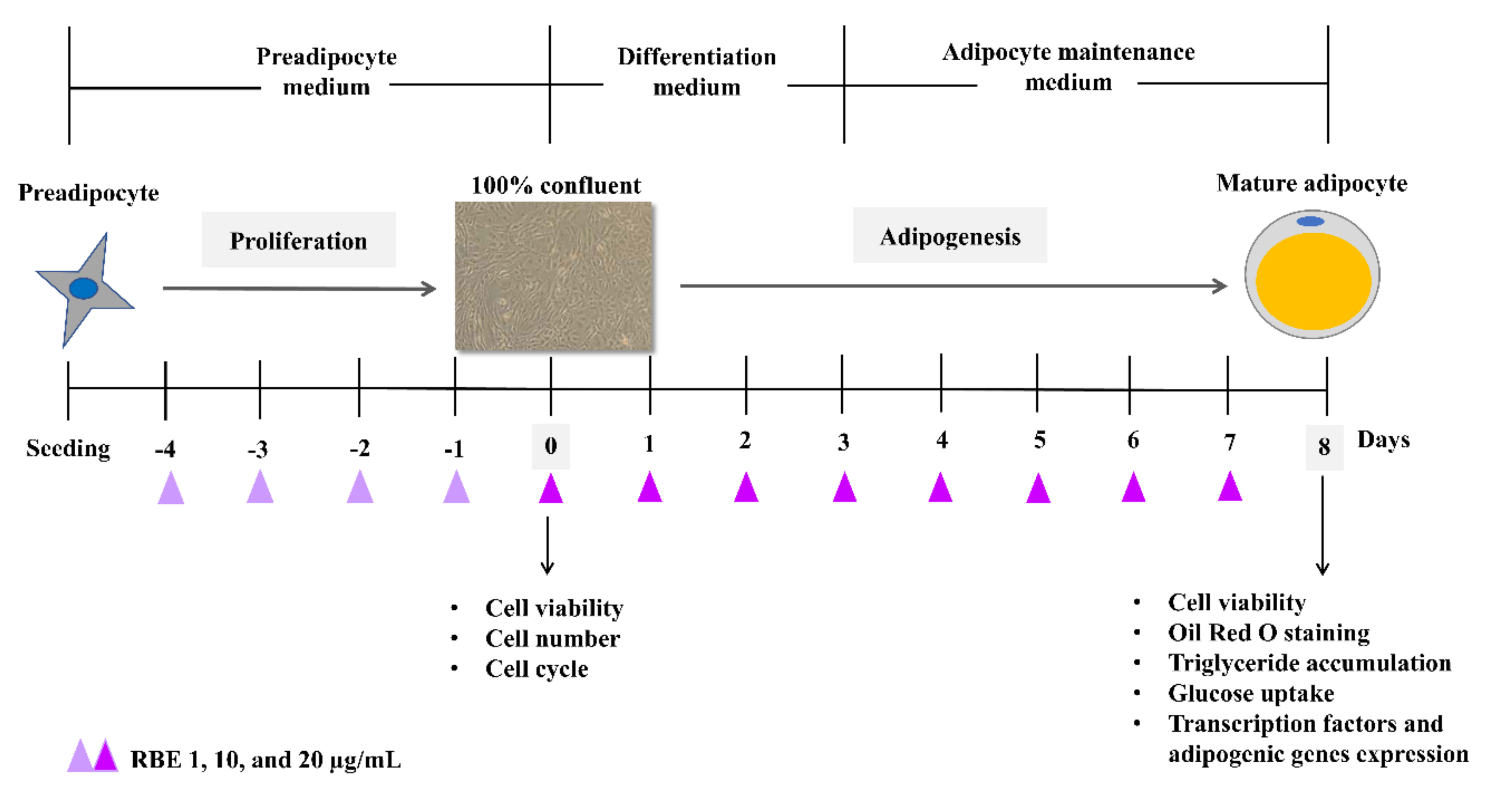
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cell Number and Viability
2.7. Cell Cycle
2.8. Real-Time Calcium Imaging Analysis
2.9. Oil Red O Staining
2.10. Determination of Triglyceride Level
2.11. Glucose Uptake
2.12. Determination of mRNA Expression
2.13. Determination of Akt1
2.14. Lipolysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phytochemical Composition in RBE
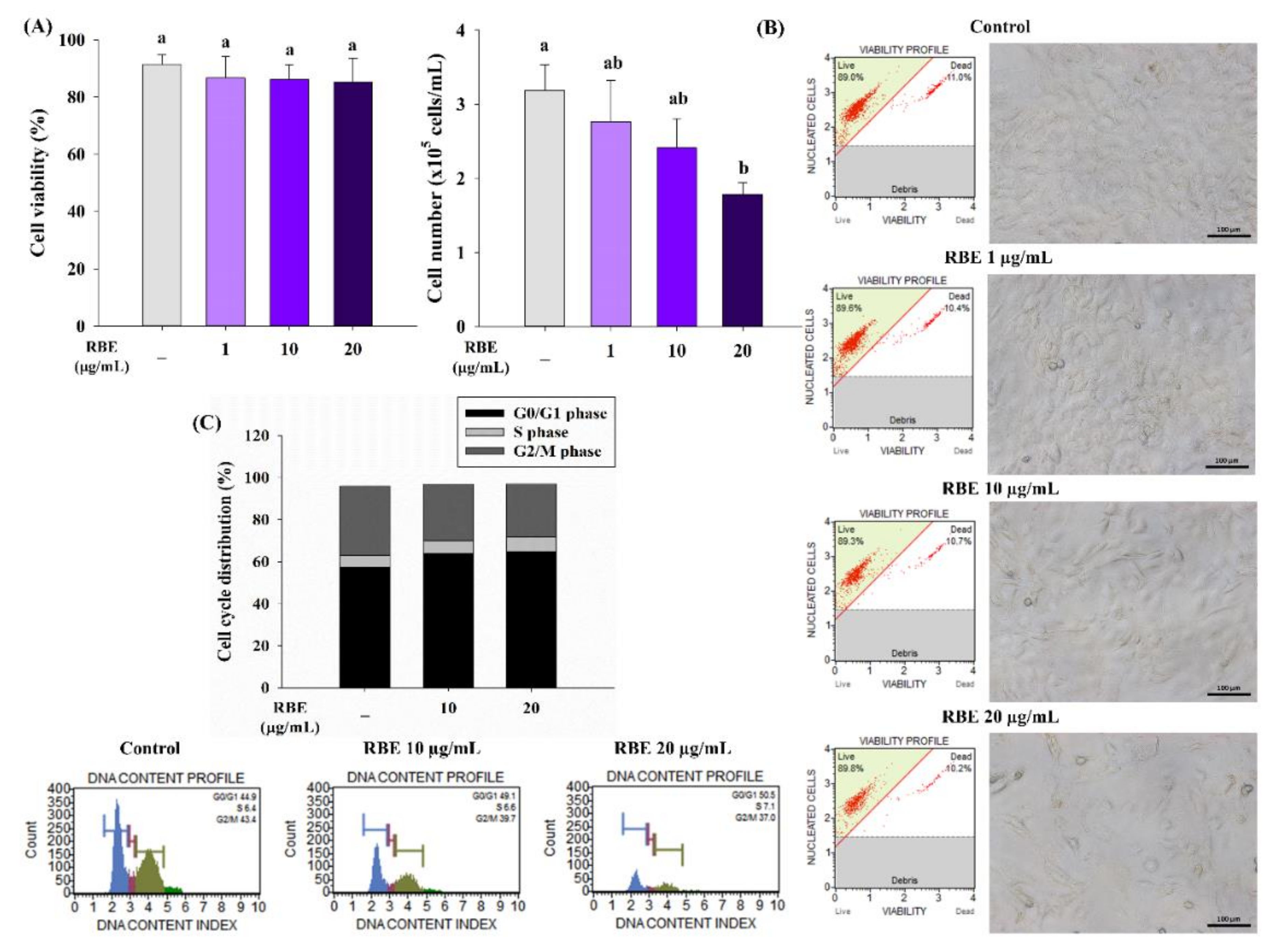
3.2. RBE Inhibited Cell Proliferation of Preadipocytes
3.3. Effect of RBE on Intracellular Calcium Signaling in Preadipocytes
3.4. Effect of RBE on Adipogenesis
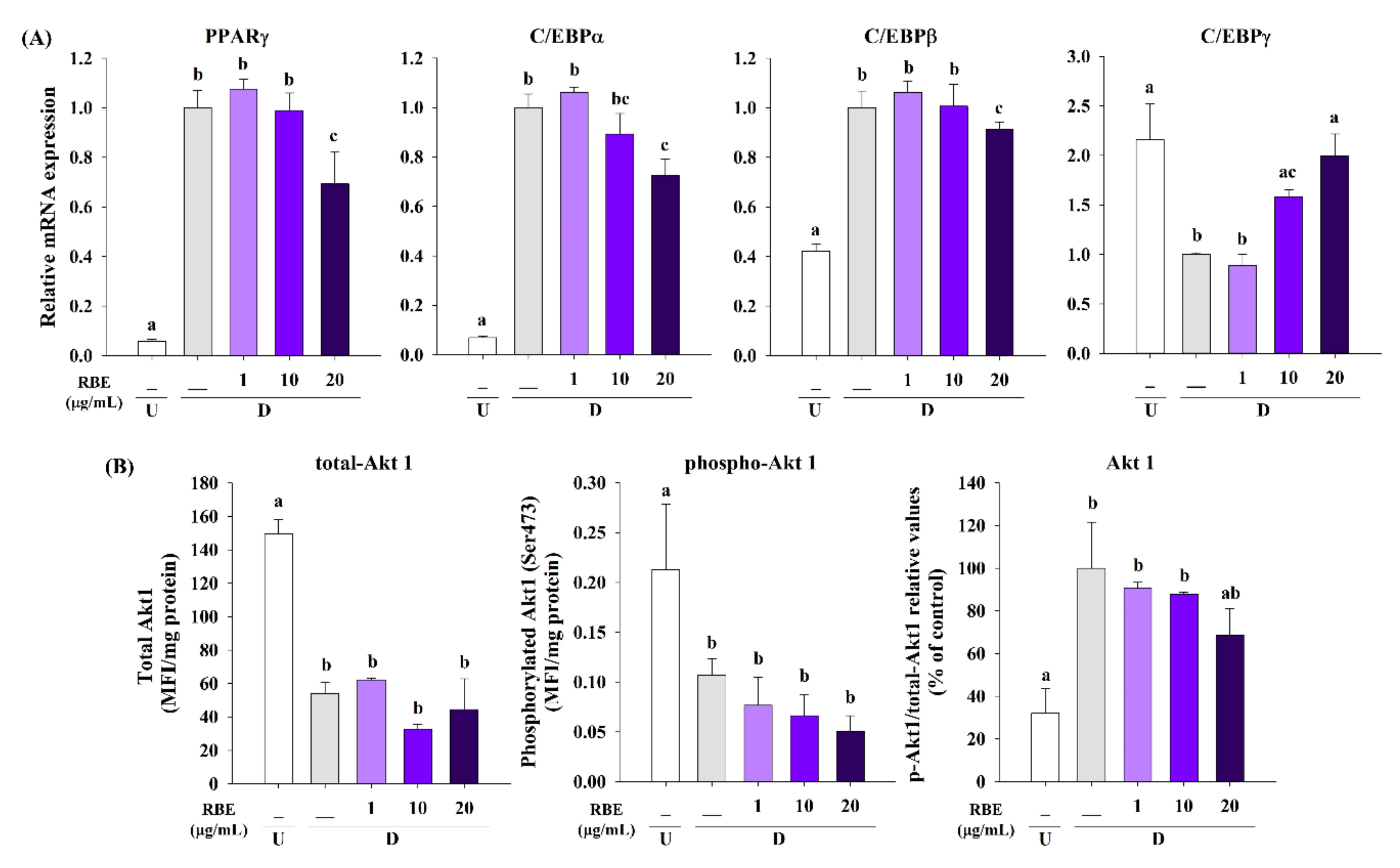
3.5. Effect of RBE on Transcription Factors and Akt1 Signaling in Late Phase of Adipogenesis
3.6. Effect of RBE on Adipogenic Gene Expression
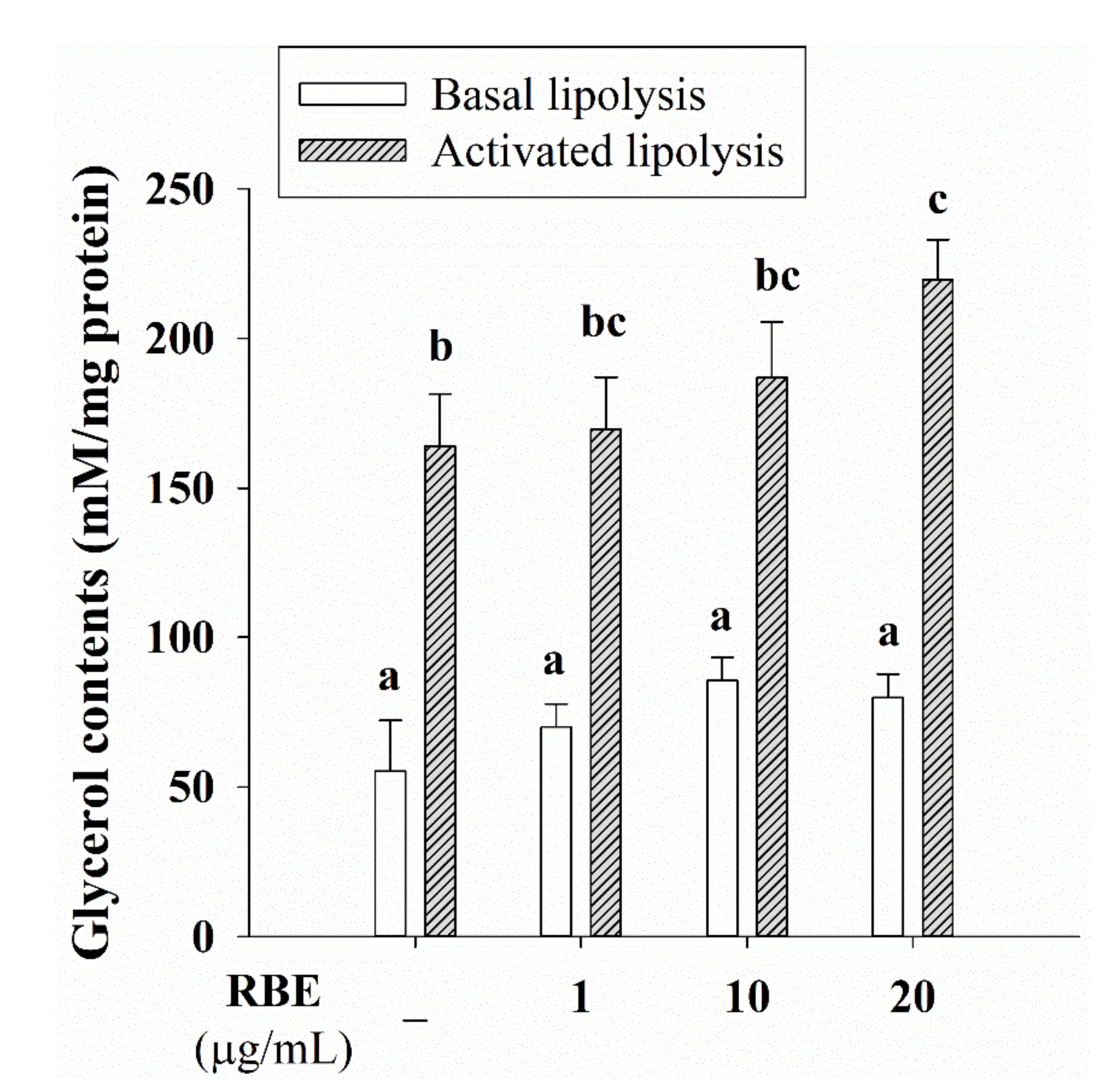
3.7. Effect of RBE on Glucose Uptake, the Glut4 mRNA Expression, and Lipolysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | acetyl CoA carboxylase |
| AdipoQ | adiponectin |
| AdipoQ-R1,R2 | adiponectin receptor-1,2 |
| aP2/Fabp4 | fatty acid binding protein 4 |
| ATGL | adipose triglyceride lipase |
| β-actin | Beta-actin |
| C3G | cyanidin-3-O-glucoside |
| [Ca2+]i | intracellular calcium concentration |
| CE | catechin equivalent |
| C/EBPα,β,γ | CCAAT-enhancer binding protein-alpha, beta, gamma |
| FasN | fatty acid synthase |
| Fura-2AM | Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester |
| GAE | gallic acid equivalent |
| Glut4 | glucose transporter 4 |
| HSL | hormone-sensitive lipase |
| IBMX | 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine |
| InsR | insulin receptor |
| LPL | lipoprotein lipase |
| 2-NBDG | 2-(N-(7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl) amino)-2-Deoxyglucose |
| P3G | peonidin-3-O-glucoside |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma |
| RBE | Riceberry rice extract |
| UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS | ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time of flight-mass spectrometry |
References
- Engin, A. The definition and prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. In Obesity and Lipotoxicity, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Engin, A.B., Engin, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 960, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Stern, J.H.; Scherer, P.E. The cell biology of fat expansion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.E.; O’Rahilly, S.; Rochford, J.J. Adipogenesis at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liu, M. Adipose tissue in control of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 231, R77–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Halvorsen, Y.-D.; Ellis, P.N.; Wilkison, W.O.; Zemel, M.B. Role of intracellular calcium in human adipocyte differentiation. Physiol. Genom. 2000, 3, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Chen, W.; Bai, W. The target cells of anthocyanins in metabolic syndrome. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 921–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Jeon, M.; Kim, Y.S. Delphinidin, a major anthocyanin, inhibits 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte differentiation through activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. BioFactors 2016, 42, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Villavicencio, M.L.; Vinqvist-Tymchuk, M.; Kalt, W.; Matar, C.; Aguilar, F.J.A.; Villanueva, M.d.C.E.; Haddad, P.S. Fermented blueberry juice extract and its specific fractions have an anti-adipogenic effect in 3T3-L1 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Olejnik, A.; Rychlik, J.; Grajek, W. Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit lipid metabolism and modulate leptin and adiponectin secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Olejnik, A.; Rychlik, J.; Grajek, W. Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Park, H.J.; Kang, S.N.; Jang, S.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Ko, Y.-G.; Kim, G.-S.; Cho, J.-H. Blueberry peel extracts inhibit adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and reduce high-fat diet-induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chayaratanasin, P.; Caobi, A.; Suparpprom, C.; Saenset, S.; Pasukamonset, P.; Suanpairintr, N.; Barbieri, M.A.; Adisakwattana, S. Clitoria ternatea flower petal extract inhibits adipogenesis and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by downregulating adipogenic gene expression. Molecules 2019, 24, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leardkamolkarn, V.; Thongthep, W.; Suttiarporn, P.; Kongkachuichai, R.; Wongpornchai, S.; Wanavijitr, A. Chemopreventive properties of the bran extracted from a newly-developed Thai rice: The Riceberry. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangthip, P.; Surasiang, R.; Charoensiri, R.; Leardkamolkarn, V.; Komindr, S.; Yamborisut, U.; Vanavichit, A.; Kongkachuichai, R. Amelioration of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, oxidative stress and inflammation in steptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed a high fat diet by riceberry supplement. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittorntrum, B.; Chunhabundit, R.; Kongkachuichai, R.; Srisala, S.; Visetpanit, Y. Cytoprotective and cytotoxic effects of rice bran extracts on H2O2-induced oxidative damage in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Thai J. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Arjinajarn, P.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Chueakula, N.; Jaikumkao, K.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Norkaew, O.; Chattipakorn, N.; Lungkaphin, A. Riceberry bran extract prevents renal dysfunction and impaired renal organic anion transporter 3 (Oat3) function by modulating the PKC/Nrf2 pathway in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjinajarn, P.; Chueakula, N.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Jaikumkao, K.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Norkaew, O.; Chattipakorn, N.; Lungkaphin, A. Anthocyanin-rich Riceberry bran extract attenuates gentamicin-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somintara, S.; Leardkamolkarn, V.; Suttiarporn, P.; Mahatheeranont, S. Anti-tumor and immune enhancing activities of rice bran gramisterol on acute myelogenous leukemia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posuwan, J.; Prangthip, P.; Leardkamolkarn, V.; Yamborisut, U.; Surasiang, R.; Charoensiri, R.; Kongkachuichai, R. Long-term supplementation of high pigmented rice bran oil (Oryza sativa L.) on amelioration of oxidative stress and histological changes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed a high fat diet; Riceberry bran oil. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poosri, S.; Thilavech, T.; Pasukamonset, P.; Suparpprom, C.; Adisakwattana, S. Studies on Riceberry rice (Oryza sativa L.) extract on the key steps related to carbohydrate and lipid digestion and absorption: A new source of natural bioactive substances. NFS J. 2019, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiranusornkij, L.; Thamnarathip, P.; Chandrachai, A.; Kuakpetoon, D.; Adisakwattana, S. Comparative studies on physicochemical properties, starch hydrolysis, predicted glycemic index of Hom Mali rice and Riceberry rice flour and their applications in bread. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chusak, C.; Pasukamonset, P.; Chantarasinlapin, P.; Adisakwattana, S. Postprandial Glycemia, Insulinemia, and Antioxidant Status in Healthy Subjects after Ingestion of Bread made from Anthocyanin-Rich Riceberry Rice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamboj, A.; Gupta, R.; Rana, A.; Kaur, R. Application and analysis of the Folin Ciocalteu method for the determination of the total phenolic content from extracts of Terminalia bellerica. EJBPS 2015, 2, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Pękal, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Evaluation of aluminium complexation reaction for flavonoid content assay. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kou, X.; Fugal, K.; McLaughlin, J. Comparison of HPLC methods for determination of anthocyanins and anthocyanidins in bilberry extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suantawee, T.; Elazab, S.T.; Hsu, W.H.; Yao, S.; Cheng, H.; Adisakwattana, S. Cyanidin Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Pancreatic β-Cell Gene Expression through Activation of L-type Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channels. Nutrients 2017, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Nam, D.; Kim, K.H.; Huh, J.-E.; Lee, J.-D. Effect of gambisan on the inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 789067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaharan, T.; Ming, C.H.; Palanisamy, U.D. Syzygium aqueum leaf extract and its bioactive compounds enhances pre-adipocyte differentiation and 2-NBDG uptake in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E.; Kołodziejski, P.A.; Sassek, M.; Sliwowska, J.H. Kisspeptin-10 inhibits proliferation and regulates lipolysis and lipogenesis processes in 3T3-L1 cells and isolated rat adipocytes. Endocrine 2017, 56, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsa, P.; Chaiwarith, J.; Voranitikul, J.; Chaiwongkhajorn, J.; Rattanapanone, N.; Lanberg, R. Identification of phenolic compounds in colored rice and their inhibitory potential against α-amylase. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2019, 46, 672–682. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, V.; Annicotte, J.-S.; Escote, X.; Vendrell, J.; Langin, D.; Fajas, L. Cyclin G2 regulates adipogenesis through PPARγ coactivation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Kim, J.N.; Han, S.N.; Nam, J.-H.; Na, H.-N.; Ha, T.J. Black soybean anthocyanins inhibit adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldolesi, J. Inhibition of adipogenesis: A new job for the ER Ca2+ pool. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turovsky, E.; Turovskaya, M.; Zinchenko, V.; Dynnik, V.; Dolgacheva, L.P. Insulin induces Ca2+ oscillations in white fat adipocytes via PI3K and PLC. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2016, 10, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, C.; Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Aoyagi, R.; Ueda, F.; Kimura, M.; Kobata, K.; Tago, K.; Tamura, H. Coffee extract inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocyes by interrupting insulin signaling through the downregulation of IRS1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cordes, K.R.; Farese, R.V.; Walther, T.C. Lipid droplets at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, A.; Wabitsch, M.; Seidel, B.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Berthold, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Kiess, W. Adiponectin expression in humans is dependent on differentiation of adipocytes and down-regulated by humoral serum components of high molecular weight. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Catecholamine-induced lipolysis in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.-S.; Seo, C.-R.; Jang, H.H.; Song, N.-J.; Kim, J.-K.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Han, J.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, K.W. Black rice (Oryza sativa L.) extracts induce osteoblast differentiation and protect against bone loss in ovariectomized rats. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Yen, G.-C. Effects of flavonoids and phenolic acids on the inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8404–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Park, Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, E.-H. Anti-adipogenic activity of rutin in 3T3-L1 cells and mice fed with high-fat diet. Biofactors 2006, 26, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-H.; Kee, J.-Y.; Park, J.; Kim, D.-S.; Shin, S.; Youn, D.-H.; Kang, J.; Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Park, J.-H. Lipin1-mediated repression of adipogenesis by rutin. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, R.; Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tamura, H. Coffee inhibits adipocyte differentiation via inactivation of PPARγ. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, b14-00378. [Google Scholar]
- Aranaz, P.; Navarro-Herrera, D.; Zabala, M.; Miguéliz, I.; Romo-Hualde, A.; López-Yoldi, M.; Martínez, J.A.; Vizmanos, J.L.; Milagro, F.I.; González-Navarro, C.J. Phenolic compounds inhibit 3T3-L1 adipogenesis depending on the stage of differentiation and their binding affinity to PPARγ. Molecules 2019, 24, 1045. [Google Scholar]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kongthitilerd, P.; Suantawee, T.; Cheng, H.; Thilavech, T.; Marnpae, M.; Adisakwattana, S. Anthocyanin-Enriched Riceberry Rice Extract Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Downregulating Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Their Targeting Genes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082480
Kongthitilerd P, Suantawee T, Cheng H, Thilavech T, Marnpae M, Adisakwattana S. Anthocyanin-Enriched Riceberry Rice Extract Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Downregulating Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Their Targeting Genes. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082480
Chicago/Turabian StyleKongthitilerd, Phutthida, Tanyawan Suantawee, Henrique Cheng, Thavaree Thilavech, Marisa Marnpae, and Sirichai Adisakwattana. 2020. "Anthocyanin-Enriched Riceberry Rice Extract Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Downregulating Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Their Targeting Genes" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082480
APA StyleKongthitilerd, P., Suantawee, T., Cheng, H., Thilavech, T., Marnpae, M., & Adisakwattana, S. (2020). Anthocyanin-Enriched Riceberry Rice Extract Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Downregulating Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Their Targeting Genes. Nutrients, 12(8), 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082480






